What are the 3 types of latent print? The 3 fingerprint class types are arches, loops, and whorls. Arches would be the least everyday sort of fingerprint, occurring no more than 5% of times.
What are latent fingerprints made of?
How are fingerprints made?
What is the purpose of fingerprints?
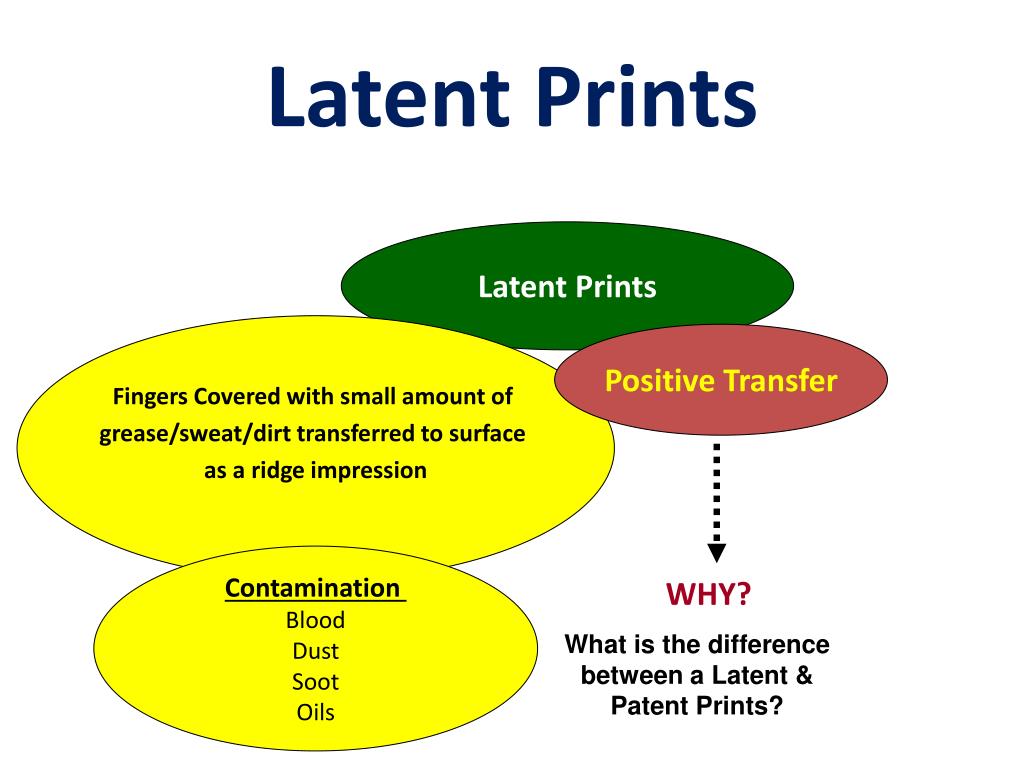
What are the types of latent prints?
In general, there are four classes of fingerprint powders-regular, luminescent, metallic and thermoplastic. In the past, powder dusting, ninhydrin dipping, iodine fuming and silver nitrate soaking were the most commonly used techniques for latent print development.
What are the three categories of latent prints?
Although every fingerprint is different, they're all variations on three broad categories: the arch, which looks a bit like a cross-section of a hill; the loop, which is teardrop-shaped; and the whorl, which is reminiscent of a whirlpool.
What are the three types of prints?
3 Types of Fingerprints- Latent, Patent, and Plastic.
What are the 3 ways latent prints can be made visible?
Latent prints are formed when the body's natural oils and sweat on the skin are deposited onto another surface. Latent prints can be found on a variety of surfaces; however, they are not readily visible and detection often requires the use of fingerprint powders, chemical reagents or alternate light sources.
What are the main types of fingerprints?
The Federal Bureau of Investigation (FBI) recognizes eight different types of fingerprint patterns: radial loop, ulnar loop, double loop, central pocket loop, plain arch, tented arch, plain whorl, and accidental.
What are the three main groups for fingerprints?
All fingerprints can be classified into three basic patterns: loops, whorls, and arches.
What are the 3 classification of crime scene prints?
Friction ridge patterns are grouped into three distinct types—loops, whorls, and arches—each with unique variations, depending on the shape and relationship of the ridges: Loops - prints that recurve back on themselves to form a loop shape.
How are latent prints collected?
Latent prints are typically collected from a crime scene by specialists trained in forensic science techniques to reveal or extract fingerprints from surfaces and objects using chemical or physical methods.
Where do you find latent fingerprint?
Latent prints are impressions produced by the ridged skin, known as friction ridges, on human fingers, palms, and soles of the feet.
What are the latent fingerprints?
A latent print is an impression of the friction skin of the fingers or palms of the hands that has been transferred to another surface. The permanent and unique arrangement of the features of this skin allows for the identification of an individual to a latent print.
What type of fingerprints are latent?
The strict definition of a “Latent” fingerprint is a fingerprint that is not apparent to the eye but can be made sufficiently visible, as by dusting or fuming, for use in identification. Latent fingerprints typically do not fluoresce on their own.
What is an example of a latent fingerprint?
These are surfaces of which the latent print is absorbed into the material. Examples include paper, cardboard, and untreated woods. Various chemical treatments are used to develop latent prints in porous materials.
What are latent prints composed of?
Since sweat is colorless in nature, its deposition on a surface also produces colorless impressions, which are called latent fingerprints. Latent fingerprint residues consist of secretions of the eccrine (sweat), sebaceous, and apocrine glands present on the palm, head, and nose.
What are the three large groups of fingerprint pattern and how do they differ from one another?
Friction ridge patterns are grouped into three distinct types—loops, whorls, and arches—each with unique variations, depending on the shape and relationship of the ridges: Loops - prints that recurve back on themselves to form a loop shape.
What type of surfaces are latent fingerprints found?
Non-porous Surfaces These are mainly smooth surfaces of which the latent print resides on the surface. Examples of non-porous surfaces include glass, plastics, metals, and varnished wood. Latent prints on non-porous surfaces tend to be fragile, so they must be preserved as soon as possible.
What are the three possible conclusions of a fingerprint comparison?
In these instances, no conclusion can be made and the report will read “inconclusive.” The three possible results that can be made from a fingerprint examination are therefore exclusion, identification, or inconclusive.
What is a latent print?
Latent Prints are one of three categories of fingerprints that can be found at the scene of a crime.
How are latent prints visualised?
Latent prints are visualised using magnesium powder, which is gently brushed over these hard and shiny surfaces in order to illuminate them.
Why is it important to dust latent prints?
Likewise it is imperative that when ‘dusting’ the crime scene for prints that only those individuals who are directly involved in the collating of information are present and that they are correctly adorned in protective clothing so as to reduce the risk of contamination to print and other trace evidence to be found there.
What chemicals can be used to show up latent prints?
Likewise some chemicals can be used in order to show up these otherwise invisible prints. One such chemical is Cyanoacrylate, which can be found in ordinary everyday super glue and can be used as a means of showing up the latent print by releasing a vapour that reacts to the salt and oil in the fingerprint. Other chemicals such as Iodine and Silver Nitrate are also used in the display of latent prints.
What is an impression print?
Impressed prints are those that have been made in soft material or tissue by pressing down with the finger or hand. These prints can be photographed or in certain circumstances moulds made if they are very fragile.
Why do my fingers make prints?
These prints are created because the fingers have tiny outlets for the expulsion of sweat and these outlets pick up salts, oils and tiny particles of dirt along the way. You may think that your hands and fingers are clean but at any given time your fingers are picking up these tiny molecules in everyday life; a common means of picking up these tiny particles is the passing of paper from one individual to another. Paper – and paper of many different types – although looking clean can carry a thin film of dirt and sweat particles that are passed on.
What are latent prints?
Latent Prints. The human skin is composed of numerous layers: the epidermis on top, followed by the papillae, and then the dermis. The form and pattern of ridges on the surface of the skin is determined by the dermal papillae. These ridges, known as minutiae, are formed pre-birth, and stay with the individual throughout their life.
What is the best way to make a latent print?
The application of aluminium powder is the most common method of developing latent prints. The fine powder is applied with a brush, after which it adheres to perspiration residues and body oil deposits, visualising the print. The Magna Brush can be used to apply magnetic-sensitive powder.
Why is it important to treat latent prints?
It is necessary to treat latent prints in order to enhance them for collection and comparison. Many forms of print enhancement are based on the fact that latent prints contain numerous different compounds that will react to certain tests.
What are the ridges on a fingerprint?
There are four basic bifurcations (divides) in fingerprints; where a ridge divides, where a ridge ends , a lake, and an independent ridge. Fingerprints can be visible, plastic or latent.
What causes a fingerprint to be left behind?
It is a combination of these ridges and the sweat that causes a fingerprint to be left behind when the finger comes into contact with a surface . The fingerprints left behind, which are unique to an individual, are composed of a collection of loops, whorls and arches.
What are the four types of whorls?
Whorls are divided into four types; plain, central pocket whorl, double whorl, and accidental . Arches are characterised by ridge lines that enter the print from one side and exit the other side.
Is a fingerprint visible?
Fingerprints can be visible, plastic or latent. Visible prints are left in a substance such as paint or blood, clearly visible. Plastic prints are left in some kind of soft surface, such as putty or wet paint, and are also visible. However latent prints are left in bodily oils, and may require treatment to be visualised.
What is latent print?
The latent print discipline is founded on the premises of the individuality and persistence of friction ridge skin (Wertheim and Maceo 2002). These particular characteristics of friction ridge skin were first observed as early as the 1600s, but they were more substantially established after several studies conducted in the late 1800s by such pioneers as Dr. Henry Faulds and Sir Francis Galton (Ashbaugh 1999). The results of these studies provided the initial support for the tenet that friction ridge skin could be used to individualize. More scientifically rigorous studies of the individuality and persistence of friction ridge skin have been conducted since these early studies, and research is ongoing in both of these areas (Berry et al. 1989; Maltoni et al. 2003).
What are the three conclusions of latent print?
Within the forensic latent print discipline, examiners may reach three mutually exclusive conclusions: individualization (identification), exclusion, and inconclusive (SWGFAST 2003). SWGFAST has established specific standards for these three conclusions that have achieved general acceptance within the latent print community. These standards specifically define each conclusion, relate the requisite considerations of the standards, and provide the basic principles upon which the standards are based. Unlike other forensic disciplines with varying degrees of association (see Scientific Working Group on Shoeprint and Tire Tread Evidence [SWGTREAD] 2006), friction ridge impressions are only individualized, excluded, or inconclusively compared. Probable or possible identification conclusions are outside the acceptable limits of the friction ridge identification science (SWGFAST 2006) (see Statistics and Probability Modeling section for additional discussion). The FBI Latent Print Unit adheres to the SWGFAST Standards for Conclusions (2003).
Why are there shortages of latent print examiners?
To compound this situation, a shortage of qualified latent print examiners exists because of a lack of funding to staff these positions and a lack of consistency in the education, training, and skill level of latent print examiners. To increase the number of qualified latent print examiners and maintain the consistency and accuracy of latent print examinations, the latent print community needs to determine the minimum qualifications necessary for latent print examiner trainees, establish a standard training curriculum and certification program that can be implemented nationally, and require annual proficiency testing of certified latent print examiners.
What are the three types of errors in science?
Scientists recognize three general types of errors that can occur in science: systematic error, random error, and human error (Skoog et al. 1998). Systematic error and random error refer to errors encountered with instrumentation or measuring devices in science; this is generally where the error rate for a scientific test is derived. Human error is generally treated separately in most sciences, and in many sciences, it is not discussed as a rate or probability (Skoog et al. 1998). The following discussion addresses errors and error rates, both in general and as they specifically pertain to the latent print discipline. This discussion does not address cases of intentional misattributions, such as fabrication or fraud, because these are not truly errors.
How have fingerprints been quantified?
For more than 100 years, fingerprint pioneers and statisticians alike have attempted to quantify fingerprint individuality through statistical modeling (Pankanti et al. 2002; Stoney and Thornton 1986). Although no model of fingerprint individuality to date has been comprehensive enough for the fingerprint community to accept, the fingerprint discipline has benefited significantly from these studies, which have established general support for the premise of the individuality of friction ridge arrangements.
Is the latent print on the exhibit 10 a fingerprint?
When reporting or testifying to an exclusion decision, an examiner may state, “The latent print on Government’s Exhibit 10, a revolver, is not a fingerprint of John Doe.”. The statement conveys the specificity of the conclusion but does not address the rigorous standard under which this conclusion is effected.
What is a latent print?
LATENT FINGERPRINT: the latent prints are those print that are not visible by our naked eyes. These prints are formed by the sweat and oil that are left behind an object. These prints can be made visible by various development techniques.
How to preserve a latent print?
But if the print is on immovable large object, the prints are preserved by ‘lifting’. The most popular lifter is a broad adhesive tape. The fingerprint powder is applied to the latent print, the adhesive side of tape is placed on the print then the tape is pulled up, the powder is transferred to the tape. The tape is then placed on the labeled card that provides a good background contrast with the powder.
How to get latent fingerprints?
The procedure for developing latent fingerprints involves spraying the nin hydrin solution on the surface containing the impressions. The surface is then heated for short time.
What is the latent fingerprint development method?
IODINE FUMING METHOD: this latent fingerprint development method is useful for porous and semi-porous surfaces such as paper, cardboard, etc where the fats and oils of the greasy prints absorbed on the surface . When vapors of iodine are sprayed onto the surface, a temporary yellow- brown color was developed.
What happens after latent fingerprint development?
After the latent fingerprint development method , the prints must be preserved for future comparison and use in court of evidence.
What are latent prints?
Latent prints are impressions produced by the ridged skin, known as friction ridges, on human fingers, palms, and soles of the feet. Examiners analyze and compare latent prints to known prints of individuals in an effort to make identifications or exclusions. The uniqueness, permanence, and arrangement of the friction ridges allow examiners to positively match two prints and to determine whether two friction ridge impressions originated from one source.
What resolution is required for a friction ridge impression?
Digital images of friction ridge impressions for examination will only be accepted if they were captured at a resolution in excess of 3 mega pixels, high resolution with the camera set at right angles to the substrate being photographed. The image must contain a reference scale at the same level as the impression. Images must be submitted in TIFF format without any other compression applied.
Can fingerprints be obtained from rough surfaces?
In fingerprint comparisons the continuity of the ridge flow is vital to the outcome of the comparisons. Smoother surfaces usually deliver better quality impressions, but depending on the specific surface, it is possible to obtain fingerprints from rough or textured surfaces. It is therefore recommended that investigators contact the section for guidance when in doubt about the suitability of items for submission.
What are latent fingerprints made of?
Even if you don't realize it, you are leaving fingerprints everywhere! Latent fingerprints are made of the sweat and oil on the skin’s surface. This type of fingerprint is invisible to the naked eye and requires additional processing in order to be seen.
How are fingerprints made?
Patent fingerprints, on the other hand, can be made by blood, grease, ink, or dirt. This type of fingerprint is easily visible to the human eye. Plastic fingerprints are three-dimensional impressions and can be made by pressing your fingers in fresh paint, wax, soap, or tar.
What is the purpose of fingerprints?
In general, the purpose of collecting fingerprints is to identify an individual. This person may be applying for a job, wanting to volunteer around children, hoping to buy a gun, a criminal suspect, a victim of a crime, or a witness to an event where your identity needs to be confirmed. There are three types of fingerprints ...
