
Types of Symmetry
- Translation Symmetry If the object is translated or moved from one position to another, the same orientation in the forward and backward motion is called translational symmetry. ...
- Rotational Symmetry When an object is rotated in a particular direction, around a point, then it is known as rotational symmetry or radial symmetry. ...
- Reflexive Symmetry ...
- Glide Symmetry ...
What are the four types of symmetry?
Types of symmetries are rotational symmetry, reflection symmetry, translation symmetry, and glide reflection symmetry. These four types of symmetries are examples of different types of symmetry on a flat surface called planar symmetry.
What are the different types of symmetry in geometry?
Types of Symmetry
- Translation Symmetry. If the object is translated or moved from one position to another, the same orientation in the forward and backward motion is called translational symmetry.
- Rotational Symmetry. ...
- Reflexive Symmetry. ...
- Glide Symmetry. ...
What types of symmetry can a shape have?
What are the types of symmetry for Class 7?
- Line Symmetry. Figure is symmetrical only about one axis. …
- Lines Symmetry. Figure is symmetrical with only about two lines. …
- Lines Symmetry. An example of three lines of symmetry is an equilateral triangle. …
- Lines Symmetry. Four lines of symmetry can be seen in a square, that has all the sides equal.
What are the types of math problems?
Three Types of Math Word Problems
- Part-Part-Whole. Understanding that a whole quantity can be broken into sets and that parts can be combined to make a whole may seem like common sense, but young learners must ...
- Join And Separate. Basic word problems pose questions that can be solved with addition and subtraction. ...
- Multiplication And Division. ...
- Combining The Three Types. ...
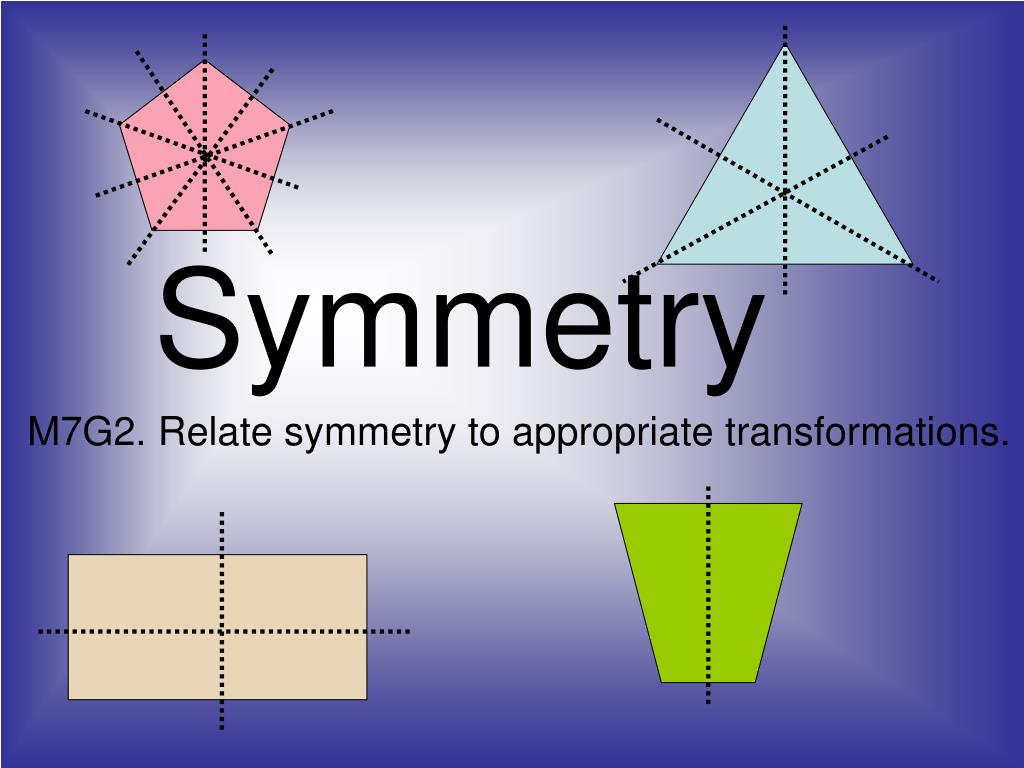
What are the 3 basic types of symmetry?
Animals can be classified by three types of body plan symmetry: radial symmetry, bilateral symmetry, and asymmetry.
What are the types of symmetry?
There are four types of symmetry that can be observed in various situations, they are:Translation Symmetry.Rotational Symmetry.Reflection Symmetry.Glide Symmetry.
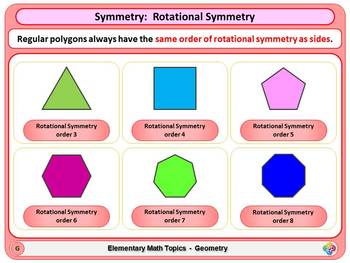
What is order 3 in symmetry?
The order of symmetry is a number used to describe how many times the object will appear to be the same while rotating through 360°. If it only matches up twice, it is Order 2; if it matches the original shape three times, it is Order 3, and so on.
What are the types of symmetry and explain it?
There are four main types of symmetry, which are: translation, rotation, reflection, and glide reflection. However, it is reflectional symmetry – also known as mirror symmetry or line symmetry – that is the main type of symmetry in maths taught in schools.
What is symmetry in math example?
What is Symmetry in Math? Symmetry is defined as a proportionate and balanced similarity that is found in two halves of an object, that is, one-half is the mirror image of the other half. For example, different shapes like square, rectangle, circle are symmetric along their respective lines of symmetry.
What are lines of symmetry math?
In mathematics, an object is said to have symmetry if it can be divided into two identical halves. The line that divides the object into its identical halves is called the line of symmetry. For example, in the given image, the line passing through the middle of the flower is its line of symmetry.
How many lines of symmetry are there?
twoBut basically there are two types of lines of symmetry, they are: Vertical Line of Symmetry. Horizontal Line of Symmetry.
What is the order of symmetry?
The number of positions in which a figure can be rotated and still appears exactly as it did before the rotation, is called the order of symmetry. For example, a star can be rotated 5 times along its tip and look at the same every time. Hence, its order of symmetry is 5.
What is rotational symmetry maths?
Rotational symmetry is the number of times a shape can “fit into itself” when it is rotated 360 degrees about its centre. E.g. A rectangle has a rotational symmetry of order 2 shown below where one vertex is highlighted with a circle and the centre of the shape is indicated with an. 'x'.
What is symmetry in shapes?
Something is symmetrical when it is the same on both sides. A shape has symmetry if a central dividing line (a mirror line) can be drawn on it, to show that both sides of the shape are exactly the same.
What is symmetry in maths for Class 7?
A figure is said to be symmetrical about a line l if it is identical on either side of l. In the adjoining figure, / is the line of symmetry or axis of symmetry. Regular polygons have equal sides and equal angles. They have multiple (i.e. more than one) lines of symmetry.
What is symmetry in maths for Class 6?
1. A figure has line symmetryif a line can be drawn dividing the figure into two identical parts. The line is called a line of symmetry.
What are the 4 types of symmetry in art?
While designers most often use the symmetrical balance, most painters tend to look towards the slight shifts that are available in inverted symmetry, near symmetry, biaxial symmetry, radial symmetry, and even asymmetry is used to place focus on one particular part or figure within the work.
What are the four types of symmetries?
Types of symmetries are rotational symmetry, reflection symmetry, translation symmetry, and glide reflection symmetry. These four types of symmetries are examples of different types of symmetry on a flat surface called planar symmetry.
How many types of symmetry elements are there?
Symmetry Operations and Elements There are 3 types of symmetry operations: rotation, reflection, and inversion.
What are the five symmetry elements?
There are five types of symmetry operations including identity, reflection, inversion, proper rotation, and improper rotation. The improper rotation is the sum of a rotation followed by a reflection.
What is symmetry in geometry?
In geometry, symmetry is defined as a balanced and proportionate similarity that is found in two halves of an object. It means one-half is the mirror image of the other half. The imaginary line or axis along which you can fold a figure to obtain the symmetrical halves is called the line of symmetry. If an object is symmetrical, it means that it is ...
How to tell if a shape has symmetry?
The symmetry of shapes can be identified whether it is a line of symmetry, reflection or rotational based on the appearance of the shape. The shapes can be regular or irregular. Based on their regularity, the shapes can have symmetry in different ways. Also, it is possible that some shapes does not have symmetry.
What is reflection symmetry?
Reflection symmetry is a type of symmetry in which one half of the object reflects the other half of the object. It is also called mirror symmetry or line of symmetry. A classic example of reflection symmetry can be observed in nature, as represented in the below figure. Read more about reflection symmetry here.
What is a symmetrical shape?
Symmetrical shapes or figures are the objects where we can place a line such that the images on both sides of the line mirror each other. The below set of figures form symmetrical shapes when we place a plane or draw the lines.
How many lines of symmetry can be seen in a square?
Four lines of symmetry can be seen in a square, that has all the sides equal.
What does it mean when an object is symmetrical?
If an object is symmetrical, it means that it is equal on both sides. Suppose, if we fold a paper such that half of the paper coincides with the other half of the paper, then the paper has symmetry. Symmetry can be defined for both regular and irregular shapes. For example, a square is a regular ...
How many lines are there in a figure?
Figure is symmetrical with only about two lines. The lines may be vertical and horizontal lines as viewed in the letters H and X. Thus, we can see here two lines symmetry.
When is an object symmetrical?
An object is said to be symmetrical when it has similar parts / design around the imaginary axis.
What is the object that has translation symmetry?
If the same object is present with similar orientation and axis at a different position then the object is said to have translation symmetry.
What is reflexive symmetry?
In reflexive symmetry, the object forms mirror image around the central axis.
When an object is in rotational symmetry, what is the object?
An object is said to be in rotational symmetry when rotating the object around the central point will produce the same image.
Is A symmetrical around the axis O?
So we can say that letter ” A ” is symmetrical around axis O.
What are the different types of symmetry?
The types of symmetry considered in basic geometry include reflectional symmetry, rotation symmetry, translational symmetry and glide reflection symmetry , which are described more fully in the main article Symmetry (geometry) .
What is symmetry in geometry?
Given a structured object X of any sort, a symmetry is a mapping of the object onto itself which preserves the structure. This can occur in many ways; for example, if X is a set with no additional structure, a symmetry is a bijective map from the set to itself, giving rise to permutation groups. If the object X is a set of points in the plane with its metric structure or any other metric space, a symmetry is a bijection of the set to itself which preserves the distance between each pair of points (i.e., an isometry ).
What is an automorphism in algebra?
In abstract algebra, an automorphism is an isomorphism from a mathematical object to itself. It is, in some sense, a symmetry of the object, and a way of mapping the object to itself while preserving all of its structure. The set of all automorphisms of an object forms a group, called the automorphism group.
What is symmetric matrix?
In linear algebra, a symmetric matrix is a square matrix that is equal to its transpose (i .e., it is invariant under matrix transposition ). Formally, matrix A is symmetric if
What is relation symmetry?
We call a relation symmetric if every time the relation stands from A to B, it stands too from B to A. Note that symmetry is not the exact opposite of antisymmetry .
What is the purpose of isometries?
Isometries have been used to unify the working definition of symmetry in geometry and for functions, probability distributions, matrices, strings, graphs, etc.
What is symmetries in Lie groups?
Symmetry is a type of invariance: the property that a mathematical object remains unchanged under a set of operations or transformations.
What is the type of symmetry that is obtained by drawing the line of symmetry?
The halves obtained by drawing the line of symmetry reflect each other. So, this type of symmetry can also be called reflection symmetry.
What is the line of symmetry?
Line of Symmetry. An imaginary line that cuts a shape into two exact or identical halves is named the line of symmetry. In math, this line of symmetry represents the symmetry in shape along one axis only. Many shapes can be divided into halves by more than one line, so a shape can have multiple lines of symmetry.
How to see symmetry in letters?
This line of symmetry can be seen with the letter "B". Draw a line in the middle of the letter, from left to right. This will give two halves that are mirror images of each other. Some irregular polygons (where not all sides are the same length) may also have a single horizontal line of symmetry.
Why is symmetry important in math?
Mathematically speaking, symmetry is meaningful because it allows us to determine whether there will any changes when a shape is rotated, flipped, or translated.
How to draw a vertical line of symmetry?
A vertical line runs from top to bottom. If a shape can be divided into two halves by drawing a vertical line through it, this represents a vertical line of symmetry. To apply this line of symmetry practically, take a paper image of the letter "M". Draw a line through the middle of the letter, from top to bottom.
What is the term for the parts of an object that are divided into two identical parts?
When these shapes can be divided into two identical parts, these parts are called replicas or mirror images of each other. Symmetry can also be used in math to keep track of what happens to objects as they are turned, flipped, or slid to different positions.
How many lines of symmetry does a rectangle have?
Notice that the rectangle in the figure has two diagonal lines of symmetry (as represented by the dashed lines). Squares, which are just a special case of rectangles, will also have this sort of symmetry.
What are the three types of symmetry?
There are three basic types of symmetry: reflection symmetry, rotational symmetry, and point symmetry .
What is symmetry in math?
Mathematically, symmetry means that one shape becomes exactly like another when you move it in some way: turn, flip or slide. For two objects to be symmetrical, they must be the same size and shape, with one object having a different orientation from the first. There can also be symmetry in one object, such as a face. If you draw a line of symmetry down the center of your face, you can see that the left side is a mirror image of the right side. Not all objects have symmetry; if an object is not symmetrical, it is called asymmetric.
What is reflection symmetry?
Sometimes called line symmetry or mirror symmetry, reflection symmetry is when an object is reflected across a line, like looking in a mirror. The face mentioned before is an example of reflection symmetry. Here are some more examples of reflection symmetry.
What is the first image of symmetry?
When working with symmetry, the initial image is called the pre-image , and the second image is called the image because it is the final step in the process. Just like the answer to a math problem is the final step in that process, the image is what is created when you rotate something 90 degrees or flip it about the x -axis. There are three basic types of symmetry: rotational symmetry, reflection symmetry, and point symmetry.
Why is point symmetry called origin symmetry?
Point symmetry is often called origin symmetry because the point is frequently the origin on the coordinate plane. Many playing cards have point symmetry - they look the same from top and bottom. Items with point symmetry look the same from other directions, too.
How to tell if two objects are symmetrical?
For two objects to be symmetrical, they must be the same size and shape, with one object having a different orientation from the first. There can also be symmetry in one object, such as a face. If you draw a line of symmetry down the center of your face, you can see that the left side is a mirror image of the right side.
What is it called when an object is not symmetrical?
Not all objects have symmetry; if an object is not symmetrical, it is called asymmetric. When working with symmetry, the initial image is called the pre-image, and the second image is called the image because it is the final step in the process. Just like the answer to a math problem is the final step in that process, ...
Why do architects use symmetry?
hen part of a design is repeated to make a balanced pattern, we say the design has Artists use symmetry to make designs that are pleasing to the eye.Architects use symmetry to produce a sense of balance in their buildings. Symmetry is also a feature of animals, plants, and mechanical objects. The butterfly, fan, and ribbon below illustrate three kinds of symmetry.
How to make a strip pattern?
Making a strip pattern or a wallpaper design requires a series of “draw and move” steps.You draw a basic design element.Then, you slide your pencil to a new position and repeat the element.You slide in the same way to a new position and repeat the element again, and so on.The slide movements from one position to the next are called
Does a pinwheel have reflection symmetry?
The pinwheel design at the right does not have reflection symmetry. However, it can be turned less than a full turn around its center point in a counterclockwise direction to positions in which it looks the same as it does in its original position. Figures with this property are said to have The windmill, snowflake, and wagon wheel pictured below also have rotation symmetry.
Symmetry in Mathematics
Line of Symmetry
- The imaginary line or axis along which you fold a figure to obtain the symmetrical halves is called the line of symmetry. It basically divides an object into two mirror-image halves. The line of symmetry can be vertical, horizontal or diagonal. There may be one or more lines of symmetry.
Types of Symmetry
- Symmetry may be viewed when you flip, slide or turn an object. There are four types of symmetry that can be observed in various situations, they are: 1. Translation Symmetry 2. Rotational Symmetry 3. Reflection Symmetry 4. Glide Symmetry
Symmetrical Shapes
- The symmetry of shapes can be identified whether it is a line of symmetry, reflection or rotational based on the appearance of the shape. The shapes can be regular or irregular. Based on their regularity, the shapes can have symmetry in different ways. Also, it is possible that some shapes does not have symmetry. For example, a tree may or may not have symmetry. These can be bett…
Overview
Symmetry occurs not only in geometry, but also in other branches of mathematics. Symmetry is a type of invariance: the property that a mathematical object remains unchanged under a set of operations or transformations.
Given a structured object X of any sort, a symmetry is a mapping of the object o…
Symmetry in geometry
The types of symmetry considered in basic geometry include reflectional symmetry, rotation symmetry, translational symmetry and glide reflection symmetry, which are described more fully in the main article Symmetry (geometry).
Symmetry in calculus
Let f(x) be a real-valued function of a real variable, then f is even if the following equation holds for all x and -x in the domain of f:
Geometrically speaking, the graph face of an even function is symmetric with respect to the y-axis, meaning that its graph remains unchanged after reflection about the y-axis. Examples of even functions include |x|, x , x , cos(x), and cosh(x).
Symmetry in linear algebra
In linear algebra, a symmetric matrix is a square matrix that is equal to its transpose (i.e., it is invariant under matrix transposition). Formally, matrix A is symmetric if
By the definition of matrix equality, which requires that the entries in all corresponding positions be equal, equal matrices must have the same dimensions (as matrices of different sizes or shapes cannot be equal). Consequently, only square matrices can be symmetric.
Symmetry in abstract algebra
The symmetric group Sn (on a finite set of n symbols) is the group whose elements are all the permutations of the n symbols, and whose group operation is the composition of such permutations, which are treated as bijective functions from the set of symbols to itself. Since there are n! (n factorial) possible permutations of a set of n symbols, it follows that the order (i.e., the number of elements) of the symmetric group Sn is n!.
Symmetry in representation theory
In quantum mechanics, bosons have representatives that are symmetric under permutation operators, and fermions have antisymmetric representatives.
This implies the Pauli exclusion principle for fermions. In fact, the Pauli exclusion principle with a single-valued many-particle wavefunction is equivalent to requiring the wavefunction to be antisymmetric. An antisymmetric two-particle state is represented as a sum of states in which on…
Symmetry in set theory
We call a relation symmetric if every time the relation stands from A to B, it stands too from B to A. Note that symmetry is not the exact opposite of antisymmetry.
Symmetry in metric spaces
An isometry is a distance-preserving map between metric spaces. Given a metric space, or a set and scheme for assigning distances between elements of the set, an isometry is a transformation which maps elements to another metric space such that the distance between the elements in the new metric space is equal to the distance between the elements in the original metric space. In a two-dimensional or three-dimensional space, two geometric figures are congruent if they are rela…