
There are three primary categories of tax expenses:
- · Deduction, exemption, and total profit or deductibility where tax expenses are taxable reductions due to federal tax law
- · Favorable tax rates on certain services
- · Tax deductions reimbursable and non-reimbursable. The Joint Taxation Committee (JCT) reports the reductions in income related to specific schemes. ...
What is an example of tax expenditure?
Tax expenditures are provisions of the tax code that can reduce how much a taxpayer owes and therefore federal revenue. Examples include special tax credits, deductions, exclusions, exemptions, deferrals, and preferential tax rates. Tax expenditures have the same net effect on the federal budget as spending programs.
What is the purpose of the Tax Expenditure Budget?
A. The tax expenditure budget displays the estimated revenue losses from special exclusions, exemptions, deductions, credits, deferrals, and preferential tax rates in federal income tax law.
Are tax expenditures revenue losses or spending?
Tax Expenditures. The budget generally treats tax expenditures as revenue losses instead of as spending. An exemption is made for the portion of refundable tax credits that exceeds individuals’ positive income tax liabilities. Here, the net refunds are counted as spending. OMB’s tables show only the revenue losses of tax expenditures,...
Are other expenditures spending substitutes?
Other expenditures have no direct spending analogy, but can instead be viewed as departures from an income tax with a comprehensive base. Marron and Toder (2013) estimate that provisions that could be viewed as spending substitutes then amounted to over 4 percent of gross domestic product.
What are examples of tax expenditures?
Tax expenditures are provisions of the tax code that can reduce how much a taxpayer owes and therefore federal revenue. Examples include special tax credits, deductions, exclusions, exemptions, deferrals, and preferential tax rates. Tax expenditures have the same net effect on the federal budget as spending programs.
What are 5 things that the government spends tax money on?
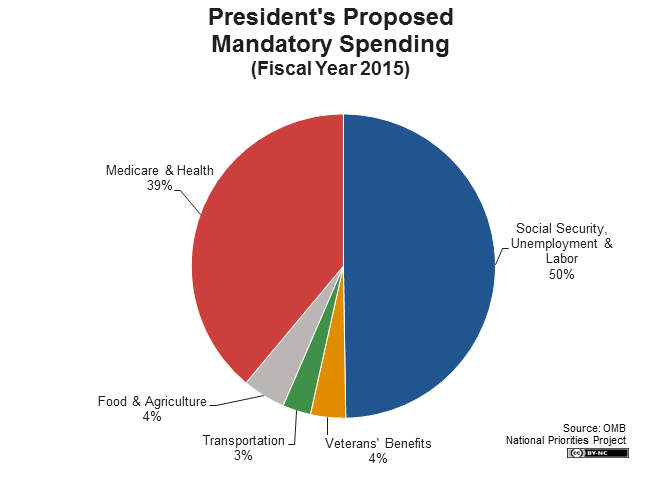
Mandatory spending consists primarily of Social Security, Medicare, and Medicaid. Several welfare programs are smaller items, including food stamps, child tax credits, child nutrition programs, housing assistance, the earned income tax credit, and temporary assistance for needy families.
What are 3 ways tax dollars are spent?
The country's budget The three biggest categories of expenditures are: Major health programs, such as Medicare and Medicaid. Social security. Defense and security.
What are the top 3 federal expenditures?
Mandatory expenditures, such as Social Security, Medicare, and the Supplemental Nutrition Assistance Program, account for about 65% of the budget.
What are our taxes spent on?
In 2021, the federal government spent $6.82 trillion Federal government spending pays for everything from Social Security and Medicare to military equipment, highway maintenance, education, and more. In 2021, the federal government spent the most on Income Security.
What the government spends tax money on?
The rest includes investing in education, investing in basic infrastructure such as roads, bridges, and airports; maintaining natural resources, farms, and the environment; investing in scientific and medical research; enforcing the nation's laws to promote justice, and other basic duties of the federal government.
What are 2 examples of discretionary spending?
Types of Discretionary ExpensesVacations and travel expenses.Automobiles.Alcohol and tobacco.Restaurants and other entertainment-related expenses.Coffee and specialty beverages.Hobby and sports-related expenses, such as crafting, sewing, and gym memberships.
What are the different types of taxes?
Taxes on What You EarnIndividual Income Taxes. ... Corporate Income Taxes. ... Payroll Taxes. ... Capital Gains Taxes. ... Sales Taxes. ... Gross Receipts Taxes. ... Value-Added Taxes. ... Excise Taxes.More items...
What are 3 facts about taxes?
Everyone who earns a paycheck pays a federal income tax. Forty-three of the 50 states charge their citizens an income tax. The seven states that do not have a state income tax are Alaska, Florida, Nevada, South Dakota, Texas, Washington, and Wyoming. In 1691, England taxed the number of windows on a house.
What are two types of government spending?
There are two types of spending in the federal budget process: discretionary and mandatory.
What are the main categories of US federal government spending quizlet?
Federal expenditures fall into five main categories: health insurance (Medicaid and Medicare), retirement benefits (Social Security), national defense, interest on the debt and "other spending" (a broad category that covers spending on education, housing, transportation, agriculture, etc.)
Which of the following are categories of federal government expenditures?
The U.S. Treasury divides all federal spending into three groups: mandatory spending, discretionary spending and interest on debt. Together, mandatory and discretionary spending account for more than ninety percent of all federal spending, and pay for all of the government services and programs on which we rely.
What are 3 facts about taxes?
Everyone who earns a paycheck pays a federal income tax. Forty-three of the 50 states charge their citizens an income tax. The seven states that do not have a state income tax are Alaska, Florida, Nevada, South Dakota, Texas, Washington, and Wyoming. In 1691, England taxed the number of windows on a house.
What was the use of money collected from taxes?
The money collected from taxes is used to support the development and provide resources to the people in the country.
How do taxes help the economy?
How do taxes affect the economy in the long run? Primarily through the supply side. High marginal tax rates can discourage work, saving, investment, and innovation, while specific tax preferences can affect the allocation of economic resources. But tax cuts can also slow long-run economic growth by increasing deficits.
Which of the 9 types of taxes is the largest source of revenue for the government?
As shown in figure 1 above, income taxes are the largest tax base in the United States. Income taxes (including taxes on individual and corporate income; and for the federal government, deductions from payrolls for social insurance and retirement) are a major source of revenue for federal, state and local governments.
What is tax expenditure?
Tax expenditures are provisions of the tax code that can reduce how much a taxpayer owes and therefore federal revenue. Examples include special tax credits, deductions, exclusions, exemptions, deferrals, and preferential tax rates. Tax expenditures have the same net effect on the federal budget as spending programs.
Why is it important to pay attention to tax expenditures?
Paying attention to tax expenditures is an important step to addressing the nation’s fiscal health, and they should be part of broader tax reform discussions . However, tax expenditures are not regularly reviewed and their outcomes are not measured as closely as other government spending. Periodic reviews and evaluations could help determine how successful tax expenditures are at achieving their intended goals, and how their benefits and costs compare to other programs with similar goals.
Do tax expenditures compete with other priorities?
However, unlike federal discretionary spending, tax expenditures do not compete with other priorities in the annual appropriations process, and many are not subject to congressional reauthorization. Instead, many tax expenditures operate like mandatory spending programs (such as Medicare), with eligibility rules and formulas that provide benefits to those who wish to participate.
Can research tax credit be improved?
Tax Policy: The Research Tax Credit's Design and Administration Can Be Improved
Who could develop a framework for evaluating tax expenditure performance?
The Office of Management and Budget (OMB) and the Treasury could develop a framework for evaluating tax expenditure performance
Is tax expense comparable to discretionary spending?
Tax Expenditures Are Comparable in Size to Federal Discret ionary Spending
Benefits for the taxpayers
Taxes saving plans are gaining from the third and fifth highest tax expenditures. The levy and the interest received on the assets will be postponed before the retirement starts. In this sense, more taxpayers are in the lower array than the gains of the postponement.
Benefits of the tax expenditures
Many tax spending has been integrated indefinitely into the tax law. In comparison, their extent of coverage would not depend on the budget process's status, which closely parallels the treatment of mandated procurement schemes.
What are some examples of tax expenditures?
Examples are the deduction for mortgage income on personal residences and the exclusion of interest on state and local bonds.
What is tax expenditure?
Tax expenditures are special provisions of the tax code such as exclusions, deductions, deferrals, credits, and tax rates that benefit specific activities or groups of taxpayers. The Congressional Budget and Impoundment Control Act of 1974 defines tax expenditures as “revenue losses attributable to provisions of the Federal tax laws which allow ...
What percentage of income tax will be deductible in 2021?
Exclusions, deductions, and deferrals of income recognition, excluding itemized deductions, will account for 63 percent of individual income tax expenditures in fiscal year 2021, refundable credits for 18 percent, special rates for 11 percent, itemized deductions for 7 percent, and nonrefundable credits for 1 percent. (figure 1).
What is itemized deduction?
A special category of deductions , called itemized deductions, is valuable only to taxpayers whose sum of itemized deductions exceeds the standard deduction amounts available to all tax filers. The largest itemized deductions are those for home mortgage interest and charitable contributions. In tax year 2017, about 27 percent of tax units (tax returns plus nonfiling units) claimed itemized deductions. Following the increase in the standard deduction and new limits on deductibility of state and local taxes from the 2017 Tax Cuts and Jobs Act, only about 11 percent of tax units will claim itemized deductions in tax year 2020. However, an itemized deduction claimed mostly by higher-income taxpayers is not necessarily unfair, if the standard deduction is worth more to lower-income taxpayers than claiming the deduction. Some itemized deductions may still be objectionable because they are inefficient or inappropriate as a matter of policy.
Why are itemized deductions objectionable?
Some itemized deductions may still be objectionable because they are inefficient or inappropriate as a matter of policy. Credits reduce tax liability dollar for dollar by amount of credit. For example, the child tax credit reduces liability by $2,000 per child for taxpayers eligible to use it fully.
Why are deductions and exclusions important?
Deductions and exclusions typically reduce tax liability more for higher-income taxpayers facing higher marginal income tax rates than for lower-income taxpayers in lower rate brackets, since a deduction is worth more at a higher rate and higher-income taxpayers often spend more on the subsidized item.
What are the refundable credits?
The major refundable credits are the earned income tax credit and the health insurance premium assistance tax credit, which are fully refundable, and the child credit, which is refundable for those with earnings above a threshold amount. Some forms of income benefit from preferential rates.
What is the tax expenditure budget?
The tax expenditure budget displays the estimated revenue losses from special exclusions, exemptions, deductions, credits, deferrals, and preferential tax rates in federal income tax law.
How do expenditure costs change?
Expenditure costs change with the growth of the economy, changes in the quantities and prices of subsidized activities , and—for some provisions—changes in marginal tax rates applied to individual and corporate income and other tax law provisions.
How much is JCT spending in 2021?
JCT’s tax expenditures for fiscal 2021 (including outlay effects) added up to $1.6 trillion. The combined revenue loss for all provisions does not equal the sum of the losses for each provision because of how the provisions interact.
Which agency is the best for tax subsidy?
Complicating matters is that the ideal administrative agency for a tax subsidy might or might not be the Internal Revenue Service (IRS), regardless of classification. For example, because the earned income credit is a direct cash transfer that is based largely on wage reporting, the IRS might serve appropriately as the administrative agency. For other tax expenditures that promote specific activities, administration by an agency with the required programmatic expertise may be preferable.
Is a refundable tax credit counted as spending?
The budget generally treats tax expenditures as revenue losses instead of as spending. Accordingly, only the portion of refundable tax credits, such as the earned income tax credit, that offsets individuals’ positive income tax liabilities are shown in OMB’s tables as tax expenditures, while the portion that is refundable and exceeds tax liabilities is counted in spending. On the other hand, JCT’s tables include both the revenue loss and outlay effects of refundable credits. Both OMB and JCT display the outlay effects in footnotes.
Does the Office of Tax Analysis estimate annual expenditures?
Both the Office of Tax Analysis in the Treasury and the JCT estimate tax expenditures annually. The items included in each, along with their estimated values, are generally similar but do not always match. OMB publishes the Office of Tax Analysis’s estimates in its Analytical Perspectives volume that accompanies each year’s Budget of the US Government.
Does charitable deduction reduce tax liability?
For example, the deduction for charitable contributions reduces tax liability for people who itemize on their tax returns rather than take a standard deduction and donate to qualifying charitable organizations. Tax expenditures can also reduce tax liability for individuals Congress wishes to assist.
What is federal tax expenditure?
Policy Basics: Federal Tax Expenditures. “Tax expenditures” are subsidies delivered through the tax code as deductions, exclusions, and other tax preferences. In fiscal year 2019, tax expenditures reduced federal income tax revenue by roughly $1.3 trillion, and they reduced payroll taxes and other revenues by an additional $140 billion.
How do tax expenditures help?
Tax expenditures reduce the amount of tax that households or corporations owe. To benefit from a tax expenditure, a taxpayer must undertake certain actions or meet certain criteria. For example, some households that have a mortgage can reduce their taxes by claiming a tax deduction for their spending on mortgage interest, and corporations can receive a tax subsidy for investing in machinery.
What is spending through the tax code?
Spending Through the Tax Code. Tax expenditures are intended to promote policy goals. The distinction between these tax breaks and spending is often artificial and without economic basis. Education is one example. On the spending side of the budget, the federal government provides Pell Grants to help low- and moderate-income students afford college.
Why do we need to reduce tax expenditures?
Many policymakers have proposed cutting or overhauling tax expenditures to reduce the deficit, increase investments made on the spending side of the budget, reduce tax rates, better target the breaks towards households that need the most help to engage in whatever activity the breaks are intended to promote, or a combination of those aims. Tax expenditures lose revenue because they shrink the “tax base” — that is, they reduce the amount of income that is subject to tax. That means scaling back tax expenditures raises revenue by increasing the size of the tax base, so it is often called “base broadening.”
Why do tax expenditures lose revenue?
Tax expenditures lose revenue because they shrink the “tax base” — that is, they reduce the amount of income that is subject to tax. That means scaling back tax expenditures raises revenue by increasing the size of the tax base, so it is often called “base broadening.”. Topics:
What are some exceptions to the tax credit?
Notable exceptions are tax credits, such as the Earned Income Tax Credit and the Child Tax Credit, that can be received in whole or in part as a tax refund by households whose incomes are too low to owe much federal income tax. These tax credits reduce poverty and raise the after-tax incomes of working families in low-paying jobs, and also help reduce racial and gender inequities.
What is another example of government subsidy?
Child care is another example. On the spending side of the budget, the government provides some households a subsidy for their child care costs through a spending program (the Child Care Development Fund). It also provides a tax credit for child care to some families, which is another form of spending to subsidize child care costs.
Benefits For The Taxpayers
Types of Tax Expenses
- There are three primary categories of tax expenses: · Deduction, exemption, and total profit or deductibility where tax expenses are taxable reductions due to federal tax law · Favorable tax rates on certain services · Tax deductions reimbursable and non-reimbursable. The Joint Taxation Committee (JCT) reports the reductions in incomerelated to spe...
Benefits of The Tax Expenditures
- Many tax spending has been integrated indefinitely into the tax law. In comparison, their extent of coverage would not depend on the budget process's status, which closely parallels the treatment of mandated procurement schemes. Eligibility and rewards thresholds are governed by federal statute on both permanent and temporary tax expenses. However, the actual volume of money d…