
What are three things that can cause mutations?
What chemicals cause genetic mutations?
- Carcinogens.
- Ethylene Dichlorides.
- Flame Retardants.
- Hair Dyes.
- Hydrocarbons, Halogenated.
- Mutagens.
- Furylfuramide.
- Ethylene Dibromide. DNA.
What three factors that are known causes of mutations?
Mutations are caused by environmental factors known as mutagens. Types of mutagens include radiation, chemicals, and infectious agents. Mutations may be spontaneous in nature. What are two environmental factors that can cause mutations? Mutations can also occur as the result of exposure to environmental factors such as smoking, sunlight and ...
What types of mutations are you familiar with?
What types of mutations are you familiar with? Missense mutation: This type of mutation is a change in one DNA base pair that results in the substitution of one amino acid for another in the protein made by ; Nonsense mutation: A nonsense mutation is also a change in one DNA base pair.
What can be true of mutations?
The DNA sequence is specific to each organism. It can sometimes undergo changes in its base-pairs sequence. It is termed as a mutation. A mutation may lead to changes in proteins translated by the DNA. Usually, the cells can recognize any damage caused by mutation and repair it before it becomes permanent. The mutations are of three types:
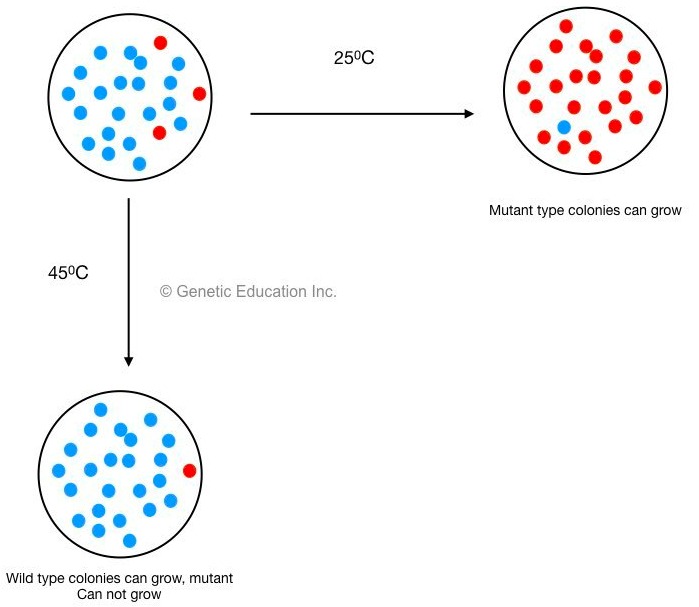
What are 3 causes of mutations?
Mutations can result from errors in DNA replication during cell division, exposure to mutagens or a viral infection.
What are the 4 mutation types?
Germline mutations occur in gametes. Somatic mutations occur in other body cells. Chromosomal alterations are mutations that change chromosome structure. Point mutations change a single nucleotide.
What are the 3 types of point mutation and what happens in each?
There are three types of point mutations: deletions, insertions, and substitutions. Deletions occur when a nucleotide is deleted. Insertions happen when a new nucleotide is inserted into the genome. Substitutions happen when a nucleotide is swapped for another nucleotide.
What are the main types of mutation?
Types of Mutations There are three types of DNA Mutations: base substitutions, deletions and insertions.
What are the 2 main types of mutations?
Errors during DNA replication are not the only reason why mutations arise in DNA. Mutations, variations in the nucleotide sequence of a genome, can also occur because of damage to DNA. Such mutations may be of two types: induced or spontaneous.
What are the 3 types of DNA?
There are three different DNA types:A-DNA: It is a right-handed double helix similar to the B-DNA form. ... B-DNA: This is the most common DNA conformation and is a right-handed helix. ... Z-DNA: Z-DNA is a left-handed DNA where the double helix winds to the left in a zig-zag pattern.
What are examples of mutation?
Hereditary mutations include cystic fibrosis, hemophilia, and sickle cell disease. Other mutations can happen on their own during a person's life. These are called sporadic, spontaneous, or new mutations. They affect only some cells.
What is mutation and types of mutation?
In biology,, a mutation is the permanent alteration of thenucleotide sequence of the genome of an organism,virus, or extrachromosomal DNA or other genetic elements. Mutations in the structure of genes can be classified as Small-scale Mutationsand Large Scale Mutations.
What are examples of mutation?
Hereditary mutations include cystic fibrosis, hemophilia, and sickle cell disease. Other mutations can happen on their own during a person's life. These are called sporadic, spontaneous, or new mutations. They affect only some cells.
What is mutation and types of mutation?
In biology,, a mutation is the permanent alteration of thenucleotide sequence of the genome of an organism,virus, or extrachromosomal DNA or other genetic elements. Mutations in the structure of genes can be classified as Small-scale Mutationsand Large Scale Mutations.
What are genetic mutations?
A genetic mutation is a change to a gene's DNA sequence to produce something different. It creates a permanent change to that gene's DNA sequence. Genetic variations are important for humans to evolve, which is the process of change over generations. A sporadic genetic mutation occurs in one person.
What is harmful mutation?
Harmful mutations may cause genetic disorders or cancer. A genetic disorder is a disease caused by a mutation in one or a few genes. A human example is cystic fibrosis. A mutation in a single gene causes the body to produce thick, sticky mucus that clogs the lungs and blocks ducts in digestive organs.
What are the different types of mutations?
The types of mutations include: Silent mutation: Silent mutations cause a change in the sequence of bases in a DNA molecule, but do not result in a change in the amino acid sequence of a protein (Figure 1).
What type of mutation results in the substitution of one amino acid for another in the protein made by a gene?
Missense mutation: This type of mutation is a change in one DNA base pair that results in the substitution of one amino acid for another in the protein made by a gene (Figure 1).
What is a frameshift mutation?
A frameshift mutation shifts the grouping of these bases and changes the code for amino acids. The resulting protein is usually nonfunctional. Insertions, deletions, and duplications can all be frameshift mutations.
What is a duplication in biology?
Duplication: A duplication consists of a piece of DNA that is abnormally copied one or more times. This type of mutation may alter the function of the resulting protein.
What is the difference between insertion and deletion?
Insertion or Deletion: An insertion changes the number of DNA bases in a gene by adding a piece of DNA. A deletion removes a piece of DNA. Insertions or deletions may be small (one or a few base pairs within a gene) or large (an entire gene, several genes, or a large section of a chromosome).
Do mutations change amino acids?
Figure: Some mutations do not change the sequence of amino acids in a protein. Some swap one amino acid for another. Others introduce an early stop codon into the sequence causing the protein to be truncated. Insertion or Deletion: An insertion changes the number of DNA bases in a gene by adding a piece of DNA.
What is mutation in DNA?
A mutation is a change that occurs in our DNA sequence, either due to mistakes when the DNA is copied or as the result of environmental factors such as UV light and cigarette smoke. What is DNA? Facts. DNA or deoxyribonucleic acid is a long molecule that contains our unique genetic code.
How do mutations occur?
How do we inherit mutations? 1 Each of our genes is a copy from either our mum or our dad. If there is a mutation in one of these genes, this can be passed on from parent to child along with the rest of their genes. 2 Small inherited changes can make big differences to our bodies. For example, the most common mutation to cause cystic fibrosis? is the loss of three letters in a gene called CFTR . 3 Even though mutation is common, inherited diseases are relatively rare. This is because inherited diseases are often recessive, which means that a person must have two copies of the mutated gene to get the disease.
What is a copy number variation?
Copy number variation? (CNV) is a type of mutation where large chunks of DNA are inserted, repeated or lost. These regions of DNA can be between 10,000 and 5,000,000 bases long.
What is genetic disorder?
A genetic disorder is a disease that is caused by a change, or mutation, in an individual’s DNA sequence.
What are different versions of a gene called?
Different versions of a gene are called alleles. Alleles are described as either dominant or recessive depending on their associated traits.
What is inheritance in genetics?
Inheritance is the process by which genetic information is passed on from parent to child. This is why members of the same family tend to have similar characteristics.
What is substitution in biology?
Substitution – when one or more bases in the sequence is replaced by the same number of bases (for example, a cytosine? substituted for an adenine? ).
What are the types of mutations that occur during replication of DNA in the cell nucleus?
The following are some of the types of gene mutations that can occur: Tautomerism: This occurs during replication of DNA in the cell nucleus. Tautomers are mismatched pairs of nucleotide bases.
What are the causes of gene mutations?
Mutagens are external factors that can cause alterations to DNA. Examples of potentially harmful environmental factors include toxic chemicals, X-rays and pollution.
When Do Gene Mutations Occur?
Mutations frequently occur just before the process of mitosis when DNA is being replicated in the cell nucleus. During mitosis or meiosis, mishaps can occur when chromosomes are not lined up correctly or fail to separate properly. Chromosomal mutations in the germ cells can be inherited and passed along to the next generation.
What is frameshift mutation?
Frameshift mutations: These are point mutations that result when a nucleotide pair is added or omitted in a gene sequence that shifts how codons are read. Such mutations often result in different amino acids being added to the protein being synthesized. An example is beta thalassemia, a blood disorder caused by mutations to the HBB gene.
What are some examples of mutations in germline cells?
Defective genes on chromosomes are passed on, as well as too many or too few chromosomes per cell when these mutations happen in germline cells. Gene mutation examples include severe genetic disorders, cell overgrowth, tumor formation and heightened risk of breast cancer.
What happens when one nucleotide is replaced with another?
Missense mutation: This happens when one nucleotide is replaced with another. Substitutions of bases can interfere with normal protein syntheses and functioning. For instance, a single point mutation on the hemoglobin beta (HBB) gene causes sickle cell anemia blood disorders.
What causes cancer in cells?
Carcinogens are mutagens that cause cancer such as UV radiation. Various types of spontaneous mutations happen due to mistakes in cell division or reproduction, as well as during DNA replication or transcription.
