Details of the three types of ECG leads can be found by clicking on the following links:
- Limb Leads (Bipolar)
- Augmented Limb Leads (Unipolar)
- Chest Leads (Unipolar)
What are the best tips for EKG lead placement?
To ECG placement Operator/Doctor
- Place understanding in a recumbent position if the patient will endure.
- Place the patient’s arms somewhere near their side to loosen up their shoulders.
- Patient’s legs ought to be uncrossed.
- Electrical gadgets, for example, cell phones ought to be away from the patient as these gadgets may meddle with the machine.
Where do you place a 5 lead ECG?
Where do you place a 5 lead ECG?
- GREEN.
- RL (right leg), on the lower chest, just above and to the right of the umbilicus.
- BROWN.
- (representing any of the six precordial leads ), generally in the V 1 position at the fourth intercostal space, right sternal border.
What is a 5 lead EKG?
What is a 5 lead ECG? 5 -electrode system Uses 5 electrodes (RA, RL, LA, LL and Chest) Monitor displays the bipolar leads (I, II and III) AND a single unipolar lead (depending on position of the brown chest lead (positions V1–6))
What are EKG leads?
Each of the twelve electrocardiogram leads, records specific information from the different areas of the heart. Naturally, each lead provides more information from the nearest wall tan distant walls (electrically speaking). For example: the inferior leads provide more information from the inferior wall of the heart than the rest of the walls.
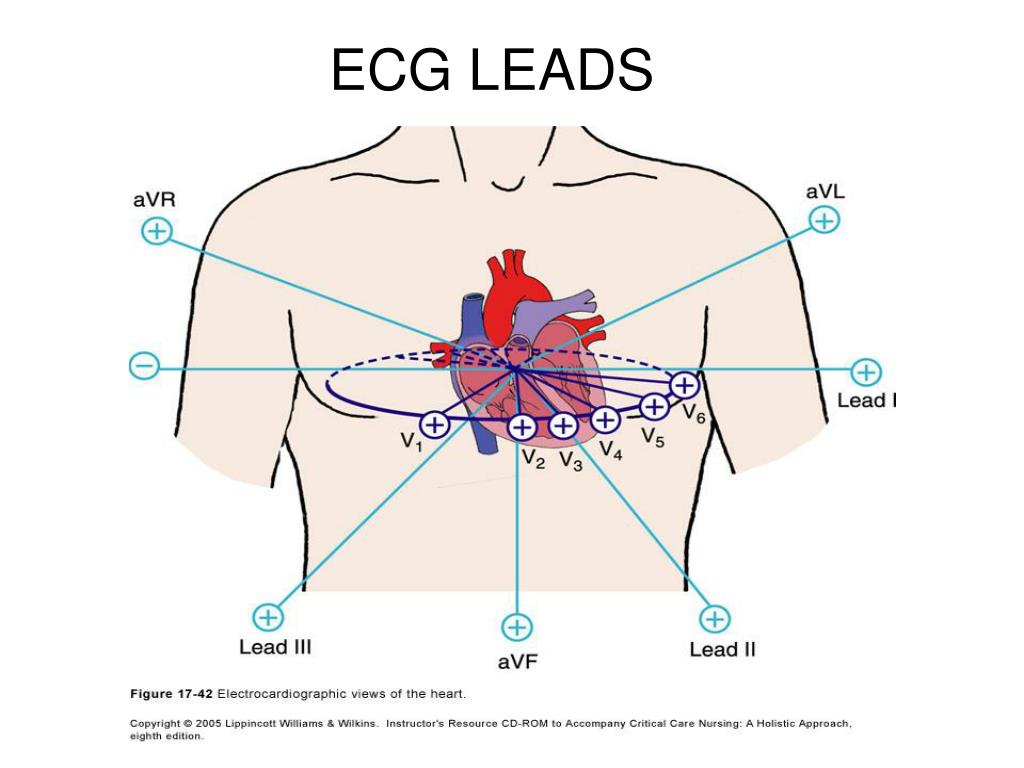
What are the 3 ECG leads?
ECG Leads I, II and III (Willem Einthoven's original leads) Leads I, II and III compare electrical potential differences between two electrodes.
Where are 3 ECG leads placed?
Position the 3 leads on your patient's chest as follows, taking care to avoid areas where muscle movement could interfere with transmission:WHITE.RA (right arm), just below the right clavicle.BLACK.LA (left arm), just below the left clavicle.RED.LL (left leg), on the lower chest, just above and left of the umbilicus.
What are the names of the leads ECG?
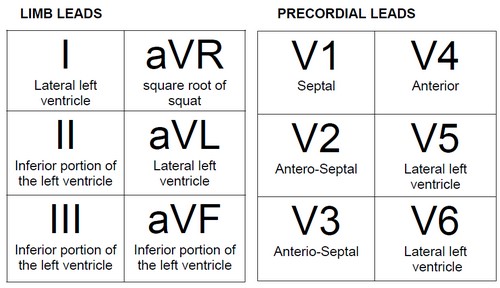
The standard EKG leads are denoted as lead I, II, III, aVF, aVR, aVL, V1, V2, V3, V4, V5, V6. Leads I, II, III, aVR, aVL, aVF are denoted the limb leads while the V1, V2, V3, V4, V5, and V6 are precordial leads.
What are the 3 bipolar leads?
Einthoven described a system of three bipolar leads located at the right arm, left arm, and left leg to form a triangle. Lead I represents the potential difference between the right and left arm; an electrical impulse moving from right to left generates a positive ECG deflection in this lead.
How many types of ECG leads are there?
Details of the three types of ECG leads can be found by clicking on the following links: Limb Leads (Bipolar) Augmented Limb Leads (Unipolar) Chest Leads (Unipolar)
Which ECG lead is most important?
The most useful lead is V4R, which is obtained by placing the V4 electrode in the 5th right intercostal space in the mid-clavicular line.
What is a 5 lead ECG used for?
An electrocardiogram (ECG) is a non-invasive method of monitoring the electrophysiology of the heart. Electrodes are placed on the patient's torso, and the electrical activity of the heart is measured from several leads (voltage difference between electrodes).
How many leads are in a standard ECG?
12 leadsThe information from these 12 leads is combined to form a standard electrocardiogram.
Why is it called a 12-lead?
Put simply, a lead is like a perspective. In 12-lead ECG, there are 10 electrodes providing 12 perspectives of the heart's activity using different angles through two electrical planes - vertical and horizontal planes.
What is unipolar and bipolar lead in ECG?
Unipolar leads register activity in the heart which is directed towards, or located below the electrode, whereas bipolar leads register the voltage between two electrodes. The unipolar leads also compare the difference between the heart's activity and the voltage from what is known as an indifferent electrode.
What is the difference between bipolar and unipolar leads?
A unipolar lead is a single conductor lead with an electrode located at the tip. A bipolar lead has two separate and isolated conductors within a single-lead; the distal electrode is located at the tip of the lead and the other one is usually about 2 cm more proximal.
Why is it called unipolar lead?
These are termed unipolar leads because there is a single positive electrode that is referenced against a combination of the other limb electrodes.
What is the purpose of a 3-lead ECG tracing?
3-lead ECGs are used most often for recording a 24-hour reading. A 24-hour reading is a frequently used tool for the diagnosis of heart problems and is reimbursed as a long-term reading.
Where should ECG chest leads be placed?
The position for V4 is in the 5th intercostal space , in line with the middle of the clavicle (mid-clavicular). V3 sits midway between V2 and V4. Follow the 5th intercostal space to the left until your fingers are immediately below the beginning of the axilla, or under-arm area.
What is the difference between 3-lead and 5 lead ECG?
3-lead is usually used on transport monitors, and monitors two different areas of the heart (one lateral, two inferior). 5-lead is preferred in an ICU, to monitor the third (anterior) area.
How do you remember ECG lead placement?
Once all electrodes have been applied, attach the associated limb leads, with the cable for each lead lying inferior to the electrode (to reduce tension on the wire). Some people find the mnemonic “Ride Your Green Bike” useful for remembering the placement of the limb leads, starting clockwise from the right wrist.
How many electrodes are there on the heart?
Performed while you are lying still, this EKG records your heart’s electrical activity from 12 electrodes (sticky patches) on your chest, arms, and legs at the same time. A resting 12-lead EKG can be part of a routine checkup to screen for heart conditions before any signs or symptoms develop.
What is the phone number for EKG?
Precise diagnosis options that combine the latest EKG technologies with the experience and skills of our experienced doctors and care providers. Make An Appointment. If you are a new patient and want to request and appointment or need help finding a doctor, please call 650-723-6459, Option 3. If you are a returning patient, call 650-723-6459, ...
What type of EKG is used at Stanford?
The types of EKG we use at Stanford include: Cardiopulmonary exercise test (CPET): A cardiopulmonary exercise test (CPET) is an evaluation of the cardiopulmonary system. This test is used to detect any cardiac or pulmonary diseases. Learn more about a cardiopulmonary exercise test.
What is a cardiopulmonary exercise test?
Learn more about a cardiopulmonary exercise test. Exercise EKG (stress test): A stress test (also called treadmill test or exercise EKG) is given while a patient walks on a treadmill or pedals a stationary bicycle to monitor the heart during stress ir exercise. Breathing and blood pressure rates are also monitored.
How long does it take to get a signal averaged EKG?
During this procedure, multiple ECG tracings are obtained over a period of approximately 20 minutes in order to capture abnormal heartbeats which may occur only intermittently.
Where are electrodes placed on the patient?
Patients will lie on a bed or table. Small, sticky patches (electrodes) are placed on the chest, wrists and ankles. Areas on arms, legs, and chest where the electrodes will be placed are cleaned and may be shaved to provide a good contact with the skin.
Can you have an EKG after a tracing?
Generally, there is no special care following an EKG. Notify the doctor if any symptoms you had prior to the test occur. These include chest pain, shortness of breath, dizziness, or fainting. The doctor may give additional or alternate instructions after the procedure, depending on the patient’s needs. EKG Tracings.
What is the purpose of an ECG electrode?
ECG Electrodes are small sensor pads (self adhesive,disposable, pre gelled) applied on the skin to enable detection of the electrical activity of the heart, ...
Where is the red electrode in the rib cage?
RA: placed the red electrode within the frame of rib cage,right under the clavicle near shoulder ( see chart in follow picture) LA: the yellow electrode is placed below left clavicle, which is in the same level of the Red electrode.
What is the electrode used to measure the electrical potential of the heart?
The electrical signals from the heart are measured with surface electrodes. The resulting electrode potential in the heart conducts to the body surface. Standardized electrode positions are used to record the ECG. The three types of electrode systems are
What is the connection point of a lead aVF?
Lead aVF. Two resistors are connected to right arm and left arm. The middle point of the resistor connection is connected with negative terminal. Left leg is connected with the positive terminal of the amplifier. Here also right leg acts as a reference terminal.
What is augmented unipolar limb lead?
A person named Wilson introduced augmented unipolar limb lead system. In this system, ECG is recorded between single exploratory electrode and central terminal. Central terminal relates to the center of the body. Two equal and large resistors are used. Pair of limb electrodes is connected to the resistors. The center joint connection of this resistive network forms the central terminal. The remaining portion of the limb electrode forms the exploratory electrode. In this lead system, a very small increase in ECG voltage can be found. Three types of connections are used.
What is a lead ECG?
A lead is a glimpse of the electrical activity of the heart from a particular angle. Put simply, a lead is like a perspective. In 12-lead ECG, there are 10 electrodes providing 12 perspectives of the heart's activity using different angles through two electrical planes - vertical and horizontal planes.
What is an ECG?
What is Electrocardiogram. As a non-invasive yet most valuable diagnostic tool, the 12-lead ECG records the heart's electrical activity as waveforms. When interpreted accurately, an ECG can detect and monitor a host of heart conditions - from arrhythmias to coronary heart disease to electrolyte imbalance. Since the first telecardiogram recorded in ...
Why are there 6 frontal leads?
The Einthoven's triangle explains why there are 6 frontal leads when there are just 4 limb electrodes. The principle behind Einthoven's triangle describes how electrodes RA, LA and LL do not only record the electrical activity of the heart in relation to themselves through the aVR, aVL and aVF leads.
How many transverse leads are there in the heart?
By using 6 chest electrodes, you get 6 transverse leads that provide information about the heart's horizontal plane: V1, V2, V3, V4, V5, and V6. Like the augmented leads, the transverse leads are unipolar and requires only a positive electrode. The negative pole of all 6 leads is found at the center of the heart.
How many frontal leads are there?
By using 4 limb electrodes, you get 6 frontal leads that provide information about the heart's vertical plane:
Which leads require a positive electrode?
Leads I, II, and III require a negative and positive electrode (bipolarity) for monitoring. On the other hand, the augmented leads-aVR, aVL, and aVF-are unipolar and requires only a positive electrode for monitoring.
When was the first telecardiogram performed?
Since the first telecardiogram recorded in 1903 , huge strides have been made in the recording and interpretation of ECG. Today, the 12-Lead ECG remains a standard diagnostic tool among paramedics, EMTs, and hospital staff.
What is the purpose of F-ECG?
Fontaine bipolar precordial leads (F-ECG) are used to increase the sensitivity of epsilon wave detection. Named after French cardiologist and electrophysiolgist Guy Hugues Fontaine (1936-2018). Leads are placed as shown: Right Arm ( RA) over the manubrium; Left Arm ( LA) over the xiphoid process;
Where to place right sided leads?
A complete set of right-sided leads is obtained by placing leads V1-6 in a mirror-image position on the right side of the chest (see diagram, below).
What is Lewis lead?
Lewis lead (S5-lead) The Lewis lead configuration can help to detect atrial activity and its relationship to ventricular activity. Named after Welsh cardiologist Sir Thomas Lewis (1881-1945) who first described in 1913. Useful in: Observing flutter waves in atrial flutter.
Where to place electrodes for heart?
To get best results – Place electrodes on the chest wall equidistant from the heart (rather than the specific limbs)
Which bipolar leads record the atrial potentials?
Instead of regular leads I, II, and III there are now three bipolar chest leads that are termed FI, FII, and FIII which record the potentials developed in the right ventricle, from the infundibulum to the diaphragm. The vertical bipolar lead FI, (similar to aVF) magnifies the atrial potentials and can be used to record:
