Music Intervals Chart
| Semitones | Interval | Abbreviation | Example |
| 0 | Unison | PP or P1 | C – C |
| 1 | Minor 2nd | m2 | C – Db |
| 2 | Major 2nd | M2 | C – D |
| 3 | Augmented 2nd | A2 | C – D# |
- perfect intervals.
- major intervals.
- augmented intervals.
- minor intervals.
- diminished intervals.
How to identify perfect, major, and minor intervals?
How to Identify Perfect, Major, and Minor Intervals. 🔗. Here are two methods for identifying intervals. 🔗. The first method involves thinking of the lower note of an interval as the tonic (the first note of the scale). Remember that all the notes above the tonic in a major scale are perfect or major. Determine if the upper note is in the ...
What are major and perfect intervals?
There are three intervals that are what we call perfect intervals:
- a perfect 4th
- a perfect 5th
- a perfect 8ve (or octave)
What are two types of intervals?
Intervals are of three types, namely, closed intervals, open intervals and semi open or semi closed intervals. Let us discuss about them. But, before discussing the types of intervals, it is important to learn about an important term – the endpoint. In intervals, an endpoint is a value that is either the start value or the end value of the ...
What is a major interval in music?
Major Intervals. The major interval contains a half step more than the minor interval. There are four intervals which are known as the major intervals, namely: a major second, a major third, a major sixth, and a major 7th Minor Intervals. A minor interval contains half a step less than a major interval.

What are the 3 types of music intervals?
In music theory, an interval is a difference in pitch between two sounds. An interval may be described as horizontal, linear, or melodic if it refers to successively sounding tones, such as two adjacent pitches in a melody, and vertical or harmonic if it pertains to simultaneously sounding tones, such as in a chord.
How many types of intervals are there in music?
Measured as described above, the scale yields four perfect intervals: prime, or unison; octave; fourth; and fifth.
What are the 12 musical intervals?
Western music typically uses 12 notes – C, D, E, F, G, A and B, plus five flats and equivalent sharps in between, which are: C sharp/D flat (they're the same note, just named differently depending on what key signature is being used), D sharp/E flat, F sharp/G flat, G sharp/A flat and A sharp/B flat.
What are the 5 intervals?
5.1. Intervals such as the unison, fourth, fifth, and octave can be classified as “ perfect ” but never “major” or “minor”. Conversely, the intervals of the second, third, sixth, and seventh can be major or minor but never perfect in quality.
What are the two types of intervals?
The space between any two pitches is called an interval. Whole steps and half steps are two types of intervals. A whole step can also be called a major 2nd, and half steps are sometimes called minor 2nds.
What are the 4 perfect intervals?
Perfect intervals are the unison, fourth, fifth, and octave. They occur naturally in the major scale between scale note 1 and scale notes 1, 4, 5, and 8.
What are intervals examples?
An interval comprises the numbers lying between two specific given numbers. For example, the set of numbers x satisfying 0 ≤ x ≤ 5 is an interval that contains 0, 5, and all numbers between 0 and 5.
What are major intervals?
Major intervals can be augmented by adding a half step. Major intervals can be augmented by adding a semitone. For example, since C to A is a major sixth (9 half steps), C to A# is an augmented sixth (10 half steps). For example, since C to A is a major sixth (9 semitones), C to A# is an augmented sixth (10 semitones).
What are the intervals of notes?
An INTERVAL is the distance between two notes /pitches. Intervals are named by size and quality: Interval Size: The size is an Arabic number. (e.g., 1, 2, 3, 4) To determine the size, count the note names between the two notes given (inclusive).
How do you name intervals in music?
9:4211:02How to Identify Musical Intervals (Music Theory) - YouTubeYouTubeStart of suggested clipEnd of suggested clipFirst you count alphabetically from the lower to the upper note of the interval inclusively. AndMoreFirst you count alphabetically from the lower to the upper note of the interval inclusively. And this gives us the interval.
What is a 2nd interval in music?
A second is a musical interval encompassing two adjacent staff positions (see Interval number for more details). For example, the interval from C to D is a major second, as the note D lies two semitones above C, and the two notes are notated on adjacent staff positions.
What are the eight kinds of melodic intervals?
By way of summary, we have distinguished no less than seven different types of melodic intervals: voiced melodic intervals, interrupted melodic intervals, cross-voice melodic intervals, unvoiced outer intervals, unvoiced inner intervals, distance intervals, and tied note intervals.
What are Intervals in Music?
In music, the term interval refers to the pitch difference between any two notes. Or, in other words, the distance in pitch between these two sounds.
Explaining Intervals
As I mentioned above, an interval is a variation in pitch between two sounds. As a result, the larger the interval existing between two notes, the more they’re different in terms of pitch.
Laying the Basis for Understanding Intervals
Wow! That was a lot of information to absorb, so how about we go back to the very basis of an interval — its building blocks. I’m referring to semitones (also known as half steps) and tones (also called whole steps).
Naming Intervals
Now that you’re familiar with the building blocks of intervals; the semitones and tones (the two smallest intervals in western music), we can move on to look at larger intervals and how you can name them.
What are Melodic Intervals?
These are the opposite of harmonic intervals. They describe when two notes are played “as part of a melody ” in succession (one after the other).
What is an interval in music?
Melodic and harmonic intervals. In music theory, an interval is a difference in pitch between two sounds. An interval may be described as horizontal, linear, or melodic if it refers to successively sounding tones, such as two adjacent pitches in a melody, and vertical or harmonic if it pertains to simultaneously sounding tones, such as in a chord.
What is the smallest interval in music?
In Western music, intervals are most commonly differences between notes of a diatonic scale. The smallest of these intervals is a semitone. Intervals smaller than a semitone are called microtones. They can be formed using the notes of various kinds of non-diatonic scales.
What is a diatonic interval?
Diatonic and chromatic. Main article: Diatonic and chromatic. In general, A diatonic interval is an interval formed by two notes of a diatonic scale. A chromatic interval is a non-diatonic interval formed by two notes of a chromatic scale.
What are the intervals between the notes of a chromatic scale?
The table shows the most widely used conventional names for the intervals between the notes of a chromatic scale. A perfect unison (also known as perfect prime) is an interval formed by two identical notes. Its size is zero cents. A semitone is any interval between two adjacent notes in a chromatic scale, a whole tone is an interval spanning two semitones (for example, a major second ), and a tritone is an interval spanning three tones, or six semitones (for example, an augmented fourth). Rarely, the term ditone is also used to indicate an interval spanning two whole tones (for example, a major third ), or more strictly as a synonym of major third.
How many intervals are there in a diatonic scale?
As shown in the table, a diatonic scale defines seven intervals for each interval number, each starting from a different note (seven unisons, seven seconds, etc.). The intervals formed by the notes of a diatonic scale are called diatonic. Except for unisons and octaves, the diatonic intervals with a given interval number always occur in two sizes, which differ by one semitone. For example, six of the fifths span seven semitones. The other one spans six semitones. Four of the thirds span three semitones, the others four. If one of the two versions is a perfect interval, the other is called either diminished (i.e. narrowed by one semitone) or augmented (i.e. widened by one semitone). Otherwise, the larger version is called major, the smaller one minor. For instance, since a 7-semitone fifth is a perfect interval ( P5 ), the 6-semitone fifth is called "diminished fifth" ( d5 ). Conversely, since neither kind of third is perfect, the larger one is called "major third" ( M3 ), the smaller one "minor third" ( m3 ).
How many semitones are there in a tritone?
A semitone is any interval between two adjacent notes in a chromatic scale, a whole tone is an interval spanning two semitones (for example, a major second ), and a tritone is an interval spanning three tones, or six semitones (for example, an augmented fourth). Rarely, the term ditone is also used to indicate an interval spanning two whole tones ...
What is a chord in music?
Chords are sets of three or more notes. They are typically defined as the combination of intervals starting from a common note called the root of the chord . For instance a major triad is a chord containing three notes defined by the root and two intervals (major third and perfect fifth). Sometimes even a single interval ( dyad) is considered a chord. Chords are classified based on the quality and number of the intervals that define them.
What is a major interval?
Major intervals are those which are part of the major scale. The major scale should always be your starting point when working out an interval. There are 2 example below. The first showing a major 6th interval in the key of C major, the second showing a major 3rd interval in the key of E major. Minor intervals are one semitone smaller ...
How to identify intervals?
There are two styles of questions you may be asked about intervals. In the first style you are asked to identify an interval, either as a stand-alone question or as part of a phrase of music. You are given both notes and all you have to do is name the interval. Always remember to count from the lowest to the highest note. Even if on the music the higher note comes first. Always count from low to high.
How to know if an interval is major or minor?
How to remember if a music interval is Major/Minor or Perfect. When you see a list the intervals and their descriptors you can see it is quite easy to remember which intervals are major/minor or perfect. As you can see above the Perfect intervals are at each side, unison and octave, and in the middle, 4th and 5th.
What is a perfect interval?
If an interval is a unison (1st), 4th, 5th or Octave (8th) it is called a perfect interval. Both notes in a Perfect interval are in the major scale. The example below shows the interval of a Perfect 5th. One of the features of perfect intervals is the fact that if you invert them (turn them upside down) they remain perfect.
How to get better at identifying intervals?
As with most things in music, the best way to get better at identifying intervals is to practice! Test your understanding of the quality of a music interval. Click here to take a test on the quality of intervals.
How to learn music theory?
A Clear Path To Learning Music Theory 1 A simple step-by-step course that takes you from complete beginner to grade 2 music theory 2 Multi-faceted learning - audio, video, mind maps, clear musical examples 3 Built in quizzes to check your understanding
Is minor second part of minor scale?
The minor second isn't part of the minor scale. This is why it is important to remember to work out intervals from the major scale, not think of them as part of the minor scale. There are 2 examples below. The first shows a minor 7th in the key of G major, the second shows a minor 2nd in the key of D major.
What Are Intervals in Music Theory?
In simple words, interval means the distance in pitch between any two notes. If the interval between any two notes is larger, the pitch difference between the two notes will also be greater.
What Are Examples of an Interval in Music?
An example of an interval can be the song Amazing Grace, which begins with a perfect fourth.
What Are the Different Types of Intervals in Music?
This type of interval occurs when you play two notes at the same time.
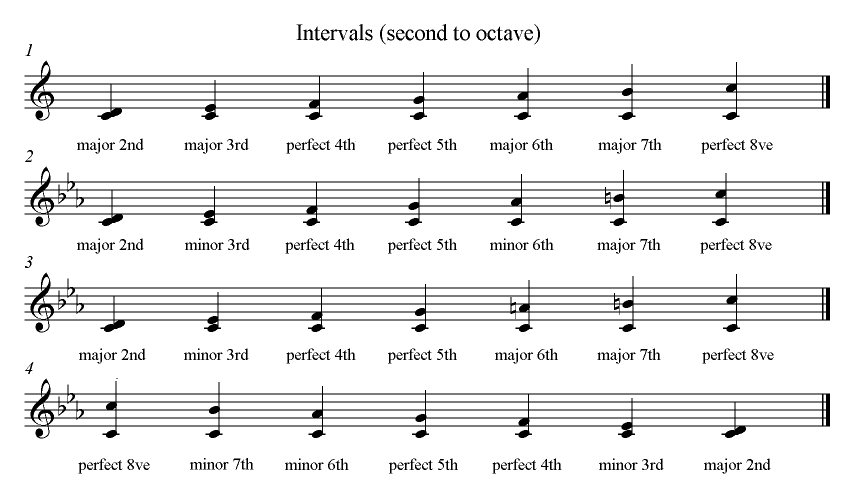
What is a Music Interval Chart?
The music interval chart helps in gaining a proper understanding of the intervals. In it, the things such as name, semitones, abbreviations, etc., are mentioned.
What is a Music Interval Calculator?
A music interval calculator enables us to determine the interval between two notes. The calculator differentiates between enharmonic equivalents and also tells about the diminished and augmented intervals.
Summary of Intervals in Music
Intervals are the measured distance between any two notes in pitch. The three types of intervals are the type of interval, the distance between notes, and the type of interval. Any note with a greater interval will also have a greater pitch difference between the notes.
What is music theory interval?
Music theory intervals are the DNA of music. When you move from one note to the next, you're playing an interval. Read on to see what they mean and how you can use them. Menu.
How to play intervals?
There are actually two ways to play intervals: harmonicand melodic. Harmonic intervals are when you play the two notes at the same time, (like in a chord). Melodic intervals are when you play one note, then the other one, (like in a melody).
What is the interval called when you go from the root to the third?
If we go from the root to the third, that is an interval called a third. If we go from the root to the sixth, that is an interval called a sixth. From the root to the fourth is called... you got it: a fourth. That’s pretty much all there is to this basic interval stuff.
Why is the piano the easiest instrument to learn?
(Even if you don’t claim to be “a piano player”.) The piano is one of the easiest instruments to understand music theory on because the notes are all laid out in a straight line.
What happens if you play the same note twice?
Unless you played the same note twice, you played an interval. Actually, I take that back: even if you played the same note twice you played an interval called a unison. The point is that music is made of intervals, intervals, intervals everywhere!

What Is An Interval in Music?
Semitones and Tones
- Semitones and tonesor half steps and whole steps, are the building blocks of intervals. We use different combinations of them to make up all the different types of scales and chords that make music sound so different.
Names of The Intervals
- Now that we know about the two smallest intervals, semitones and tones, we can start looking at some larger intervals and how we describe them. We describe intervals using numbers depending on how many letter names of the musical alphabet there are between the two notes. For example, the notes C and D are two letter notes apart and so is an interval of a 2nd. But if we look at the n…
Interval Quality
- Now we’re going to cover the interval quality. As we don’t just refer to intervals with the number, we also refer to the type of interval. I’ll explain why we need to distinguish the interval quality with the example below. Both of these intervals are a third: In the first example, C to Eb is three letter notes: C – D – Eb and so is a 3rd. And in the second example, C to E natural is also three letter n…
Music Intervals Chart
- To help make sense of all the intervals here’s a chart with the number of semitones (half-steps), the name, the abbreviation and an example of the notes of all the intervals.
Compound Intervals
- All the intervals that we’ve looked at up until now have been up to one octave. These are called simple intervals. But, you can also get intervals that are larger than one octave. For example C to E the octave above. These types of intervals are called compound intervals. There are two different ways to name compound intervals which I cover in more depth in my compound intervalsguide h…
Conclusion
- That about sums up musical intervals for now. I’ll be updating this post with some more examples when intervals can get a little bit more complicated with double flats and double sharps and key signatures.
What Are Intervals in Music?
Explaining Intervals
- As I mentioned above, an interval is a variation in pitch between two sounds. As a result, the larger the interval existing between two notes, the more they’re different in terms of pitch. The opposite is also true. The smaller the interval we’re talking about between two sounds, the less different they are as far as their pitch goes. You may have come across an interval described as linear, m…
Laying The Basis For Understanding Intervals
- Wow! That was a lot of information to absorb, so how about we go back to the very basis of an interval — its building blocks. I’m referring to semitones (also known as half steps) and tones (also called whole steps). Musicians use numerous combinations of semitones and tones to form all the various kinds of chords and scales that create different sounds in music. Let’s take a clos…
Naming Intervals
- Now that you’re familiar with the building blocks of intervals; the semitones and tones (the two smallest intervals in western music), we can move on to look at larger intervals and how you can name them. In music, an interval gets its name by combining two factors: the number and the quality.
What Are Compound Intervals?
- Up until now, I only mentioned intervals up to one octave. Why? Because intervals larger than that are called compound intervals. Such intervals are an article on their own.
What Are Melodic Intervals?
- These are the opposite of harmonic intervals. They describe when two notes are played “as part of a melody” in succession (one after the other).
Overview
In music theory, an interval is a difference in pitch between two sounds. An interval may be described as horizontal, linear, or melodic if it refers to successively sounding tones, such as two adjacent pitches in a melody, and vertical or harmonic if it pertains to simultaneously sounding tones, such as in a chord.
In Western music, intervals are most commonly differences between notes of a diatonic scale. Th…
Size of intervals used in different tuning systems
In this table, the interval widths used in four different tuning systems are compared. To facilitate comparison, just intervals as provided by 5-limit tuning (see symmetric scale n.1) are shown in bold font, and the values in cents are rounded to integers. Notice that in each of the non-equal tuning systems, by definition the width of each type of interval (including the semitone) changes depending on the note that starts the interval. This is the art of just intonation. In equal temperam…
Size
The size of an interval (also known as its width or height) can be represented using two alternative and equivalently valid methods, each appropriate to a different context: frequency ratios or cents.
The size of an interval between two notes may be measured by the ratio of their frequencies. When a musical instrument is tuned using a just intonation tuning system, the size of the main intervals …
Main intervals
The table shows the most widely used conventional names for the intervals between the notes of a chromatic scale. A perfect unison (also known as perfect prime) is an interval formed by two identical notes. Its size is zero cents. A semitone is any interval between two adjacent notes in a chromatic scale, a whole tone is an interval spanning two semitones (for example, a major second), and a tritone is an interval spanning three tones, or six semitones (for example, an augmented fo…
Interval number and quality
In Western music theory, an interval is named according to its number (also called diatonic number) and quality. For instance, major third (or M3) is an interval name, in which the term major (M) describes the quality of the interval, and third (3) indicates its number.
The number of an interval is the number of letter names or staff positions (line…
Shorthand notation
Intervals are often abbreviated with a P for perfect, m for minor, M for major, d for diminished, A for augmented, followed by the interval number. The indications M and P are often omitted. The octave is P8, and a unison is usually referred to simply as "a unison" but can be labeled P1. The tritone, an augmented fourth or diminished fifth is often TT. The interval qualities may be also abbreviated with perf, min, maj, dim, aug. Examples:
Inversion
A simple interval (i.e., an interval smaller than or equal to an octave) may be inverted by raising the lower pitch an octave or lowering the upper pitch an octave. For example, the fourth from a lower C to a higher F may be inverted to make a fifth, from a lower F to a higher C.
Audio playback is not supported in your browser. You can download the audio …
Classification
Intervals can be described, classified, or compared with each other according to various criteria.
An interval can be described as
• Vertical or harmonic if the two notes sound simultaneously
• Horizontal, linear, or melodic if they sound successively. Melodic intervals can be ascending (lower …