Classification By Function
- Excitatory Neurotransmitters Excitatory neurotransmitters have an excitatory effect, making it more likely for the neuron to fire an action potential. The excitatory process of neurotransmission can influence energy and mood in some cases, like epinephrine.
- Inhibitory Neurotransmitters This type of neurotransmitter will have inhibitory effects on the neuron. ...
- Modulatory Neurotransmitters ...
What are the 4 classes of neurotransmitters?
What are the types of neurotransmitters quizlet?
- Acetylchline (Ach) involved in voluntary motor control; found in synapses where axons connect to muscles and body organs; contributes to regulation of attention, learning, sleeping, dreaming, and memory.
- Dopamine. …
- Glutamate. …
- GABA (gamma-aminobutyric acid) …
- Norepinephrine. …
- Serotonin. …
- endorphins.
What are all the types of neurotransmitters?
Understanding 7 Major Neurotransmitters
- Glutamate
- GABA (γ-aminobutyric acid)
- Dopamine
- Adrenaline (Epinephrine)
- Serotonin
- Oxytocin
- Acetylcholine
What is the most common neurotransmitter?
The list of neurotransmitters include
- Rapidly acting type. These neurotransmitters act very fast, like in a fraction of seconds. ...
- Slow acting type. From specific tissues. ...
- Classical neurotransmitters. ...
- Acetylcholine. ...
- Dopamine. ...
- Norepinephrine. ...
- Epinephrine. ...
- Serotonin. ...
- Glutamate. ...
- GABA (gamma-aminobutyric acid) GABA is another neurotransmitter present predominantly in the brain. ...
What are the criteria for a neurotransmitter?
the criteria are: (i) a neurotransmitter must be synthesized in a neuron and released from a presynaptic terminal, (ii) a neurotransmitter should reproduce the specific responses that are evoked by the stimulation of presynaptic neurons at the postsynaptic neuron or effector cells, (iii) the effect of the chemical should be blocked by antagonists …

What are the 2 major neurotransmitter classes?
The conventional neurotransmitters can be divided into two main groups: small molecule neurotransmitters and neuropeptides.
What are the two functions of neurotransmitters?
These messages help you move your limbs, feel sensations, keep your heart beating, and take in and respond to all information your body receives from other internal parts of your body and your environment. Neurotransmitters carry chemical signals (“messages”) from one neuron (nerve cell) to the next target cell.
What is a neurotransmitter and what are the 2 types?
Types of neurotransmitters Neurotransmitters have different types of actions: Excitatory neurotransmitters encourage a target cell to take action. Inhibitory neurotransmitters decrease the chances of the target cell taking action. In some cases, these neurotransmitters have a relaxation-like effect.
What are the 2 major types of neurotransmitter receptors and what is the main difference between their actions?
There are two major types of neurotransmitter receptors: ionotropic and metabotropic. Ionotropic means that ions can pass through the receptor, whereas metabotropic means that a second messenger inside the cell relays the message (i.e. metabotropic receptors do not have channels).
What are the classifications of neurotransmitters?
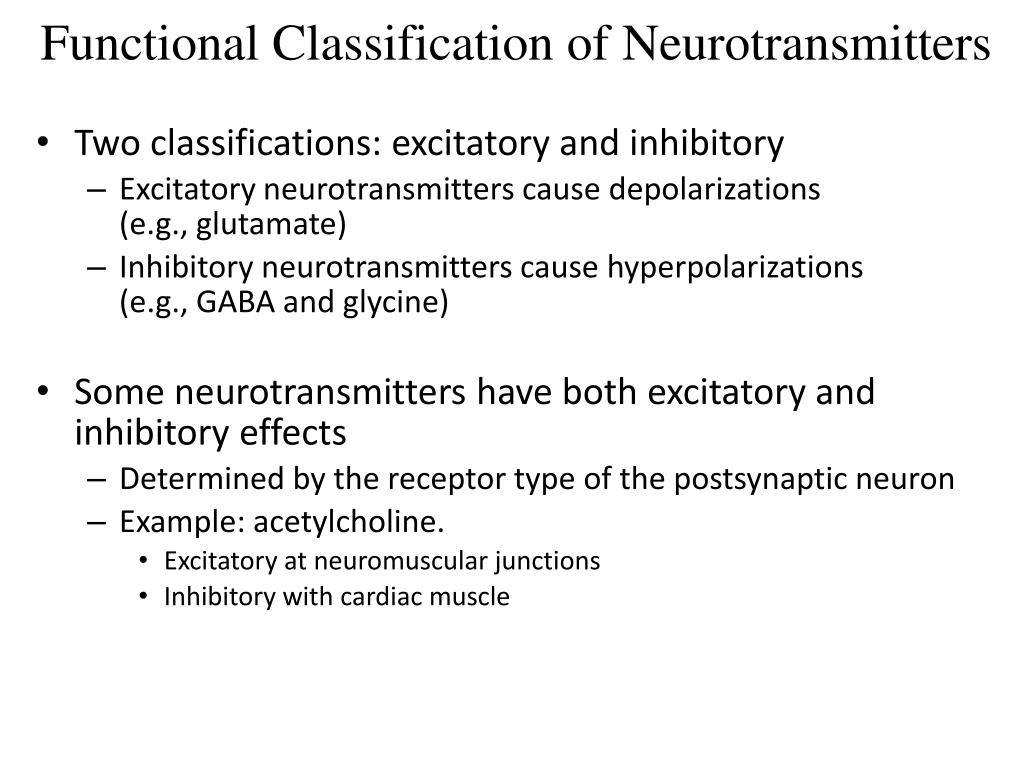
Classification. Neurotransmitters can be classified as either excitatory or inhibitory. Excitatory neurotransmitters function to activate receptors on the postsynaptic membrane and enhance the effects of the action potential, while inhibitory neurotransmitters function to prevent an action potential.
What are the major types of neurotransmitters?
Neurotransmitters all serve a different purpose in the brain and body. Although there are several different minor and major neurotransmitters, we will focus on these major six: acetylcholine, dopamine, norepinephrine, serotonin, GABA, and glutamate.
How many types of neurotransmitters are there?
To date, scientists have identified more than 60 distinct types of neurotransmitters in the human brain, and most experts say there are more left to discover. These powerful neurochemicals are at the center of neurotransmission, and, as such, are critical to human cognition and behavior.
Which of the following is not a functional classification of neurotransmitters?
Fundamentals of the Nervous System and Nervous TissueQuestionAnswerWhich of the following is FALSE regarding chemical synapses?They transmit nerve impulses directly from one neuron to another.Which of the following is NOT a functional classification of neurotransmitters?chemical50 more rows
What is the function of neurotransmitters quizlet?
Neurotransmitters are chemical messengers. The role of the neurotransmitter is to carry messages from one neuron to another - through 'carrying messages'.
What are excitatory and inhibitory neurotransmitters?
An excitatory transmitter promotes the generation of an electrical signal called an action potential in the receiving neuron, while an inhibitory transmitter prevents it. Whether a neurotransmitter is excitatory or inhibitory depends on the receptor it binds to.
What are neurotransmitters quizlet?
Definition of neurotransmitter. A chemical that is released from a nerve cell which thereby transmits an impulse from a nerve cell to another nerve, muscle, organ, or other tissue. A neurotransmitter is a messenger of neurologic information from one cell to another.
Why are the two major neurotransmitters groups known as cholinergic synapses or adrenergic synapses?
Synapses of the autonomic system are classified as either cholinergic, meaning that acetylcholine (ACh) is released, or adrenergic, meaning that norepinephrine is released. The terms cholinergic and adrenergic refer not only to the signaling molecule that is released but also to the class of receptors that each binds.
What is the function of neurotransmitters quizlet?
Neurotransmitters are chemical messengers. The role of the neurotransmitter is to carry messages from one neuron to another - through 'carrying messages'.
What are three neurotransmitters and their functions?
They include serotonin, dopamine, glutamate, and acetylcholine. Neurotransmitters serve several functions, such as regulating appetite, the sleep-wake cycle, and mood. Low levels of any neurotransmitter can lead to problems, including fibromyalgia and Alzheimer's disease.
What are the functions of neurotransmitters and hormones?
Hormones: Hormones have diverse functions in controlling growth, development, and reproduction. Neurotransmitters: Neurotransmitters are involved in the transmission of nerve signals. Hormones: Hormones are capable of regulating target organs or tissues.
What is the function of neurotransmitter Mcq?
Neurotransmitters are activated in response to stress in order to: Encourage effective coping. Attenuate the psychological effect of the stressor. Prepare an individual to adapt to the challenge.
What are the four neurotransmitters?
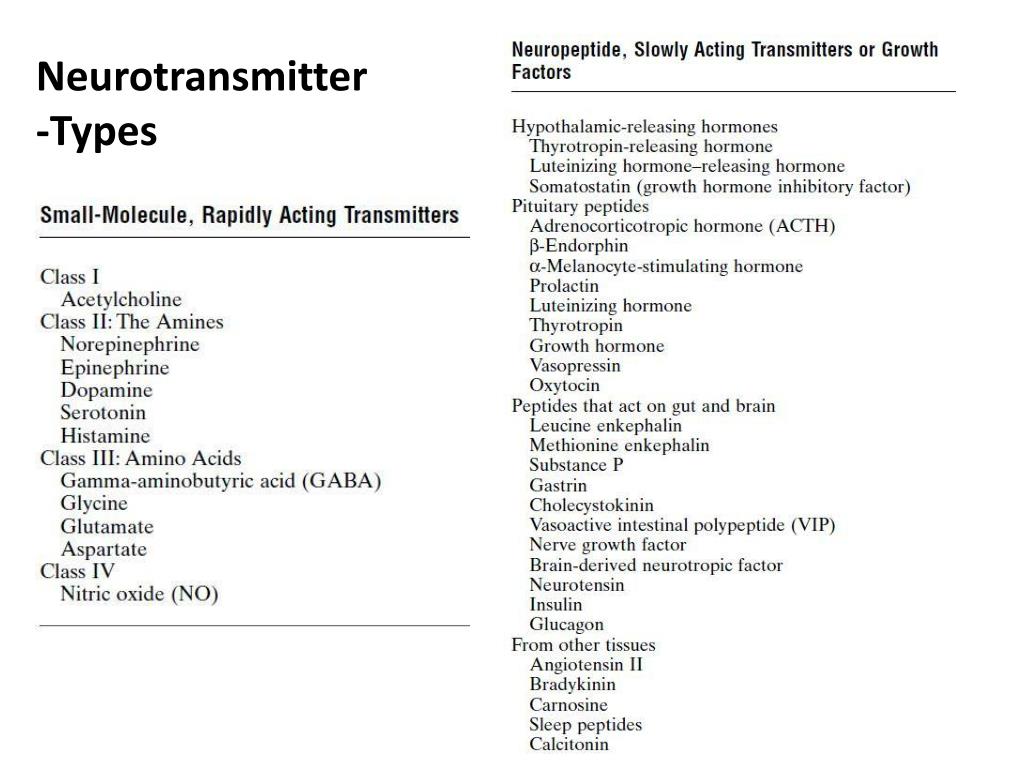
By the 1950s, the list of neurotransmitters (defined by the criteria described in Box A) had expanded to include four amines—epinephrine, norepinephrine, dopamine, and serotonin —in addition to ACh. Over the following decade, three amino acids—glutamate, γ-aminobutyric acid (GABA), and glycine—were also shown to be neurotransmitters. Subsequently, other small molecules were added to the list, and considerable evidence now suggests that histamine, aspartate, and ATP should be included (Figure 6.3). The most recent class of molecules discovered to be transmitters are a large number of polypeptides; since the 1970s, more than 100 such molecules have been shown to meet at least some of the criteria outlined in Box A.Figure 6.3Examples of small-molecule and peptide neurotransmitters. Small-molecule transmitters can be subdivided into acetylcholine, the amino acids, purines, and biogenic amines. The catcholamines, so named because they all share the catechol moiety (i.e., a hydroxylated benzene ring), make up a distinctive subgroup within the biogenic amines. Serotonin and histamine contain an indole ring and an imidazole ring, respectively. Size differences between the small-molecule neurotransmitters and the peptide neurotransmitters are indicated by the space-filling models for glycine, norepinephrine, and methionine enkephalin. (Carbon atoms are black, nitrogen atoms blue, and oxygen atoms red.)
How many amino acids are in a neuropeptide?
Neuropeptides vary in length, but usually contain between 3 and 36 amino acids. Note that one peptide can include the sequence of other neuroactive peptides. For example, β-endorphin contains both α-endorphin and methionine enkephalin (more...)
What is the function of neurotransmitters?
Neurotransmitters are substances which neurons use to communicate with one another and with their target tissues in the process of synaptic transmission (neurotransmission). Neurotransmitters are synthetized in and released from nerve endings into the synaptic cleft. From there, neurotransmitters bind to receptor proteins in ...
What are the most important neurotransmitters in the nervous system?
There are more than 40 neurotransmitters in the human nervous system; some of the most important are acetylcholine, norepinephrine, dopamine, gamma-aminobutyric acid (GABA), glutamate, serotonin, and histamine.
What is the difference between excitatory and inhibitory neurotransmitters?
Classification of neurotransmitters. Excitatory neurotransmitters function to activate receptors on the postsynaptic membrane and enhance the effects of the action potential, while inhibitory neurotransmitters function to prevent an action potential.
Which neurotransmitter causes depolarization of the postsynaptic cells?
So, the type of the synapse and the response of the target tissue depends on the type of neurotransmitter. Excitatory neurotransmitters cause depolarization of the postsynaptic cells and generate an action potential; for example acetylcholine stimulates muscle contraction.
What is the function of acetylcholine?
Regulates the sleep cycle, essential for muscle functioning. Its main function is to stimulate muscle contraction. However, the only exception to this, where acetylcholine is an inhibitory neurotransmitter, is at the parasympathetic endings of the vagus nerve. These inhibit the heart muscle through the cardiac plexus.
What is the function of glutamate?
Sensory neurons and cerebral cortex. Functions. Regulates central nervous system excitability, learning process, memory. Glutamate is the most common neurotransmitter in the central nervous system; it takes part in the regulation of general excitability of the central nervous system, learning processes, and memory.
What is the name of the hormone that regulates neurotransmission?
Vasopressin; also known as antidiuretic hormone (ADH) In this article, we are going to discuss the mechanism of neurotransmission, the classification of neurotransmitters, and some clinical notes about disorders associated with both excess and shortage of some neurotransmitters.