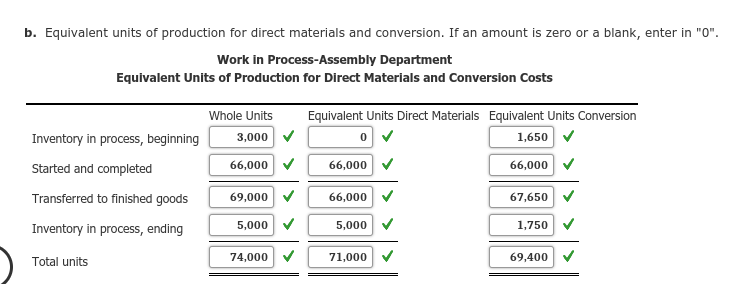
Therefore, proper costing methodology for 100 units in process would entail 80 equivalent units of material, and 60 equivalent units of conversion (i.e., labor and overhead).
How do I find equivalent units?
How do you find equivalent units? Equivalent units. are calculated by multiplying the number of physical (or actual) units on hand by the percentage of completion of the units. If the physical units are 100 percent complete, equivalent units will be the same as the physical units.
How do you calculate conversion costs?
Calculate conversion cost by adding together labor and manufacturing costs. Conversion costs include all costs except the direct cost of the raw materials. Labor and manufacturing costs can include anything from salaries to rent to regulatory inspections. Only include costs incurred directly during the manufacturing of the product.
How do I calculate equivalent units of production?
Calculate Equivalent Units of Production. Here’s the formula: The number of partially completed units x percentage of completion = equivalent units of production. Plugging in the information that you have from the parts maker, there are 300 partially completed units. These 300 units are 50 percent completed.
How to convert between units using conversion factors?
Steps for Unit Conversions
- Look at the units you have. We have 5000 minutes; the units we currently have are minutes.
- Figure out the units you want. Our question wants us to find out how many days this is equivalent to. ...
- Find the conversion factors that will help you step by step get to the units you want. ...
- Arrange the conversion factors so unwanted units cancel out.
What is the conversion cost per equivalent?
Definition: A cost per equivalent unit is defined as the sum of the costs added this period and the beginning work in process costs divided by the equivalent units.
What is equivalent unit?
Equivalent units are notional whole units that are equivalent to the number of incomplete units adjusted for their stage of completion. For example, if there are 200 incomplete units in a process at the end of a period and they are 75% complete then this is equivalent to 150 (200 × 0.75) whole (complete) units.
What are the equivalent units for materials and conversion using the weighted average method?
Equivalent units = number of physical units × percentage of completion. Units completed and transferred out are 100 percent complete. Thus equivalent units are the same as the physical units. Equivalent units = number of physical units × percentage of completion.
Why do we calculate equivalent units separately for materials and conversion costs?
Because direct materials, direct labor, and manufacturing overhead typically enter the production process at different stages, equivalent units must be calculated separately for each of these production costs.
Why are equivalent units needed in a process costing system?
Why do we need to calculate equivalent units? Equivalent units must be calculated in order to allocate manufacturing costs to both the completed units and the units still in inventory.
How do you find equivalents?
Calculating Molar Equivalents To calculate molar equivalents for each reagent, divide the moles of that reagent by the moles of the limiting reagent: Note that the molar equivalency of sodium benzoate is 1. This is because sodium benzoate is the limiting reagent.
How do you calculate conversion costs?
The total conversion cost formula is: Conversion Costs = Direct Labor Costs + Manufacturing Overheads.
Which of the following is correct for calculation of equivalent units of production under process costing?
Option d is the correct answer In a process costing system, the output of one process becomes the input for another process so to make a unit 100% complete and ready to move to the next stage, equivalent units of production need to be calculated.
What are examples of equivalent units of production?
For example, if 500 units are completed as far as materials, but are only 40% completed as far as direct labor and manufacturing overhead, the equivalent units are 500 for materials and 200 (40% of 500) for direct labor and manufacturing overhead.
Which of the following is not included in conversion costs?
Which of the following is not included in conversion costs? Direct materials.
Which costs are included in conversion costs when using process costing?
Labor and overhead are also called conversion costs because they “convert” the materials into a product. If materials, labor, and overhead are added at different times in the production process, two separate calculations of equivalent units are necessary, one for the materials and one for conversion costs.
What is the equivalent production explain in terms of its effect on complete unit cost?
In short, if 100 units are in process but you have only expended 40% of the processing costs on them, then you are considered to have 40 equivalent units of production. Equivalent units is a cost accounting concept that is used in process costing for cost calculations.
What are examples of equivalent units of production?
For example, if 500 units are completed as far as materials, but are only 40% completed as far as direct labor and manufacturing overhead, the equivalent units are 500 for materials and 200 (40% of 500) for direct labor and manufacturing overhead.
What is equivalent production explain with example?
The formula of equivalent production is : Equivalent units of work-in-progress = Actual no. of units in progress of manufacture x Percentage of work completed. For example, if 70% work has been done on the average on 200 units still in process, then 200 such units will be equal to 140 completed units.
What is number of equivalent in chemistry?
By this definition, the number of equivalents of a given ion in a solution is equal to the number of moles of that ion multiplied by its valence. For example, consider a solution of 1 mole of NaCl and 1 mole of CaCl 2. The solution has 1 mole or 1 equiv Na +, 1 mole or 2 equiv Ca2+, and 3 mole or 3 equiv Cl −.
What are equivalent units of production quizlet?
Equivalent units of production are: A measure representing the percentage of a unit's cost that has been completed. The best cost system to use for a company producing a continuous stream of similar items would be a: Process costing system.
Why do managers use conversion costs?
Managers and sometimes, business owners use conversion costs to find out if there is any wastage that can be eliminated.
What is the difference between prime and conversion cost?
Prime cost uses both direct material and direct labour to complete a product while conversion cost does not include a direct material cost . Certain cost elements are included in one and excluded on another like prime cost does not include overhead expenses which are applied in conversion cost. The main objective of the prime cost is to set the price of a product with the desired profits. In contrast, the conversion cost is calculated in order, to sum up, and resolve any manufacturing inefficiency. Prime cost is calculated and presented at the beginning of the cost sheet, but there is a set a standard that required the calculation of conversion cost until and unless the manger desires it.
What is the purpose of prime cost?
The main objective of the prime cost is to set the price of a product with the desired profits. In contrast, the conversion cost is calculated in order, to sum up, and resolve any manufacturing inefficiency.
What is cost incurred?
Costs Incurred Incurred Cost refers to an expense that a Company needs to pay in exchange for the usage of a service, product, or asset. This might include direct, indirect, production, operating, & distribution charges incurred for business operations. read more.
Does prime cost include direct material?
Prime cost uses both direct material and direct labour to complete a product while conversion cost does not include a direct material cost. Certain cost elements are included in one and excluded on another like prime cost does not include overhead expenses which are applied in conversion cost.
How to find equivalent units?
To simply calculate equivalent units, you can multiply the number of physical items by the percentage of the work done on them. For two items that are 50% done, you would have one equivalent unit (2 x 50% = 1). When the items are completely finished, the number of equivalent units is equal to the physical items.
What are equivalent units of production?
Equivalent units of production are a concept used to understand how much money partially completed products are worth to a company. They are useful for process costing, which is the analysis of money flow within the manufacturing process.
What are the ways to calculate equivalent units of production?
You can calculate equivalent units of production using the weighted average method or the first-in first-out method. The weighted average method does not take into account any inventory that might have been started in an earlier period and finished during the time period relevant to the calculations. This can make it more appropriate for a time period at the beginning of a project or year when there is no beginning inventory. The first-in first-out method does factor in this beginning inventory, so it can be used in more situations.
Why is equivalent unit important?
The advantage to calculating equivalent units is that you can refer to whole units rather than partially completed ones , which simplifies accounting calculations. By knowing the equivalent units of production for materials, overhead costs and labor costs, an accountant can estimate how much more money or time is required to finish those products. Calculating equivalent units of production can also help create a financial report or understand where the money in your institution is currently invested.
How many equivalent units of production did previous cats have?
1,500 equivalent units of production to finish previous cats + 6,000 cats completed in January + 1,200 equivalent units of production done on cats not yet completed = 8,700 equivalent units of production
What does an accountant do when calculating units in progress?
The accountant finds out how much work is complete on the units in progress and converts it into a percentage if necessary.
How many units of production are there in 3,000 items in progress?
3,000 items in progress x 40% of materials added = 1,200 material equivalent units of production for the ending work-in-progress cat inventory
Why are equivalent units measured separately?
This is done because direct materials costs are often added entirely (or mostly) at the beginning of the manufacturing process, whereas conversion costs are incurred more evenly throughout the process.
What are the three departments of chocolate production?
In the production process, each bar of chocolate passes through three departments: mixing, molding, and packaging. The molding department doesn’t add any direct materials to the process. (In contrast, the mixing department adds materials such as cocoa butter, sugar, milk, etc.) So every single unit of production in the molding department’s ...
What is the method used to calculate yield?
Dividing materials input quantities by output quantities is the method used to calculate yield.
What is conduit in construction?
A conduit is a tube that encircles and protects the underground cable. In the process of making the plastic conduit, called extrusion, the melted plastic (resin) is pressed through a die to form a tube. Scrap is produced in this process. Information from the cost of production reports for three months is as follows, ...
Does the cost of direct materials increase or decrease between periods?
may increase or decrease between periods, depending on the fluctuation of the cost of the direct materials.
What is total conversion cost?
total conversion costs for the period divided by total equivalent units of direct materials cost for the period.
What is total direct materials cost divided by?
total direct materials cost for the period divided by total equivalent units of conversion costs for the period.