
Types and Examples of Implicit Memory
- Procedural Memory One example of implicit memory is procedural memory, which is the reason that you don’t have to think about performing certain motor functions, you simply do them. ...
- Priming Priming describes the psychological phenomenon in which a past experience alters our response to an event in the present. ...
- Classic Conditioning ...
- Associative vs. Non-associative ...
- Illusion-of-Truth Phenomenon ...
What are some examples of implicit memory?
Some lighthearted examples of implicit memory are:
- Riding a bicycle.
- Taking a shower.
- Brushing your teeth every morning.
- Word recognition.
- Swinging a baseball bat.
- Simple tasks like boiling water.
- The process of tying your shoelaces.
What two types of explicit memory were described by?
Understanding Explicit Memory
- Sensory memory. This involves what you’re currently taking in with your senses. It’s the shortest type of memory.
- Short-term memory. Short-term memories tend to last for less than a minute, though they can sometimes become long-term memories.
- Long-term memory. Long-term memories can last for days to years. ...
What type of memory has an essentially limitless capacity?
Long-term memory is a form of memory that has a potentially limitless capacity, meaning that there seems to be no limit on the amount of information.
What are implicit memories?
Implicit memory is a type of long-term memory that encapsulates a whole variety of information that we don’t even think of. It is divided into procedural memory, priming, and classical conditioning, three systems that allow you to perform several activities like walking, playing instruments, driving, and holding a conversation with someone.
What are the three types of implicit memories?
There are several types of implicit memory, including procedural memory, priming, and conditioning. Together, these subtypes help you carry out everyday tasks, from riding a bike to having a conversation with someone.
Which of the following is a type of implicit memory?
Implicit memory refers to the influence of experience on behaviour, even if the individual is not aware of those influences. The three types of implicit memory are procedural memory, classical conditioning, and priming.
What is an example of implicit memory?
Some examples of implicit memory include singing a familiar song, typing on your computer keyboard, and brushing your teeth. Riding a bike is another example. Even after going years without riding one, most people are able to hop on a bike and ride it effortlessly.
What are the 4 types of memory?
There is much that researchers do not understand about human memory and how it works. This article explores the types of memory and what a person can do to improve their recall....Most scientists believe there are at least four general types of memory:working memory.sensory memory.short-term memory.long-term memory.
What is the meaning of implicit memory?
Implicit memory, often referred to as nondeclarative memory, does not require the conscious or explicit recollection of past events or information, and the individual is unaware that remembering has occurred. Implicit memory is usually thought of in terms of procedural memory, but also involves the process of priming.
Is reading an implicit memory?
Types of of Implicit Memory Procedural Learning: Procedural memory is part of of implicit memory that is responsible for knowing how to perform a of particular types of action, such as reading, tying shoes and riding a bike.
What is implicit learning examples?
Examples from daily life, like learning how to ride a bicycle or how to swim, are cited as demonstrations of the nature of implicit learning and its mechanism. It has been claimed that implicit learning differs from explicit learning by the absence of consciously accessible knowledge.
Is language an implicit memory?
The studies discussed in the Section “Implicit Memory and Language” show that the implicit memory system plays an important role in acquiring the grammar, or rules, of language at all levels of linguistics structure (Table 1).
What is implicit memory quizlet?
Implicit memory. unconscious, procedural, unaware memory state. affects behavior in a number of ways w/o us realizing it. Implicit memory tests. test with category generation, free association, general knowledge, word.
Which of the following is true of implicit memory quizlet?
Which of the following is true of implicit memory? Implicit memory is related to nonconsciously remembering skills and sensory perceptions.
Which of the following is not an example of an implicit memory?
Which of the following is NOT an example of implicit memory? Semantic memory.
Which is true about implicit memory?
Implicit memory is sometimes referred to as unconscious memory or automatic memory. Implicit memory uses past experiences to remember things without thinking about them. The performance of implicit memory is enabled by previous experiences, no matter how long ago those experiences occurred.
What are the different types of implicit memory?
Within implicit memory, there are several different types. Here, they are divided into three classes: procedural memory, priming, and classical conditioning. Each is thought to involve different structures in the brain.
What is implicit memory?
Definition. Implicit memory, sometimes referred to as unconscious memory, automatic memory, or non-declarative memory, is one of the two categories of long-term memory in humans. The other is called explicit memory, also known as declarative memory. Whereas explicit memory is the conscious memory of specific facts, events, and personal experiences, ...
What is the difference between explicit and implicit memory?
The difference between implicit and explicit memory is that explicit memories can be consciously recalled, whereas implicit memories are just ‘known’ without conscious thought involved. An example of explicit memory is being able to recall a particularly challenging music lesson.
What are the two types of memories?
Within long-term memory, there is a fundamental classification of memory into two types. These are implicit and explicit memories.
What is priming in psychology?
Priming describes the psychological phenomenon in which a past experience alters our response to an event in the present. The change is usually reflected in the accuracy or the processing time of the reaction. The responses refer to activities such as identifying, classifying, or locating an item.
What is procedural memory?
If carrying out a task is ‘second nature’ to you, and doesn’t require you to actively think about how to do it, then you are using procedural memory. Sometimes, this is referred to as ‘ muscle memory.’. Often, the tasks are complex, but the individual can do them without thinking.
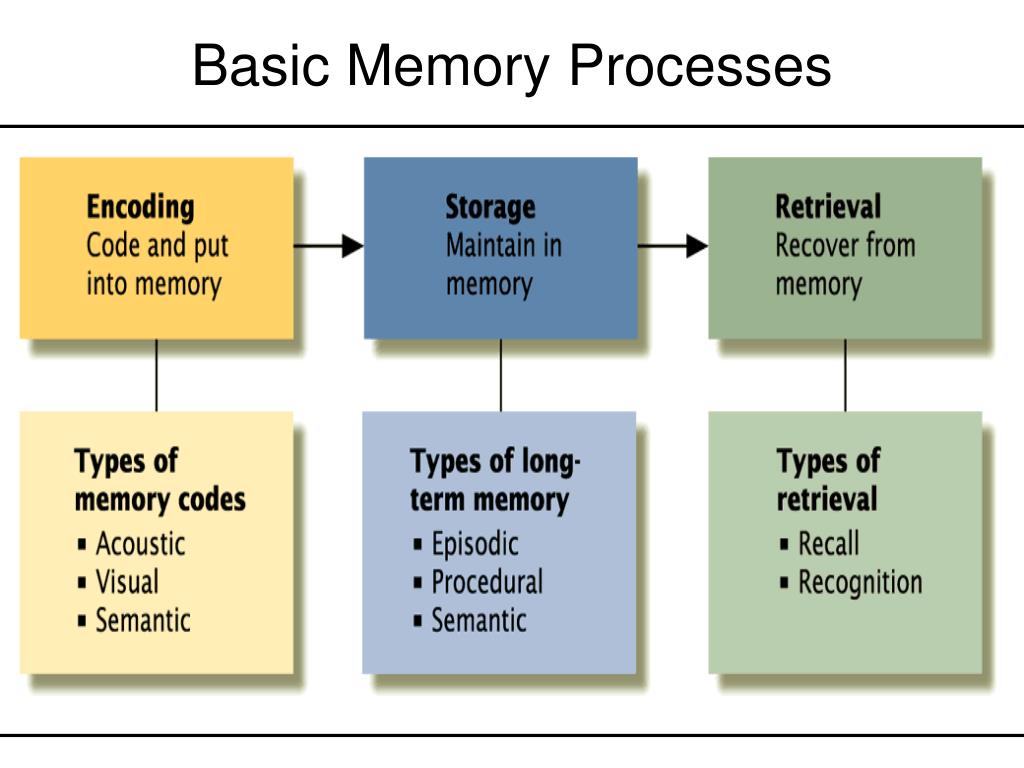
How to interpret memory?
One way of interpreting memory is to focus on what stage the memory is in; i.e., how long is the memory available to the individual? Sensory memory is the brief storage of information that results from a stimulus. Most of these memories are forgotten, but if we identify the information as valuable, it forms a working memory, part of our short-term memory.
What is implicit memory?
One of the two main types of long-term human memory. In psychology, implicit memory is one of the two main types of long-term human memory. It is acquired and used unconsciously, and can affect thoughts and behaviours. One of its most common forms is procedural memory, which allows people to perform certain tasks ...
When was explicit implicit memory introduced?
Although the explicit–implicit distinction was introduced during the 1980s, the sort of contrast that it captures is not new; related distinctions between conscious and unconscious memories, to take just one example, have been around for more than a century (for historical considerations, see Roediger, 1990b; Schacter, 1987). The critical development during the past decade has been the systematic demonstration, exploration, and attempted explanation of dissociations between explicit and implicit memory. Some of these dissociations have been provided by experiments demonstrating that brain-damaged amnesic patients with severe impairments of explicit memory can exhibit intact implicit memory; others come from studies showing that specific experimental variables produce different and even opposite effects on explicit and implicit memory tasks.
What are the two forms of unconscious memory?
Modern discoveries in neuropsychology concerning the organization of memory allow us to hypothesize that some synaptical cortical and subcortical circuits form the seat of unconscious mental functions. The possibility of identifying, in the explicit and implicit memory respectively, the repressed and unrepressed unconscious opens new and stimulating perspectives for an integration of neuroscience with psychoanalysis, and for a possible anatomic localization of the functions of these two different forms of unconscious. This depends on a presupposition: that the experiences, emotions, phantasies, and defences that help organize an individual's unconscious psychic reality, from birth throughout life, are stored in the nervous structures concerning memory, both implicit and explicit. This is, after all, in line with Freud's conviction: 'latent conceptions, if we have any reason to suppose that they exist in the mind—as we had in the case of memory—let them be denoted by the term "unconscious"' (1912, p. 260).
How is implicit memory measured?
Evidence for implicit memory arises in priming, a process whereby subjects are measured by how they have improved their performance on tasks for which they have been subconsciously prepared. Implicit memory also leads to the illusory truth effect, which suggests that subjects are more likely to rate as true those statements that they have already heard, regardless of their truthfulness.
Why are infants only capable of implicit memory?
Empirical evidence suggests infants are only capable of implicit memory because they are unable to intentionally draw knowledge from pre-existing memories. As people mature, they are usually capable of intentional recollection of memory, or explicit memory.
How does memory serve as an object?
Jacoby and Kelly posited that memory could serve as both an object and a tool. Memory is treated as an object in recall or recognition ; it can be inspected and described to others. In this case, the focus is on the past. However, memory (from the past) can be used as a tool to perceive and interpret present events. When riding a bicycle, one's focus is on travelling down the road, rather than the specifics of keeping balance. A bicyclist may not even be able to specify the particulars of balancing. In this case, the past memory of keeping one's balance serves as a tool rather than an object.
How did unconscious influences affect memory?
Unconscious influences of memory were found to alter the subjective experiences of participants. In one such study, participants judged that the white background noise was lower when they read words they had already been presented, thus misattributing their ease of perceiving the word to less noisy environment.
What is implicit memory?
Implicit memory, also known as unconscious memory or automatic memory, refers to perceptional and emotional unconscious memories which influence our behavior (Dew & Cabeza, 2011). The impact which implicit memory has on our current behavior occurs without our conscious retrieval of memories. Hence, implicit memory enables our prior experiences ...
Where is implicit memory located?
The cerebellum which is essential for procedural memories is located at the base of the brain.
What is priming in cognitive psychology?
Priming: Priming is a non conscious form of human implicit memory concerned with perceptual identification of words and objects.
What are the two types of long term memory?
Our long-term memory can be fundamentally divided into two distinct types, namely implicit memory and explicit memory (Squire, 2004). It should be noted that the formation of explicit memories requires several rounds of stimulation, significant effort and considerable time.
Why is implicit memory important?
Hence, implicit memory enables our prior experiences to improve our performance of various tasks without our conscious and explicit awareness of such experiences.
Which ganglia is responsible for implicit memory?
The basal ganglia ’s constitution explains why implicit memory involves subconsciously driven sensorimotor behavior which we typically remain unaware of.
Which part of the brain is responsible for memory?
& Cabeza, 2011). The cerebellum which is essential for procedural memories is located at the base of the brain.
What is the difference between explicit and implicit memory?
on October 31, 2019. Information that you have to consciously work to remember is known as explicit memory, while information that you remember unconsciously and effortlessly is known as implicit memory. People often focus more on the topic of explicit memory, but researchers are becoming increasingly interested in how implicit memory works ...
What is Explicit Memory?
When you're trying to intentionally remember something (like a formula for your statistics class or a list of dates for your history class), this information is stored in your explicit memory. People use these memories every day, from remembering information for a test to recalling the date and time of a doctor's appointment.
Why is mood important in memory?
Studies have also suggested that mood can also play an important role in the formation and recall of explicit and implicit memories.
What are some examples of things that are remembered through explicit memory?
Other examples of things that are remembered through explicit memory include: All of the items on your shopping list. Birth dates of friends and family members. Important events from your life such as your school graduation, wedding, or another notable milestone. Names and locations of different countries on a map.
What is semantic memory?
Semantic memory: These are memories of facts, concepts, names, and other general knowledge.
When you're trying to intentionally remember something, what is stored in your explicit memory?
When you're trying to intentionally remember something (like a formula for your statistics class or a list of dates for your history class), this information is stored in your explicit memory. People use these memories every day, from remembering information for a test to recalling the date and time of a doctor's appointment.
What are some examples of events that enter our memory?
For example, on the way to class, you might hear a catchy pop song on the radio. Days later, you find yourself still humming that same tune.
What are some examples of implicit memory?
This type of memory is not conscious. An implicit memory example might include brushing your teeth. See more implicit memory examples that are easy to remember. runner tie shoe laces as example implicit ...
What is implicit in adulthood?
An adult is able to wash one's face or body without thinking of how to do so. As an adult who has done so for many years, tying one's shoes is implicit. An adult is able to button pants and shirts without considering the steps ahead of time. As a literate adult, signing his name to a check is implicit.
What is episodic memory?
episodic memory - personalized memories like your wedding. semantic memory - facts and names like the date of your wedding. Unlike implicit memories which become automatic, explicit memories always need to be recalled by the thinker. Advertisement.
What are some tasks that can be completed without thinking of each step?
Making a bed is a common task that most can complete without thinking of each step. Taking a shower is able to be completed without considering various steps ahead of time. Eating is executed by adults without forethought of the process. Locking the door to one's house is a step that is done without recall memory.
Is it implicit to sign a check?
As a literate adult, signing his name to a check is implicit. For a seamstress, fixing a hem is implicit. Brushing one's teeth is able to be completed without recalling specific steps. Combing one's hair is an automatic task.
Do you need to look at each key to type?
When a skilled typist is typing on a keyboard, she does not need to look at each key. Instead, she is able to type without recalling the placement of each key. Once a person has learned how to ride a bike, repeated riding is implicit memory. The rider does not need to specifically recall each motion that needs to be completed.
Is driving a car implicit memory?
For experienced drivers, driving a car is an example of implicit memory. The driver of the car drives without conjuring up each task that is necessary to be completed while driving. For many adults, it is not necessary to read a recipe or specifically recall the steps for cooking pasta. Driving to an established workplace is a part ...
What is explicit memory?
Explicit long-term memories are memories we consciously and deliberately took time to form and recall. Explicit memory holds information such as your best friend’s birthday or your phone number. It often includes major milestones in your life, such as childhood events, graduation dates, or academic work you learned in school.
What are the three types of sensory memory?
There are three types of sensory memory: iconic, which is obtained through sight; echoic, which is auditory; and haptic, which is through touch. 2
Why Do We Have Different Types of Memory?
Your short-term memory allows you to process and understand the information in an instant. When you read a paragraph in a book and understand it, that’s your short-term memory at work.
How Are Memories Made?
Memories are made in three distinct stages. It starts with encoding. Encoding is the way external stimuli and information make their way into your brain. This could occur through any of your five senses.
What is semantic memory?
Semantic memories are general facts and bits of information you absorbed over the years. For instance, when you recall a random fact while filling in a crossword puzzle, you pull that memory from your semantic memory.
How much memory can we hold?
There is no limit to how much our long-term memory can hold and for how long. We can further split long-term memory into two main categories: explicit and implicit long-term memory.
When does sensory memory stop?
When a sensory experience keeps recurring, and you start to attach other memories to it , the sensory experience stops living in your sensory memory. It might move to your short-term memory or more permanently to your long-term memory.
What is explicit memory?
Memory experts have also distinguished explicit memory, in which information is consciously recalled, from implicit memory, the use of saved information without conscious awareness that it’s being recalled.
What is semantic memory?
Semantic memory is someone’s long-term store of knowledge: It’s composed of pieces of information such as facts learned in school, what concepts mean and how they are related, or the definition of a particular word. The details that make up semantic memory can correspond to other forms of memory. One may remember factual details about a party, for instance—what time it started, at whose house it took place, how many people were there, all part of semantic memory—in addition to recalling the sounds heard and excitement felt. But semantic memory can also include facts and meanings related to people, places, or things one has no direct relation to.
What is the short term memory of something?
Sensory memories are what psychologists call the short-term memories of just-experienced sensory stimuli such as sights and sounds. The brief memory of something just seen has been called iconic memory, while the sound-based equivalent is called echoic memory. Additional forms of short-term sensory memory are thought to exist for the other senses as well.
What is procedural memory?
The term describes long-term memory for how to do things, both physical and mental, and is involved in the process of learning skills —from the basic ones people take for granted to those that require considerable practice. A related term is kinesthetic memory, which refers specifically to memory for physical behaviors.
What is a person's memory?
A person’s memory is a sea of images and other sensory impressions, facts and meanings, echoes of past feelings, and ingrained codes for how to behave—a diverse well of information. Naturally, there are many ways (some experts suggest there are hundreds) to describe the varieties of what people remember and how.
What is autobiographical memory?
A related concept is autobiographical memory, which is the memory of information that forms part of a person’s life story. However, while autobiographical memory includes memories of events in one’s life (such as one’s sixteenth birthday party), it can also encompass facts (such as one’s birth date) and other non-episodic forms of information.
When is short term memory used?
Short-term memory is used when, for instance, the name of a new acquaintance, a statistic, or some other detail is consciously processed and retained for at least a short period of time. It may then be saved in long-term memory, or it may be forgotten within minutes. With working memory, information—the preceding words in a sentence one is reading, for example—is held in mind so that it can be used in the moment.

Definition
Overview of Memory
- There are several different memory systems in the brain. In psychology, memory can be classified in a few different ways, including the stage of the memory, the type of memory, and the process of creating the memory. One way of interpreting memory is to focus on what stage the memory is in; i.e., how long is the memory available to the individual? Sensory memory is the brief storage of i…
Implicit vs. Explicit Memory
- The difference between implicit and explicit memoryis that explicit memories can be consciously recalled, whereas implicit memories are just ‘known’ without conscious thought involved. An example of explicit memory is being able to recall a particularly challenging music lesson. You might remember the names of the pieces played and the classmates present. However, the impr…
Types and Examples of Implicit Memory
- Within implicit memory, there are several different types. Here, they are divided into three classes: procedural memory, priming, and classical conditioning. Each is thought to involve different structures in the brain.
Overview of Memory
- In the brain, there are multiple separate memory systems. Memory may be characterised in many ways in psychology, including the stage of the memory, the kind of memory, and the process of memory formation. Focusing on what stage the memory is at, i.e., how long the memory is accessible to the person, is one approach to understanding memory. Sensory memory is the te…
Implicit vs. Explicit Memory
- Explicit memories may be actively remembered, while implicit memories are simply “known” without any conscious thought. Being able to remember a particularly difficult music lesson is one example of explicit memory. You may recall the titles of the works that were performed as well as the students that were there. However, you have an implicit recall of the improvements you mad…
Types and Examples of Implicit Memory
- There are various distinct forms of implicit memory. Procedural memory, priming, and classical conditioning are the three categories here. Each is assumed to engage various brain areas.
Procedural Memory
- Procedural memory is an example of implicit memory, and it explains why you don’t have to think about completing some motor actions; you just execute them. Riding a bike, typing, tying your shoes, or playing a video game are just a few examples. You are employing procedural memory if doing a job is’ second nature ‘to you and does not need you to consciously think about how to ex…
Priming
- Priming is a psychological phenomenon in which a previous experience influences our reaction to a current situation. The shift is frequently reflected in the reaction’s accuracy or processing time. Identifying, categorising, and finding an object are among the actions mentioned in the replies. Due to the link between the phrases “cat” and “mouse,” if someone is exposed to the word “mous…
Classic Conditioning
- When two unrelated stimuli (one neutral and one biological) are coupled in order to generate a new response to the neutral stimulus, this is known as classical conditioning. It’s a sort of association learning. Pavlov’s dog is the greatest illustration of this; classical conditioning is also known as Pavlovian conditioning. Ivan Pavlov discovered that in the presence of the technician …
Associative vs. Non-Associative
- Implicit memory may also be classified as associative or non-associative. When behaviour changes in the absence of any identifiable stimulus, this is known as non-associative learning. This differs from associative learning, such as classical conditioning, in which we automatically learn that two stimuli are linked and behave appropriately. Habituation and sensitization are the …
Illusion-Of-Truth Phenomenon
- The illusion-of-truth effect, also known as the illusory truth effect, is a phenomenon in which the more we hear something, the more we perceive it to be true. People are more likely to believe the veracity of material they are acquainted with. This phenomenon has the potential to create misleading recollections. Unconscious bias is a sort of illusory truth, and it reflects implicit mem…
References
- Radvansky, G. A. (2017). Human Memory Third Edition. London: Taylor and Francis.
- Roediger, H. L. (1990). Implicit memory: Retention without remembering. American Psychologist, 45(9), 1043–1056. doi: 10.1037/0003-066x.45.9.1043
- Squire, L. R., & Zola, S. M. (1996). Structure and function of declarative and nondeclarative memory systems. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of …
- Radvansky, G. A. (2017). Human Memory Third Edition. London: Taylor and Francis.
- Roediger, H. L. (1990). Implicit memory: Retention without remembering. American Psychologist, 45(9), 1043–1056. doi: 10.1037/0003-066x.45.9.1043
- Squire, L. R., & Zola, S. M. (1996). Structure and function of declarative and nondeclarative memory systems. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 93(24)...
- Squire, L. R., & Dede, A. J. (2015). Conscious and unconscious memory systems. Cold Spring Harbor perspectives in biology, 7(3), a021667. https://doi.org/10.1101/cshperspect.a021667
Overview
In psychology, implicit memory is one of the two main types of long-term human memory. It is acquired and used unconsciously, and can affect thoughts and behaviours. One of its most common forms is procedural memory, which allows people to perform certain tasks without conscious awareness of these previous experiences; for example, remembering how to tie one's shoes or ride a bicycle without consciously thinking about those activities.
Evidence and current research
Advanced studies of implicit memory began only in the 1980s. In early research, subjects were presented with words under different conditions and were given two types of tests: recognition memory tests and perceptual identification tests. These studies provided evidence that effects of memory on perceptual identification was independent of recognition memory. Jacoby & Brooks argued that perceptual identity effects reflect very rapid, context-specific learning. Unconscious …
Development
Empirical evidence suggests infants are only capable of implicit memory because they are unable to intentionally draw knowledge from pre-existing memories. As people mature, they are usually capable of intentional recollection of memory, or explicit memory. However, amnesic patients are usually the exception to developing memory, but are still capable of undergoing priming, to some extent. Since procedural memory is based on automatic responses to certain stimuli, amnesic p…
Memory as tool vs. memory as object
Jacoby and Kelly posited that memory could serve as both an object and a tool. Memory is treated as an object in recall or recognition; it can be inspected and described to others. In this case, the focus is on the past. However, memory (from the past) can be used as a tool to perceive and interpret present events. When riding a bicycle, one's focus is on travelling down the road, rather than the specifics of keeping balance. A bicyclist may not even be able to specify the parti…
Illusion-of-truth effect
The illusion-of-truth effect states that a person is more likely to believe a familiar statement than an unfamiliar one. In a 1977 experiment participants were asked to read 60 plausible statements every two weeks and to rate them based on their validity. A few of those statements (some of them true, others false) were presented more than once in different sessions. Results showed that participants were more likely to rate as true statements the ones they had previously heard (eve…
Procedural memory
A form of implicit memory used every day is called procedural memory. Procedural memory lets us perform some actions (such as writing or riding a bike) even if we are not consciously thinking about it.
In one experiment two groups of people, one composed of amnesic patients with heavily impaired long-term memory, and the other composed by healthy subjects, were asked several times to sol…
Evidence for the separation of implicit and explicit memory
Evidence strongly suggests that implicit memory is largely distinct from explicit memory and operates through a different process in the brain. Recently, interest has been directed towards studying these differences, most notably by studying amnesic patients and the effect of priming.
The strongest evidence that suggests a separation of implicit and explicit memory focuses on studies of amnesic patients. As was previously discussed in the section on procedural memory, …
See also
• Explicit memory
• Implicit association test
• Implicit cognition
Origin and Development
- Origin and Development
The discovery of implicit memory and the explicit memory stemmed from the treatment of the neuroscience patient, Henry Gustav Molaison (Squire, 2009). An attempt to cure his epilepsy via a bilateral medial temporal lobotomy destroyed parts of Molaison’s brain. Consequently, he suffer…
What Is Implicit Memory?
- What is Implicit Memory?
The impact which implicit memory has on our current behavior occurs without our conscious retrieval of memories. Hence, implicit memory enables our prior experiences to improve our performance of various tasks without our conscious and explicit awareness of such experiences.
What Is Explicit Memory?
- What is Explicit Memory?
Recalling information from explicit memory involves some degree of conscious effort – information is consciously brought to mind and “declared”. For example, declarative knowledge involves “knowing that” London is the capital of England, zebras are animals, and the date of you…
The Relationship Between The Two Memory Systems
- The Relationship between the Two Memory Systems
While recent evidence suggests a significant impact of implicit memory’s priming on explicit memory’s fact recalling, the two memory systems are thought to work independently with fundamentally distinct rules of operation (Squire, 2004). The study of amnesic patients implies …