Types of systematic error
- Instrumental error. Some of the instruments do not have a perfectly zero offset. ...
- Observational error. There can be some errors in reading the data. ...
- Environmental error. Some of the experiments (specially, chemical experiments) depend on the environmental conditions like pressure, temperature, humidity, etc. ...
What are some examples of systematic errors?
Systematic Error
- The two main types of measurement error are random error and systematic error.
- Random error causes one measurement to differ slightly from the next. ...
- Systematic error always affects measurements the same amount or by the same proportion, provided that a reading is taken the same way each time. ...
Can you explain my examples of systematic error?
Typical causes of systematic error include observational error, imperfect instrument calibration, and environmental interference. For example: Forgetting to tare or zero a balance produces mass measurements that are always "off" by the same amount. An error caused by not setting an instrument to zero prior to its use is called an offset error.
What are examples of systematic and random error?
Types of Errors
- Gross Errors. This category basically takes into account human oversight and other mistakes while reading, recording, and readings.
- Random Errors. ...
- Systematic Errors: Environmental Errors: This type of error arises in the measurement due to the effect of the external conditions on the measurement.
What is an example of a systematic error?
i) Systematic errors
- a. Instrumental errors. When an instrument is not calibrated properly at the time of manufacture, instrumental errors may arise.
- b. Imperfections in experimental technique or procedure. These errors arise due to the limitations in the experimental arrangement. ...
- c. Personal errors. ...
- d. Errors due to external causes. ...
- e. Least count error. ...

What are the types of systematic errors Class 11?
Types of systematic errors:Instrumental error.Personal error.Error due to external causes.Error due to imperfection.
How many systematic errors are there?
two typesThere are two types of systematic error which are offset error and scale factor error.
What is systematic error explain the different types of it?
The systematic errors are those errors that tend to be in one direction, either positive or negative. Systematic error can be categorised into: i) Instrumental errors that arise from the errors due to imperfect design or calibration of the measuring instrument, zero error in the instrument, etc.
Which of the following are examples of systematic errors?
An error is considered systematic if it consistently changes in the same direction. For example, this could happen with blood pressure measurements if, just before the measurements were to be made, something always or often caused the blood pressure to go up.
What are 3 types of systematic errors?
There are four types of systematic error: observational, instrumental, environmental, and theoretical.
What are the 3 types of errors in science?
Three general types of errors occur in lab measurements: random error, systematic error, and gross errors. Random (or indeterminate) errors are caused by uncontrollable fluctuations in variables that affect experimental results.
What are the major types of errors?
Types of Errors(1) Systematic errors. With this type of error, the measured value is biased due to a specific cause. ... (2) Random errors. This type of error is caused by random circumstances during the measurement process.(3) Negligent errors.
What is a systematic error in research?
Systematic error means that your measurements of the same thing will vary in predictable ways: every measurement will differ from the true measurement in the same direction, and even by the same amount in some cases.
Are systematic errors Human errors?
“Human error” is not a source of experimental error. You must classify specific errors as random or systematic and identify the source of the error. Human error cannot be stated as experimental error.
Which of the following is not systematic error?
Personal error is not a systematic error.
Why are systematic errors more problematic than random errors?
Systematic errors are much more problematic than random errors because they can skew your data to lead you to false conclusions. If you have systematic error, your measurements will be biased away from the true values.
What happens if you have systematic error?
If you have systematic error, your measurements will be biased away from the true values. Ultimately, you might make a false positive or a false negative conclusion (a Type I or II error) about the relationship between the variables you’re studying.
What are the two types of measurement errors?
There are two main types of measurement error: 1 Random error is a chance difference between the observed and true values of something (e.g., a researcher misreading a weighing scale records an incorrect measurement). 2 Systematic error is a consistent or proportional difference between the observed and true values of something (e.g., a miscalibrated scale consistently registers weights as higher than they actually are).
How does random error affect precision?
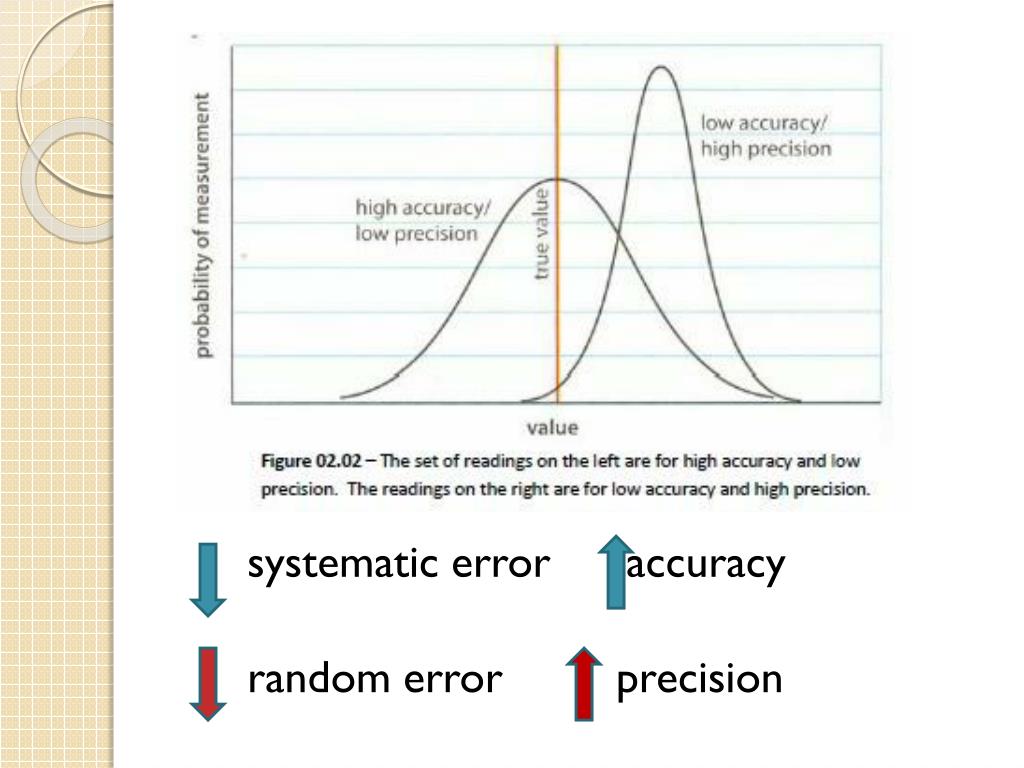
Random error mainly affects precision, which is how reproducible the same measurement is under equivalent circumstances. In contrast, systematic error affects the accuracy of a measurement, or how close the observed value is to the true value.
What is systemic error?
Systematic error means that your measurements of the same thing will vary in predictable ways: every measurement will differ from the true measurement in the same direction, and even by the same amount in some cases.
How to reduce random error?
While you can’t eradicate it completely, you can reduce random error by taking repeated measurements, using a large sample, and controlling extraneous variables.
What is random error?
There are two main types of measurement error: Random error is a chance difference between the observed and true values of something (e.g., a researcher misreading a weighing scale records an incorrect measurement).
What causes errors in measurement?
Personal errors: Peculiar habits of the person during measurement can cause errors. Most such errors are in the same direction. If a proper formula is not used for calculation then it will lead to an introduction of error.
What is error in math?
An error is defined as the difference between the actual or true value and the measured value. An error should not be confused with a mistake, the mistake can be avoided, while the error cannot be avoided but they can be reduced (minimized).
What is a fluctuating condition?
Fluctuating conditions: for e.g. variation in temperature or in the environment may introduce an error in the measurement. In heat or electrical experiments, there is a possibility of such errors.
How does systematic error affect measurements?
Systematic error always affects measurements the same amount or by the same proportion, provided that a reading is taken the same way each time. It is predictable. Random errors cannot be eliminated from an experiment, but most systematic errors can be reduced.
What are the two types of random errors?
Key Takeaways: Random Error vs. Systematic Error 1 The two main types of measurement error are random error and systematic error. 2 Random error causes one measurement to differ slightly from the next. It comes from unpredictable changes during an experiment. 3 Systematic error always affects measurements the same amount or by the same proportion, provided that a reading is taken the same way each time. It is predictable. 4 Random errors cannot be eliminated from an experiment, but most systematic errors may be reduced.
Why is random error important?
If you take multiple measurements, the values cluster around the true value. Thus, random error primarily affects precision. Typically, random error affects the last significant digit of a measurement. The main reasons for random error are limitations of instruments, environmental factors, and slight variations in procedure.
Is measurement error a mistake?
Error is not a "mistake"—it's part of the measuring process. In science, measurement error is called experimental error or observational error. There are two broad classes of observational errors: random error and systematic error.
Can random errors be avoided?
Random errors are unavoidable, but cluster around the true value. Systematic error can often be avoided by calibrating equipment, but if left uncorrected, can lead to measurements far from the true value.

What Is A Systematic Error?
Types of Systematic Errors
- There are two types of systematic error which are offset error and scale factor error. These two types of systematic errors have their distinct attributes as will be seen below.
Causes of Systematic Errors in Research
- The two primary causes of systematic error are faulty instruments or equipment and improper use of instruments. There are other ways systematic error can happen in your experiments, and these could be the research data, confounding, the procedure you used to gather your data, and even your analysis method. Briefly, we will discuss the two primary causes of systematic error and als…
Effects of Systematic Error in Research
- The effect of a systematic error in research is that it will move the value of your measurements away from their original value by the same percentage or the same proportion while in the same direction. The consequence is that shifting the measurement does not affect your reliability. This is because irrespective of how many times you repeat the measurement, you will get the same v…
How Do You Identify Systematic Errors?
- You cannot easily detect a Systematic error in your study. In fact, you may not recognize systematic errors even with the visualization method. You need to make use of statistical analysis to identify the type of error present in your research and assess the error. When your study findings have the desired outcome, then there is no systematic error. You can also identify the s…
Examples of Systematic Errors in Research
- We are going to look at the following examples to better understand the concept of systematic error. Example one: Let's assume some researchers are carrying out a study on weight loss. At the end of the research, the researchers realized the scale added 15pounds to each of the sample data, they then concluded that their finding is inaccurate because the scale used gave a wrong r…
How to Minimize Or Avoid Systematic Errors in Research
- Once you can identify the cause of a systematic error, you should be able to reduce its effect on your data to a great extent. The issue, however, is that systematic errors are not easily detectable. This is because your equipment cannot talk, so you won't get a warning signal, and regardless of how many times you conduct the test, you will arrive at the same result which can be confusing. …
Are Random Or Systematic Errors Worse?
Random Error
- Random error affects your measurements in unpredictable ways: your measurements are equally likely to be higher or lower than the true values. In the graph below, the black line represents a perfect match between the true scores and observed scores of a scale. In an ideal world, all of your data would fall on exactly that line. The green dots represent the actual observed scores fo…
Reducing Random Error
- Random error is almost always present in research, even in highly controlled settings. While you can’t eradicate it completely, you can reduce random error using the following methods.
Systematic Error
- Systematic errormeans that your measurements of the same thing will vary in predictable ways: every measurement will differ from the true measurement in the same direction, and even by the same amount in some cases. Systematic error is also referred to as bias because your data is skewed in standardized ways that hide the true values. This may lead...