Disadvantages of Electromagnetism
- Electromagnets heat up very fast
- It takes a lot of energy to use
- If cranked up to high it could be dangerous
- There is radiation that comes from electromagnetism, and those types of radiation are showed in the electromagnetic spectrum
What are the disadvantages of electromagnetism?
Disadvantages of Electromagnetism 1 Electromagnets heat up very fast 2 It takes a lot of energy to use 3 If cranked up to high it could be dangerous 4 There is radiation that comes from electromagnetism, and those types of radiation are showed in the electromagnetic... More ...
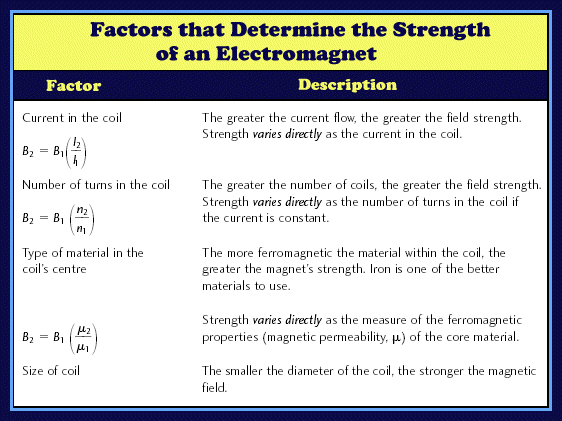
How does current affect the strength of an electromagnet?
Note that if the current changes direction, so does the magnetic field. If an electromagnet consists only of coiled wire (if it has nothing but air in its middle) then the magnet will not be very strong.
What is an electromagnet?
An electromagnet is a type of magnet in which the magnetic field is produced by an electric current. Sus Electromagnets usually consist of wire wound into a coil. A current through the wire creates a magnetic field which is concentrated in the hole, denoting the center of the coil.
What is the maximum strength of magnetic field possible from an electromagnet?
So the maximum strength of the magnetic field possible from an iron core electromagnet is limited to around 1.6 to 2 T. The magnetic field created by an electromagnet is proportional to both the number of turns in the winding, N, and the current in the wire, I, hence this product, NI, in ampere -turns, is given the name magnetomotive force.

What 3 things can make an electromagnet weaker?
Factors that affect the strength of electromagnets are the nature of the core material, strength of the current passing through the core, the number of turns of wire on the core and the shape and size of the core.
What makes an electromagnet weak?
Changing the metal core for a different metal will make the electromagnet stronger or weaker. Iron cores make for very strong fields. Steel cores make weaker fields.
What are the advantages and disadvantages of electromagnets?
AdvantagesDisadvantagesNo power supply neededDirect field onlyCling to vertical surfacesDeteriorate with wearNo electrical contact problemsHave to be pulled from test surfaceInexpensiveNo control over field strength3 more rows
What makes electromagnets stronger and weaker?
Magnetic Field Strength for Electromagnets The number of turns of wire within the coil. The amount of current flowing in the coil. The type of core material.
Do electromagnets lose strength?
In alternating current (AC) electromagnets, used in transformers, inductors, and AC motors and generators, the magnetic field is constantly changing. This causes energy losses in their magnetic cores that is dissipated as heat in the core.
Which of the following would decrease the strength of an electromagnet?
Hence removing iron core would also decrease magnetic field strength.
What's the advantages and disadvantages?
As nouns, the difference between disadvantage and advantage is that disadvantage is a weakness or undesirable characteristic; a con while the advantage is any condition, circumstance, opportunity, or means, particularly favorable to success, or any desired end.
What is the advantage and disadvantage of an electromagnet compared to a permanent magnet?
We can change the strength of the magnetic field of an electromagnet by varying current. We can either increase or decrease its strength. This is not possible in case of permanent magnets. 2.
Are electromagnets expensive?
Compared to permanent magnets, electromagnets can be, size for size, less expensive. The electromagnet is usually cheaper because fewer materials are used to make it. Depending on your needs, an Electromagnet's magnetic strength can be altered for the same design size.
How long does an electromagnet last?
So how long should my permanent magnet last? Your permanent magnet should lose no more than 1% of its magnetic strength over a period of 100 years provided it is specified and cared for properly.
What are the factors affecting the strength of the electromagnet Class 7?
Factors affecting the strength of electromagnetA. the number of turns in the coil.B. the current flowing in the coil.C. the length if air gap between the poles.D. all.
What factors affect magnetic field strength?
Explanation: The answer is "all of these affect the strength of a magnet" The proximity to the object, the size of the object, the material of the object it is sticking to, and the temperature of the object all affect magnetic pull. Magnetism is the force by which objects are attracted to or repelled by other objects.
What factors affect magnetic field strength?
Explanation: The answer is "all of these affect the strength of a magnet" The proximity to the object, the size of the object, the material of the object it is sticking to, and the temperature of the object all affect magnetic pull. Magnetism is the force by which objects are attracted to or repelled by other objects.
On what factors strength of electromagnet depends?
The strength of magnetic field of an electromagnet depends on: The number of turns of wire wound around the coil, and. The amount of current flowing through the wire.
What factors affect the strength of a magnet?
Factors that can affect a magnet's strength include:Heat.Radiation.Strong electrical currents in close proximity to the magnet.Other magnets in close proximity to the magnet.Neo magnets will corrode in high humidity environments unless they have a protective coating.
What factors strength an electromagnet?
The strength of an electromagnet depends on:The strength of the current passing through the coil, the greater the current, the greater the strength. ... The number of turns in the coils, the greater the number of coils, the greater the strength. ... Whether the core is made up of a soft or hard magnetic material.
Why isn't my electromagnet working?
In other words, the electromagnet will not work if something is preventing electric current from flowing from the battery through the wire.
What happens when you turn on an electromagnet?
When turned on, electromagnets act just like permanent magnets, but if you turn them off, their magnetic properties disappear. Electromagnets are an important part of many electronic devices, like motors, loudspeakers, and hard drives. You can create an electromagnet with a simple coil of wire and a battery.
How to unwind a magnet wire?
Rotate the iron bolt to unwind the magnet wire from the spool. Do not pull the wire off the spool and wrap it around the bolt while still holding the bolt; this will cause the wire to get tangled. Use your fingers to keep the wire tight against the bolt, and wrap each successive turn tightly against the previous one. If these instructions are not clear, watch the video to see how to wind the magnet.
How to keep magnet wires from knotting?
Use a paper towel holder to hold the magnet wire spool while winding your magnets, or make an improvised one using a pencil and a cardboard box (Figure 3). This will help you keep your coils neat and prevent knots in the wire.
What is the magnetic field around a wire?
The magnetic field around a straight wire is not very strong. But if the wire is wrapped in a coil, the fields produced in each turn of the coil add up to create a stronger magnetic field. When the coil is wrapped in the shape of a cylinder, it is called a solenoid. When electric current flows through the solenoid, it creates a magnetic field very similar to that of a bar magnet (Figure 1).
What is the purpose of electromagnets?
Electromagnets, or magnets that use the magnetic field created by electrical current flowing through a wire , lie at the heart of many electrical devices, ranging from simple things like doorbells to complex machines like particle accelerators.
How to label magnets with number of turns?
Use masking tape and a pen or fine-point marker to label each magnet with the total number of turns.
What is the advantage of an electromagnet over a permanent magnet?
The main advantage of an electromagnet over a permanent magnet is that the magnetic field can be quickly changed by controlling the amount of electric current in the winding. However, unlike a permanent magnet that needs no power, an electromagnet requires a continuous supply of current to maintain the magnetic field.
How is an electromagnet oriented?
To concentrate the magnetic field, in an electromagnet the wire is wound into a coil with many turns of wire lying side by side.
What is the name of the magnetic field created by a current?
Magnetic field created by a current. The magnetic field created by an electromagnet is proportional to both the number of turns in the winding, N, and the current in the wire, I, hence this product, NI, in ampere -turns, is given the name magnetomotive force.
Why does an electromagnet have a large voltage spike?
An electromagnet has significant inductance, and resists changes in the current through its windings. Any sudden changes in the winding current cause large voltage spikes across the windings. This is because when the current through the magnet is increased, such as when it is turned on, energy from the circuit must be stored in the magnetic field. When it is turned off the energy in the field is returned to the circuit.
How many poles does an electromagnet have?
Each electromagnet has two poles, so the total force on a given magnet due to another magnet is equal to the vector sum of the forces of the other magnet's poles acting on each pole of the given magnet. This model assumes point-like poles instead of the finite surfaces, and thus it only yields a good approximation when the distance between the magnets is much larger than their diameter.
What is the magnetic core made of?
The material of a magnetic core (often made of iron or steel ) is composed of small regions called magnetic domains that act like tiny magnets (see ferromagnetism ). Before the current in the electromagnet is turned on, the domains in the iron core point in random directions, so their tiny magnetic fields cancel each other out, and the iron has no large-scale magnetic field. When a current is passed through the wire wrapped around the iron, its magnetic field penetrates the iron, and causes the domains to turn, aligning parallel to the magnetic field, so their tiny magnetic fields add to the wire's field, creating a large magnetic field that extends into the space around the magnet. The effect of the core is to concentrate the field, and the magnetic field passes through the core more easily than it would pass through air.
What is the effect of current flowing in a wire?
An electric current flowing in a wire creates a magnetic field around the wire, due to Ampere's law (see drawing below). To concentrate the magnetic field, in an electromagnet the wire is wound into a coil with many turns of wire lying side by side.
Why do electromagnets turn on and off?
Because they use an electrical current to produce a magnetic field, electromagnets can be turned on and off. When the electrical current is active, the electromagnet produces a magnetic field. When it’s not active, the electromagnet doesn’t produce a magnetic field. Therefore, electromagnets be used to selectively create a magnetic field ...
What is the core of an electromagnet?
Most electromagnets are designed with a coil of wire wrapped around a core consisting of a ferromagnetic material, such as iron. As electricity flows through the wire, it creates a concentrated magnetic field in the center of the coil.
Why are electromagnets called electromagnets?
They are called “electromagnets” because they rely on an electrical current to produce a magnetic field.
Where do permanent magnets come from?
While permanent magnets occur naturally in Earth’s crust, electromagnets are man-made. The device’s origins can be traced back to 1820 when a Danish scientist named Christian Orsted discovered that by producing an electrical current through a coiled wire, he could produce a magnetic field. Just a few years, William Sturgeon turned Orsted’s idea into a reality by building one of the world’s first electromagnets out of copper wire.
Do you need a power supply for an electromagnet?
When using an electromagnet, though, you’ll need a power supply to provide an electrical current. Some electromagnets are plugged into an electrical outlet, whereas others contain a battery bank. Permanent magnets, on the other hand, don’t require a power source since they are naturally ferromagnetic.
Can you use an electromagnet as a permanent magnet?
The primary advantage of using an electromagnet over a permanent magnet is that you can control its magnetic field. You turn on and off the device’s magnetic field, and with many electromagnets, you can even control the power of the magnetic field. When using an electromagnet, though, you’ll need a power supply to provide an electrical current.
What to use if you didn't purchase the Strength of an Electromagnet kit?
If you did not purchase the Strength of an Electromagnet kit, follow the same steps using a D battery, battery holder, and a nail (Figure 3) .
What are the materials used to make an electromagnet?
Materials used to create an electromagnet include: a straw, a wooden pencil, metal nails of various sizes, alligator clips, paper clips, sandpaper, a spool of copper wire, tape, a D cell battery, a battery holder and scissors.
How to make a field stronger?
You can make the field even stronger by wrapping the wire around a ferromagnetic core, like a nail. A solenoid with a ferromagnetic core is commonly called an electromagnet. Unlike a permanent magnet, an electromagnet can be turned on and off using electrical current.
What is the magnet in the video?
Explain that the magnet in the video is an electromagnet . An electromagnet is a magnet that can be turned on and off using electrical current. This allows you to pick things up and then turn the magnet off to drop them, like the crane in the video. Demonstrate the electromagnet you made in the Prep Work section.
How to turn off a magnet?
You turned the magnet on by connecting both alligator clips to the battery. This allows electrical current to flow. You turned the magnet off by disconnecting at least one of the alligator clips, which stops current from flowing. (Note: you can connect this to open and closed circuits if you have previously covered those topics in your classroom.)
How to increase the current of a magnet?
The amount of current can be increased by using multiple batteries or thicker wire (see variations—you will need to purchase additional materials to test this). Core material. Ferromagnetic materials (iron, steel) make the magnet much stronger than non-ferromagnetic materials like paper, wood, or air.
Do variables affect the strength of an electromagnet?
Many variables affect the strength of this electromagnet, and there are some variables that do not affect the strength. While the underlying physics are more advanced (see Additional Background section), middle school students can still do an experiment to identify the relationships between these variables and the strength of the electromagnet. Table 1 provides a summary of some variables and how they do or do not affect the strength of the magnet, but this list is not exhaustive.
What are the factors that affect the magnetic field of an electromagnet?
Factors Affecting the Strength of the Magnetic Field of an Electromagnet: Factors that affect the strength of electromagnets are the nature of the core material, strength of the current passing through the core, the number of turns of wire on the core and the shape and size of the core.
What is the strength of the magnetic field produced by the solenoid?
Operational Definition: The strength of the magnetic field produced by the solenoid is operationally defined as the number of pins that can be attracted to one end of the core. Materials: A box of pins, insulated copper wire, 10 cm long iron rod, 10 cm long wooden rod, connecting wires.
What is the theory that the greater the number of turns, the stronger the magnetic field?
Hypothesis : The larger the number of turns, the stronger the magnetic field. Operational Definition: The strength of the magnetic field produced by the solenoid is operationally defined as the number of pins that can be attracted to one end of the core.
Which is more attracted by the coil with the soft iron rod or the wooden rod?
The number of pins attracted by the coil with the soft iron rod is significantly more than the coil with the wooden rod.
How does the polarity of a solenoid change?
The polarity at the ends of the solenoid is changed by changing the direction of the current , as shown in Figure. The direction of the magnetic field at any point can be shown by a plotting compass.
How many turns of wire round the soft iron rod?
The apparatus is set up as shown in Figure, with 20 turns of wire round the soft iron rod.
Do electric devices use strong magnetic fields?
Problem: Some electric devices make use of very strong electromagnets while others need electromagnets that produce weaker magnetic fields. What are the factors that affect the strength of the magnetic field of an electromagnet?
What are genshin impact elements weak to?
Genshin Impact Elements Weakness Guide — What Elements Are Weak To Others. First things first: elements in Genshin Impact don't function quite like the type-effectiveness you might expect to see in Pokemon or Persona. As opposed to having strict rules for which type trumps what, Genshin Impact's elements are arranged in a more reactive way.
What is electro overload?
Electro: Overload — Triggers an elemental explosion. The damage is Pyro-based, as opposed to Electro, which may come as a surprise.

Objective
Introduction
- Electromagnets, or magnets that use the magnetic field created by electrical current flowing through a wire, lie at the heart of many electrical devices, ranging from simple things like doorbells to complex machines like particle accelerators. The strength of electromagnets varies, but some electromagnets are strong enough to lift entire trains! So how does an electromagnet …
Materials and Equipment
- Strength of an Electromagnet Kit, available from our partner Home Science Tools. Includes:
- You will also need to gather these items, not included in the kit:
Contact Us
- What is your Science Buddies kit order number?
- Please describe how you need help as thoroughly as possible: Examples Good Question I'm trying to do Experimental Procedure step #5, "Scrape the insulation from the wire. . ." How do I know when I'...
Related Links
Overview
An electromagnet is a type of magnet in which the magnetic field is produced by an electric current. Electromagnets usually consist of wire wound into a coil. A current through the wire creates a magnetic field which is concentrated in the hole, denoting the center of the coil. The magnetic field disappears when the current is turned off. The wire turns are often wound around a magnetic core made from a ferromagnetic or ferrimagnetic material such as iron; the magnetic core concent…
History
Danish scientist Hans Christian Ørsted discovered in 1820 that electric currents create magnetic fields. British scientist William Sturgeon invented the electromagnet in 1824. His first electromagnet was a horseshoe-shaped piece of iron that was wrapped with about 18 turns of bare copper wire (insulated wire didn't exist yet). The iron was varnished to insulate it from the windings. When a current was passed through the coil, the iron became magnetized and attracte…
Applications of electromagnets
A portative electromagnet is one designed to just hold material in place; an example is a lifting magnet. A tractive electromagnet applies a force and moves something.
Electromagnets are very widely used in electric and electromechanical devices, including:
• Motors and generators
• Transformers
Simple solenoid
A common tractive electromagnet is a uniformly-wound solenoid and plunger. The solenoid is a coil of wire, and the plunger is made of a material such as soft iron. Applying a current to the solenoid applies a force to the plunger and may make it move. The plunger stops moving when the forces upon it are balanced. For example, the forces are balanced when the plunger is centered in the solenoid.
Physics
An electric current flowing in a wire creates a magnetic field around the wire, due to Ampere's law (see drawing below). To concentrate the magnetic field, in an electromagnet the wire is wound into a coil with many turns of wire lying side by side. The magnetic field of all the turns of wire passes through the center of the coil, creating a strong magnetic field there. A coil forming the shape of a straight tube (a helix) is called a solenoid.
Side effects
There are several side effects which occur in electromagnets which must be provided for in their design. These generally become more significant in larger electromagnets.
The only power consumed in a DC electromagnet under steady state conditions is due to the resistance of the windings, and is dissipated as heat. Some large electromagnets require water cooling systems in the windings to carry off the waste heat.
High-field electromagnets
When a magnetic field higher than the ferromagnetic limit of 1.6 T is needed, superconducting electromagnets can be used. Instead of using ferromagnetic materials, these use superconducting windings cooled with liquid helium, which conduct current without electrical resistance. These allow enormous currents to flow, which generate intense magnetic fields. Superconducting magnets are limited by the field strength at which the winding material ceases to be supercondu…
See also
• Dipole magnet – the most basic form of magnet
• Electromagnetism
• Electropermanent magnet - a magnetically hard electromagnet arrangement
• Explosively pumped flux compression generator