What are the three main categories of muscle fibers?
Types of Muscle Fiber
- Type I (slow twitch oxidative), red in color
- Type IIA (fast twitch oxidative glycolytic), red in color
- Type IIX (fast twitch glycolytic), white in color
What are the three distinct types of skeletal muscle fibers?
Three types of fibers are defined by this classification scheme are:
- Slow oxidative (SO)
- Fast oxidative (FO)
- Fast glycolytic (FG)
What are the three types of muscles describe each?
The three main types of muscle include:
- Skeletal muscle – the specialised tissue that is attached to bones and allows movement.
- Smooth muscle – located in various internal structures including the digestive tract, uterus and blood vessels such as arteries.
- Cardiac muscle – the muscle specific to the heart.
Which muscle fibers are best suited for anaerobic exercise?
Anaerobic Exercise
- Physiology. The anaerobic energy system produces significantly less ATP than its aerobic counterpart and leads to the build-up of lactic acid.
- Anaerobic Capacity and Anaerobic Power. Anaerobic capacity: Maximal work performed during maximum-intensity short term physical effort; reflects the energy output capacity of anaerobic glycolysis.
- Benefits. ...
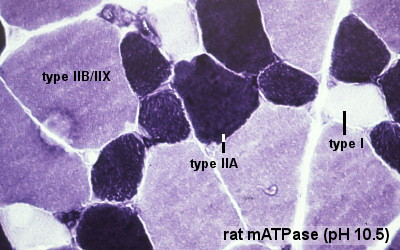
What are the 3 types of muscles and their functions?
The three main types of muscle include:Skeletal muscle – the specialised tissue that is attached to bones and allows movement. ... Smooth muscle – located in various internal structures including the digestive tract, uterus and blood vessels such as arteries. ... Cardiac muscle – the muscle specific to the heart.
What are the three 3 types of muscles?
Overview. The 3 types of muscle tissue are cardiac, smooth, and skeletal. Cardiac muscle cells are located in the walls of the heart, appear striped (striated), and are under involuntary control.
What are the three types of muscle fibers quizlet?
Based on all these structural and functional characteristics, skeletal muscle fibers are classified into three main types:slow oxidative fibers.fast oxidative-glycolytic fibers.fast glycolytic fibers.
What are the 3 ways in which the muscle fibers produce ATP?
The three mechanisms for ATP regeneration are creatine phosphate, anaerobic glycolysis, and aerobic metabolism.
What are the 3 types of skeletal muscles and examples?
They make up between 30 to 40% of your total body mass. Tendons (tough bands of connective tissue) attach skeletal muscle tissue to bones throughout your body. Your shoulder muscles, hamstring muscles and abdominal muscles are all examples of skeletal muscles.
What is the difference between the 3 types of muscle tissue?
Each type of muscle tissue in the human body has a unique structure and a specific role. Skeletal muscle moves bones and other structures. Cardiac muscle contracts the heart to pump blood. The smooth muscle tissue that forms organs like the stomach and bladder changes shape to facilitate bodily functions.
What are the 3 types of muscles and examples quizlet?
The three types of muscle tissue are skeletal, cardiac, and smooth. Skeletal muscle is attached to bones, has cylindrical cells, is striated, multinucleate, and voluntary control. Cardiac is the heart, branched cells, striated, uni or dinucleate, and involuntary.
What are the three main muscle types quizlet?
There are three different types of muscle tissue: skeletal, smooth, and cardiac.
What are Type 1 muscle fibers quizlet?
Type I- slow twitch muscle fibers are smaller in size, slower to fatigue, and produce long term contractions ( stabilization ). Noting the "s" words may help you to remember these characteristics. Since they are smaller in size, it makes sense that they produce less force.
What are type 1 muscle fibers?
Type I Fibers (Slow Twitch/Red) Type I fibers are a “slow twitch” muscle fiber. They are called slow twitch as they generate force at a slower rate comparably with type II. These fibers also have a slower rate of fatigue.
What is type 2 muscle fiber?
Fast-twitch muscle fibers provide bigger and more powerful forces, but for shorter durations and fatigue quickly. They are more anaerobic with less blood supply, hence they are sometimes referred to as white fibers or type II.
What are muscle Fibres?
Muscle tissue contains something called muscle fibers. Muscle fibers consist of a single muscle cell. They help to control the physical forces within the body. When grouped together, they can facilitate organized movement of your limbs and tissues.
What are the two criteria to consider when classifying the types of muscle fibers?
Two criteria to consider when classifying the types of muscle fibers are how fast some fibers contract relative to others, and how fibers produce ATP. Using these criteria, there are three main types of skeletal muscle fibers. Slow oxidative (SO) fibers contract relatively slowly and use aerobic respiration (oxygen and glucose) to produce ATP.
Which fibers produce ATP?
Slow oxidative (SO) fibers contract relatively slowly and use aerobic respiration (oxygen and glucose) to produce ATP. Fast oxidative (FO) fibers have fast contractions and primarily use aerobic respiration, but because they may switch to anaerobic respiration (glycolysis), can fatigue more quickly than SO fibers.
What is the function of myoglobin in muscle fibers?
The myoglobin stores some of the needed O 2 within the fibers themselves (and gives SO fibers their red color). All of these features allow SO fibers to produce large quantities of ATP, which can sustain muscle activity without fatiguing for long periods of time.
What is FG fiber?
FG fibers are used to produce rapid, forceful contractions to make quick, powerful movements. These fibers fatigue quickly, permitting them to only be used for short periods. Most muscles possess a mixture of each fiber type. The predominant fiber type in a muscle is determined by the primary function of the muscle.
What is the purpose of SO fibers?
SO fibers are extensively supplied with blood capillaries to supply O 2 from the red blood cells in the bloodstream. The SO fibers also possess myoglobin, an O 2 -carrying molecule similar to O 2 -carrying hemoglobin in the red blood cells. The myoglobin stores some of the needed O 2 within the fibers themselves ...
Why are FO fibers oxidative?
They are oxidative because they produce ATP aerobically, possess high amounts of mitochondria, and do not fatigue quickly. However, FO fibers do not possess significant myoglobin, giving them a lighter color than the red SO fibers.
What are the three main types of skeletal muscle fibers?
Using these criteria, there are three main types of skeletal muscle fibers recognized (Table 1). Slow oxidative (SO) fibers contract relatively slowly and use aero bic respiration (oxygen and glucose) to produce ATP. Fast oxidative (FO) fibers have relatively fast contractions and primarily use aerobic respiration to generate ATP.
What is the primary metabolic pathway used by muscle fibers?
The primary metabolic pathway used by a muscle fiber determines whether the fiber is classified as oxidative or glycolytic. If a fiber primarily produces ATP through aerobic pathways, then it is classified as oxidative. More ATP can be produced during each metabolic cycle, making the fiber more resistant to fatigue.
Which type of muscle has a fast contraction?
Lastly, fast glycolytic (FG) fibers have relatively fast contractions and primarily use anaerobic glycolysis. Most skeletal muscles in a human body contain all three types, although in varying proportions. The speed of contraction is dependent on how quickly myosin’s ATPase hydrolyzes ATP to produce cross-bridge action.
What are the different types of muscles?
The types of muscle tissue have different functions within your body: 1 Skeletal muscle. These muscles are attached to your skeleton by tendons and control the voluntary movements of your body. Examples include walking, bending over, and picking up an object. 2 Smooth muscle. Smooth muscles are involuntary, meaning that you can’t control them. They’re found in your internal organs and eyes. Examples of some of their functions include moving food through your digestive tract and changing the sizes of your pupil. 3 Cardiac muscle. Cardiac muscle is found in your heart. Like smooth muscle, it’s also involuntary. Cardiac muscle contracts in a coordinated way to allow your heart to beat.
What type of muscle fibers are striated?
This causes the muscle tissue to be striated, or have a striped appearance. Skeletal muscle fibers are classified into two types: type 1 and type 2. Type 2 is further broken down into subtypes. Type 1. These fibers utilize oxygen to generate energy for movement.
What is the skeletal muscle made of?
Skeletal muscle. Each one of your skeletal muscles is made up of hundreds to thousands of muscle fibers that are tightly wrapped together by connective tissue. Each muscle fiber contains smaller units made up of repeating thick and thin filaments.
What muscle is involuntary?
Cardiac muscle. Cardiac muscle is found in your heart. Like smooth muscle, it’s also involuntary. Cardiac muscle contracts in a coordinated way to allow your heart to beat. Muscle fibers and muscles work to cause movement in the body.
What are the characteristics of cardiac muscle fibers?
Cardiac muscle fibers have some unique features. Cardiac muscle fibers have their own rhythm . Special cells, called pacemaker cells, generate the impulses that cause cardiac muscle to contract. This typically happens at a constant pace, but can also speed up or slow down as necessary.
What are some examples of muscle tissue?
These muscles are attached to your skeleton by tendons and control the voluntary movements of your body. Examples include walking, bending over, and picking up an object.
Why do muscle fibers develop?
It’s possible for muscle fibers to develop issues. This can be due to things like direct injury, a nerve condition, or another underlying health condition. Conditions affecting muscle fibers can, in turn, affect the function of a specific muscle or muscle group. Last medically reviewed on May 12, 2020.