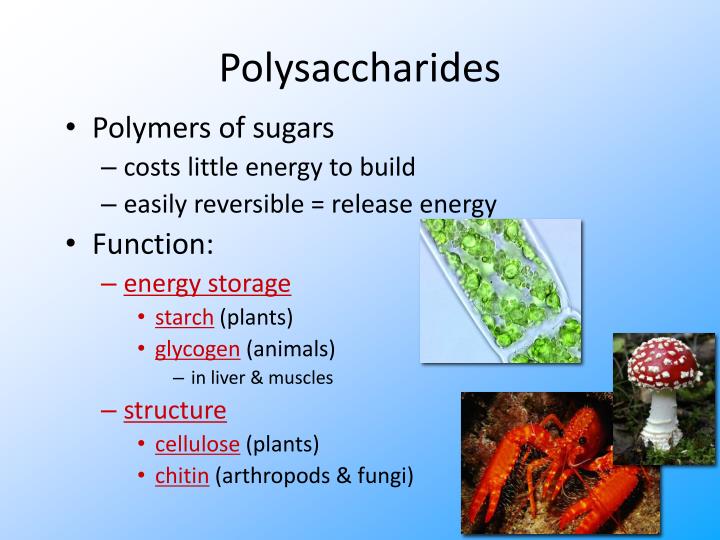
Polysaccharides are categorised into two main types depending upon the type of monomer present in the molecule:
- Homopolysaccharides
- Heteropolysaccharides
What are examples of three polysaccharides?
What are the 3 Types of Polysaccharides?
- Starch. Starch refers to a digestible energy source obtained from plants. ...
- Cellulose. Cellulose is a mostly-indigestible polysaccharide also composed of thousands of glucose molecules. ...
- Glycogen. Glycogen is a complex, multi-branched polysaccharide whose primary function is energy storage. ...
Which are examples of polysaccharides?
What are food examples of polysaccharides?
- Cereal foods, cornmeal, pretzels, flours, oats, instant noodles, pasta, rice.
- Potato, corn.
- Small amounts in other root vegetables and unripe fruit.
What are the examples of polysaccharide?
- Polysaccharides which are used for the purpose of energy storage will provide easy access to the monosaccharides which is constituted inside. ...
- Polysaccharides which are found in cell walls of plants are called structural polysaccharides. ...
- Storage polysaccharides are responsible for being converted to energy later for body functions. ...
What are examples of polysaccharide found in foods?
Examples of Polysaccharides: 1. Starch. An energy source from glucose units that are widely obtained from plants. Many starches are cereal grains, bread, pasta, pastries, cookies, potatoes, tapioca, wheat, oats, rye, barely, rice and yams to name a few. They are a polysaccharide energy source when digested in the body.
What are the 2 most common polysaccharides?
Cellulose and chitin are examples of structural polysaccharides. Cellulose is used in the cell walls of plants and other organisms and is said to be the most abundant organic molecule on Earth.
What are the main polysaccharides?
The main functions of polysaccharides are structural support, energy storage, and cellular communication. Examples of polysaccharides include cellulose, chitin, glycogen, starch, and hyaluronic acid.
What are two types of polysaccharides and what are their purposes functions?
Polysaccharides generally perform one of two functions: energy storage or structural support. Starch and glycogen are highly compact polymers that are used for energy storage. Cellulose and chitin are linear polymers that are used for structural support in plants and animals, respectively.
What are the 2 polysaccharides found in plants?
Plant polysaccharides are divided into two categories: namely, storage polysaccharides such as starch,49 and structural polysaccharides such as cellulose.
What are polysaccharides give two examples?
Starch, cellulose, gum and glycogen are polysaccharides.
What are the classification of polysaccharides?
Polysaccharides can be broadly classified into two classes: Homo-polysaccharides – are made up of one type of monosaccharide units. ex: cellulose, starch, glycogen. Hetero-polysaccharides – are made up of two or more types of monosaccharide units.
What are the two properties of polysaccharides?
Polysaccharides are characterized by the following chemical properties: Not sweet in taste. Many of which are insoluble in water. Do not form crystals when desiccated.
How many polysaccharides are there?
There are two main storage polysaccharides— starch and glycogen.
What is the difference between storage polysaccharides and structural polysaccharides?
Storage polysaccharides: Which are used as food storage or reserve energy, such as starch and glycogen. Structural polysaccharides: They primarily contribute to the creation of structural components of cells including cell walls, such as cellulose, hemicellulose, and lignin.
Which are examples of polysaccharides?
Starch, cellulose, and glycogen are some examples of polysaccharides. In the food industry, the addition of polysaccharides acts as dietary fiber and stabilizers. Polysaccharides are also formed as products of bacteria, for example, in yogurt production).
What are polysaccharides made of?
Polysaccharides are formed by the combination of a large number of monosaccharides through the glycosidic bond. These are high molecular weight polymers of monosaccharides. Most of the carbohydrates found in nature are polysaccharides.
Is starch is a polysaccharide?
Starch is a polysaccharide comprising glucose monomers joined in α 1,4 linkages. The simplest form of starch is the linear polymer amylose; amylopectin is the branched form.
What are the 4 main polysaccharides?
Types Of PolysaccharidesGlycogen: It is made up of a large chain of molecules. ... Cellulose: The cell wall of the plants is made up of cellulose. ... Starch: It is formed by the condensation of amylose and amylopectin. ... Inulin: It is made up of a number of fructofuranose molecules linked together in chains.
What are three important polysaccharides and their functions?
Three important polysaccharides, starch, glycogen, and cellulose, are composed of glucose. Starch and glycogen serve as short-term energy stores in plants and animals, respectively. The glucose monomers are linked by α glycosidic bonds.
How many polysaccharides are there?
There are two main storage polysaccharides— starch and glycogen.
What is the simplest polysaccharide?
monosaccharidesRelatively complex carboyhydrates are known as polysaccharides. The simplest carbohydrates are monosaccharides, which are small straight-chain aldehydes and ketones with many hydroxyl groups added, usually one on each carbon except the functional group.
What are the four examples of polysaccharides?
The four main examples of polysaccharides are cellulose, starch, glycogen and chitin. Starch and glycogen are storage polysaccharides, while cellul...
What are polysaccharides made of?
The linear or branched chains formed by the joining of monosaccharide units with glycosidic linkages are called polysaccharides.
What are the functions of polysaccharides?
a. They serve as storage of reserve food material in plants and animals. b. They form the structural components of the bodies of living organisms.
What are the food sources of polysaccharides?
a. Tubers- Potato, sweet potato, tapioca contain starch b. Seeds grains- such as rice, wheat, corn etc. contain starch c. Fruits- Pectin d. Gums an...
Are polysaccharides good or bad?
Polysaccharides are natural polymers found in plants, animals and microbes. They have high nutritive values and are essential for the good immune s...
1. What are polysaccharides?
Polysaccharide is a type of carbohydrate. Carbohydrates are an extremely important source of food and they provide energy that is needed for the su...
2. What are the types of carbohydrates?
Mainly three types of carbohydrates are found in all-natural and processed foods. They are – monosaccharides, disaccharides, polysaccharides. Carbo...
3. What are the characteristics of polysaccharides?
Here are some characteristic features of polysaccharides-Polysaccharides are not sweetpolysaccharides are insoluble in waterPolysaccharides are hyd...
4. Where can I find the study material related to polysaccharides?
The study material on polysaccharides is provided on Vedantu’s website. The links can be easily accessible. The study material is available in PDF...
5. What are the types of polysaccharides?
Polysaccharides can be divided into two categories, they are as follows-Homopolysaccharides - polysaccharides that consist of the same type of mono...
6. Describe the Classification of Polysaccharides.
Polysaccharides can be classified into two classes, namely, homopolysaccharides and heteropolysaccharides. The former type is made up of monosaccha...
7. What are the Examples of Structural Polysaccharides?
Some examples of structural polysaccharides are arabinoxylans, chitin, pectins and cellulose. Arabinoxylans are present in both the primary as well...
8. Which are the Three Main Polysaccharides Associated with Human Nutrition?
Starch, Cellulose and Glycogen are the three main polysaccharides associated with human nutrition and the first two are obtained from plants; where...
What are Polysaccharides?
Polysaccharides are major classes of biomolecules. They are long chains of carbohydrate molecules, composed of several smaller monosaccharides. These complex bio-macromolecules functions as an important source of energy in animal cell and form a structural component of a plant cell. It can be a homopolysaccharide or a heteropolysaccharide depending upon the type of the monosaccharides.
Which polysaccharide contains the same type of monosaccharides?
A polysaccharide that contains the same type of monosaccharides is known as a homopolysaccharide. Some of the important homopolysaccharides are: Glycogen: It is made up of a large chain of molecules. It is found in animals and fungi. Cellulose: The cell wall of the plants is made up of cellulose.
What are glycolipids and glycoproteins used for?
These glycolipids and glycoproteins are used to send messages or signals between and within the cells. They provide support to the cells. The cell wall of plants is made up of polysaccharide cellulose, which provides support to the cell wall of the plant.
What is the component of Chondroitin 4?
Chondroitin-4-sulfate: Its component sugars are D-glucuronic acid and N-acetyl-D-galactosamine-4-O-sulfate. It is present in the cartilages. Gamma globulin: N-acetyl-hexosamine, D-mannose, D-galactose are the component sugars of this polysaccharide. It is found in the blood.
What are some examples of monosaccharides?
Monosaccharides– Glucose and galactose are examples of monosaccharides.
What are the two basic compounds that make up carbohydrates?
A carbohydrate is a biomolecule consisting of carbon, hydrogen, and oxygen atoms. The two basic compounds that makeup carbohydrates are – Aldehydes and Ketones. Carbohydrates are found in all-natural and processed foods. The three types of carbohydrate are: Monosaccharides– Glucose and galactose are examples of monosaccharides.
Where is starch found?
Starch: It is formed by the condensation of amylose and amylopectin. It is found largely in plants, fruits, seeds, etc. Inulin: It is made up of a number of fructofuranose molecules linked together in chains. It is found in the tubers of dahlia, artichoke, etc.
What are structural polysaccharides?
Structural Polysaccharides: ADVERTISEMENTS: They are polysaccharides that take part in forming the structural frame work of the cell walls in plants and skeleton of animals. Structural polysaccharides are of two main types: chitin and cellulose. 1.
What is the component of starch?
Starch consists of two components, amylose and amylopectin (Fig. 9.7). Amylose is more soluble in water than amylopectin. In general, 20-30% of starch consists of amylose and the rest as amylopectin. Waxy starch of some varieties of Maize and other cereals consists entirely of amylopectin.
How are successive glucose units linked?
The successive glucose units are linked together by 1-4 α-linkages, that is, the link is between carbon atom 1 of one and carbon atom 4 of the other (Fig. 9.8). A molecule of water is lost during the formation of the linkage. A straight chain of amylose consists of 200-1000 glucose units.
What is waxy starch?
Waxy starch of some varieties of Maize and other cereals consists entirely of amylopectin. On the other hand, the starch of some varieties of Pea having wrinkled surface may have as much as 98% of amylose. Both amylose and amylopectin are formed by the condensation of α -D-glucose (pyranose forms).
How many units of glucose are in Amylopectin?
Amylopectin contains a large number of glucose units (2000-200,000). Besides a straight chain it bears several side chains which may be branched further.
How many glucose residues are in a glucose chain?
It has about 30,000 glucose residues and a molecular weight of about 4.8 million. Glucose residues are arranged in a highly branched bush like chains. There are two types of linkages 1-4 α -linkages in the straight part and 1-6 linkages in the area of branching. The straight part is helically twisted with each turn having six glucose units. The distance between two branching points is 10-14 glucose residues.
What is the type of mucosubstance?
Mucosubstances. Type # 1. Food Storage Polysaccharides: They are those polysaccharides which serve as reserve food. At the time of need, storage polysaccharides are hydrolysed. Sugars thus released become available to the living cells for production of energy and biosynthetic activity.
What are the two classes of polysaccharides?
Polysaccharides can be classified into two classes, namely, homopolysaccharides and heteropolysaccharides. The former type is made up of monosaccharide units and examples include cellulose, glycogen and starch. The latter type is made up of two or more types of monosaccharide units. Eg: Agar
What are the three main polysaccharides?
Starch, Cellulose and Glycogen are the three main polysaccharides associated with human nutrition and the first two are obtained from plants; whereas glycogen is the storage polysaccharide made by the human liver and muscles. Share this with your friends. Share.
What is a Polysaccharide?
Polysaccharide is a long chain of carbohydrates whose molecules consist of numerous sugar molecules bonded together by glycosidic linkages. Polysaccharide examples: Starch, Cellulose or Glycogen are polysaccharides Carbohydrates. As we know carbohydrates are a major source of food and necessary for getting energy for the survival of living organisms. Consisting of Carbon, Hydrogen and Oxygen atoms, carbohydrates are made up of two basic compounds, namely aldehydes and ketones.
What is the name of the polysaccharide that has more than one monosaccharide?
When more than one kind of monosaccharide is present in the polysaccharide structure, it is known as heteropolysaccharide or heteroglycan. In contrast, homopolysaccharide or homoglycan is the kind of polysaccharide which has the same type of monosaccharides.
What are the two basic compounds that make up carbohydrates?
Consisting of Carbon, Hydrogen and Oxygen atoms, carbohydrates are made up of two basic compounds, namely aldehydes and ketones. Polysaccharides are one of the three carbohydrates found in all natural and processed foods and the other two carbohydrates are monosaccharides and disaccharides. Monosaccharide Examples: Glucose and Galactose.
What are some examples of heteropolysaccharides?
Examples of heteropolysaccharides are hyaluronic acid, heparin, chondroitin-4-sulfate and gamma globulin. Hyaluronic acid is made up of N-acetyl-glucosamine and is found in connective tissues and skin.
Where is starch produced?
Insulin is composed of numerous fructofuranose molecules linked together in chains, it is found in tubers of artichoke, dahlia, etc.
What is the classification of polysaccharides?
Polysaccharides may be classified according to their composition as either homopolysaccharides or heteropolysaccharides.
How many monosaccharides are in a polysaccharide?
By convention, a polysaccharide consists of more than ten monosaccharide units, while an oligosaccharide consists of three to ten linked monosaccharides. The general chemical formula for a polysaccharide is C x (H 2 O) y. Most polysaccharides consist of six-carbon monosaccharides, resulting in a formula of (C 6 H 10 O 5) n.
How do polysaccharides form?
Polysaccharides form when monosaccharides or disaccharides link together by glycosidic bonds. The sugars participating in the bonds are called residues. The glycosidic bond is a bridge between the two residues consisting of an oxygen atom between two carbon rings. The glycosidic bond results from a dehydration reaction ...
Why are polysaccharides insoluble in water?
Because they are rich in hydrogen bonds, they are usually insoluble in water. Examples of storage polysaccharides are starch in plants and glycogen in animals. Polysaccharides used for cellular communication are often covalently bonded to lipids or proteins, forming glycoconjugates.
What is the chemical test for polysaccharides?
A common chemical test for polysaccharides is the periodic acid-Schiff (PAS) stain . Periodic acid breaks the chemical bond between adjacent carbons not participating in a glycosidic linkage, forming a pair of aldehyde. The Schiff reagent reacts with the aldehydes and yields a magenta purple color. PAS staining is used to identify polysaccharides in tissues and diagnose medical conditions that alter carbohydrates.
What is the bonding reaction of glycosidic bonds?
The glycosidic bond results from a dehydration reaction (also termed a condensation reaction). In the dehydration reaction a hydroxyl group is lost from a carbon of one residue while a hydrogen is lost from a hydroxyl group from another residue.
When does a glycosidic bond form?
An α (1→4) glycosidic bond forms when the two carbon atoms have the same stereochemistry or the OH on carbon-1 is below the sugar's ring. A β (1→4) linkage forms when the two carbon atoms have different stereochemistry or the OH group is above the plane.
What are some examples of starch?
Starch food sources often are referred to as "starchy carbohydrates" and include foods like corn, potatoes and rice. Other examples include bread, cereal and pasta. These foods are the most common form of carbohydrates in your diet, comprising an estimated one-third of the foods you eat. The body breaks starches down into glucose, ...
What fruits and vegetables contain cellulose?
Many fruits and vegetables contain some aspect of cellulose, including in the skins of apples and pears, in the covering of whole grains like wheat bran and in plant leaves like spinach. Seeds and nuts also contain cellulose. Advertisement.
What is cellulose in food?
Cellulose is another polysaccharide commonly found in foods. Cellulose provides a protective covering and/or structure to fruits and vegetables and their seeds. It gives foods a crunchy texture and is undigestible in the body. However, cellulose does act as a source of dietary fiber, adding bulk to your stool and helping to maintain regular digestive processes. Many fruits and vegetables contain some aspect of cellulose, including in the skins of apples and pears, in the covering of whole grains like wheat bran and in plant leaves like spinach. Seeds and nuts also contain cellulose.
What is the prefix for carbohydrate?
Carbohydrates can be divided into several categories: monosaccharides, disaccharides and polysaccharides. Chemically speaking, the prefix before "saccharides" indicates how many saccharide chains are attached to the molecule. Polysaccharides have many chains and must be broken down into smaller portions before they can be fully digested.
Do polysaccharides taste sweet?
Although polysaccharides are a form of sugar, many of their food sources rarely taste sweet. Video of the Day.
How many glycosidic bonds are there in glucose?
It had 1,4 glycosidic bonds which are arranged in long chains. Each beta glucose molecule is rotated 180 degrees from the previous molecule. This enables hydrogen bonds to form between the OH groups in adjacent chains.
What is the chain of glucose monomers joined by?
It is a chain of glucose monomers joined by alpha 1,4 glycosidic bonds and formed into a helix.
Which type of bond gives cellulose its high tensile strength?
The large numbers of hydrogen bonds which give cellulose high tensile strength.
Is polysaccharide large?
Polysac charides are very large. What does this mean?
