A Brief Summary on Cell Organelles
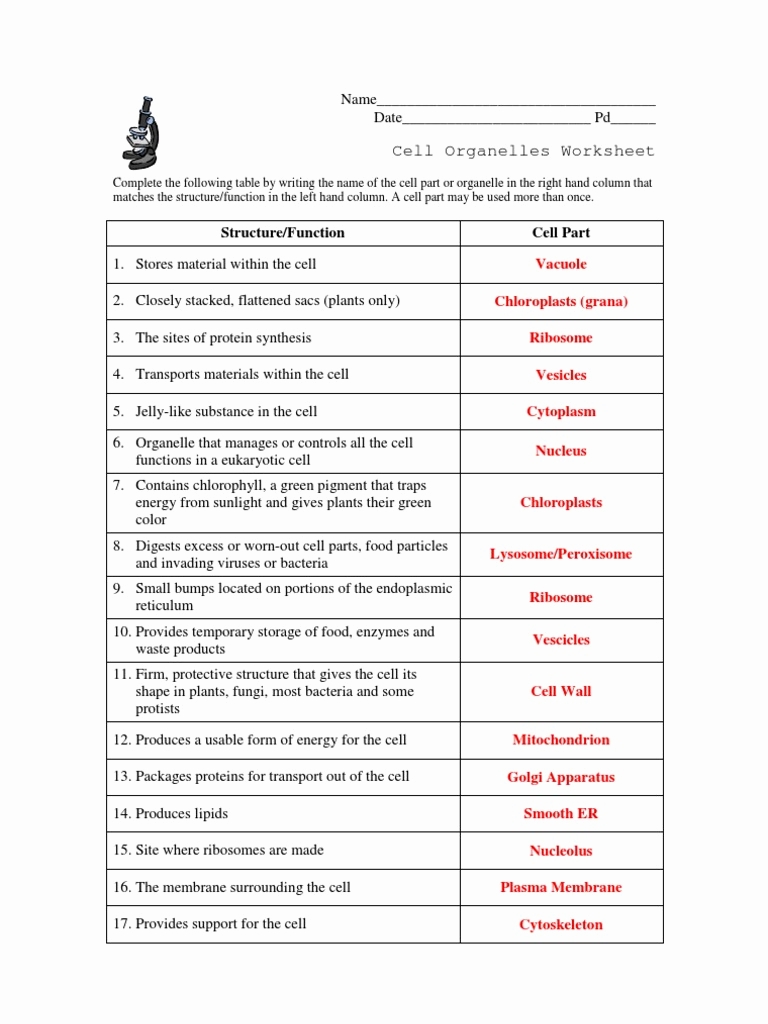
| Cell Organelles | Structure | Functions |
| Cell membrane | A double membrane composed of lipids and ... | Provides shape, protects the inner organ ... |
| Centrosomes | Composed of centrioles and found only in ... | It plays a major role in organizing the ... |
| Chloroplasts | Present only in plant cells and contains ... | Sites of photosynthesis. |
| Cytoplasm | A jelly-like substance, which consists o ... | Responsible for the cell’s metabolic act ... |
| Organelle | Function |
|---|---|
| Nucleus | DNA Storage |
| Mitochondrion | Energy production |
| Smooth Endoplasmic Reticulum (SER) | Lipid production; Detoxification |
| Rough Endoplasmic Reticulum (RER) | Protein production; in particular for export out of the cell |
What are the two main types of organelles?
What are the 7 types of organelles?
- cell membrane. The thin, flexible outer layer of a cell controls what enters and leaves the cell.
- Cytoplasm. The gel-like fluid in a cell is usually water and holds other organelles in place.
- Heart.
- vacuole.
- chloroplasts.
- mitochondria.
- cell membrane.
What are the primary cellular organelles and their functions?
Types of organelles and their functions
- Cell Membrane. Cell membrane is also called plasma membrane or cytoplasmic membrane. ...
- Cell Wall. Cell wall is a non-living structure forming the outer covering for the plasma membrane of fungi and plants.
- Cytoplasm. ...
- Nucleus. ...
- Endoplasmic reticulum. ...
- Mitochondria. ...
- Plastids. ...
- Ribosomes. ...
- Cytoskeleton. ...
- Golgi apparatus. ...
Which are examples of organelles?
What is an example of an organelle?
- Nucleus The nucleus is one of the primary organelles that distinguish eukaryotic cells from prokaryotic cells.
- Endoplasmic Reticulum
- Mitochondrion
- Golgi Apparatus
- Centriole
- Cell Wall
- Chloroplasts
- Vacuole
What is the main function of the organelle?
- This membrane has two layers made from four different sheets of liquid. ...
- The mitochondrion is the organelle that is responsible for producing energy. ...
- The Smooth Endoplasmic Reticulum or SER is tasked with both producing lipids and with detoxification.
- The Rough Endoplasmic Reticulum or RER is responsible for the production of protein. ...
What are organelles and their functions?
Organelles are small structures within the cytoplasm that carry out functions necessary to maintain homeostasis in the cell. They are involved in many processes, for example energy production, building proteins and secretions, destroying toxins, and responding to external signals.
What are the types organelles?
In this regard, there are two types of organelles: (1) membrane-bound organelles (included are double-membraned and single-membraned cytoplasmic structures) and (2) non-membrane-bound organelles (also referred to as biomolecular complexes or proteinaceous organelles).
How many types of organelles are there?
6 Cell OrganellesNucleus. Known as the cell's “command center,” the nucleus is a large organelle that stores the cell's DNA (deoxyribonucleic acid). ... Ribosomes. Ribosomes are the protein factories of the cell. ... Endoplasmic reticulum. Encyclopædia Britannica, Inc. ... Golgi apparatus. ... Chloroplasts. ... Mitochondria.
What are the 8 types of cell organelles?
5.6: Cell OrganellesRibosome Review.The Nucleus.Mitochondria. Mitochondrial Compartments.Endoplasmic Reticulum.Golgi Apparatus.Vesicles and Vacuoles.Centrioles.Ribosomes.More items...•
What are the 12 organelles in a cell?
Within the cytoplasm, the major organelles and cellular structures include: (1) nucleolus (2) nucleus (3) ribosome (4) vesicle (5) rough endoplasmic reticulum (6) Golgi apparatus (7) cytoskeleton (8) smooth endoplasmic reticulum (9) mitochondria (10) vacuole (11) cytosol (12) lysosome (13) centriole.
What are the four categories of organelles?
Terms in this set (4)Nucleus and Ribosomes. genetic control of the cell.Endoplasmic Recticulum, Golgi Apparatus,lysosomes, Vacuoles and Peroxisomes. make, distribute, and break down molecules.Mitochondria and Chloroplasts. energy processing.Cytoskeleton, Plasma membrane, and Cell Wall.
What are the main organelles of a cell?
Single membrane-bound organelles: Vacuole, Lysosome, Golgi Apparatus, Endoplasmic Reticulum are single membrane-bound organelles present only in a eukaryotic cell. Double membrane-bound organelles: Nucleus, mitochondria and chloroplast are double membrane-bound organelles present only in a eukaryotic cell.
What is organelles and give examples?
Organelles are the components of the cell. The cell organelles are further classified based on the presence or absence of the membrane. The examples of organelles are Endoplasmic Reticulum, Golgi Apparatus, ribosomes, mitochondria, vacuole, lysosome, etc.
What is the function of endoplasmic?
The endoplasmic reticulum can either be smooth or rough, and in general its function is to produce proteins for the rest of the cell to function. The rough endoplasmic reticulum has on it ribosomes, which are small, round organelles whose function it is to make those proteins.
What are the 14 organelles in an animal cell?
1) Nucleolus; 2) Nucleus; 3) Ribosome (dots); 4) Vesicle; 5) Rough endoplasmic reticulum (RER); 6) Golgi apparatus; 7) Cytoskeleton; 8) Smooth endoplasmic reticulum (SER); 9) Mitochondrion; 10) Vacuole; 11) Cytosol (It's not an organelle.
What is the main function of this organelle in the cell?
An organelle is a subcellular structure that has one or more specific jobs to perform in the cell, much like an organ does in the body. Among the more important cell organelles are the nuclei, which store genetic information; mitochondria, which produce chemical energy; and ribosomes, which assemble proteins.
What are the 13 organelles in an animal cell?
The thirteen parts of an animal cell are vacuoles, cytoplasm, vesicles, centrioles, ribosomes, nuclear membrane, cell membrane, cytoskeleton, mitochondria, endoplasmic reticulum, nucleolus, Golgi apparatus and nucleus.
What are the 14 organelles in an animal cell?
1) Nucleolus; 2) Nucleus; 3) Ribosome (dots); 4) Vesicle; 5) Rough endoplasmic reticulum (RER); 6) Golgi apparatus; 7) Cytoskeleton; 8) Smooth endoplasmic reticulum (SER); 9) Mitochondrion; 10) Vacuole; 11) Cytosol (It's not an organelle.
What are class7 organelles?
Cell Organelles: These are active, living, permanent extremely small structures present in the cytoplasm and are concerned with cell function. The various cell organelles present in a typical cell are: i) Endoplasmic reticulum: A system of membranes within the cytoplasm of plant and animal cells.
What are the 13 organelles in an animal cell?
The thirteen parts of an animal cell are vacuoles, cytoplasm, vesicles, centrioles, ribosomes, nuclear membrane, cell membrane, cytoskeleton, mitochondria, endoplasmic reticulum, nucleolus, Golgi apparatus and nucleus.
What is cell and its types?
Cells are of two types: eukaryotic, which contain a nucleus, and prokaryotic cells, which do not have a nucleus, but a nucleoid region is still present. Prokaryotes are single-celled organisms, while eukaryotes may be either single-celled or multicellular.
What are the organelles without membranes?
Organelles without membrane: include cell wall, ribosomes and cytoskeleton. These organelles are present in both prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells.
Why are vacuoles important?
They are responsible for storage of the food or nutrients that are needed by a cell . They also store waste products and these waste products are eventually thrown out by vacuoles. So, because of the presence of vacuoles, the cell is protected from contamination. Plant cells have larger vacuoles as compared to animal cells.
What is the largest organelle in eukaryotic cells?
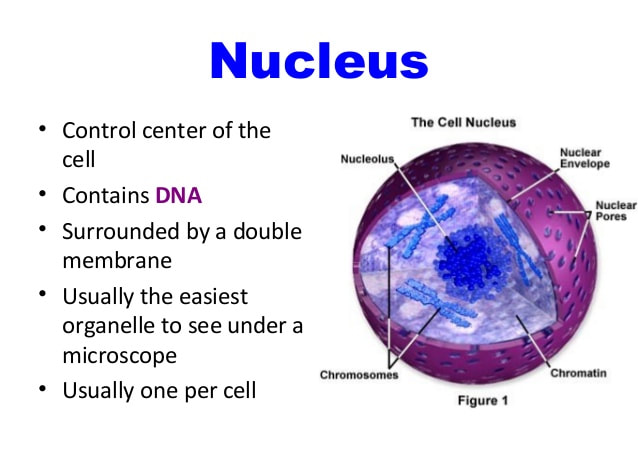
Nucleus is a double membraned and the largest organelle present in all eukaryotic cells. It acts as the storehouse of the cell`s DNA and functions as the control centre of the cellular activities. This round nucleus is surrounded by a nuclear membrane and is dark in colour. The nuclear membrane is a porous membrane and forms a wall between cytoplasm and nucleus. Nucleus contains tiny spherical bodies called nucleolus. It also carries other essential structure called chromosomes. Chromosomes are a thread like structures which carry other important component called gene.
What is the cytoplasm?
Cytoplasm is a jelly-like substance found between cell membrane and nucleus. All the cell organelles are embedded in the cytoplasm. It is composed of water, organic and inorganic compounds. Cytoplasm is one of the essential components of the cell that is present in both plant and animal cells. Cytoplasm functions by controlling all the metabolic activities taking place within the cell and most of the chemical reactions are carried within it.
What are the functional structures inside a cell?
Organelles are the functional structures contained inside the cell. Every single species is composed of cells including both single celled and multicellular organisms. Apart from providing shape and structure to an organism, the cell performs different functions in order to keep the entire system active. So, the functional structures called organelles inside the cell are responsible to keep the entire system active.
What is the cell wall of fungi?
Cell wall is a non-living structure forming the outer covering for the plasma membrane of fungi and plants. Cell wall gives shape to the cell and protects the cell from damage and infection. It also helps in cell-to-cell interaction and provides a barrier to undesirable macromolecules. The cell wall of algae is composed of cellulose, galactans, mannans and minerals like calcium carbonate. And the cell wall of plants has a composition of cellulose, hemicellulose, pectin and proteins. The cell wall of young plants is capable of growth which is gradually diminished while the cell matures and then forms the secondary wall on the inner side of the cell. The middle lamella layer mainly consists of calcium pectate which holds different neighbouring cells together. The cell wall and middle lamellae may be traversed by plasmodesmata connecting the cytoplasm of neighbouring cells.
Which organelle stores food or different nutrients?
Ans. Vacuoles are the cell organelles that store food or different nutrients required for the cell.
What is the process of autophagy?
Autophagy (aka “self-eating”) is a process that cells recycle some of their existed proteins and organelles due to the shortage of nutrient supply. Damaged proteins or organelles will be put on a “garbage tags”.
What organelle produces energy for plants?
Chloroplasts are organelles that conduct photosynthesis and produce energy for the plant cells. Chloroplasts convert the light energy of the Sun into sugars (a process called “ photosynthesis ”) that can be used by cells. At the same time, the reaction produces oxygen (O 2) and consumes carbon dioxide (CO 2 ).
What is an organelle?
What is organelle? An organelle is a tiny cellular structure that performs specific functions within a cell. You can think of organelles as a cell’s internal organs. For example, the nucleus is the cell’s brain, and the mitochondria are the cell’s hearts.
What is the nucleus?
Nucleus. The nucleus (plural: nuclei) is a membrane-bound organelle that stores most of our genetic information (genome). The key feature that separates eukaryotic cells (animals, plants, and fungi) from prokaryotic cells (bacteria and archaea) is the presence of a nucleus.
What is the function of mitochondria?
Mitochondrion (plural: mitochondria) is a rod-shaped organelle that is considered the power generators of the cell. Mitochondrion performs cellular respiration, which converts glucose and oxygen to adenosine triphosphate (ATP). ATP is the biochemical energy “currency” of the cell for all activities.
Which organelle generates ATP?
Mitochondrion generates ATP like a hydraulic dam. It happens via the electron transport chain across the IMM. Mitochondria (in plant cells, chloroplasts, too) are the only organelles that have their own DNA other than the nucleus. Mitochondrial DNA (mtDNA) is circular and encoded only 13 genes.
Which organelle contains fluid?
Vacuole is a membrane-bound organelle that contains a mass of fluid.
What is the organelle that is bound by lipids?
Magnetosomes are another kind of prokaryotic organelle, practically unique in being bound by a lipid bilayer. These structures are formed by actin-like cytoskeletal structures that are involved in shaping and locating the organelle within the cell.
What are the main structures involved in intracellular digestion?
Lysosomes are the main structures involved in intracellular digestion. They contain a number of hydrolytic enzymes that are activated by the acidic pH of these organelles. These enzymes are synthesized in their inactive forms in the cytoplasm before being transported into the organelle through transmembrane channels. Lysosomes can fuse with other organelles, such as phagosomes, for bulk digestion. This plays an important role in immunity as well, when pathogenic microorganisms are ingested by cells of the immune system and destroyed through the action of powerful hydrolytic enzymes.
Which organelle is responsible for ATP generation?
Heterotrophs often rely on mitochrondria for aerobic respiration and ATP generation. Autotrophs channel the energy of solar radiation or other chemical processes to forge the high-energy bonds in ATP. The membranous structures of both these organelles are important in the generation of ATP.
What are the chemicals that are needed for the organelle to function?
In addition, the organelle needs to contain the right chemicals – proteins, amino acids, lipids, carbohydrates or their monomers, along with co-factors, enzymes and signaling molecules. These molecules have to be specifically, and often actively, transported into these subcellular compartments.
How are organelles classified?
Organelles can be classified in a number of ways. The simplest classification is based on their origin: whether they are present in prokaryotes or eukaryotes. While many important biochemical pathways between these two cell lineages share a common ancestry, a complex cell plan sets most eukaryotic cells apart.
What are the properties of membranes?
The properties of a membrane are due to its origin, such as with mitochondria or plastids, or due to its specific function, as seen with the nuclear membrane. A few organelles are not membrane-bound and are present as large complexes made of RNA and protein, such as ribosomes. Images below are representations of plant, ...
What is the organelle?
Organelle Definition. The term organelle is derived from the word ‘ organ ’ and refers to compartments within the cell that perform a specific function. These compartments are usually isolated from the rest of the cytoplasm through intracellular membranes. These membranes could be similar to the plasma membrane or made from a different complement ...
What is the ER in eukaryotes?
Found in eukaryotic cells, Endoplasmic reticulum (ER) is the organelle that forms an interconnected network of flattened sacs (cisternae). Like some of the other organelles found in eukaryotes, ER is enclosed in a membrane. The ER is divided into two regions that vary in structure and function.
What organelle encapsulates the contents of the cell?
The plasma membrane is the organelle that encapsulates the contents of the cell. Apart from encapsulating cell contents, the plasma membrane also plays a vital role in regulating the movement of substances in and out of the cell. As such, it is actively involved in such both passive and active transportation to and from the cell.
What is the role of mitochondria in respiration?
Also known as the powerhouse, mitochondria play an important role in respiration where they generate ATP (adenosine triphosphate) from substrates in the presence of oxygen. Using their DNA, mitochondria are able to encode for some of the components they require to perform their functions.
Where are plastids found?
Plastids are a type of organelle found in plant cells and algae. Like mitochondria, plastids are membrane-bound organelles that contain nucleoids. As such, they are also semi-autonomous organelles.
Which organelle is the largest?
Mitochondria are some of the largest organelles within a cell.
What are the components of the nucleus?
Nucleus / DNA. * Some of the main components of the nucleus include the chromatic, nucleoplasm/nuclear sap and the nucleolus. * The nucleus houses DNA (the hereditary material) as well as various proteins and the nucleolus. In eukaryotic cells, the nucleus is enclosed in a nuclear membrane.
What is the plasma membrane made of?
These processes also help maintain balance even when conditions outside the cell change. The plasma membrane is made up of two layers of phospholipids (phospholipids bilayer). Also see Cell Membrane.
What are Cell Organelles?
Cell organelles are the chemical components within a cell and outside the cell that function in different capacities. Some provide support, while others are for movement and much more.
What is the category of organelles that do not have a membrane?
One category of organelles is without a membrane. Non-membrane organelles are also called “intracellular” or “internal” organelles because they do not have a membrane around them. They are found in both prokaryotic cells and eukaryotic cells, and they include the cell wall, nucleolus, ribosomes, and cytoskeleton.
Which organelle is found in animal cells?
The endoplasmic reticulum is another single-membrane organelle found in animal cells. They usually have a rough or rugose appearance.
Which organelle is always found near the nucleus?
The nucleolus is made up of proteins to form an oval-shaped structure that can vary in size. This organelle is always found near the nucleus, and it produces ribosomes used by a cell for protein synthesis.
What are ribosomes made of?
Ribosomes are also composed of proteins, but their shape can vary depending on their type and the particular organism. Their main functions are:
What are the functions of lysosomes?
Lysosomes are organelles found in animal cells, and they have a single membrane. They function as digestive vesicles that contain hydrolytic enzymes. The different functions of lysosomes are as follows:
Which part of the cell produces energy?
Mitochondria are the powerhouses of cells responsible for producing energy in a process called cellular respiration. The endoplasmic reticulum and mitochondria work together to provide the cell with the energy needed for necessary functions. Ribosomes are involved in protein synthesis, which is an essential function for the cell.
What is the heart and soul of an organelle?
So that really is the heart and soul of an organelle: To be compartmentalized and allow a high concentration of proteins or acid, or whatever to create that environment so that a particular function can be performed. William Gahl, M.D., Ph.D.
What is the function of the organelle?
Organelle. An organelle is a subcellular structure that has one or more specific jobs to perform in the cell, much like an organ does in the body. Among the more important cell organelles are the nuclei, which store genetic information; mitochondria, which produce chemical energy; and ribosomes, which assemble proteins.
What is the organelle in a cell?
Narration. An organelle is a specific structure within a cell, and there are many different types of organelles. Organelles are also called vesicles within a cell.

Organelle Definition
Examples of Organelles
- In eukaryotic organisms, nearly every cell has a nucleus (exceptions include mammalian red blood cells). The other common organelles seen are mitochondria, plastids (among autotrophs), endoplasmic reticula, Golgi apparatus, lysosomes, and vacuoles. Some special cells like neurons also contain synaptic vesicles. All of these structures are membrane ...
Types of Organelles
- Organelles can be classified in a number of ways. The simplest classification is based on their origin: whether they are present in prokaryotes or eukaryotes. While many important biochemical pathways between these two cell lineages share a common ancestry, a complex cell plan sets most eukaryotic cells apart. The origin of this particular kind of complexity is not well known. Eu…
Functions of Organelles
- The activities of a single cell mirror those of an organism. The cell ingests nutrients, digests and transforms them, metabolizes them to form larger molecules, respires and releases wastes. Most cells even contribute to the maintenance of the extracellular environment, not unlike the existence of many specieswithin social structures.
Related Biology Terms
- Apoptosis – Programmed cell death that occurs in multicellular organisms, preceded by distinct changes to the morphology and biochemistryof the cell. Common during development and also used to prev...
- Endosymbionts– Organisms that live within other organisms.
- Motor Proteins– Proteins that function as molecular motors, converting chemical energy to …
- Apoptosis – Programmed cell death that occurs in multicellular organisms, preceded by distinct changes to the morphology and biochemistryof the cell. Common during development and also used to prev...
- Endosymbionts– Organisms that live within other organisms.
- Motor Proteins– Proteins that function as molecular motors, converting chemical energy to mechanical energy, while moving along a suitable surface.
- Upregulation – In genetics, refers to an increase in the number of RNA transcripts produced off a gene. Can also refer to the increase in the number of receptors found on a cell surface.
Quiz
- 1. Which of these is a function of mitochondria? A. ATP and GTP generation B. Cell division C. Transmission of nuclear genetic material D.All of the above 2. Which of these statements is true about intracellular transport? A. Motor proteins called kinesins carry the synaptic vesicles along an actin-based pathway B. Centrosomes are important in the segregation of chromosomes duri…