Roles of Decomposers and Detritivores
- Food Chain Organisms in this level of the food chain provide nutrients for the producers (plants) who in turn are eaten by the consumers in the next level who are then eaten by tertiary consumers. ...
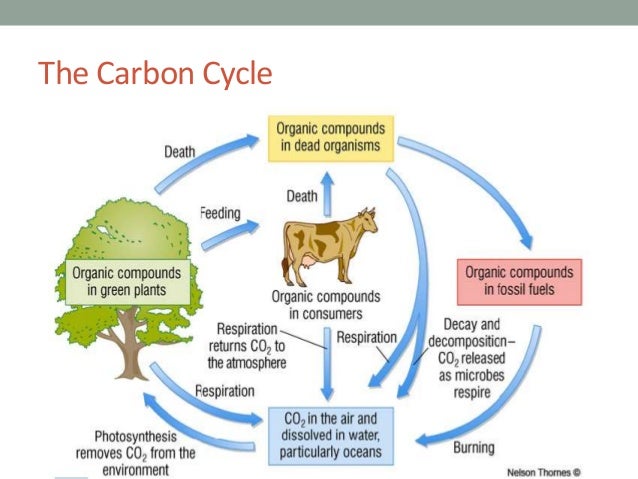
- Nutrient Cycling Decomposers are involved in virtually all of the nutrient cycles on the planet. ...
- Nitrogen Fixation ...
- Ecosystem Maintenance ...
What are 3 things decomposers do?
Different decomposers Each helps recycle food in its own way. Fungi release chemicals to break down dead plants or animals into simple substances. They absorb some of these substances for growth, but others enter the soil. Earthworms digest rotting plant and animal matter as they swallow soil.
What are 5 examples of decomposers?
Terrestrial Ecosystem DecomposersBeetle, are the shredders that feed upon detritus.Earthworms feed upon detritus.Millipede, another shredder that feeds upon detritus.Mushroom is a kind of fungi that breed on the ground or the dead material.Pillbug, another shredder that feeds upon detritus.More items...
Why are decomposers useful to the living world?
Decomposers in ecosystems act as environmental cleaners by decaying dead plants and animals. They aid in the recycling of nutrients. They make room for a new life in the biosphere by decaying the dead.
What is the best Decomposer?
0:003:18An example of an animal decomposer is an earthworm earthworms eat dead plants and animals the wasteMoreAn example of an animal decomposer is an earthworm earthworms eat dead plants and animals the waste that earthworms leave behind is rich in nutrients nutrients help plants to grow.
What are 3 examples of Decomposer?
Decomposers (fungi, bacteria, invertebrates such as worms and insects) have the ability to break down dead organisms into smaller particles and create new compounds. We use decomposers to restore the natural nutrient cycle through controlled composting.
What are 3 types of decomposers?
1:015:13And nutrients for growth and development. We will focus on four main types of decomposers fungiMoreAnd nutrients for growth and development. We will focus on four main types of decomposers fungi insects worms and bacteria fungi breakdown and recycle organic material by pre digesting fungi produce
What are decomposers give 2 examples?
The micro-organisms that decompose/ convert the dead remains of plants and animals to humus are called decomposers. The two common examples of decomposers are bacteria and fungi.
What are decomposers Class 10 examples?
- Examples of decomposers are bacteria, mushrooms, mold, (and if you include detritivores) worms, and springtails. Note: Decomposers also recycle dead plants and animals into chemical nutrients such as carbon and nitrogen. They are released back into the soil, air and water as food for living plants and animals.
What is a decomposer?
Decomposer Definition. A decomposer is an organism that decomposes, or breaks down, organic material such as the remains of dead organisms. Decomposers include bacteria and fungi. These organisms carry out the process of decomposition, which all living organisms undergo after death. Decomposition is an important process because it allows organic ...
Why do dead organisms need nutrients?
A dead organism provides nutrients for decomposers like bacteria and fungi to use in order to grow and reproduce, propagating their own species. The side effect of this basic need to survive is that organic material and nutrients are cycled throughout the ecosystem as other organisms consume the bacteria and fungi.
What is the difference between a decomposer and a detritivor?
The difference lies in the way decomposers and detritivores break down organic material. Detritivores must digest organic material within their bodies in order to break it down and gain nutrients from it. Decomposers do not need to digest organic material internally in order to break it down; instead, they can break down matter through biochemical reactions. Organisms that are detritivores include invertebrates such as earthworms, woodlice, sea stars, slugs, and fiddler crabs.
What is the first to eat dead organisms?
Decomposers and Scavengers. Scavengers are the first to arrive at a dead organism’s remains, and they directly eat the dead plant and animal material. Once scavengers are done with the remains, decomposers and detritivores take over and consume the parts that the scavengers have left behind. Many predators will scavenge on occasion; examples ...
Why do decomposers decompose?
The reason decomposers decompose, however, is simply because they need to survive. Decomposers are heterotrophic, which means they get their energy from ingesting organic material.
What are the stages of decomposition?
When an organism dies and decomposers do the work of decomposition, the organism’s remains go through five stages of decomposition: fresh, bloat, active decay, advanced decay, and dry/remains. There are two main processes that occur in a decomposing organism: autolysis and putrefaction.
What are the two processes that occur in a decomposing organism?
There are two main processes that occur in a decomposing organism: autolysis and putrefaction. Autolysis is when cellular enzymes in the dead organism’s own body break down cells and tissues, while putrefaction is when microbes grow and reproduce throughout the body after death.
What are the main decomposers of the ecosystem?
Fungi are the main decomposers in many ecosystems, particularly in forests. One of their main functions is to help release nitrogen and phosphorous from dead decaying matter. They do this through a series of specialized proteins and enzymes in their cell walls and hyphae (root-like filaments).
Why are decomposers important?
The organisms that occupy the decomposer level of a biome are essential to life on Earth. They break down dead plant and animal matter so the nutrients in them are recycled back into the ecosystem to be used again. Fungi are the main decomposers in many ecosystems, particularly in forests.
What is the role of decomposer bacteria in the food chain?
Decomposer bacteria are responsible for fixing nitrogen in the soil, meaning they transform nitrogen into a form that can be used by other organisms in the food chain. Specifically, the bacteria take atmospheric nitrogen and turn it into molecules such as ammonia, nitrate and nitrite which can be used by plants.
How do decomposers help plants?
The plants in the consumer level rely on decomposers to break down dead organic material to release the nutrients and elements like carbon, oxygen and phosphorus back into the soil. This along with energy from the sun powers the process of photosynthesis in plants. When organisms in the consumer level eat the producers, they extract the energy from the food and excrete waste that goes back into the decomposers food chain. This is the constant process of ingesting, excreting and recycling that goes on in an ecosystem.
How do decomposers clean up dead material?
Decomposers clean up the dead material by processing it and returning the nutrients to the soil for the producers. If the decomposer community is damaged or dies, the whole biogeochemical cycle of an ecosystem is affected. Should this happen on a larger scale, the entire planet would be in peril.
What are the key organisms in the decomposer?
Bacteria are also key organisms at the decomposer level. There are other organisms in nature such as earthworms, some insects, sea cucumbers and woodlice that also break down decaying material, but they need to ingest it first unlike fungi that use chemical and biological processes.
What are the functions of the food chain?
Organisms in this level of the food chain provide nutrients for the producers (plants) who in turn are eaten by the consumers in the next level who are then eaten by tertiary consumers. Fungi release enzymes that break down dead organic matter and release it into the soil while earthworms excrete nutrient-rich waste ...
How Do Decomposers Work?
Often, when an animal dies, a scavenger, such as a vulture or hyena, will consume larger chunks of the body, but while scavengers do break down dead animals, they aren't decomposers, because they're not reducing the animal into chemicals that become part of the soil. Decomposers reduce dead animals, plants, and feces into chemicals such as nitrogen and carbon. Those chemicals become part of the soil and those nutrients can then be used by living plants and the animals that consume them.
What are decomposers responsible for?
They are responsible for eliminating dead and dying organisms, and in the process, they release nutrients into the soil. 4:25. You must c C reate an account to continue watching.
Why are decomposers used in wastewater treatment plants?
Decomposers are being used in some wastewater treatment plants to make the water we have used in our homes clean and ready for human consumption again. Scientists and engineers are using our knowledge of decomposers to develop biodegradable products made of various plant materials that can be broken down by decomposers so that they won't linger in the environment.
What is a decomposer?
A decomposer is a living organism that feeds on dead organisms and as a result, produces soil nutrients. Study the definition and examples of decomposers, how they work, how people use them, and the job categories of living organisms. Updated: 09/23/2021
What are some examples of decomposers?
Decomposers have the job of 'recycling' dead organisms and waste into non-living elements. Examples of decomposers include bacteria, fungi, some insects, and snails, which means they are not always microscopic. Fungi, such as the Winter Fungus, eat dead tree trunks.
What are the parts of dead leaves that are broken down?
In the case of dead leaves, for example, the first decomposers on the scene break down the easy-to-decompose parts of the leaves, such as sugars and amino acids. The structural, tougher parts of the leaves, made of cellulose or lignin, are broken down by decomposers that arrive later. How People Use Decomposers.
What do fungi eat?
Fungi, such as the Winter Fungus, eat dead tree trunks. Decomposers can break down dead things, but they can also feast on decaying flesh while it's still on a living organism. Dung beetles, as you may have accurately concluded from their name, break down feces from other animals.
What Do Decomposers Do?
A decomposer in science is “an organism that feeds on and breaks down dead animal or plant matter” and breaks down the waste of other organisms. This process helps provide organic nutrients for the ecosystem where it lives.
Why are decomposers important?
Decomposers play an important role in food chains and are considered biotic factors in natural ecosystems. Explore examples of decomposers in different ecosystems to better understand what these organisms look and act like.
Why can't you find decomposers in the desert?
You won’t find many decomposers in deserts because they typically like moist areas. Many of the desert decomposers you can find are insects.
What is a grassland decomposer?
Grassland decomposers can sometimes be found in forests or deserts since those are similar environments. Acidobacteria: type of bacteria that thrive in savannas. Termite: insect that breaks down cellulose from dead wood. Turkey tail mushroom: fungus that grows on and feeds on dead logs.
What are the two main types of decomposers?
There are two main kinds of decomposers, scavengers and decom posers. Scavengers find dead plants and animals and eat them. Decomposers break down what’s left of dead matter or organism waste. The different decomposers can be broken down further into three types: fungi, bacteria, and invertebrates.
What is the dead plant and animal that decomposers eat called?
Terrestrial decomposers live on land in all different types of ecosystems. The dead plants and animals they consume are called detritus.
What are some examples of decomposers?
As you can see, certain types of insects and fungi are the most common decomposers in a variety of ecosystems. You can explore more specific species examples to see how different types of beetles or worms, for example, break down dead matter.
How to prepare solution of waste decomposer?
Waste decomposer is the basic material required for preparing a mass multiplication solution of useful microbes. In this article I will discuss both techniques of preparation for large scale farm lands as well as for urban gardens in cities.
What is the role of waste decomposer in farm soil?
Waste decomposer acts as quick decomposer of waste compounds in the soil and has been prepared from cow dung by Krishan Chandra.
How much jaggery to put in plastic bucket?
Fill the plastic bucket with 20 litres of water, add 200 grams jaggery in the bucket and 3 grams of waste decomposer.
How long does manure last?
The shelf life of this manure is three years. Once you have prepared the solution of microbes in your farm or home garden then you can use the same solution to make more manure again and again. Farmers or garden enthusiast doesn’t need to depend on costly fertilizers or pesticides after using this manure.
How to use waste decomposer?
Waste decomposer can be used in the form of bio-pesticides. Dilute the prepared solution with water in 1:3 and apply as a foliar spray to control pest and diseases. It increases soil health and improves fertility of the soil. This prepared solution can be used for seed treatments before sowing.
How long does it take to prepare manure?
In comparison to other manures that takes months to be prepared, you can prepare this solution within a week. Dependency of various types of manures, fertilizers, pesticides, insecticides and fungicides is reduced to zero after using waste decomposer.
How often should I spray a plant with a sanding solution?
Mix 3 parts of this solution in 10 parts of water i.e. 30% solution. You can spray this solution in the form of a spray once after every 7 days on your plants.

Food Chain
Nutrient Cycling
- Decomposers are involved in virtually all of the nutrient cycles on the planet. The plants in the consumer level rely on decomposers to break down dead organic material to release the nutrients and elements like carbon, oxygen and phosphorus back into the soil. This along with energy from the sun powers the process of photosynthesis in plants. When...
Nitrogen Fixation
- Decomposer bacteria are responsible for fixing nitrogen in the soil, meaning they transform nitrogen into a form that can be used by other organisms in the food chain. Specifically, the bacteria take atmospheric nitrogen and turn it into molecules such as ammonia, nitrate and nitrite which can be used by plants. In some plants like legumes, the bacterium Rizobium lives in nodul…
Ecosystem Maintenance
- Decomposers are like the housekeepers of an ecosystem. Without them, dead plants and animals would keep piling up with the nutrients the soil needs trapped inside. Decomposers clean up the dead material by processing it and returning the nutrients to the soil for the producers. If the decomposer community is damaged or dies, the whole biogeochemical cycle of an ecosystem i…