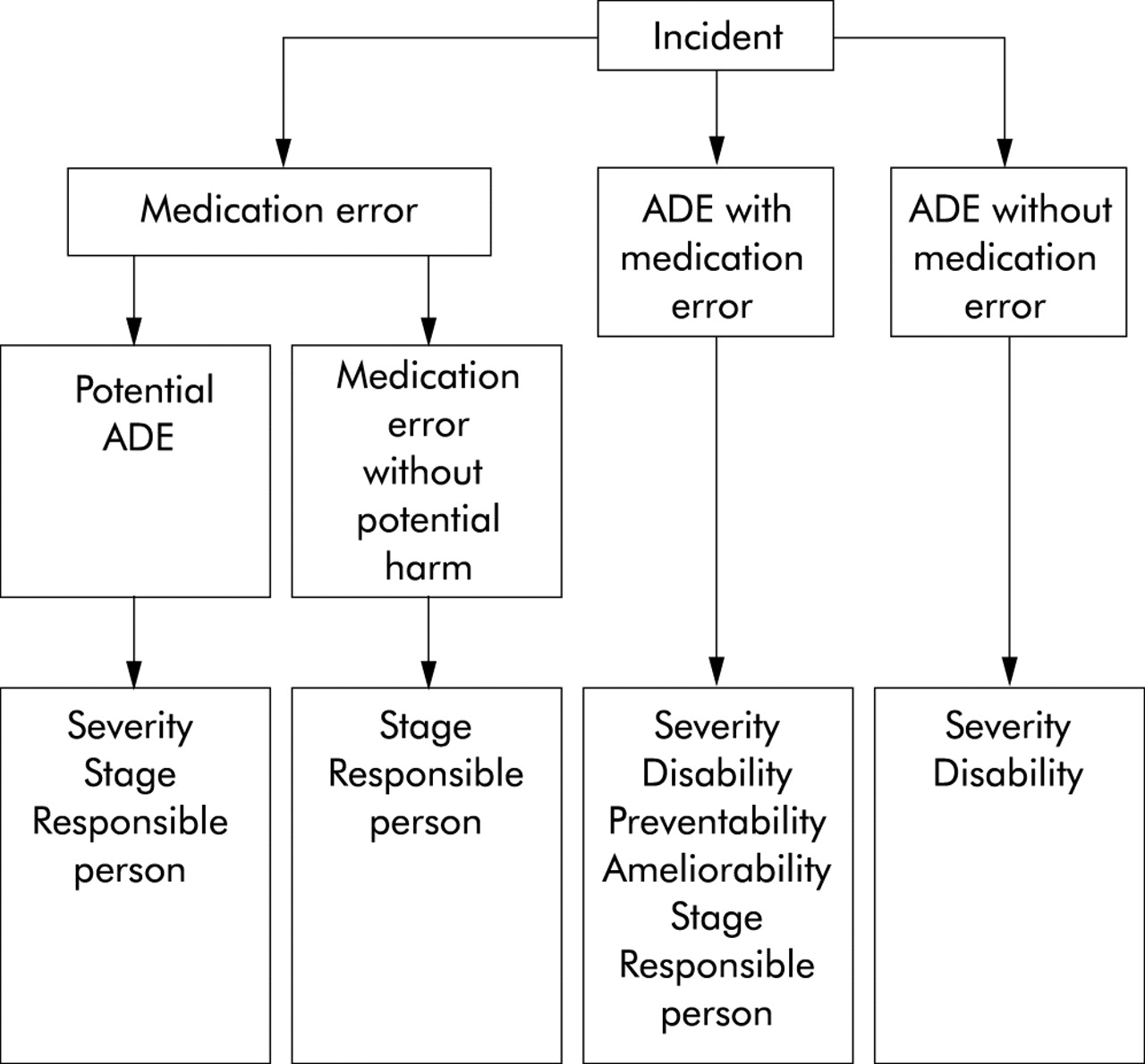
The different types of medication errors include (but are not necessarily limited to):
- Prescribing errors , wherein the selection of a drug is incorrect based on the patient’s allergies or other indications. ...
- Omission errors , in which there is a failure to give a medication dose before the next one is scheduled.
- Wrong time errors , wherein a medication is given outside the predetermined interval from its scheduled time.
- Prescribing.
- Omission.
- Wrong time.
- Unauthorized drug.
- Improper dose.
- Wrong dose prescription/wrong dose preparation.
- Administration errors include the incorrect route of administration, giving the drug to the wrong patient, extra dose, or wrong rate.
What are the categories of medication errors?
The researchers considered three types of medication error of increasing severity: where a mistake was caught and corrected before it was made; where the mistake was made but there was no potential harm to the patient; and where the patient might have been harmed but was not.
What are some examples of medication errors?
Examples of medication errors are given below: (this is not an exhaustive list) Omissions – any prescribed dose not given Wrong dose administered, too much or too little
What are some examples of common medical errors?
What are the most common medical errors?
- Misdiagnosis. Error in diagnosis is a common medical error. ...
- Delayed Diagnosis. A delayed diagnosis can be as detrimental as a misdiagnosis. ...
- Medication Error. One of the most common mistakes that occurs in the course of medical treatment is an error in medication.
- Infection. ...
- Bad medical devices. ...
What are 5 common drug errors?
- Misheard drug orders or recommendations during verbal/telephone communication. ...
- Unsafe “overrides” with automated dispensing cabinets (ADCs). ...
- Unsafe practices associated with IV push medications. ...
- Wrong route (intraspinal injection) errors with tranexamic acid. ...
- Unsafe labeling of prefilled syringes and infusions by 503b compounders. ...

What are the most common types of medication errors?
The three most common dispensing errors are: dispensing an incorrect medication, dosage strength or dosage form; miscalculating a dose; and failing to identify drug interactions or contraindications. Errors caused by drug administration can be made by the health care provider or by the patient themselves.
What are the 5 top medical errors?
The top five medical errors are misdiagnosis, delayed diagnosis, medication error, infection, and harmful medical devices. The top five medical errors are responsible for most instances of medical malpractice in health care.
What are the different types of medical errors?
Medical errors typically include surgical, diagnostic, medication, devices and equipment, and systems failures, infections, falls, and healthcare technology. Missed diagnoses or injuries from medication are common in outpatient settings.
What are examples of medication errors?
If a medication error occurred, but didn't hurt anyone, it's called a potential adverse drug event. An example of a medication error is taking an over-the-counter product that contains acetaminophen (Tylenol, others) when you're already taking a prescription pain medicine that contains this exact ingredient.
What is the most common cause of medical errors?
Residents encounter medical errors at all levels of training. Fatigue due to long duty hours, lack of experience, job over load and inadequate supervision by senior were major causes of these errors. Medical errors committed by residents have inadequate disclosure to senior physicians.
What's the most common type of medical error in hospitals?
Misdiagnosis. The most common type of medical error is error in diagnosis. This is not surprising, since the right diagnosis is the key to your entire medical error. A wrong diagnosis can result in delay in treatment, sometimes with deadly consequences.
What are the three different categories of medical errors?
Medication events (including adverse drug events/reactions) Healthcare-associated infections (HAIs) Surgical errors. Laboratory errors.
What are 2 common medical errors related to patient safety?
Misdiagnosis, falls, infections, mistakes during treatment and getting the wrong medication are the most common PSIs experienced.
What are the common medication errors in nursing?
The frequently perpetrated types of MAEs include wrong dose, wrong time, wrong drug, wrong route, omission of doses, wrong patient, lack of documentation, and technical errors [8,9,10,11].
What is the most common reason for medication administration errors?
The most common types of reported errors were wrong dosage and infusion rate. The most common causes were using abbreviations instead of full names of drugs and similar names of drugs. Therefore, the most important cause of medication errors was lack of pharmacological knowledge.
What are risk factors for medication errors?
Conclusion: Older age, overburdened healthcare system, number of prescribed drugs, comorbidities, Charlson comorbidity index, and multiple prescribers to one patient are significant risk factors for the occurrence of medication errors.
What is the most common preventable medical error?
More than two-thirds (70 percent) of the adverse events found in this study were thought to be preventable, with the most common types of preventable errors being technical errors (44 percent), diagnosis (17 percent), failure to prevent injury (12 percent) and errors in the use of a drug (10 percent).
What are the most common patient safety issues?
Patient safety issues were commonly described surrounding the following: lack of basic nursing care, in particular in relation to feeding, hydration and pressure area care; misdiagnosis, often due to diagnostic overshadowing and communication difficulties; delayed investigations and treatment; non-treatment decisions ...
What is medication error?
Medication errors are any preventable events that may cause or lead to inappropriate medication use or patient harm. This is the definition by the national coordinating council for medication error reporting and prevention (nccmerp).
What is the role of patient education in healthcare?
Patients should understand the key pieces of information about every medication taken. Patient education assists patients in becoming more informed and empowers them to be advocators of their own safety.
What enzyme is used to remove drugs from the body?
for instance, g6pd (glucose 6 phosphate dehydrogenase) is an enzyme that helps to remove medications from the body. a patient with this enzyme deficiency taking a medication that depends upon this enzyme for metabolism could result in serious harm or even death.
What happens if a provider fails to document a medication?
Failure to document the drugs administered to a patient; another provider then checks the medication chart and sees no medication and gives the patient another second dose.
What is capture error?
A capture error is the one that occurs when focus on the task is diverted elsewhere and therefore the distraction captures the person’s attention, preventing the person from detecting the error or causing an error to be made.
How many times should you read the label on a prescription?
Always read the label three times and check with the medication order before administering the medication.
Why is there lack of information to prescribers?
Lack of information to the prescribers due to unavailable drug information such as updated drug warnings.
How are medical errors costly?
Medical errors are not only monetarily costly, but costly in terms of loss of trust in the healthcare system by patients, reduced patient satisfaction, and degraded morale among healthcare professionals, who often feel helpless to change the situation .
What is an omission error?
Omission errors , in which there is a failure to give a medication dose before the next one is scheduled.
Why are medical errors not a result of incompetence or recklessness?
It’s important to note that one of the main conclusions of the Institute’s report is that the majority of medical errors occur not as a result of incompetence or recklessness on the part of nurses and other healthcare workers, but rather as a result of faulty systems, fragmented processes, and working conditions (e.g., nurses exhausted from working double shifts).
What is an improper dosing error?
Improper dosing errors , wherein a greater or lesser amount of a medication is delivered than is required to manage the patient’s condition.
What happens when you see multiple providers in different settings?
When patients see multiple healthcare providers in different settings-whether by choice or otherwise-the result is often fragmentation of information. One doctor may not have access to the same patient information as another-one of the primary causes of medication errors.
Why do nurses make errors?
Additionally, lack of proper lighting, heat/cold, and other environmental factors can cause distractions that lead to errors. Lack of knowledge/understanding : Nurses who lack complete knowledge about how a drug works, its various names (generic and brand), its side effects, its contraindications, etc. can make errors.
What are the challenges of healthcare?
Healthcare workers face more challenges today than ever before. Doctors are seeing more patients every hour of every day, and all healthcare staff, including doctors, nurses, and administrators, must adapt to the demands of new technology in healthcare, such as electronic health records (EHR) systems and Computerized Provider (Physician) Order Entry (CPOE) systems.
How to classify medication errors?
Medication errors: definitions and classification 1 To understand medication errors and to identify preventive strategies, we need to classify them and define the terms that describe them. 2 The four main approaches to defining technical terms consider etymology, usage, previous definitions, and the Ramsey–Lewis method (based on an understanding of theory and practice). 3 A medication error is ‘a failure in the treatment process that leads to, or has the potential to lead to, harm to the patient’. 4 Prescribing faults, a subset of medication errors, should be distinguished from prescription errors. A prescribing fault is ‘a failure in the prescribing [decision-making] process that leads to, or has the potential to lead to, harm to the patient’. The converse of this, ‘balanced prescribing’ is ‘the use of a medicine that is appropriate to the patient's condition and, within the limits created by the uncertainty that attends therapeutic decisions, in a dosage regimen that optimizes the balance of benefit to harm’. This excludes all forms of prescribing faults, such as irrational, inappropriate, and ineffective prescribing, underprescribing and overprescribing. 5 A prescription error is ‘a failure in the prescription writing process that results in a wrong instruction about one or more of the normal features of a prescription’. The ‘normal features’ include the identity of the recipient, the identity of the drug, the formulation, dose, route, timing, frequency, and duration of administration. 6 Medication errors can be classified, invoking psychological theory, as knowledge-based mistakes, rule-based mistakes, action-based slips, and memory-based lapses. This classification informs preventive strategies.
What is prescription error?
A prescription error is ‘a failure in the prescription writing process that results in a wrong instruction about one or more of the normal features of a prescription’. The ‘normal features’ include the identity of the recipient, the identity of the drug, the formulation, dose, route, timing, frequency, and duration of administration.
What is a prescribing fault?
A prescribing fault is ‘a failure in the prescribing [decision-making] process that leads to, or has the potential to lead to, harm to the patient’. The converse of this, ‘balanced prescribing’ is ‘the use of a medicine that is appropriate to the patient's condition and, within the limits created by the uncertainty that attends therapeutic decisions, in a dosage regimen that optimizes the balance of benefit to harm’. This excludes all forms of prescribing faults, such as irrational, inappropriate, and ineffective prescribing, underprescribing and overprescribing.
What are the four main approaches to defining technical terms?
The four main approaches to defining technical terms consider etymology, usage, previous definitions, and the Ramsey–Lewis method (based on an understanding of theory and practice).
Is there overlap in prescribing?
It is possible to define individually the various types of prescribing faults, listed above, but there is considerable overlap amongst them and it is preferable to unify them into a single definition of their opposite, which I call ‘balanced prescribing’, defined as ‘the use of a medicine that is appropriate to the patient's condition and, within the limits created by the uncertainty that attends therapeutic decisions, in a dosage regimen that optimizes the balance of benefit to harm’[20]. This definition excludes all forms of prescribing faults.
Does phenylephrine include medications?
Thus, the definition covers a wide range of compounds. However, it does not include medications when they are used to probe systems for nondiagnostic purposes, such as the use of phenylephrine to study baroreceptor reflexes in a physiological or pharmacological experiment.
Is medication the same as a medicine?
A medication (the object) can be considered to be the same as a medicinal product, which has been defined in terms of what a medicinal product is and what it does.
What are Medication Errors?
The National Coordinating Council for Medication Error and Prevention (NCCMERP) has approved the following as its working definition of medication error: “... any preventable event that may cause or lead to inappropriate medication use or patient harm, while the medication is in the control of the health care professional, patient, or consumer. Such events may be related to professional practice, health care products, procedures, and systems including: prescribing; order communication; product labeling, packaging and nomenclature; compounding; dispensing; distribution; administration; education; monitoring; and use”.
What are dispensing errors?
The term dispensing error refers to medication errors linked to the pharmacy or to whatever health care professional dispenses the medication. These include errors of commission (e.g. dispensing the wrong drug, wrong dose or an incorrect entry into the computer system) and those of omission (e.g. failure to counsel the patient, screen for interactions or ambiguous language on a label). Errors may be potential -- detected and corrected prior to the administration of the medication to the patient. 6 The three most common dispensing errors are: dispensing an incorrect medication, dosage strength or dosage form; miscalculating a dose; and failing to identify drug interactions or contraindications.
Why are preventable errors occurring?
Preventable errors occur because systems for safely prescribing and ordering medication are not appropriately used.
How does e-prescribing work?
E-prescribing Utilization of electronic prescribing by entering orders on a computer, better known as Computerized Physician Order Entry (CPOE), is a technology that could help prevent many medication errors. CPOE systems allow physicians to enter prescription orders into a computer or other device directly, thus eliminating or significantly reducing the need for handwritten orders. E-prescribing and CPOE can reduce medication errors by eliminating illegible and poorly handwritten prescriptions, ensuring proper terminology and abbreviations, and preventing ambiguous orders and omitted information. 13 More advanced CPOE software incorporates additional safety features that allow the physician to have access to accurate patient information, including patient demographic information such as age, medication history and medication allergies.
How many people are affected by medication errors?
Medication errors are among the most common medical errors, harming at least 1.5 million people every year. The extra medical costs of treating drug-related injuries occurring in hospitals alone are at least to $3.5 billion a year, and this estimate does not take into account lost wages and productivity or additional health care costs, the report says. 1 Medication error morbidity and mortality costs are estimated to run $77 billion dollars per year. 2 Patient safety is a major public health concern. The Academy of Managed Care Pharmacy (AMCP) recognizes the importance of this issue and supports programs that help achieve the goal of improved patient safety and prevention of medication errors. AMCP’s Framework for Quality Drug Therapy, 3 emphasizes and promotes public safety, continuous monitoring for accuracy in dispensing, reliability in the transmission of prescription and medication orders, and continuous review and upgrade of pharmacy operating systems.
How can electronic technology improve patient safety and reduce medication errors?
One way in which electronic technology can improve patient safety and reduce medication errors is through the use of standard machine-readable codes ("bar codes"). Medication bar coding is a tool that can help ensure that the right medication and the right dose are administered to the right patient.
What are the causes of errors in prescribing?
Errors in prescribing can occur when an incorrect drug or dose is selected, or when a regimen is too complex.
What are the factors that contribute to medication errors?
According to our findings, inadequate pharmacological knowledge was one of the human factors associated with medication errors. Le Grognec et al. suggested lack of awareness and the route of administration to have a significant role in the incidence of medication errors.[27] In contrast, Stratton et al. reported that only 5% of the nursing staff considered lack of knowledge as an effective factor on the incidence of medication errors.[5] Numerous studies have indicated medication errors to be the result of lack of in-service training and inadequate knowledge of nursing graduates.[28,29] Many researchers have recommended increasing pharmacological knowledge of nurses as a strategy to reduce serious medication errors. Therefore, nurses are required to update their knowledge about medicines, especially new drugs.[30]
How many nurses have medication errors?
The mean number of medication errors committed by each nurse during the 3-month period of the study was 7.4. In Jordan, Mrayyon et al. reported that at least 42.1% of nurses had committed one medication error and within 3 months. They calculated the mean number of errors of each nurse as 2.2.[11] Lisby et al. performed a study in the hospitals of Denmark and found the rate of nursing medication errors to be lower than what we found.[21] This considerable difference between our findings and rates of medication errors reported in other countries can be due to negative reactions of colleagues, teachers, and administrators after reporting an error,[22] lack of drug monitoring, and absence of a definite medication error reporting and archiving system.[11] However, Iranian managers and executives should know that in order to adopt suitable policies, it is necessary for the nurses to report their errors. Otherwise, inappropriate ethical and treatment decisions will be made.[23] On the other hand, proper planning and a comprehensive system to monitor the process of error reporting can reduce the number of errors and prevent complications.
Why are medication errors important in nursing?
Since most cases of medication errors are not reported by nurses, nursing managers must demonstrate positive responses to nurses who report medication errors in order to improve patient safety.
How many medication errors were made in intravenous injections?
Most medication errors (60.78%) had been made in intravenous injections of drugs. There were no statistically significant relationships between medication errors and years of working experience, age, and working shifts. However, a significant relationship was observed between frequency of errors in intravenous injections and gender. A significant relation was also found between errors in oral drug administration and number of patients.
What is a data collection tool?
Data collection tool was a self-made questionnaire which had been prepared and adjusted based on literature review.[ 17,18,19,20] The questionnaire contained 10 questions about demographic characteristics and 7 specific items about medication errors (types, causes, the most common method, etc.). Nurses with more than one case of medication error had to select only one item. The content validity of the questionnaire had been established by literature review and opinions of experts. The reliability of the questionnaire had been approved by test–retest method (r = 0.9). The questionnaires were anonymous and often filled out by the participants. Data analyses were performed by descriptive statistics (tables, graphs, mean, and standard deviation) and inferential statistics. SPSS for Windows 16.0 (SPSS Inc., Chicago, IL, USA) was used in this study and Pvalues less than 0.05 were considered significant.
What are the most common medication errors?
The most common types of reported medication errors were inappropriate dosage and infusion rate [Figure 1]. The most common causes of medication errors were using abbreviations (instead of full names of drugs) in prescriptions and similarities in drug names. Therefore, the most important cause of medication errors was lack of adequate pharmacological information [Tables [Tables11and and22].
Why is it important to report medication errors?
Reporting medication errors is an ethical duty to maximize the benefits of patient care. It can thus improve patient safety and health. Therefore, managers should have a positive attitude toward the reporting of medication errors by nurses.
How are medication errors classified?
Medication errors are classified based on multifaceted criteria and there is a need to standardize the recommendations and make them a central goal all over the globe for the best practice. Nurses are the frontlines of clinical settings, encouraged to be one integrated body to prevent the occurrence of medication errors. Thus, systemizing the guidelines are required such as education and training, independent double checks, standardized procedures, follow the five rights, documentation, keep lines of communication open, inform patients of drug they receive, follow strict guidelines, improve labeling and package format, focus on the work environment, reduce workload, ways to avoid distraction, fix the faulty system, enhancing job security for nurses, create a cultural blame-free workspace, as well as hospital administration, should support and revise processes of error reporting, and spread the awareness of the importance of reporting.
How many errors are there in medication?
Moreover, 0.078 errors per patient, and 0.029 errors per medication mainly because of dosing errors, drug omission, and wrong frequency errors.[62] A previous study showed that (94.0%) out of 430 errors were omissions and only 6.0% of errors caused a major impact on patients’ life but was not considered as a life–alarming errors.[63] Medication errors are also related to the problem of wrong phenomena. These incorporate errors of course of medication, doses, timing, patient, and inability to follow up the patient. [53, 64]
What is the best protocol for assessing medication errors?
Grouping of medication errors occurrence into contextual, modular, or mental (psychological) is considered an ideal protocol to assess how errors happen. Contextual order assesses the specific time, place, medications, and individuals who are included. Modular characterization analyses the manners in how errors occur (i.e, by omission, repetition, or substitution). Mental order is preferred, as it clarifies occasions as opposed to just prescribing them. Its burden is that it focuses on humans as opposed to frameworks wellsprings of errors. The accompanying mental grouping depends on crafted by Reason on errors and there are four distinct types of medication errors. [33, 34]
What are the factors that contribute to medication errors?
Lack of knowledge and miscalculation of doses are the factors contributing to medication errors. [36, 37, 39]It is noticed that competence skills in drug calculation are prerequisites to nursing registration and examining their learning abilities rather than follow strict protocol which imped nurses thinking skills. [11, 92]Moreover, focusing on continuing education with clinical and theoretical support will help in the prevention of medication error occurrence. [15, 93–95]
What is medication error?
A medication error is characterized by ignoring the condition of shaping harm, hazard, or any evadable frequency to happen amid the procedure from medicine ordering to patient consumption. [10, 11]It might be characterized by National Coordinating Council for Medication Error Reporting and Prevention (NCCMERP) as any preventable occasion that may cause, or prompt improper medicine use or patient harm while the medicine is in the control of the healthcare worker, patient, or buyer. [12, 13]The measurement of medication errors may vary widely in clinical settings due to the different ways of recognizing and defining the status of medication errors, how to calculate error rates, variation in numerator/dominator, and the process, documentation, and culture of settings technologies. [14–16]
What are knowledge based errors?
Knowledge-based errors that are connected to any kind of knowledge which could be related to expert, specific, or general. As a general knowledge, health care providers should understand that allergic reactions, for instance, could be associated with penicillins, however, realizing that the patient is allergic to penicillin can be considered specific knowledge. On the other hand, experts are those who may know that co-fluampicil has penicillin. As a result, Knowledge-based errors might be provoked when ignoring any of that information. In an Australian examination, correspondence issues with trouble in getting to suitable medication dosing data added to knowledge-based errors. [35–39]When being educated about medication is being given dispensed to patients could reduce the incidence of medication errors.[40] Errors can be blocked from occurrence through computerized prescribing entry orders, bar-coded medicine frameworks, and cross-checking by others (for instance, medicine specialists and nurses). [41, 42]A study showed that before implantation of electronic Bar-Coded Medication Administration (BCMA-e MAR), wrong time (33.9%), omission (27.7%), wrong technique (18.0%), wrong dose (13.3%), and unauthorized drug (2.9%) were happening frequently. However, after the implementation of BCMA- e MAR, errors have been declined.[43] In another study, error rates were reduced more than a half after applying BCMA- e MAR. [44]
What is the fourth type of error?
The fourth type is ‘Memory-based errors ’ (so-called lapses). For instance, giving penicillin to a patient, with a known history of allergy, but forgetting that the patient is allergic. These are difficult to keep away from; however, computerized prescribing frameworks and cross-checking can reduce the error incidence. [50, 51]
What is a medication error?
While there is no uniform definition of a medication error, The National Coordinating Council for Medication Error Reporting and Prevention defines a medication error as: “… any preventable event that may cause or lead to inappropriate medication use or patient harm while the medication is in the control of the healthcare professional, patient, or consumer. Such events may be related to professional practice, health care products, procedures, and systems, including prescribing; order communication; product labeling, packaging, and nomenclature; compounding; dispensing; distribution; administration; education; monitoring; and use.” However, there is no widely accepted uniform definition. Unfortunately, untoward medical errors and underreported medication errors result in significant morbidity and mortality. In order of frequency: medication errors, motor vehicle accidents, breast cancer, AIDS, and medication errors. Consider that two of the most common causes of death are related to healthcare-related events. [4] [3] [5] [6]
How common are medication errors?
Medication errors are most common at the ordering or prescribing stage. Typical errors include the healthcare provider writing the wrong medication, wrong route or dose, or the wrong frequency. These ordering errors account for almost 50% of medication errors. Data show that nurses and pharmacists identify anywhere from 30% to 70% of medication-ordering errors. It is obvious that medication errors are a pervasive problem, but the problem is preventable in most cases. [19]
How can medication errors be reduced?
The best method to enhance patient safety is to develop a multi-faceted strategy for education and prevention. Emphasis should be put on healthcare providers working as a team and communicating as well as encouraging patients to be more informed about their medications. With a culture of safety, dispensing medication errors can be reduced.
What is medication misadventure?
A medication misadventure is an iatrogenic incident that is inherent to medication therapy. Medication misadventure includes medication errors, adverse drug reactions, and adverse drug events. It is created through omission or commission of medication administration. Medication misadventures always are undesirable and unexpected; they may or may not be independent of preexisting pathology; and might be due to human or system error, idiosyncratic, or immunologic response. [13] [14] [15]
Why are there errors in the drug ordering process?
The most common reasons for errors include failure to communicate drug orders, illegible handwriting, wrong drug selection chosen from a drop-down menu, confusion over similarly named drugs, confusion over similar packaging between products, or errors involving dosing units or weight.
What is sentinel event?
The Joint Commission defines a sentinel event as “an unexpected occurrence involving death or serious physical or psychological injury, or the risk thereof. Serious injury specifically includes loss of limb or function. The phrase ‘or the risk thereof’ includes any process variation for which a recurrence would carry a significant chance of a serious adverse outcome.” Sentinal events may include medication errors, adverse drug events, and medication misadventures. Sentinel events cause significant morbidity or mortality and are possibly preventable. [16] [17] [18]
What is the scope of the Common Formats?
The scope of the Common Formats encompasses all errors, including events that those that have the potential to affect the patient, near-misses, and those that have a patient affect. [23] [24] [25]
Why is the FDA recommending labeling and packaging?
FDA has published several guidances to help manufacturers design their drug labels, labeling, packaging, and select drug names in a way to minimize or eliminate hazards that can contribute to medication errors.
How to prevent medication errors?
Looking for ways to reduce medication errors#N#FDA looks for ways to prevent medication errors. Before drugs are approved for marketing, FDA reviews the drug name, labeling, packaging, and product design to identify and revise information that may contribute to medication errors. For example, FDA reviews: 1 Proposed proprietary (brand) names to minimize confusion among drug names. With the help of simulated prescriptions and computerized models, FDA determines the acceptability of proposed proprietary names to minimize medication errors associated with product name confusion. 2 Container labels to help healthcare providers and consumers select the right drug product. If a drug is made in multiple strengths – e.g., 5 mg, 10 mg, and 25 mg, – the labels of those three containers should be easy to differentiate. The label design may use different colors or identify the strength in large bold numbers and letters. 3 Prescribing and patient information to ensure the directions for prescribing, preparing, and use are clear and easy to read.
Why do we need barcodes?
This system is intended to help reduce the number of medication errors that occur in hospitals and other healthcare settings.
What is the FDA looking for in a life threatening situation?
Life threatening situation. Birth defect. FDA looks for ways to prevent medication errors. Before drugs are approved for marketing, FDA reviews the drug name, labeling, packaging, and product design to identify and revise information that may contribute to medication errors. For example, FDA reviews:
How many reports does the FDA receive?
The U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) receives more than 100,000 U.S. reports each year associated with a suspected medication error. FDA reviews the reports and classifies them to determine the cause and type of error. The reports come from drug manufacturers, and healthcare professionals and consumers through MedWatch, ...
Why are proposed proprietary names used?
Proposed proprietary (brand) names to minimize confusion among drug names. With the help of simulated prescriptions and computerized models, FDA determines the acceptability of proposed proprietary names to minimize medication errors associated with product name confusion.
Why do we need container labels?
Container labels to help healthcare providers and consumers select the right drug product. If a drug is made in multiple strengths – e.g., 5 mg, 10 mg, and 25 mg, – the labels of those three containers should be easy to differentiate.
