What are the 2 types of Specific Defense?
- 1. Humoral Immune response: WBC With B Cell They attach to the Pathogen and clump them together. Then the antibodies signal WB Cells to engulf and destroy the pathogens. But the Humoral Response is not over yet some of these White blood cells keep a few of these Antibodies and Recognize the Pathogen.
- 2. Cell Mediated Immune Response
Why are specific defenses called specific defenses?
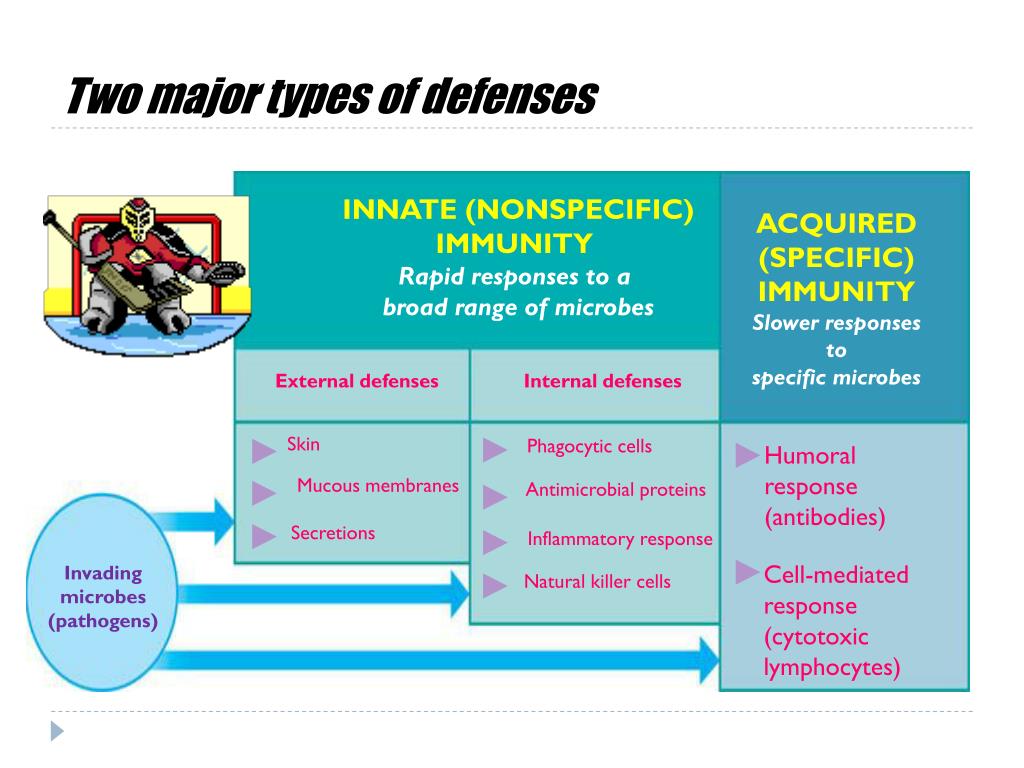
The specific defenses are called “specific” because they are directed against very specific targets. The elements of the first two walls of defense are general defenses that can be effective against any type of pathogen.
What is a non specific defense against pathogens?
The first two walls of defense are commonly referred to as “non-specific” defenses because they can be effective against any type of pathogen. When looking at the effect of helper T-cells, cytotoxic T-cells, and B-cells; each cell will only be effective in helping defend against one specific type of pathogen.
What types of cells carry out specific defenses against pathogens?
The specific defenses are carried out by 3 different cell types: helper T-cells, cytotoxic T-cells, and B-cells. These cells are produced in the bone marrow and are released into the blood in an inactive state. Inactive helper T-cells, cytotoxic T-cells, and B-cells are referred to as being naïve.
What are the different types of affirmative defenses?
Three types of affirmative defenses are frequently used in criminal law: justification defense, alibi, and excuse defenses. As its name suggests, this defense type is commonly used when the defendant did not commit the alleged crime.
What is the specific defense mechanism?
Which system has the ability to work against specific pathogens?
What are the organs of the immune system?
What are the two types of lymphocytes?
What is the immune system's response to a pathogen?
Which immune system takes care of cells that are infected by viruses or cells that are cancerous?
Which cells are also known as antigen presenting cells?
See 4 more
About this website
Specific and Non-Specific Defense Mechanism Against Infectious ...
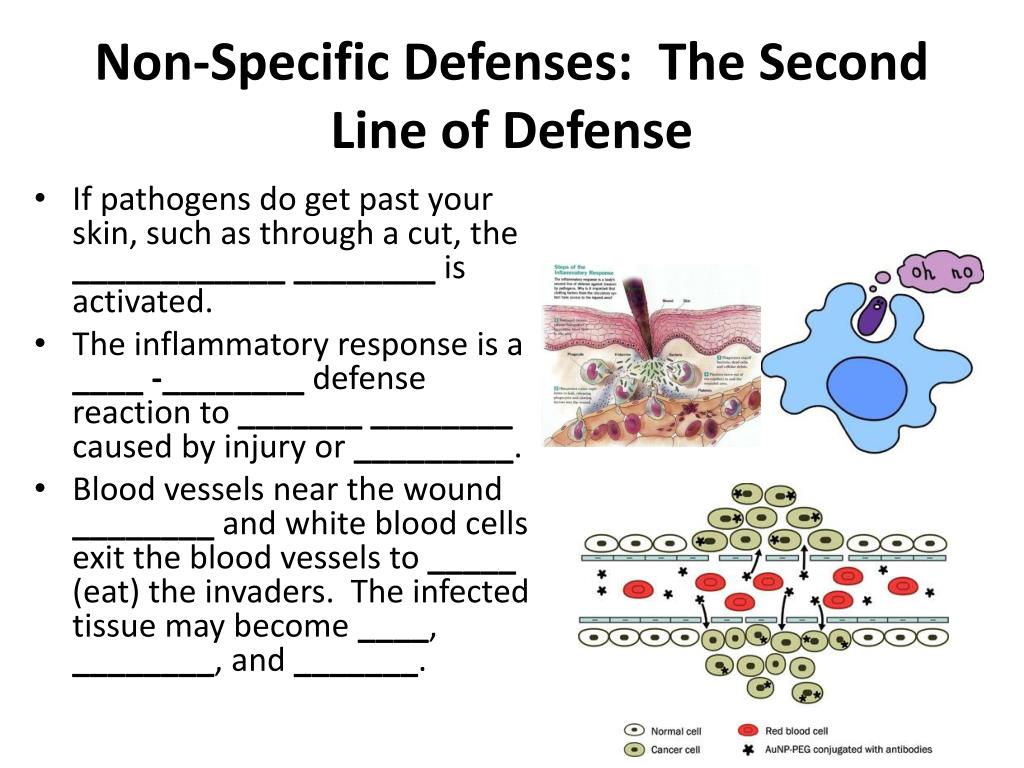
ADVERTISEMENTS: Specific and Non-Specific Defense Mechanism Against Infectious Organisms within the Host ! After entering into the host tissues the infectious organisms multiply and may cause diseases. ADVERTISEMENTS: There are some host defense mechanisms, which act against all the intruders immediately after their entry into the host; these defense mechanisms are non-specific in nature (i.e
Specific Defense (The Immune System) - CliffsNotes
The immune system is the third line of defense. It consists of mechanisms and agents that target specific antigens (Ags). An antigen is any molecule, usually a protein or polysaccharide, that can be identified as foreign (nonself) or self (such as MHC antigens described below).
Non-Specific Defense Mechanism in Human Body (With Diagram) | Biology
ADVERTISEMENTS: Non-specific defenses are the body’s first line of defense against diseases. They are not directed against a particular pathogen. Non-specific defenses guard against all infections, regardless of their cause. It is also called as innate immunity (Fig. 2). Plants and many lower animals rely only on innate immunity and do not possess the second […]
Specific Defence System - BiologyMad
There are two major aspects to our defence system – general and specific. General Defence System • Barriers • Non-specific protective cells Barriers: • Skin (inc. sweat) • Breathing System (mucus, cilia) • Digestive System (acid in stomach) • Tear Glands - lysozyme in tears keeps the surface of the eye free of bacterial infection. Non-specific Protective Cells
Welcome to the Instructional Web Site of Green River College
Welcome to the Instructional Web Site of Green River College
What is the specific defense mechanism?
Article Shared by. ADVERTISEMENTS: Specific defense mechanism is the ability of the body to develop immunity against specific pathogens, toxins or foreign things. This is possible by a special immune system that produces antibodies and/or activated lymphocytes that attack and destroy specific invading organisms or toxins.
Which system has the ability to work against specific pathogens?
The immune system has the ability to work against specific pathogens.
What are the organs of the immune system?
The Organs of the Immune System: The immune system is made of the primary lymphoid and the secondary lymphoid organs. The primary lymphoid includes the bone marrow and the thymus, while the others such as the spleen, Peyer’s patches of small intestine and the lymph nodes are included in the second category. a.
What are the two types of lymphocytes?
The lymphocytes are of two types that are functionally and phenotypically different from each other. They are the T lymphocytes and the B lymphocytes.
What is the immune system's response to a pathogen?
Memory: The immune system generates an immune response when the invader or pathogen attacks the body for the first time. This is retained in the memory and if the system encounters the same pathogen for the second time, it is eliminated rapidly offering protection against that particular pathogen.
Which immune system takes care of cells that are infected by viruses or cells that are cancerous?
The Cellular Immune System or Cell-mediated Immune System: This system takes care of cells that are infected by viruses or cells that are cancerous. Biology, Immunology, Human Body, Specific Defense Mechanism in Human Body.
Which cells are also known as antigen presenting cells?
Dendritic cells, which also originate in the bone marrow, function as antigen presenting cells (APC).
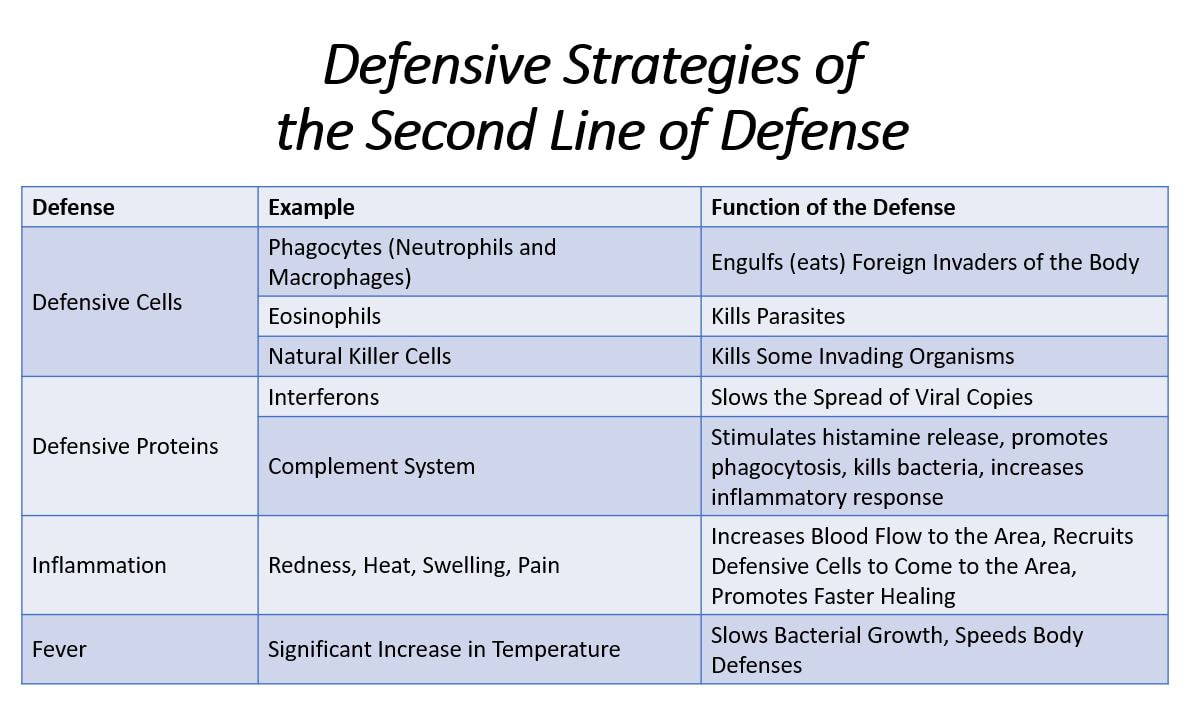
What are the nonspecific defense mechanisms that help eliminate foreign invaders?
Lymphocytes and antibodies destroy or immobilize the foreign substance. Nonspecific defense mechanisms (phagocytes, NK cells) help eliminate the invader. Memorization. Long‐lived “memory” lymphocytes are produced and can quickly recognize and respond to future exposures to the antigen or foreign cell.
What is the third line of defense?
The immune system is the third line of defense. It consists of mechanisms and agents that target specific antigens (Ags). An antigen is any molecule, usually a protein or polysaccharide, that can be identified as foreign (nonself) or self (such as MHC antigens described below).
What are the types of defenses in criminal law?
3. Alibi. Certain types of defenses in criminal law, such as the alibi defense, are affirmative defenses. This means the defendant (you) must prove the defense, and in the case of an alibi, it means that the defendant must prove ...
What are the common defenses to criminal charges?
There are many common defenses to criminal charges. A defendant may argue that there are holes in the prosecution’s case, that evidence was gathered in violation of the defendant’s constitutional rights, that another individual committed the crime, that the defendant had a justifiable reason ...
How does a defendant establish that he or she abandoned or withdrew from a crime?
For most crimes, a defendant can establish that he or she successfully abandoned or withdrew from a crime by showing that he or she stopped participating in the crime prior to its ultimate commission, that any actions undertaken by the defendant prior to abandoning the crime did not contribute to its successful completion, or that the defendant notified the police of the planned crime as soon as possible.
What is the defense to criminal liability?
1. Innocence. One of the simplest defenses to criminal liability is the defense of innocence. This defense is raised when you did not commit the crime. Remember, the prosecution has to prove every element of the crime charged against you and prove it beyond a reasonable doubt. To be innocent you do not have to prove anything.
What is the burden of proof?
The prosecution must prove the crime beyond a reasonable doubt. This breaks down as they must prove every element of the crime you have been charged with beyond a reasonable doubt. This is called the “burden of proof,” and it is a heavy one.
What evidence does a defendant offer?
Supportive evidence a defendant might offer includes testimony from someone he or she was with, surveillance footage, receipts from a restaurant, store, movie theater or sporting event, or phone records.
What is a criminal defense?
A criminal defense is a strategic argument that attempts to challenge the validity and sufficiency of the prosecution’s evidence. The prosecution, often referred to as the state, the people, or the United States for federal crimes, is the party trying to prove the criminal charges against you. The prosecution must prove ...
What is the specific defense mechanism?
Article Shared by. ADVERTISEMENTS: Specific defense mechanism is the ability of the body to develop immunity against specific pathogens, toxins or foreign things. This is possible by a special immune system that produces antibodies and/or activated lymphocytes that attack and destroy specific invading organisms or toxins.
Which system has the ability to work against specific pathogens?
The immune system has the ability to work against specific pathogens.
What are the organs of the immune system?
The Organs of the Immune System: The immune system is made of the primary lymphoid and the secondary lymphoid organs. The primary lymphoid includes the bone marrow and the thymus, while the others such as the spleen, Peyer’s patches of small intestine and the lymph nodes are included in the second category. a.
What are the two types of lymphocytes?
The lymphocytes are of two types that are functionally and phenotypically different from each other. They are the T lymphocytes and the B lymphocytes.
What is the immune system's response to a pathogen?
Memory: The immune system generates an immune response when the invader or pathogen attacks the body for the first time. This is retained in the memory and if the system encounters the same pathogen for the second time, it is eliminated rapidly offering protection against that particular pathogen.
Which immune system takes care of cells that are infected by viruses or cells that are cancerous?
The Cellular Immune System or Cell-mediated Immune System: This system takes care of cells that are infected by viruses or cells that are cancerous. Biology, Immunology, Human Body, Specific Defense Mechanism in Human Body.
Which cells are also known as antigen presenting cells?
Dendritic cells, which also originate in the bone marrow, function as antigen presenting cells (APC).