However, congenital heart defects can be broadly classified into three major categories:
- Heart Valve Defects These types of heart defects occur when the valves inside the heart leak or close-up. ...
- Heart Wall Defects These kinds of defects occur when the walls inside the heart do not develop properly. ...
- Blood Vessel Defects
- Atrial Septal Defect.
- Atrioventricular Septal Defect.
- Coarctation of the Aorta.
- Hypoplastic Left Heart Syndrome.
- Pulmonary Atresia.
- Tetralogy of Fallot.
- Total Anomalous Pulmonary Venous Return.
- Tricuspid Atresia.
What are the most common congenital heart defects?
The most common type of heart defect is a ventricular septal defect (VSD).
What are the 5 main types of congenital heart disease?
Congenital heart disease refers to a range of possible heart defects.Aortic valve stenosis. Aortic valve stenosis is a serious type of congenital heart defect. ... Coarctation of the aorta. ... Ebstein's anomaly. ... Patent ductus arteriosus. ... Pulmonary valve stenosis. ... Septal defects. ... Single ventricle defects. ... Tetralogy of Fallot.More items...
How many types of congenital heart defects are there?
18 Types of Congenital Heart Defects.
What are the four congenital heart defects?
Tetralogy of Fallot is a combination of four congenital heart defects. The four defects are a ventricular septal defect (VSD), pulmonary stenosis, a misplaced aorta and a thickened right ventricular wall (right ventricular hypertrophy). They usually result in a lack of oxygen-rich blood reaching the body.
What is the most rare heart defect?
Truncus arteriosus is a rare type of heart disease that is present at birth (congenital) in which there is a single main blood vessel, rather than the normal two, carrying blood away from the heart.
What is the difference between congenital heart disease and congenital heart defect?
A heart defect is a problem in the heart's structure. Kids who have a heart defect were born with it. Heart defects are often called "congenital," which means "present at birth." Heart defects are also sometimes referred to as "congenital heart disease."
What causes a congenital heart defect?
Researchers aren't sure exactly what causes most of these defects, but they think genetics, certain medical conditions, some medications, and environmental or lifestyle factors, such as smoking, may play a role. There are many different types of congenital heart defects.
What types of congenital heart disease is diagnosed as an children?
Types of congenital heart disease septal defects – where there's a hole between 2 of the heart's chambers (commonly referred to as a "hole in the heart") coarctation of the aorta – where the main large artery of the body, called the aorta, is narrower than normal.
Is a heart murmur a congenital heart defect?
Heart murmurs can be present at birth (congenital) or develop later in life (acquired). Some heart murmurs are harmless (innocent). An innocent heart murmur is not a sign of heart disease and doesn't need treatment. Other heart murmurs may be a sign of a serious heart condition.
How long do babies with CHD live?
About 69% survived to 18 years of age. Survival for infants with a CCHD improved over time. From 1979-1993, about 67% of infants survived to one year of life. Because medical care and treatment have gotten better over time, from 1994-2005, about 83% of infants survived to one year of life.
What is a hole in heart called?
An atrial septal defect is a birth defect of the heart in which there is a hole in the wall (septum) that divides the upper chambers (atria) of the heart. A hole can vary in size and may close on its own or may require surgery. An atrial septal defect is one type of congenital heart defect.
What is the life expectancy of a person with congenital heart disease?
Results: Patients with CHD expected to live to age 75 +/- 11 years, only 4 years less than their healthy peers. Over 85% of patients expected to live longer than our estimates of their life expectancy. Poorer health status and higher perceived risk of CHD complications related to shorter perceived life expectancy.
What are warning signs of heart problems?
SymptomsChest pain, chest tightness, chest pressure and chest discomfort (angina)Shortness of breath.Pain in the neck, jaw, throat, upper belly area or back.Pain, numbness, weakness or coldness in the legs or arms if the blood vessels in those body areas are narrowed.
Atrial septal defect
An atrial septal defect is a hole in the wall of the heart between the left and right atria, which are the two upper chambers of the heart. The hole causes blood to flow from the left atrium and mix with the right atrium, instead of going to the rest of the body.
Ventricular septal defect
A ventricular septal defect is a hole in the wall between the left and right ventricles, which are the two lower chambers of the heart. Blood may flow from the left ventricle and mix with blood in the right ventricle, instead of going to the rest of the body. If the hole is large, the heart and lungs may need to work harder to pump blood.
Patent ductus arteriosus
This common type of simple congenital heart defect occurs when a connection between the heart’s two major arteries, the aorta and the pulmonary artery, does not close properly after birth. This leaves an opening through which blood can flow when it should not. In many cases, small openings may close on their own.
Pulmonary stenosis
Pulmonary stenosis is a type of heart valve disease in which the pulmonary valve is too narrow or stiff. This affects how well blood can move from the heart to the pulmonary artery, the blood vessel that connects the heart to the lungs. Many children with pulmonary stenosis do not need treatment.
Tetralogy of Fallot
Tetralogy of Fallot is the most common complex congenital heart disorder and is a combination of four defects:
How many types of congenital heart defects are there?
There are many different types of congenital heart defects. Congenital heart defects can be broken down into common categories, such as: cyanotic congenital heart disease, ductal dependent congenital heart disease, critical congenital heart disease, and other acyanotic or less acute congenital heart defects.
What is congenital heart disease?
Congenital heart disease is an abnormality or structural problem of the heart or circulatory system that an infant is born with. Congenital heart defects can involve the walls of the heart, the valves and the arteries, or veins near the heart. These defects occur during fetal development, and some can be detected while fetuses are still in the womb with ultrasound and fetal echocardiogram. Other types of heart defects are detected at birth if a baby is born with symptoms like blue coloring or through a simple screening.
What causes a baby to be blue?
These types of congenital heart defects cause a baby to appear blue at birth (called cyanosis). The blue color occurs because deoxygenated blood flows out into the body. Common cyanotic heart defects include: 1 Tetralogy of Fallot 2 Transposition of great arteries 3 Tricuspid atresia 4 Total anomalous pulmonary venous return 5 Truncus arteriosus 6 Hypoplastic left heart syndrome
Why does a baby turn blue at birth?
These types of congenital heart defects cause a baby to appear blue at birth (called cyanosis). The blue color occurs because deoxygenated blood flows out into the body. Common cyanotic heart defects include:
How many congenital heart defects are critical?
About 25% of all congenital heart defects are considered critical, meaning they will require surgery or a procedure within a baby's first year of life.
What is the heart center?
The Heart Center at Children's Health, including Pediatric Heart Specialists, provides expert diagnosis and effective treatment for the full spectrum of pediatric heart conditions so that children can have healthy childhoods. Learn more about how we care for congenital heart defects at the Heart Center.
How many children are living with congenital heart disease?
There are approximately 3 million children and adults living with congenital heart disease.
How many types of heart defects are there?
At least 18 distinct types of congenital heart defects are recognized, with many additional anatomic variations. Recent progress in diagnosis and treatment (surgery and heart catheterization) makes it possible to fix most defects, even those once thought to be hopeless.
What happens if a child has a heart defect?
If your child is born with a heart defect today, the chances are better than ever that the problem can be overcome and that a normal adult life will follow. As diagnosis and treatment continue to advance, scientists will develop better treatments for these and other defects. Your cardiologist will discuss your particular heart defect, treatment options and expected results.
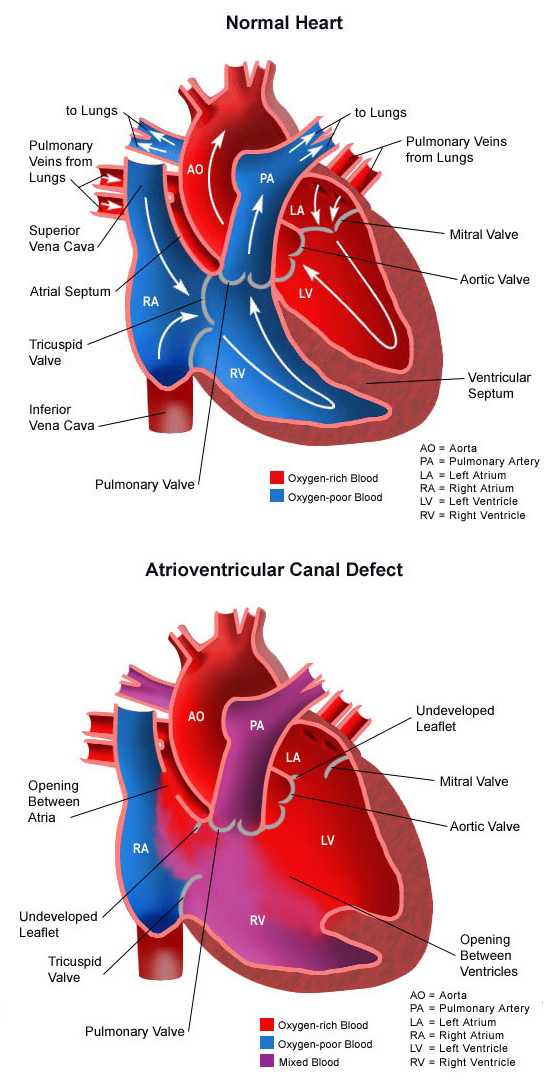
What is CAVC in medical terms?
Complete Atrioventricular Canal defect (CAVC) A large hole in center of the heart affecting all four chambers where they would normally be divided. When a heart is properly divided, the oxygen-rich blood from the lungs does not mix with the oxygen-poor blood from the body.
What is the defect in the septum between the heart's two upper chambers?
This defect allows oxygen-rich blood to leak into the oxygen-poor blood chambers in the heart. ASD is a defect in the septum between the heart's two upper chambers (atria). The septum is a wall that separates the heart's left and right sides. More information about Atrial Septal Defect.
What are the problems with the heart?
A heart defect that features four problems. They are: a hole between the lower chambers of the heart. an obstruction from the heart to the lungs. The aorta (blood vessel) lies over over the hole in the lower chambers. The muscle surrounding the lower right chamber becomes overly thickened.
What is the term for an underdeveloped left side of the heart?
The chamber may be smaller, underdeveloped, or missing a valve. Hypoplastic Left Heart Syndrome (HLHS) — An underdeveloped left side of the heart. The aorta and left ventricle are too small and the holes in the artery and septum did not properly mature and close.
What is a thickened or fused heart valve?
A thickened or fused heart valve that does not fully open. The pulmonary valve allows blood to flow out of the heart, into the pulmonary artery and then to the lungs.
How many types of congenital heart defects are there?from childrens.com
There are many different types of congenital heart defects. Congenital heart defects can be broken down into common categories, such as: cyanotic congenital heart disease, ductal dependent congenital heart disease, critical congenital heart disease, and other acyanotic or less acute congenital heart defects.
What is congenital heart disease?from childrens.com
Congenital heart disease is an abnormality or structural problem of the heart or circulatory system that an infant is born with. Congenital heart defects can involve the walls of the heart, the valves and the arteries, or veins near the heart. These defects occur during fetal development, and some can be detected while fetuses are still in the womb with ultrasound and fetal echocardiogram. Other types of heart defects are detected at birth if a baby is born with symptoms like blue coloring or through a simple screening.
What is the hole in the heart called?from webmd.com
All babies are born with a small hole in the heart called ductus arteriosus. During the first few days of life, the hole usually closes on its own. However, in some children the hole doesn't close on its own (called patent ductus arteriosus, or PDA ). Children with a ductal dependent congenital heart defect will experience cardiovascular collapse when the PDA closes. Prostaglandins, a type of medicine, help keep the ductus arteriosus open until children can undergo surgery or catheterization to fix their congenital heart defect.
What causes a baby to be blue?from childrens.com
These types of congenital heart defects cause a baby to appear blue at birth (called cyanosis). The blue color occurs because deoxygenated blood flows out into the body. Common cyanotic heart defects include: 1 Tetralogy of Fallot 2 Transposition of great arteries 3 Tricuspid atresia 4 Total anomalous pulmonary venous return 5 Truncus arteriosus 6 Hypoplastic left heart syndrome
How many people have a bicuspid aortic valve?from childrens.com
About 2% of all people have a bicuspid aortic valve, but they may not know it. "It varies widely how severe this defect can be," says Dr. Day. "For some, it doesn't leak or block blood flow, and the patient may never know they have this type of defect. In others, the valve can be really thick and doesn't open well.
How many congenital heart defects are critical?from childrens.com
About 25% of all congenital heart defects are considered critical, meaning they will require surgery or a procedure within a baby's first year of life.
What is the most serious septal defect?from webmd.com
This is the most serious septal defect. It’s when you have a hole in your heart that affects all four chambers. A CAVC prevents oxygen-rich blood from going to the right places in your body. Your doctor can repair it with patches.
What is a congenital heart defect?
When the heart or blood vessels near the heart do not develop normally before birth, a condition called congenital heart defect occurs (congenital means "existing at birth").
How many people have congenital heart defects?
Congenital heart defects occur in close to 1% of infants. Most young people with congenital heart defects are living into adulthood now. In most cases, the cause is unknown. Sometimes a viral infection in the mother causes the condition. The condition can be genetic (hereditary). Some congenital heart defects are the result ...
What is the condition where the aortic valve does not form properly?
Obstructive defects. Aortic stenosis (AS). In this condition, the aortic valve between the left ventricle and the aorta did not form properly and is narrowed, making it difficult for the heart to pump blood to the body.
What is a hole in the heart?
A hole between 2 chambers of the heart is an example of a very common type of congenital heart defect. More rare defects include those in which: The right or left side of the heart is incompletely formed (hypoplastic) Only one ventricle is present. Both the pulmonary artery and aorta arise from the same ventricle.
Which defect allows blood to pass from the right ventricle to the left ventricle?
Ventricular septal defect which allows blood to pass from the right ventricle to the left ventricle. A narrowing (stenosis) at or above the pulmonary valve that partially blocks the flow of blood from the right side of the heart to the lungs. The right ventricle is more muscular (hypertrophy) than normal.
What is the most common defect causing cyanosis in people beyond 2 years of age?
Tetralogy of Fallot is the most common defect causing cyanosis in people beyond 2 years of age. Most children with tetralogy of Fallot have open-heart surgery before school age (frequently in infancy) to close the ventricular septal defect and remove the obstructing muscle. Lifelong medical follow-up is needed.
What is the name of the Johns Hopkins Children's Center for congenital heart disease?
The Blalock-Taussig-Thomas Pediatric and Congenital Heart Center at Johns Hopkins Children’s Center provides comprehensive heart care for children and adults with congenital heart disease.
Why does congenital heart disease occur?
Congenital heart disease occurs as a result of an early developmental problem in the heart’s structure. The defect typically interferes with the normal flow of blood through the heart, which may affect breathing. Although researchers aren’t exactly sure why the heart fails to develop correctly, suspected causes include the following:
How many people in the US have congenital heart defects?
They can range from simple conditions that don’t cause symptoms to complex problems that cause severe, life-threatening symptoms. , there are currently 1 million adults and 1 million children in the United States living with congenital heart defects.
What is the difference between a cyanotic heart disease and a cyanotic heart disease?
The main difference is that cyanotic congenital heart disease causes low levels of oxygen in the blood, and acyanotic congenital heart disease ...
How long does it take for a heart defect to show up?
In other cases, the symptoms of a congenital heart defect may not appear until many years after birth. Once symptoms do develop, they may include:
How does a catheter help a heart defect?
During these procedures, the doctor will insert a thin tube into a vein in the leg and guide it up to the heart. Once the catheter is in the correct position, the doctor will use small tools threaded through the catheter to correct the defect.
When do congenital heart defects appear?
In some cases, the symptoms of a congenital heart defect may not appear until shortly after birth. Newborns with heart defects may experience:
When do you get diagnosed with a congenital heart defect?
Depending on the defect, diagnosis and treatment may begin shortly after birth, during childhood, or in adulthood. Some defects don’t cause any symptoms until the child becomes an adult, so diagnosis and treatment may be delayed. In these cases, the symptoms of a newly discovered congenital heart defect may include: shortness of breath.
How many types of congenital heart defects are there?
Congenital heart defects are structural problems arising from abnormal formation of the heart or major blood vessels. At least 18 distinct types of congenital heart defects are recognized, with many additional anatomic variations. Recent progress in diagnosis and treatment (surgery and heart catheterization) makes it possible to fix most defects, even those once thought to be hopeless.
What happens if a child has a heart defect?
If your child is born with a heart defect today, the chances are better than ever that the problem can be overcome and that a normal adult life will follow. As diagnosis and treatment continue to advance, scientists will develop better treatments for these and other defects. Your cardiologist will discuss your particular heart defect, treatment options and expected results.
What is a CAVC in the heart?
A CAVC allows blood to mix and the chambers and valves to not properly route the blood to each station of circulation.
What is the circulatory pattern of the heart?
A normal heart has valves, arteries and chambers that carry the blood in a circulatory pattern: body–heart–lungs–heart–body. When all chambers and valves work correctly, the blood is pumped through the heart, to the lungs for oxygen, back the heart and out to the body for delivery of oxygen. When valves, chambers, arteries and veins are malformed, this circulation pattern can be impaired. Congenital heart defects are malformations that are present at birth. They may or may not have a disruptive effect on a person's circulatory system.
What is the term for an underdeveloped left side of the heart?
Hypoplastic Left Heart Syndrome (HLHS) — An underdeveloped left side of the heart. The aorta and left ventricle are too small and the holes in the artery and septum did not properly mature and close.
What is the defect in the septum between the heart's two upper chambers?
This defect allows oxygen-rich blood to leak into the oxygen-poor blood chambers in the heart. ASD is a defect in the septum between the heart's two upper chambers (atria). The septum is a wall that separates the heart's left and right sides.
What is the name of the condition where blood cannot flow into the heart?
Tricuspid Atresia — There is no tricuspid valve in the heart so blood cannot flow from the body into the heart in the normal way. The blood is not being properly refilled with oxygen it does not complete the normal cycle of body–heart –lungs–heart –body.
What is the most common birth defect?
Congenital heart defects (CHDs) are the most common types of birth defects, and babies born with these conditions are living longer and healthier lives. Find more statistics about CHDs below.
What are the special needs of children with a heart condition?
Compared to children without a heart condition, children with a heart condition were more likely to have special healthcare needs, including medication needs, physical or speech therapy, and treatment for developmental or behavioral problems.
How old do babies with CHDs live?
About 69% of babies born with critical CHDs are expected to survive to 18 years of age. Survival and medical care for babies with critical CHDs are improving.
How old do non-critical CHD babies live?
About 95% of babies born with a non-critical CHD are expected to survive to 18 years of age. Thus, the population of people with CHDs is growing.
What causes infant death?
Infant Death Due to Heart Defects. Congenital heart defects are conditions present at birth that can affect the way the heart works. They can cause lifelong disability or death. They are the most common type of birth defect, affecting nearly 40,000 births in the United States each year.
How much more likely are children with CHD to receive special education services than children without birth defects?
Children with CHD are about 50% more likely to receive special education services compared to children without birth defects. 10. The occurrence and severity of a developmental disability or delay increases with how complex the heart defect is.
Is diabetes a congenital heart defect?
In a study published in the American Journal of Preventative Medicine, women with diabetes before pregnancy were about 4 times more likely to have a pregnancy affected by a congenital heart defect compared to women without diabetes.