
What are the Types of Thermosetting Plastic Materials.
- Vulcanized Rubber. This type of rubber is more hardened than natural rubber. Once it solidifies, it can’t be recycled. It’s used in the production of ...
- Bakelite.
- Duroplast.
- Urea-Formaldehyde.
- Melamine-Formaldehyde.
- Polyester.
- Vinyl Ester.
- Polyimides.
What are some examples of thermosetting plastics?
Many manufacturers have switched to thermosets as they are cost-effective and are a great replacement for some metal components. Here are some examples of thermosetting plastics. 1. Vulcanized Rubber Vulcanized rubber is a type of thermoset plastic as once it is molded, it retains its shape and can’t be recycled again.
What are the different types of thermoplastic?
Polyethylene – Polyethylene is a very common thermoplastic, and is often used to create plastic grocery bags or single-use plastic products like shampoo or water bottles. Acrylic – Acrylic is commonly used for consumer goods.
What is the difference between thermosets and thermoplastics?
The critical distinction between thermosets and thermoplastics is that while thermoplastics become viscous when heated, thermosets retain their shape. As such, thermoset plastics are commonly used in materials that are expected to experience a lot of chemical or heat stress over the product’s life span.
What are the different types of thermoset chemical systems?
Information and listings on the types of thermoset chemical systems can be found on the Engineering360 SpecSearch Database. The most common types are epoxy, phenolics, bismaleimide, and fluoropolymers. Epoxy resins exhibit high strength and low shrinkage during curing.
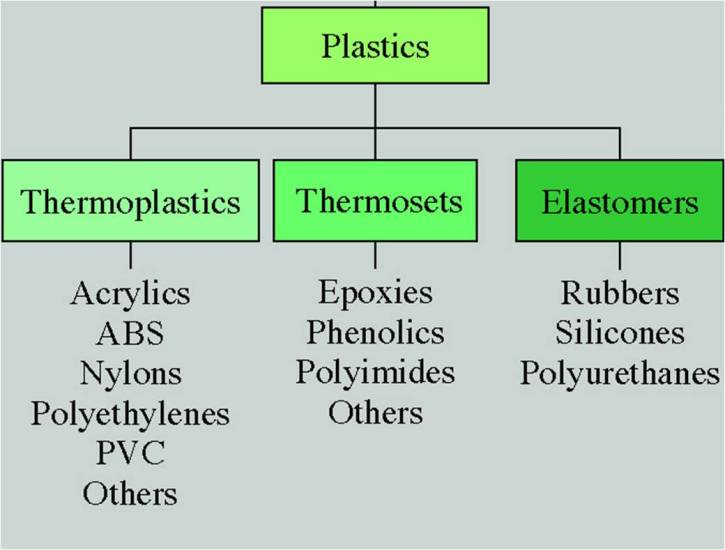
What are the three types of thermosetting plastics?
The main thermosetting plastics are epoxy resin, melamine formaldehyde, polyester resin and urea formaldehyde.
What are the types of thermosetting?
Types of Thermoset and Thermoplastic MaterialsAcrylic.Polycarbonate.Nylon.Polyvinyl Chloride (PVC)Polypropylene.Polyethylene.
What is the most common type of thermosetting plastic?
Most Common Thermoset TypesEpoxy. Epoxy, resins that exhibit high strength and low shrinkage during curing, are known for their toughness and resistance to both chemical and environmental damage. ... Phenolics. ... Bismaleimide (BMI) ... Fluoropolymers.
What are thermosetting plastics and its examples?
These are the plastics that cannot be softened by heating once they are moulded. The main thermosetting plastics are epoxy resin, melamine formaldehyde, polyester resin etc.
Which one is a type of thermosetting polymer *?
2 Thermosetting Plastic Examples: Epoxy Resin. Phenolic(Bakelite) Vinyl Ester Resin.
Is rubber a thermosetting plastic?
The liquid silicone rubber (LSR) part (right) is a popular thermoset material choice.
Is nylon a thermosetting plastic?
Nylon is classified as a “thermoplastic” (as opposed to “thermoset”) material, which refers to the way the plastic responds to heat. Thermoplastic materials become liquid at their melting point - a very high 220 degrees Celsius in the case of Nylon.
What is example of thermosetting?
Examples: Thermosetting polymers are Bakelite, vulcanized rubbers, epoxy resin, vinyl ester resin and polyurethane etc while thermosetting plastic examples are Teflon, Acrylic, Nylon etc.
What is example of thermosetting?
Examples: Thermosetting polymers are Bakelite, vulcanized rubbers, epoxy resin, vinyl ester resin and polyurethane etc while thermosetting plastic examples are Teflon, Acrylic, Nylon etc.
How many types of thermoplastics are there?
Types of thermoplastics include polyethylene (PE), polyvinyl chloride (PVC) and polystyrene (PS), which often are used for packaging. Other groups of thermoplastics are acrylics, fluoropolymers, polyesters, polyimides and nylons.
Which is thermosetting plastic material?
Thermoset plastics have been molded by Rebling for over 50 years. Examples of thermosetting plastics include Epoxy, Phenolic, and DAP. Rebling uses both the transfer and plastic injection molding processes for thermoset moldings.
What is thermosetting plastic?
Thermoset Plastics or Thermosetting Plastics. 3.1. Thermoplastics: By heating the polymer, if it turns soft, then it is called as Thermoplastic material. At room temperature, they are available in the form as Solids.
How does thermoplastic material change to liquid?
Thermoplastic material in the form of solid is converted into Thermoplastic material in the form of liquid which is done by the action of heating and the Vice-versa also takes place in another direction. Loses Strength: By heating the thermoplastic material it loses its strength.
How does thermoplastic lose its strength?
Loses Strength: By heating the thermoplastic material it loses its strength.
What are plastics made of?
They are made up of carbon, hydrogen and sometimes oxygen, chlorine, nitrogen, fluorine, sulfur, phosphorus or silicon. Majority of the times, polymers are made up of Carbon, Hydrogen, and Oxygen only. It is a low-density polymer and thereby it possesses lightweight.
What are the properties of plastics?
Properties of Plastics or Polymers: The Properties of Polymers or plastics which are essential to know for any mechanical engineer are as follows: Bond: It possesses a Covalent bond. Strength: The strength of the polymer is low when compared with Metals. Binding Energy: The formation of C, H&O atoms forms a polymer.
Why do polymers have bad conductivity?
Conductivity: The polymers possess bad electrical conductivity because of the absence of free electrons. Thermal Conductivity: The polymers possess bad thermal conductivity. Density: The polymers possess low density which means that the weight of the polymer is less and this is one of the advantages of polymers.
How does thermoset material gain strength?
Gains strength: By the action of heating, the thermoset plastic material gains strength.
What is thermosetting plastic?
Prev Article Next Article. Thermosetting plastics are also known as thermosetting polymers or thermosets. They are produced by the process of condensation polymerization and consist of long molecular chains that are cross-linked together by covalent bonds. These materials can be molded into any desired shape upon heating, but once they are cooled, ...
What is the name of the thermoset plastic?
Bakelite was the first thermoset plastic that was synthesized from synthetic components. The chemical name of Bakelite is ‘Polyoxybenzyl Methylene Glycol Anhydride,’ and its chemical formula is (#N#C 6#N#{C}_ {6} C 6#N# H 6#N#{H}_ {6} H 6#N##N#O.C#N#H 2#N#{H}_ {2} H 2#N##N#O)n. Commercially, it is also known as phenol-formaldehyde resin as it is synthesized by the condensation process between phenol and formaldehyde, under high pressure with HCl as a catalyst. However, other catalysts like ammonia and zinc chloride are also used sometimes, as per the requirement of the reaction. The product obtained from this reaction is further heated slowly till a hard substance called Bakelite is obtained. Bakelite is easily moldable in its liquifiable state, hence it is used in the manufacturing of various products. To increase the strength of the bakelite , various fillers like gypsum, mica, asbestos are also used. Bakelite has a wide application in the electrical industries for making switches, boards, sockets, and wire insulation because of its electrical insulation properties. The unique property of Bakelite is that it can be produced in different colors that is why it is widely used in the manufacturing of colorful bangles, bracelets, and artificial jewelry. The application of Bakelite is also found in various kitchenware products.
How are melamine and formaldehyde reacted?
They are synthesized by reacting Melamine with Formaldehyde under low alkaline conditions. Like urea-formaldehyde resins, it is also widely used in wood industries. Melamine polished boards have better heat and chemical resistance properties than natural boards. Melamine-Formaldehydes are fully compatible with Urea-Formaldehyde resins and are often reacted with each other for reducing the emission of formaldehyde from particleboards, and this blend of resins is called melamine-urea-formaldehyde. Melamine resins are fire-retardant that is why they are used as additives in the manufacturing of papers, paints, plastics, and flame-resistant textiles. Many other products that are manufactured using these resins are particleboards, laminates, kitchenware, and floor tiles.
What is vulcanized rubber?
Vulcanized rubber is a type of thermoset plastic as once it is molded, it retains its shape and can’t be recycled again . The untreated rubber is converted into the vulcanized rubber through a process called vulcanization. In this process, the natural rubber is treated with Sulphur and various activators like Zinc fatty acid esters at the temperature of 140-160°C. Vulcanized rubber is more hardened than natural rubber. It is used in the manufacturing of various goods as it has both electrical and thermal insulation properties. Moreover, it has good abrasion properties and is inexpensive. It is used in manufacturing tires of vehicles because it has high tensile strength, hence it reduces the chances of tire punctures. Other uses of vulcanized rubber include seat belts, toys, conveyor belts, rubber hoses, and shoe hoses.
Why is the thermosetting material rigid?
This rigidity is because of the increase in the cross-linking of polymer chains present inside the thermosetting materials due to the energy gained by the heat. In many cases, the rate of cross-linking can also be increased by adding a catalyst or by applying external pressure.
Why are thermosetting materials stronger than thermoplastics?
Thermosetting materials have a three-dimensional crosslinked molecular structure due to which they are much stronger than thermoplastics materials.
What materials maintain their stability at both high and low temperatures?
Thermoset materials maintain their stability at both high and low temperatures.
What Plastics are Thermosets?
Silicone, also known as polysiloxanes, is one of the most common types of thermoset plastics. It is used to create a wide range of products, most notably silicone oil, silicone cooking utensils, electronics and for implants.
What is the difference between thermoplastics and thermosets?
The critical distinction between thermosets and thermoplastics is that while thermoplastics become viscous when heated, thermosets retain their shape. As such, thermoset plastics are commonly used in materials that are expected to experience a lot of chemical or heat stress over the product’s life span.
What are Thermosets?
Thermosetting plastics, also known as thermosets, are essentially synthetic resins that do not melt. Thermoplastics, as we discussed in our guide to thermoplastics, are ones that can be heated, made fluid, and cooled through thermoplastic freezing over and over to form our desired shapes. By contrast, thermosets remain a solid shape even when exposed to scorching temperatures and degrade before they reach melting point.
Why use thermoset plastic?
Because the objects made from thermosets are heat-resistant, thermoset parts are commonly used in parts of a machine expected to grow hot, including tyres, weapon parts, coal plants and more. Some, like silicone, are also widely used in electrical circuits thanks to their resistance to heat. If your business requires incredibly reliable plastic parts in its operation, then a thermoset plastic might be the right option for you.
What is thermoset injection?
Rather than through thermoplastic freezing molten plastic in a cold mould, thermoset injection moulding involves setting liquid synthetic resins in a hot mould and crosslinking the polymer. Typically, thermoset plastics are then processed with fillers to reinforce the synthetic resin and minimise shrinking during this process.
What is vulcanized rubber?
Rubber that has been hardened through vulcanisation, a process named after the Roman God of Fire, forms cross-links in natural rubber polymers to create a thermoset plastic. While vulcanisation can also occur with polychloroprene rubber (CR rubber) or with room-temperature silicone, vulcanisation is most often done with naturally collected rubber and sulphur.
What is a thermoplastic?
A thermoplastic behaves like a carrier bag on a wood fire: the bag melts from the heat into a liquid-like viscous substance. A thermoset, by contrast, is like a frying pan handle – it will retain its shape and eventually produce smoke (i.e. degrade) if the heat gets too much.
What is thermoplastic material?
A thermoplastic is a plastic material that becomes moldable above a specific temperature and solidifies upon cooling. In this article, I will be explaining the top 10 properties of thermoplastic materials in a detailed manner. 3.1.1. Top 10 Properties of Thermoplastic Material:
What are the two types of plastics?
Types of Plastics: They are two types of Plastics. Thermoplastics. Thermoset Plastics or Thermosetting Plastics. 3.1. Thermoplastics: By heating the polymer, if it turns soft, then it is called as Thermoplastic material. At room temperature, they are available in the form as Solids.
How is thermoset converted to solid?
Thermoset in the form of liquid is converted into Thermoset material in the form of solid which is done by the action of heating and its Vice-versa is not possible.
How does thermoplastic material lose its strength?
Loses Strength: By heating the thermoplastic material it loses its strength. Gains strength: By the action of cooling, the thermoplastic material gains strength. Shape change: During cooling only, the thermoplastic material changes its shape. Temperature: The servicing temperature of thermoplastic material is 150°C.
What are plastics made of?
They are made up of carbon, hydrogen and sometimes oxygen, chlorine, nitrogen, fluorine, sulfur, phosphorus or silicon. Majority of the times, polymers are made up of Carbon, Hydrogen, and Oxygen only. It is a low-density polymer and thereby it possesses lightweight.
What are the properties of polymers?
The Properties of Polymers or plastics which are essential to know for any mechanical engineer are as follows: Bond: It possesses a Covalent bond. Strength: The strength of the polymer is low when compared with Metals. Binding Energy: The formation of C, H&O atoms forms a polymer.
Why do polymers have bad conductivity?
Conductivity: The polymers possess bad electrical conductivity because of the absence of free electrons. Thermal Conductivity: The polymers possess bad thermal conductivity. Density: The polymers possess low density which means that the weight of the polymer is less and this is one of the advantages of polymers.
What is thermoplastic?
A thermoplastic is a plastic material that becomes moldable above a specific temperature and solidifies upon cooling.
How is thermoplastic material converted into thermoplastic material?
Thermoplastic material in the form of solid is converted into Thermoplastic material in the form of liquid which is done by the action of heating and the Vice-versa also takes place in another direction.
What are the two main types of plastics?
The two main types of plastics are Thermoplastics and Thermosetting Plastics.
What are plastics made of?
They are made up of carbon, hydrogen and sometimes oxygen, chlorine, nitrogen, fluorine, sulfur, phosphorus or silicon. Majority of the times, polymers are made up of Carbon, Hydrogen, and Oxygen only. It is a low-density polymer and thereby it possesses lightweight.
What happens to thermoplastics during cooling?
Shape change: During cooling only, the thermoplastic material changes its shape.
How does thermoset material gain strength?
Gains strength: By the action of heating, the thermoset plastic material gains strength.
What are the chains of plastic called?
These chains are called polymers and that is why many plastics begin with “poly,” such as polypropylene, polyethylene, and polystyrene.
What are the different types of thermosets?
The most common types are epoxy, phenolics, bismaleimide, and fluoropolymers.
What is thermoset resin?
Thermoset molding compounds are designed for processes such as reaction injection molding (RIM) and resin transfer molding (RTM). Composite thermoset materials consist of a matrix and a dispersed, fibrous, or continuous second phase. Casting resins include a catalyst or hardener. Thermoset electrical resins and electronic-grade products are used in potting or encapsulating compounds, conductive adhesives, and dielectric sealants.
What is epoxy resin used for?
Most are two-part resins cured at room temperature. Depending on the formulation, epoxy resins are used as casting resins, potting agents, resin binders, or laminating resins in fiberglass or composite construction. They are also used as encapsulates, electrical conductors in microelectronic packaging, and adhesives in structural bonding applications.
What is BMI resin?
Bismaleimide (BMI) resins are aromatic polymides used in high performance structural composites requiring higher temperature use and increased toughness. Epoxy blends of BMI have exhibited use temperatures of 205° to 245 °C and increased toughness. Bismaleimide (BMI) resins have processing characteristics similar to epoxy resins ...
What is vulcanized thermosetting?
Vulcanized Thermosets. Vulcanization is a thermosetting reaction that uses a crosslinked compound or catalyst. In rubber-like materials, vulcanization results in greatly increased strength, stability, and elasticity. Traditionally, sulfur is used as the vulcanizing agent for natural rubber.
Why are thermoplastics stronger than thermoplastics?
They are generally stronger than thermoplastics due to polymer cross-linking and have a higher resistance to heat. Cured thermoset resins may soften when heated, but do not melt or flow. They tend to be more brittle than thermoplastics and many cannot be recycled due to irreversibility.
What is a reinforced product?
Filled or reinforced products consist of resins and modifiers such as pigments, plasticizers, or chopped fibers. By contrast, unfilled resins, base polymers, and raw materials do not contain additives. Typically, raw materials are available as pellets, powders, granules, or liquids.
What are thermoplastics used for?
Common Uses for Thermoplastics. Thermoplastics are commonly used for consumer goods. Since these products are never exposed to high levels of heat, it’s suitable to manufacture them out of a thermoplastic. Best of all, these products can be marketed as recyclable to environmentally conscious shoppers.
What are the two main classes of polymers?
There are two main classes of polymers: Thermoset plastics, and thermoplastics. While the names of these two kinds of plastic may seem similar, they actually have several key differences. These differences can influence the performance of these plastics, making them ideal for different use cases. In this blog post, we will go into further detail ...
What is reusable plastic made of?
For example, reusable food storage containers and plastic reusable water bottles are typically made from polycarbonate. Polycarbonate is exceptionally impact resistant, and can even be used as bulletproof glass. Polyethylene – Polyethylene is a very common thermoplastic, and is often used to create plastic grocery bags or single-use plastic ...
What is a synthetic sponge made of?
As well, synthetic sponges are often made from polyurethane. Epoxy – Epoxy resin is a liquid thermoset plastic, and upon setting it forms a solid bond that’s difficult to break. This is often used for adhesive purposes, but it can also be found in consumer goods like snowboards and bicycles.
What is the difference between polyethylene and acrylic?
Polyethylene – Polyethylene is a very common thermoplastic, and is often used to create plastic grocery bags or single-use plastic products like shampoo or water bottles. Acrylic – Acrylic is commonly used for consumer goods. If you own a recently manufactured aquarium or terrarium, it’s likely made of acrylic plastic.
Can you turn thermoset plastic into liquid?
If a thermoplastic is like butter, then thermoset plastics are like egg whites. They begin as a liquid and become solid when heat is applied. However, there’s no way to turn solid egg whites back into a liquid – instead, heating it will only burn it.
Is thermoplastic more expensive than thermoset?
Of course, they can melt, making them inappropriate for heat-focused applications. They’re also more expensive than thermoset plastics, on average. However, this higher price tag is often justified due to the various benefits of thermoplastics. They have high-impact resistance, chemical resistance, and shrink resistant.
