
The three main sources of genetic variation arising from sexual reproduction are: Crossing over (in prophase I) Random assortment of chromosomes (in metaphase I) Random fusion of gametes from different parents. What are the 3 primary mechanisms of genetic variation?
- Dominant.
- Recessive.
- Co-dominant.
- Intermediate.
What are differnet types of heredity?
There are four types of inheritance that you are expected to understand:
- Complete dominance.
- Incomplete dominance.
- Co-dominance.
- Sex-linked.
What are some non examples of heredity?
Traits can include characteristics such as height, eye color, and intelligence, as well as disorders like schizophrenia and autism spectrum disorder. Likewise, what are some non heritable traits? Examples of non-inherited traits include table manners, greeting customs, a preference for certain types of foods, and parenting skills.
What are the different types of inheritance?
- Single Inheritance. In single inheritance, a sub-class is derived from only one super class. ...
- Multi-level Inheritance. In multi-level inheritance, a class is derived from a class which is also derived from another class is called multi-level inheritance.
- Hierarchical Inheritance. ...
- Hybrid Inheritance. ...
What are the units of heredity?
gene: a unit of heredity; the functional units of chromosomes that determine specific characteristics by coding for specific proteins chromosome: a structure in the cell nucleus that contains DNA, histone protein, and other structural proteins
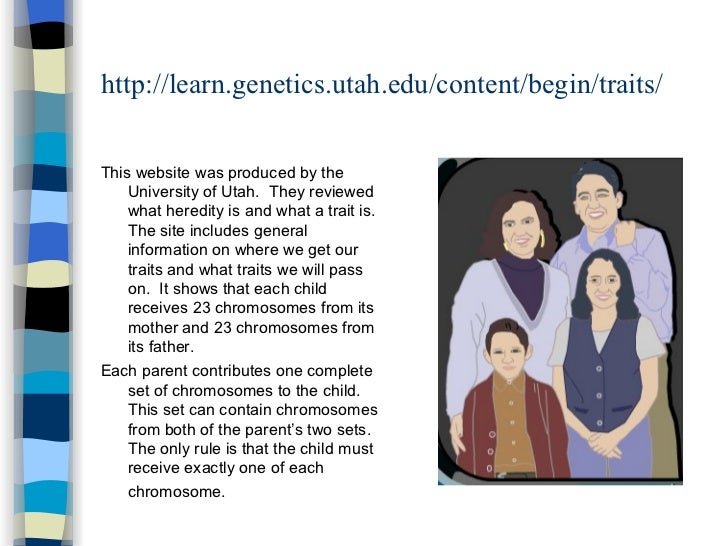
What are different types of heredity?
There are five basic modes of inheritance for single-gene diseases: autosomal dominant, autosomal recessive, X-linked dominant, X-linked recessive, and mitochondrial.
What are 3 examples of heredity?
The parents pass down these through their genes. Some easy-to-identify human traits are height, eye color, hair color, hair type, earlobe attachment and tongue rolling.
What are the 3 types of traits in genetics?
autosomal recessive – where the gene for a trait or condition is recessive, and is on a non-sex chromosome. X-linked dominant – where the gene for a trait or condition is dominant, and is on the X-chromosome. X-linked recessive – where the gene for a trait or condition is recessive, and is on the X-chromosome.
Are the 3 basic unit of heredity?
Genes are the basic functional units of heredity. Genes are a small stretch of DNA present on chromosomes. Genes code for functional proteins. Genes are inherited from one generation to another.
What is called heredity?
heredity, the sum of all biological processes by which particular characteristics are transmitted from parents to their offspring.
What are factors in heredity?
THE HEREDITY FACTOR—Genes, Chromosomes, and You - PMC.
What is heredity example?
Heredity can be defined as the transfer of genetic characters from parents to offsprings by the process of fertilization, where the nuclei of male and female gamete fuses with each other and forms the genetic material of the zygote. For example, two blue eyed parents will always give birth to a blue eyed baby.
What are 3 examples of traits?
Some character traits reveal positive aspects of a person's underlying values or beliefs.generosity.integrity.loyalty.devoted.loving.kindness.sincerity.self-control.More items...
What are hereditary traits?
Heredity is a process in which organisms acquire characteristics from their parents. These characteristics are called traits. Every individual is unique because they have a unique set of traits. The traits which are transmitted by the parent to its offspring during the process of fertilization are inherited traits.
What is basic unit of heredity?
A gene is the basic physical and functional unit of heredity. Genes are made up of DNA.
What are the two units of heredity?
Complete Answer: Genes are the units of heredity and are the instructions that make up the body's blueprint. - Option a: Genes are said to be the basic physical and functional unit of heredity. They are made up of DNA.
What is heredity What are the units of heredity?
(a) The transmission of characters from parents to the offspring's is called heredity. The units of heredity are genes. (b) According to Mendel's first law of inheritance: The characteristics (or traits) of an organism are determined by internal 'factors' which occur in pairs.
What is heredity and its examples?
Heredity can be defined as the transfer of genetic characters from parents to offsprings by the process of fertilization, where the nuclei of male and female gamete fuses with each other and forms the genetic material of the zygote. For example, two blue eyed parents will always give birth to a blue eyed baby.
What are two types of heredity?
Types of inheritanceDominant.Recessive.Co-dominant.Intermediate.
What are examples of hereditary diseases?
Genetic DisordersGenetic Disorders. Sickle Cell Disease.Cystic fibrosis. Cystic Fibrosis Liver Disease.Brain, Nerves and Spine. Huntington's Disease.Cleft lip and palate. Cleft Lip and Palate.
What is a sentence for heredity?
1. Heredity is controlled by genes. 2. Radiation has a strong effect on the heredity of fruit flies.
How many sets of chromosomes are in a recipe for heredity?
In terms of heredity, and following this classification, the recipes that determine the characteristics or traits for each person are divided into AUTOSOMAL characteristics, if they are contained in the first 22 sets of chromosomes.
What is dominant and recessive?
This whole array of characteristics or traits can manifest or express in a dominant, recessive, co-dominant, or intermediate fashion. The terms “dominant and recessive” mean that we receive the information from a recipe twice, information from the father and information from the mother, as each of them contributes with one element from each set ...
What is the other recipe that is not being expressed at this moment but that belongs to the same chromosomal?
The other recipe that is not being expressed at this moment but that belongs to the same chromosomal set (although it did not manifest in the presence of the other recipe) is called RECESSIVE character or trait because it is in RECESS, overlapping or hidden.
What is the process of heredity?
The process of heredity is universal among all living organisms. Genetic variation refers to the variation in a population or species. Genetics is the study of heredity and variation in living organisms. Transmission genetics and cytogenetics have helped scientists investigate the biological basis of heredity.
What is genetics in biology?
It is derived from the Greek word ‘genesis’ meaning grow into or to become. So, genetics is the study of heredity and hereditary variations, it is the study of the transmission of body features: i.e., similarities and difference, from parents to offspring and the laws related to this transmission. Also Read: Behavioural genetics.
What are the two types of variations?
Types of Variation. Variations can be categorised into two types: Genotypic variations: – Genotypic variations refer to the differences in the genome, it may be due to structure or number of chromosomes present in the cells or difference in the genetic constituents of the chromosomes.
What is a homozygous allele?
Homozygous – A pair of same alleles, e.g. TT (homoz ygous dominant) or tt (homoz ygous recessive)
How does transmission genetics help in understanding cellular reproduction?
In transmission genetics, organisms are crossed to study the inheritance pattern in offsprings. Cytological techniques help in understanding cellular reproduction. With the advancement of molecular biology and its tools and techniques, geneticists are able to understand the genetic basis of the inheritance of traits and variations present in various organisms.
What is variation in biology?
Variation. Any differences present between individuals of any species, caused either by genetic difference or by the effect of environmental factors, is called variation. Variation can be shown in physical appearance, metabolism, behaviour, learning and mental ability, and other obvious characters.
Which law states that in the heterozygous condition of the genotype for a pair of alleles,?
Law of dominance: States that in the heterozygous condition of the genotype for a pair of alleles, the alleles which express itself phenotypically is dominant and the one which can’t express is recessive.
