
Types of Muscle Contraction
- Isotonic muscle contractions. Isotonic contractions are those where the muscle changes length as it contracts whilst the load or resistance remains the same.
- Isometric muscle contraction. Isometric contractions occur when there is no change in the length of the contracting muscle. ...
- Isokinetic contractions. ...
What are the different kinds of muscle contractions?
Types of muscle contractions
- Tonic contraction. The word ‘tonic’ means tone. Tonic contractions then are simply the contractions that maintain the resting tone of our muscles.
- Isometric contraction. The word ‘isometric’ means same length. ...
- Isotonic contractions — concentric and eccentric contractions. The word ‘isotonic’ means same tone. ...
What type of muscle contraction generates the most force?
- Concentric contractions (shorten)
- Eccentric contractions (lengthen)
- Isometric contractions (remain the same)
What are the three types of muscle contractions Quizlet?
State and define the three types of muscle contractions. Give an example of each of the three types of muscle contractions. The mover is the force that acting to move the body part, while the antagonist is the resistance force that opposes movement. In concentric contractions the mover force is greater than the resistance force.
What are the 5 steps of muscle contraction?
What are the 5 steps of muscle contraction?
- exposure of active sites – Ca2+ binds to troponin receptors.
- Formation of cross-bridges – myosin interacts with actin.
- pivoting of myosin heads.
- detachment of cross-bridges.
- reactivation of myosin.
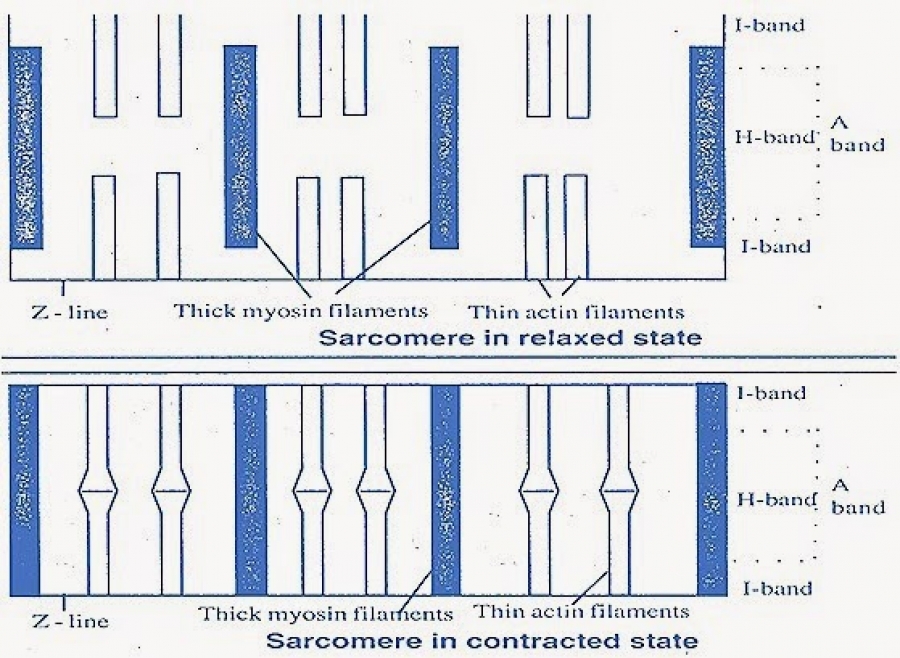
What are the 4 muscle contractions?
Isometric: A muscular contraction in which the length of the muscle does not change. isotonic: A muscular contraction in which the length of the muscle changes. eccentric: An isotonic contraction where the muscle lengthens. concentric: An isotonic contraction where the muscle shortens.
What are the two types of muscle contraction?
Isotonic contractions – these occur when a muscle contracts and changes length and there are two types:Isotonic concentric contraction – this involves the muscle shortening. ... Isotonic eccentric contraction – this involves the muscle lengthening whilst it is under tension.
What are the two basic types of muscle contractions and how do they differ?
There are 2 types of isotonic contractions: concentric and eccentric. In a concentric contraction, the muscle tension rises to meet the resistance then remains stable as the muscle shortens. During eccentric contraction, the muscle lengthens as the resistance becomes greater than the force the muscle is producing.
What is the best type of muscle contraction?
A concentric contraction is a type of muscle activation that causes tension on your muscle as it shortens. As your muscle shortens, it generates enough force to move an object. This is the most popular type of muscle contraction.
What are 3 types of muscle contractions?
1 Types of Contractions. There are three types of muscle contraction: concentric, isometric, and eccentric. Labeling eccentric contraction as “contraction” may be a little misleading, since the length of the sarcomere increases during this type of contraction.
What is isometric concentric and eccentric contraction?
Concentric contractions are when the tension in the muscle increases and the fibers shorten and contract. While isometric contractions are when you are making sure the angle of your joints do not change during the exercise, and the muscle does not shorten or lengthen. The final contraction is eccentric.
What are isotonic and isometric contractions?
Isometric contractions are contractions in which there is no change in the length of the muscle. No joint or limb motion occurs. Isotonic contractions occur when the muscle changes length, producing limb motion. Concentric contractions occur when the muscle shortens.
What is the difference between isometric and isotonic contractions?
Isotonic muscle contraction produces limb movement without a change in muscle tension, whereas isometric muscle contraction produces muscle tension without a change in limb movement.
What is eccentric muscle contraction?
Introduction. An eccentric (lengthening) muscle contraction occurs when a force applied to the muscle exceeds the momentary force produced by the muscle itself, resulting in the forced lengthening of the muscle-tendon system while contracting (Lindstedt et al., 2001).
What is tetanic contraction?
In tetanic contractions, the force increases within several (fast motor units) or even several tens (slow units) of initial stimuli, and then stabilizes at a certain level. From: Muscle and Exercise Physiology, 2019.
What are isometric muscle contractions?
Isometric exercises are tightening (contractions) of a specific muscle or group of muscles. During isometric exercises, the muscle doesn't noticeably change length. The affected joint also doesn't move. Isometric exercises help maintain strength.
What is contraction in the muscular system?
Although the term contraction implies shortening, when referring to the muscular system, it means the generation of tension within a muscle fiber. Several types of muscle contractions occur and are defined by the changes in the length of the muscle during contraction.
What type of contractions maintain constant tension in the muscle as the muscle changes length?
Isotonic contractions maintain constant tension in the muscle as the muscle changes length. Is otonic muscle contractions can be either concentric or eccentric.
What type of contraction is cross bridge cycling?
Types of Muscle Contraction: An isotonic concentric contraction results in the muscle shortening, an isotonic eccentric contraction results in the muscle lengthening. During an isometric contraction the muscle is ...
How do isotonic contractions generate force?
Key Points. Isotonic contractions generate force by changing the length of the muscle and can be concentric contractions or eccentric contractions. A concentric contraction causes muscles to shorten, thereby generating force. Eccentric contractions cause muscles to elongate in response to a greater opposing force.
What is the difference between isometric and isotonic contractions?
Isometric: A muscular contraction in which the length of the muscle does not change. isotonic: A muscular contraction in which the length of the muscle changes. eccentric: An isotonic contraction where the muscle lengthens. concentric: An isotonic contraction where the muscle shortens. A muscle fiber generates tension through actin ...
What is concentric contraction?
concentric: An isotonic contraction where the muscle shortens. A muscle fiber generates tension through actin and myosin cross-bridge cycling. While under tension, the muscle may lengthen, shorten, or remain the same. Although the term contraction implies shortening, when referring to the muscular system, it means the generation ...
Which contraction generates force without changing the length of the muscle?
In contrast to isotonic contractions, isometric contractions generate force without changing the length of the muscle, common in the muscles of the hand and forearm responsible for grip. Using the above example, the muscle contraction required to grip but not move a heavy object prior to lifting would be isometric.
What are the three categories of muscle contraction?
Here we explain isotonic, isometric, isokinetic, concentric and eccentric muscle contractions .
What muscles are contracted when you jump?
Another very common example is the quadriceps muscles at the front of the thigh when landing from a jump. As you land the thigh muscles and in particular the quad muscles at the front of the leg are strongly contracting but also lengthening at the same time.
What is the difference between isokinetic and isotonic contractions?
Isokinetic contractions. Isokinetic contractions are similar to Isotonic in that the muscle changes length during the contraction , where they differ is that Isokinetic contractions produce movements of a constant speed. To measure this a special piece of equipment known as an Isokinetic dynamometer is required.
What is the purpose of the muscles contracting in the hand?
There is no movement in the joints of the hand, but the muscles are contracting to provide a force sufficient enough to keep a steady hold on the racket. The amount of force a muscle is able to produce during an isometric contraction depends on the length of the muscle at the point of contraction.
What type of exercise puts a lot of strain through the muscle and is commonly involved in muscle injuries?
This type puts a lot of strain through the muscle and is commonly involved in muscle injuries. Plyometric training exercises (hopping and bounding) involve a lot of eccentric contractions and can lead to severe muscle soreness ( DOMS) if you overdo it too soon.
What is isotonic contraction?
Isotonic contractions are those where the muscle changes length as it contracts whilst the load or resistance remains the same. As a result, this causes movement of a body part. There are two types of Isotonic contraction:
When does isometric contraction occur?
Isometric contractions occur when there is no change in the length of the contracting muscle. This occurs when carrying an object in front of you as the weight of the object is pulling your arms down but your muscles are contracting to hold the object at the same level.
Why is it important to know the types of muscle contractions?
It is not only important for the mere fact of knowing what they consist of, but because it is relevant to know what the body is subjected to when performing physical ...
Which type of muscle contraction is the first to be present?
Auxotonic contraction. To culminate with the main types of muscle contraction, it is necessary to mention the auxotonic. This type is the combination of isotonic and isometric contraction. In this they converge as a whole; the isotonic is the first to be present and the isometric is the one that culminates in the auxotonic contraction.
What is isometric contraction?
Isometric contraction refers to the static position of the muscle in conjunction with great tension. In this, there is no evidence of lengthening or shortening of the involved muscle, therefore, it maintains its length.
What is the difference between eccentric and concentric contraction?
It is evident when extending the arm, for example, but with a constant tension in it. Concentric contraction: it occurs in the opposite way to the eccentric one.
What is the most used contraction in the day to day?
Isotonic contraction. Within the types of muscle contraction, the isotonic is considered the antithesis of the isometric. In this, there is muscle movement and, therefore, the length of each muscle involved is constantly modified. In addition, it is the most used contraction in the day to day, thanks to the movements of the body in general.
What is spinal cord contraction?
For its part, the spinal cord focuses on reflex arches or involuntary movements. Within the movements of the muscles, different types of muscle contraction stand out, which can be classified according to their stimulus or movement. Some are even classified as contraction only with exerting tension without movement.
Is isokinetic contraction the same as isotonic contraction?
Isokinetic contraction is quite similar to isotonic, due to the characteristics they share. They are even often confused on a regular basis. This type of contraction refers to the shortening and lengthening of the muscle fibers, but in a uniform and constant way.
What Are The Different Types of Muscle Contraction? (& Why We Should Care.)
Our muscles are designed to do one job. They are designed to contract.
The 3 Types of Muscle Contractions
A concentric muscle contraction occurs when the muscle length shortens.
HOW THEY FIT TOGETHER
So far, we’ve talked through the muscle contractions involved in bending the elbow during a biceps curl. To review, during this stage of movement:
WHY WE SHOULD CARE
Our nervous system wants our body to be well-developed. This is when we feel the best physically and mentally. (And we are designed to feel really really good by the way, in case you’ve never encountered this line of thinking before!)
MUSCLE CONTRACTIONS & YOGA
In yoga, we do a lot of pose holding. That’s great! This helps us develop our muscles isometrically.
NEXT STEPS
To begin assessing this, start by taking inventory of all the movements you do over the course of a week.
