
Learn About the Different Types of Cells: Prokaryotic and Eukaryotic
- Prokaryotic Cells The simplest type of cells were most likely the first type of cells that formed on Earth. These are called prokaryotic cells. ...
- Eukaryotic Cells The other, much more complex, type of cell is called the eukaryotic cell. ...
- The Evolution of Cells Since prokaryotic cells are simpler than eukaryotic cells, it is thought they came into existence first. ...
What type of cell has two chromosomes?
Diploid Cells
- two sets of chromosomes. Haploid cells have only one. The diploid chromosome number is the number of chromosomes within a cell's nucleus.
- Somatic cells. A diploid cell replicates or reproduces through mitosis. ...
- Animal organisms. The diploid chromosome number of a cell is calculated using the number of chromosomes in a cell's nucleus.
What are two examples of a secondary cell?
Secondary Cells. In the secondary cells, the reactions can be reversed by an external electrical energy source. Therefore, these cells can be recharged by passing electric current and used again and again.These are also celled storage cells. Examples of secondary cells are, lead storage battery and nickel – cadmium storage cell.
What is the smallest type of cell?
What is the smallest membrane in the cell?
- Ribosomes are smallest non-membranous cell organelle.
- whereas peroxisomes are smallest membranous cell organelle.
- The smallest organelle in an animal cell is ribosome if we consider the surface area.
What are facts about cells?
- All living things are made up of cells.
- Cells are made up of proteins and organelles.
- Groups of cells form tissues and systems.
- The main purpose of a cell is to organize. ...
- The longest cells in the human body are the motor neurons. ...
- Red blood cells carry oxygen around the body. ...
- The largest cell, a fertilized egg, is too small to be seen with the naked eye.
What are the three types of blood cells?
The three major types of blood cells are red blood cells (which carry oxygen), white blood cells (which are components of the immune system, and platelets (cell fragments that allow blood to clot).
What are the four types of eukaryotic cells?
The four types of eukaryotic cells are animal cells, plant cells, fungi cells, and protists.
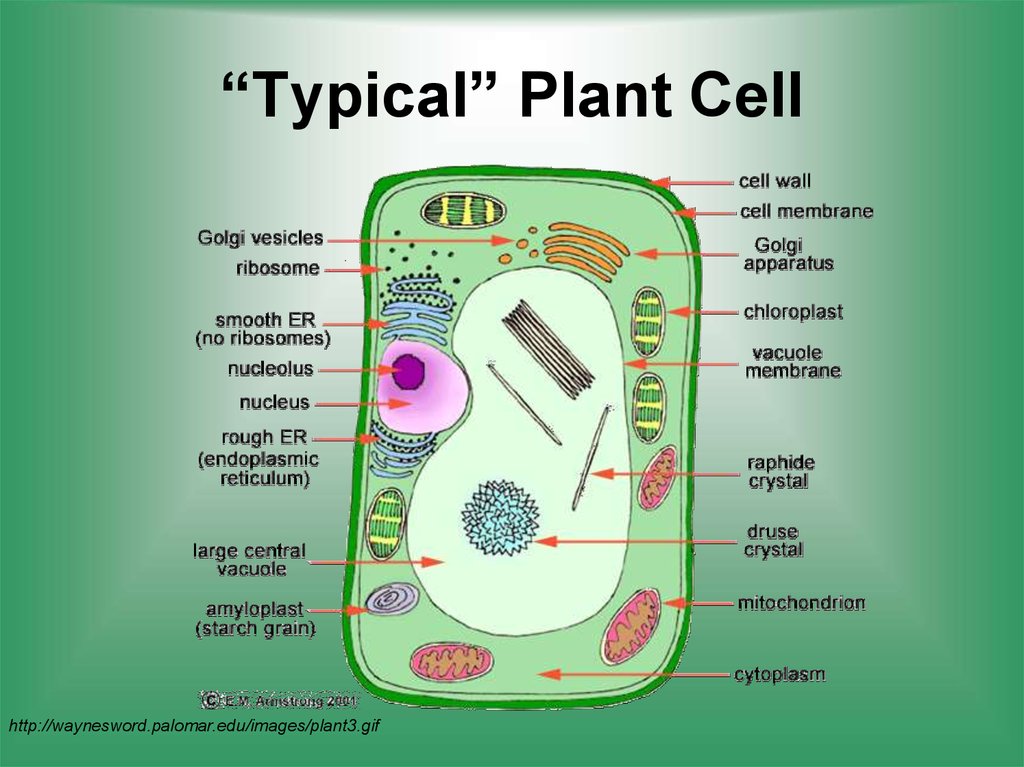
What are plant cells made of?
Plant Cells. Plants are made up of plant cells. Plant cells contain many of the organelles common to all eukaryotes, but they contain additional structures that are not found in animal cells. For example, plant cells are surrounded by a tough, cellulose-based structure called the cell wall.
What are the cells in the fungi kingdom?
Fungi Cells. The fungi kingdom consists of yeasts, mildews, molds, and mushrooms. Fungi cells contain many of the structures and organelles found in plant and animal cells, like the nucleus, mitochondria, cell membrane, mitochondria, Golgi apparatus, and endoplasmic reticulum. However, they do not contain chloroplasts.
What are the cells of the Protista?
Protist Cells. Protists are a highly diverse group of organisms, and kingdom Protista is comprised of all eukaryotes that are not animals, plants, or fungi. Protist cells contain all of the membrane-bound organelles found in animal cells, and some types also contain chloroplasts. They may also have a cell wall made from cellulose.
What are the structures of archaea?
Archaea are also unicellular prokaryotes, and they contain many of the same structures that are found in bacteria cells . However, they typically have a different composition. For example, the bacterial cell wall contains peptidoglycan, but the archaeal cell wall does not. The plasma membrane in bacterial cells (and eukaryotes) is a lipid bilayer, but the plasma membrane of archaeal cells is a lipid monolayer. Finally, the cell membrane in bacteria contains fatty acids, but the cell membranes of archaea contain a hydrocarbon called phytanyl.
Which is smaller, eukaryotic or prokaryotic?
Prokaryotic cell s are smaller and have a simpler structure than eukaryotic cells, as they do not contain membrane-bound organelles. Prokaryotic organisms are always unicellular and may be either bacteria or archaea. Bacterial and archaeal cells have the same basic structure, but some of their components are made from different materials.
What is the simplest type of cell?
Prokaryotic Cells. The simplest type of cells were most likely the first type of cells that formed on Earth. These are called prokaryotic cells. All prokaryotic cells have a cell membrane surrounding the cell, cytoplasm where all of the metabolic processes happen, ribosomes that make proteins, and a circular DNA molecule called a nucleoid where ...
Which cell theory is the most likely to be the first to come into existence?
The currently accepted theory of cell evolution is called the Endosymbiotic Theory. It asserts that some of the organelles, namely the mitochondria and chloroplast, were originally smaller prokaryotic cells engulfed by larger prokaryotic cells.
What are the organelles of eukaryotic cells?
The other, much more complex, type of cell is called the eukaryotic cell. Like prokaryotic cells, eukaryotic cells have cell membranes, cytoplasm, ribosomes, and DNA. However, there are many more organelles within eukaryotic cells. These include a nucleus to house the DNA , a nucleolus where ribosomes are made, rough endoplasmic reticulum for protein assembly, smooth endoplasmic reticulum for making lipids, Golgi apparatus for sorting and exporting proteins, mitochondria for creating energy, a cytoskeleton for structure and transporting information, and vesicles to move proteins around the cell. Some eukaryotic cells also have lysosomes or peroxisomes to digest waste, vacuoles for storing water or other things, chloroplasts for photosynthesis, and centrioles for splitting the cell during mitosis. Cell walls can also be found surrounding some types of eukaryotic cells.
What is the process of differentiation in eukaryotic cells?
Through a process called differentiation, these cells take on characteristics and jobs that can work with other types of cells to create an entire organism. There are a few unicellular eukaryotes as well.
How do organisms reproduce?
Most reproduce through a process called binary fission where basically the cell just splits in half after copying its DNA. This means that without mutations within the DNA, offspring are identical to their parent. All organisms in the taxonomic domains Archaea and Bacteria are prokaryotic organisms.
Do prokaryotic cells have a rigid cell wall?
The majority of prokaryotic cells also have a rigid cell wall that is used for protection. All prokaryotic organisms are unicellular, meaning the entire organism is only one cell. Prokaryotic organisms are asexual, meaning they do not need a partner to reproduce. Most reproduce through a process called binary fission where basically ...
Is Archaea a prokaryotic organism?
All organisms in the taxonomic domains Archaea and Bacteria are prokaryotic organisms. In fact, many of the species within the Archaea domain are found within hydrothermal vents. It is possible they were the first living organisms on Earth when life was first forming.
How many nuclei are there in a cell?
There is normally one nucleus per cell, but this is not always the case, skeletal muscle cells, for instance, have two. The nucleus contains the majority of the cell’s DNA (a small amount is housed in the mitochondria, see below). The nucleus sends out messages to tell the cell to grow, divide, or die.
Why are cells called cella?
Robert Hook first discovered cells in 1665. He gave them their name because they resembled the cella (Latin for “small rooms”) where monks lived in monasteries.
What is the difference between a sperm cell and a nerve cell?
For instance, a sperm cell resembles a tadpole , a female egg cell is spherical , and nerve cells are essentially thin tubes.
What are the functions of the plasma membrane?
To ensure each cell remains separate from its neighbor, it is enveloped in a special membrane known as the plasma membrane. This membrane is predominantly made of phospholipids, which prevent water-based substances from entering the cell. The plasma membrane contains a range of receptors, which carry out a number of tasks, including being: 1 Gatekeepers: Some receptors allow certain molecules through and stop others. 2 Markers: These receptors act as name badges, informing the immune system that they are part of the organism and not a foreign invader. 3 Communicators: Some receptors help the cell communicate with other cells and the environment. 4 Fasteners: Some receptors help bind the cell to its neighbors.
Why are daughter cells called diploids?
Both daughter cells have the same chromosomes as each other and the parent. They are referred to as diploid because they have two complete copies of the chromosomes.
What is the smallest unit of life that can replicate?
They function on their own, creating their own energy and self-replicating — the cell is the smallest unit of life that can replicate. However, cells also communicate with each other and connect to create a solid, well stuck-together animal.
What is the membrane that keeps cells separate from their neighbor?
Plasma membrane. To ensure each cell remains separate from its neighbor, it is enveloped in a special membrane known as the plasma membrane. This membrane is predominantly made of phospholipids, which prevent water-based substances from entering the cell.
Which cell type is the most modern?
Eukaryotic cells are thought to be the most modern major cell type. All multicellular organisms, including you, your cat, and your houseplants, are eukaryotes. Eukaryotic cells seem to have “learned” to work together to create multicellular organisms, while prokaryotes seem unable to do this.
Which cell has multiple chromosomes?
Eukaryotes – Complex cells with multiple chromosomes and internal organelles such as mitochondria, chloroplasts, and nuclei.
How do archaebacteria differ from other bacteria?
Key ways in which archaebacteria differ from other bacteria include: Their cell membranes, which are made of a type of lipid not found in either bacteria or eukaryotic cell membranes.
How many chromosomes are in an eukaryotic cell?
Eukaryotic cells usually have more than one chromosome, which contains large amounts of genetic information. Within the body of a multicellular organism, different genes within these chromosomes may be switched “on” and “off,” allowing for cells that have different traits and perform different functions within the same organism.
How do cells work?
In order to accomplish them, they must have: A cell membrane that separates the inside of the cell from the outside. By concentrating the chemical reactions of life inside a small area within a membrane, cells allow the reactions of life to proceed much faster than they otherwise would.
What are the characteristics of all living organisms?
Defining characteristics that allow a cell to perform these functions include: A cell membrane that keeps the chemical reactions of life together.
What material is capable of passing on traits to the cell's offspring?
Genetic material which is capable of passing on traits to the cell’s offspring. In order to reproduce, organisms must ensure that their offspring have all the information that they need to be able to carry out all the functions of life.All modern cells accomplish this using DNA, whose base-pairing properties allow cells to make accurate copies of a cell’s “blueprints” and “operating system.” Some scientists think that the first cells might have used RNA instead.
What Are The 2 Types Of Cells?
There are two distinct types of cells: prokaryotic cells and eukaryotic cells. Though the structures of prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells differ (see prokaryote eukaryote) their molecular compositions and activities are very similar.
What are the 2 types of cells give 2 examples of each type?
Cells fall into one of two broad categories: prokaryotic and eukaryotic. The single-celled organisms of the domains Bacteria and Archaea are classified as prokaryotes (pro = before karyon– = nucleus). Animal cells plant cells fungi and protists are eukaryotes (eu = true).
What are the 2 types of eukaryotic cells?
Eukaryotic cells may be classified into two groups based on the number of cells that make an individual organism: (1) unicellular eukaryotic cells and (2) multicellular eukaryotic cells. Unicellular eukaryotes include the protists. Multicellular eukaryotes include a variety of plant fungal and animal species.
What are the 2 main types of cells in the human body?
There are only two main types of cells: prokaryotic and eukaryotic. Prokaryotic cells lack a nucleus and other membrane-bound organelles. Eukaryotic cells have a nucleus and other membrane-bound organelles.
What are 2 examples of prokaryotic cells?
Examples of prokaryotes are blue-green algae bacteria and mycoplasma. Among prokaryotes bacteria are the most common and multiply very fast.
What is cell how many types of cell?
Cells are of two types: eukaryotic which contain a nucleus and prokaryotic cells which do not have a nucleus but a nucleoid region is still present. Prokaryotes are single-celled organisms while eukaryotes can be either single-celled or multicellular.
What are the two main groups into which cells are classified?
Cells fall into one of two broad categories: prokaryotic and eukaryotic. The predominantly single-celled organisms of the domains Bacteria and Archaea are classified as prokaryotes (pro– = before –karyon– = nucleus). Animal cells plant cells fungi and protists are eukaryotes (eu– = true).
