The Different Types of Spectrometers and How Useful They Are
- NMR Spectrometer NMR or Nuclear Magnetic Resonance spectrometer is a device that analyzes the molecular structure of a certain material, and it also works on measuring and observing the reactions of the nuclear spins when they are placed in a strong magnetic field. ...
- Mass Spectrometer A mass spectrometer creates various ions for the sample that is being investigated. ...
- Optical Spectrometer ...
What are the different types of optical spectrometers?
Three of the most common optical spectrometers: spectrophotometers, spectrofluorometers and Raman spectrometers are introduced. The term spectrophotometer can refer to quite a variety of instruments that measure light, with the exact definition depending on the area of science or industry.
What are the different types of mass spectrometers?
Next, we will introduce some types of mass spectrometers to help with your research. Matrix-assisted laser desorption ionization-time of flight mass spectrometry (MALDI-TOF MS) is a commonly used MS technique. MALDI is a soft ionization technique to create ions with minimal fragmentation by using a laser energy.
What is the difference between spectrometer and spectrophotometer?
Differences between spectrometer and spectrophotometer A spectrometer is a component of spectrophotometer used to measure different kinds of items. A spectrophotometer is a complete system consists of a light source that gathers light that interacted with the subject and the spectrometer for measurement. They differ in terms of usage.
What are the main components of a spectrophotometer?
The main components of a spectrophotometer are the light source, a device that separates the light into component wavelengths, a sample holder and a detector. Image 5: It is an example of a visible light spectrophotometer.

What are the two types of spectrometer?
There are two basic types of atomic spectrometers: emission and absorbance.
What are the 3 basic types of spectroscopy?
5 Different Types of SpectroscopyDefining Spectroscopy. ... Infrared (IR) Spectroscopy. ... Ultraviolet-Visible (UV/Vis) Spectroscopy. ... Nuclear Magnetic Resonance (NMR) Spectroscopy. ... Raman Spectroscopy. ... X-Ray Spectroscopy.
What are the 3 parts of spectrometer?
A spectrometer consists of three main components – entrance slit, grating and detector.
What are the types of spectrophotometer and its uses?
A spectrophotometer is an analytical instrument used to quantitatively measure the transmission or reflection of visible light, UV light or infrared light. Spectrophotometers measure intensity as a function of light source wavelength. There are two classes of spectrophotometers: single and dual beam.
What are four different types of spectroscopy?
There are many different types of spectroscopy, but the most common types used for chemical analysis include atomic spectroscopy, ultraviolet and visible spectroscopy, infrared spectroscopy, Raman spectroscopy and nuclear magnetic resonance.
What is the principle of spectrophotometer?
Spectrophotometer Principle. The spectrophotometer is an instrument which measures the amount of light that a sample absorbs. The spectrophotometer works by passing a light beam through a sample to measure the light intensity of a sample.
What is the use of spectrometer?
spectrometer, Device for detecting and analyzing wavelengths of electromagnetic radiation, commonly used for molecular spectroscopy; more broadly, any of various instruments in which an emission (as of electromagnetic radiation or particles) is spread out according to some property (as energy or mass) into a spectrum ...
What is the function of spectrometer?
A spectrometer is any instrument used to probe a property of light as a function of its portion of the electromagnetic spectrum, typically its wavelength, frequency, or energy. The property being measured is usually intensity of light, but other variables like polarization can also be measured.
Why collimator is used in spectrometer?
COLLIMATOR is used to collimate the beam of light coming. It consists of biconvex lens which converges the light in a direction and to get a parallel beam of light.
What are the 6 parts of a spectrophotometer?
Spectrophotometer: Meaning, Parts and Operation | BiotechnologyBeer Lambert's Law: ... There are six parts in a spectrophotometer: ... Light Sources: ... Monochromators: ... Cuvettes: ... Photocell or photomultiplier tube: ... λ max of proteins: ... X Max of Nucleic Acids.More items...
What are the four components of a spectrophotometer?
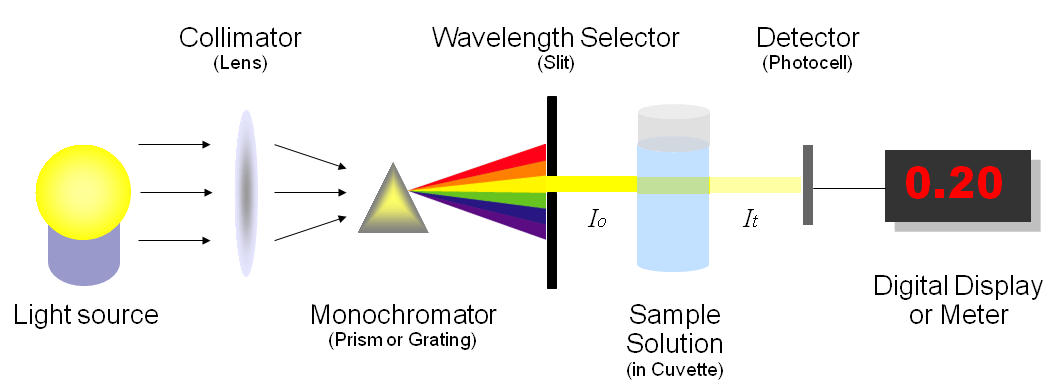
Parts of Spectrophotometer A spectrophotometer consists of four general parts; light source, an optical system (monochromator), sample holder, and detector (photometer). Any spectrophotometer requires light of various wavelengths. Commonly tungsten lamp provides a visible spectrum of light in a spectrophotometer.
What is the difference between a spectrometer and a spectrophotometer?
Like mentioned previously, spectrometers measure the radiated matter of light, while spectrophotometry measures the color it produces. Spectrophotometers are otherwise known as UV-Vis spectrometers. The output of a spectrophotometer is usually measured in the absorption spectrum of the sample.
What are the types of molecular spectroscopy?
The three types of molecular spectra are: Pure rotational spectra. Vibrational rotational spectra. Electronic band spectra.
Which spectroscopy is best?
Explanation: The most powerful spectroscopy that can give you a great idea about the structure of organic molecules is NMR. However, NMR is not enough sometimes; therefore, you will need to use Mass Spectrometry. Moreover, mass spectrometry might not help you enough, then you have to use elemental analysis, and so on.
What is the main purpose of spectroscopy?
Spectroscopy is used as a tool for studying the structures of atoms and molecules. The large number of wavelengths emitted by these systems makes it possible to investigate their structures in detail, including the electron configurations of ground and various excited states.
What are spectroscopy techniques?
Spectroscopy techniques are methods that use radiated energy to analyze properties or characteristics of materials.
What is a spectrophotometer?
The term spectrophotometer can refer to quite a variety of instruments that measure light, with the exact definition depending on the area of science or industry. In all cases the term ‘photo’ is used to indicate that the spectrometer is for the quantitative measurement of light intensity with wavelength. Within academic research (particularly chemistry and biology laboratories) the term spectrophotometer is used specifically to refer to a spectrometer which measures the absorption of light by a sample and that definition will be used here.
What is the most common measurement undertaken in a spectrophotometer?
The most common measurement undertaken in a spectrophotometer is measuring the absorption spectrum of a sample. The excitation monochromator is scanned and the change in light intensity transmitted through the sample recorded on the detector. This is then repeated with a reference sample and the absorption spectrum calculated as shown in Figure 5 for a solution of fluorescein in phosphate buffered saline.
What is the excitation side of a spectrofluorometer?
The excitation side of a spectrofluorometer is equivalent to the spectrophotometer: a white light source and an excitation monochromator. Xenon arc lamps are used as the light source as their high brightness is essential to measure the weak fluorescence emission.
Why use a Raman spectrometer?
Raman spectrometers are used to measure the Raman scattering of light from a sample. The design of a typical Raman spectrometer is shown in Figure 10 and is similar to a spectrofluorometer but with a few key differences. The white light source and excitation monochromator found in spectrofluorometers are replaced with a laser. The reason for this is twofold. The first is that ‘Raman’ is a scattering effect and the light is therefore not absorbed by the sample. This means that a broadband tuneable light source for matching to the absorption features is not required. The second reason is that the Raman effect is much weaker than fluorescence (ratio of Rayleigh scattered light to Raman scattered light is ~10 6) and sources with a high photon flux are therefore essential to maximise the signal.
How to detect light from a sample?
For detecting the light emitted by a sample there are two approaches. The first is an emission monochromator which works using the same principle as above except the light source is the emission from a sample and the monochromator selects which wavelength of light reaches the detector (Figure 3 Emission Monochromator). The second approach is to detect the spectrum of the dispersed light ‘all at once’ using an array detector (such as a CCD camera) which is called a spectrograph (Figure 3 Spectrograph). At least one emission monochromator or spectrograph is found in all spectrofluorometers and Raman spectrometers (see following sections).
What is a mass spectrometer?
Right: Mass spectrometer (Scion Instruments GC-MS spectrometer). The most ubiquitous type of spectrometer used for research are optical spectrometers; and when someone simply says ‘spectrometer’, without an additional qualifier, they are usually referring to an optical spectrometer and this diverse family of spectrometers is the focus ...
What is the goal of optical spectrometers?
The goal of any optical spectrometer is to measure the interaction (absorption, reflection, scattering) of electromagnetic radiation with a sample or the emission (fluorescence, phosphorescence, electroluminescence) of electromagnetic radiation from a sample. Optical spectrometers are concerned with electromagnetic radiation ...
What are the different types of spectrometers?
Types of Spectrometer. 1) An Optical spectrometer - The intensity of light as a function of wavelength or of frequency. Moreover, deflection is caused either by refraction in a prism or by diffraction in a diffraction grating. These spectrometers utilize the phenomenon of optical dispersion.
What is the purpose of spectrometer?
A spectrometer is an instrument that scientists use to determine information about an object or substance through the analysis of its light properties. With its help, any unknown compositions are broken down into basic elemental components or lights emitted from far away galaxies can be used to determine information about space objects, ...
What is the function of a slit in a spectrometer?
The Slit – The slit allows light to enter the spectrometer and controls the resolution.
How does a spectrometer work?
Firstly, we need to pass the light through a spectrometer. It then breaks the light into its spectral components. After that, they then digitize the signal as a function of wavelength, and read it out and display it through a computer.
When were spectrometers invented?
Early 19th century, witnessed the first spectrometers began appearing by many scientists. In older times spectrometers used a small slit and lens. One that passed light through a prism to refract the light into a spectrum projected through a tube for analysis.
When did the term spectrum come into use?
It all started since 300 BC when Euclid began work with spherical mirrors. In the late 17th century , Isaac Newton introduced the word spectrum. In order to describe the range of colours made by scattering light through a prism.
What is a spectrometer?
A spectrometer ( / spɛkˈtrɒmɪtər /) is a scientific instrument used to separate and measure spectral components of a physical phenomenon. Spectrometer is a broad term often used to describe instruments that measure a continuous variable of a phenomenon where the spectral components are somehow mixed.
What is optical spectrometer?
Optical spectrometers (often simply called "spectrometers"), in particular, show the intensity of light as a function of wavelength or of frequency. The different wavelengths of light are separated by refraction in a prism or by diffraction by a diffraction grating. Ultraviolet–visible spectroscopy is an example.
What is the difference between a mass spectrometer and a visible light spectrometer?
A mass spectrometer measures the spectrum of the masses of the atoms or molecules present in a gas. The first spectrometers were used to split light into an array of separate colors.
What is the purpose of mass spectrometer?
A mass spectrometer is an analytical instrument that is used to identify the amount and type of chemicals present in a sample by measuring the mass-to-charge ratio and abundance of gas-phase ions.
Why is spectroscopy important?
The capability of spectroscopy to determine chemical composition drove its advancement and continues to be one of its primary uses. Spectrometers are used in astronomy to analyze the chemical composition of stars and planets, and spectrometers gather data on the origin of the universe.
What Are the Different Types of Spectrometers?
Even though there are many different scientific tools that qualify as spectroscopes, the devices that are commonly and colloquially referred to as spectroscopes fall into one of the following three categories.
How Does an Optical Spectrometer Work?
Even though the different kinds of optical spectrophotometers rely on different physics phenomena and function differently, the basic operating principle behind all of them is the same.
What Are the Benefits of Spectrometer Analysis?
Just like the operating principles and applications, the benefits of spectrometer analysis carry over from one type of optical spectrometer to another. Here are some of the key advantages that optical spectrometers have in chemical analysis:
Wrapping Up Spectrometers
Even though there are many different types of spectrometers used for both scientific and commercial chemical testing purposes, the most common variant is the optical spectrophotometer.
What are the different types of spectrophotometers?
According to different wavelengths and application fields, spectrophotometers can be divided into visible spectrophotometer, ultraviolet visible spectrophotometer, infrared spectrophotometer, fluorescence spectrophotometer and atomic absorption spectrophotometer.
What is a spectrophotometer?
Spectrophotometer is also called spectrometer, which is a scientific instrument that decomposes complex light into spectral lines. Using spectrophotometry, the spectrophotometer measures the absorbance of the measured substance at a specific wavelength or within a certain wavelength range to perform qualitative and quantitative analysis ...
What is a fluorescence spectrophotometer?
Fluorescence spectrophotometer is an instrument used to scan the fluorescence spectrum emitted by liquid-like fluorescent markers. It can provide many physical parameters including excitation spectrum, emission spectrum, fluorescence intensity, quantum yield, fluorescence lifetime, fluorescence polarization, etc., which can reflect the bonding and structure of molecules from various angles. The measurement of these parameters can not only do general quantitative analysis, but also infer the conformational changes of the molecule in various environments, so as to clarify the relationship between molecular structure and function. The scanning range of excitation wavelength of a fluorescence spectrophotometer is generally 190~650nm, and the scanning range of emission wavelength is 200~800nm. Therefore, the instrument can be used for spectral scanning of liquid and solid samples (such as gel bars). The instrument is widely used in many fields, such as scientific research, clinical inspection, food inspection, teaching experiment, chemical industry, medicine, biochemistry, environmental protection and so on.
What is an atomic absorption spectrometer?
Atomic absorption spectrophotometer is also called atomic absorption spectrometer. This instrument analyzes the metal elements based on the effect of the atomic vapor of the ground state of the substance on the characteristic radiation absorption. The light source emits the characteristic spectral radiation to be measured, which is absorbed by the ground state atoms of the measured element in the sample vapor after passing through the atomizer. The content of the measured element can be obtained by measuring the size of the characteristic radiation absorbed. It can sensitively and reliably determine trace or trace elements, so it has become a powerful tool for material analysis and quality control departments to analyze major and trace metals (semi-metals).
How many beams of light are in an infrared spectrophotometer?
Infrared spectrophotometer exactly refers to the light emitted by the light source, and it is divided into two beams of equal energy and symmetry. One beam is the sample light passing through the sample, and the other beam is the reference light as the reference. After the two beams of light enter the photometer through the sample chamber, ...
What frequency is the infrared spectrum?
The general infrared spectrum refers to the infrared spectrum greater than 760nm.
What type of light source is used in the visible light zone?
The ultraviolet light zone usually uses a hydrogen lamp or a deuterium lamp; the visible light zone usually uses a tungsten lamp or a halogen lamp. The function of the monochromator is to decompose the composite light emitted by the light source and separate monochromatic light of the required wavelength from it.
What is mass spectrometry?
Mass spectrometry (MS) is a powerful analytical tool with high sensitivity and high mass accuracy. Recent technical innovations in mass spectrometry-based techniques have contributed to a range of highly sensitive and versatile instruments for high-throughput, high-sensitive, and proteome-scale profiling. Next, we will introduce some types of mass spectrometers to help with your research.
What is a triple quadrupole mass spectrometer?
The triple quadrupole mass spectrometer (TQMS or QqQ), is a tandem mass spectrometer in which the first and third quadrupoles act as mass filters and the second acts as a collision cell to fragment the selected precursors/parent ions, and to generate fragment/daughter ions.
What is the most common tandem MS?
The TQMS is probably the most famous and widely used tandem MS, which is relatively simple and easy-to-use with good reproducibility to offer various applications at a low cost. Triple quadrupole mass spectrometer can be used for structural elucidation that can provide information about fragmentation patterns.
What are the different types of spectrophotometers?
Spectrophotometers are instruments that measure and analyze the spectrum of samples. There are different types of spectrophotometers out there depending on the various application requirements. The spectrophotometer can be divided into five subcategories according to the wavelength and application context : 1 VIS spectrophotometer 2 UV-VIS spectrophotometer 3 Infrared spectrophotometer 4 Fluorescence spectrophotometer 5 Atomic absorption spectrophotometer.
What is a spectrophotometer?
Spectrophotometers are instruments that measure and analyze the spectrum of samples. There are different types of spectrophotometers out there depending on the various application requirements. The spectrophotometer can be divided into five subcategories according to the wavelength and application context :
How many wavelengths can a double beam UV-visible spectrophotometer have?
Double beam UV-visible spectrophotometer utilizes two monochromators, you can get two different wavelengths of monochromatic light. The two light beams alternately irradiate the same sample cell at regular intervals.
What is the primary use of spectrophotometry?
Enzyme assay is the primary use of spectrophotometry.
What is infrared spectroscopy?
Infrared spectroscopy is characterized by fast, low sample volume (a few micrograms to a few milligrams), strong characterization (various substances have their own specific infrared spectrum), tests capable of analyzing various states (gas, liquid, solid) without damaging the sample.
Which is better, a dual wavelength or a single beam spectrophotometer?
Dual-wave length spectrophotometer can not only measure high-concentration samples, multi-component mixed samples, but also perform better in the turbid samples with more sensitivity than the single beam machine.
Is a UV visible spectrophotometer good for pharmaceuticals?
So in general, single-beam UV-visible spectrophotometer is not suitable for high demanding pharmaceutical and quality inspection industries.
What are the different types of spectrophotometer?
Visible light spectrophotometer – This type of spectrophotometer uses a visible light from a tungsten lamp. It is typically used for routine laboratory work, specifically the portable and bench-top spectrophotometer models.
Why do scientists use spectrometers?
In a scientific study, scientists use spectrometer to find out the composition of things on earth and/or in space including the elemental components. In a laboratory setting, spectrometers can identify toxins in the bloodstream, contaminants, and diseases.
How does a spectrophotometer work?
A sample of the subject being studies is placed in the spectrophotometer.
What is the principle of spectrophotometer?
Spectrophotometer principle. A spectrophotometer is a refined version of a colorimeter . In other words, it functions the same way as a colorimeter but with added features. A colorimeter uses a filter which enables a broad range of wave lengths to pass through.
What is spectrophotometer calibration?
Spectrophotometer calibration. It is a process by which the scientist or researcher uses a calibration standard to find out the light source’s accuracy. It is vital to make sure that the device functions properly and the correct measurement is obtained. The calibration technique varies according to the make and brand.
How to calibrate a spectrophotometer?
The empty cuvette is inserted making sure that the arrow is aligned. The spectrophotometer is calibrated by pressing “set zero” button. Place the solution to know the absorbency. (8, 9, and 10)
What is nuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopy?
Nuclear Magnetic Resonance spectroscopy – it is a powerful tool used to determine the structure of organic compounds. It provides structural detail of the entire molecule as well as dynamic information of organic reactions.
How many types of infrared spectrometers are there?
There are two basic types of infrared spectrometers.
What is required to select an infrared spectrometer?
Selecting infrared spectrometers requires an analysis of performance specifications such as wavelength range, resolution, accuracy, and infrared range.
What are other performance specifications?
Operating temperature and operating humidity are other performance specifications.
