What are the functions of lysosome?
Lysosomes function as the digestive system of the cell, serving both to degrade material taken up from outside the cell and to digest obsolete components of the cell itself.
What are 3 facts about lysosomes?
A lysosome is a membrane-bound cell organelle that contains digestive enzymes. Lysosomes are involved with various cell processes. They break down excess or worn-out cell parts. They may be used to destroy invading viruses and bacteria.
What is the function of the lysosome quizlet?
A lysosome has three main functions: the breakdown/digestion of macromolecules (carbohydrates, lipids, proteins, and nucleic acids), cell membrane repairs, and responses against foreign substances such as bacteria, viruses and other antigens.
What is the function of a lysosome in an animal cell kids?
Lysosomes are organelles that contain digestive enzymes which are used to: Breakdown old and worn-out cells. Destroy invading pathogens such as bacteria and viruses.
How many lysosomes are in a cell?
There are 50 to 1,000 lysosomes per mammalian cell, but a single large or multilobed lysosome called the vacuole in fungi and plants.
Where are lysosomes found?
lysosome, subcellular organelle that is found in nearly all types of eukaryotic cells (cells with a clearly defined nucleus) and that is responsible for the digestion of macromolecules, old cell parts, and microorganisms.
Who discovered lysosomes?
Christian de DuveChristian de Duve, whose laboratory in Louvain discovered lysosomes in 1955 and defined peroxisomes in 1965, died at his home in Nethen, Belgium at the age of 95, on May 4, 2013.
What are the characteristics of lysosomes?
“Lysosomes are sphere-shaped sacs filled with hydrolytic enzymes that have the capability to break down many types of biomolecules.” In other words, lysosomes are membranous organelles whose specific function is to breakdown cellular wastes and debris by engulfing it with hydrolytic enzymes.
Define Lysosome.
Lysosomes are defined as sphere-shaped vesicles or sacs filled with hydrolytic enzymes that have the ability to break down almost all types of biom...
Who discovered Lysosomes?
Lysosomes were discovered by a Belgian biologist, Christian de Duve, and was awarded a Nobel Prize in Medicine or Physiology in the year 1974. He i...
What type of cells possesses lysosomes?
Only eukaryotic animal cells contain lysosomes. Prokaryotic cells, such as bacteria do not contain lysosomes or any of the other membrane-bound org...
Do plants cells have lysosomes?
Plants do not possess lysosomes; however, the role of lysosomes are undertaken by the vacuoles. Findings even suggest that vacuoles contain hydrol...
What is a lumen in a lysosome?
Lumen is the area within the membrane-bound exterior of the lysosome. It contains cellular debris suspended in hydrolytic enzymes. It is also acidi...
Why are Lysosomes known as Suicidal Bags?
The main function of lysosomes is to breakdown and recycle cellular debris, discarded cellular contents and foreign pathogens, however, the digesti...
Where are the enzymes needed by lysosomes made?
The enzymes are synthesized in the rough endoplasmic reticulum and once synthesized; the enzymes are brought in from the Golgi apparatus in tiny ve...
What are lysosomal storage diseases?
Any mutations that occur in the nuclear genes may result in over 30 diverse human genetic ailments. These ailments are collectively called lysosoma...
How do lysosomes help with disease?
When foreign pathogens such as bacteria enter a cell, the lysosomes can help neutralize them by digesting them. In this way they help with an organism's immune response.
What is the structure of lysosomes?
The Structure of Lysosomes. Lysosomes are round membrane-bound organelles with a single outer lysosomal membrane. The membrane is impervious to the acidic contents of the lysosome. This protects the rest of the cell from the digestive enzymes inside the membrane.
Why Are Lysosomes Acidic?
The acidic nature of the fluid inside the lysosome serves two purposes.
What happens if a lysosome leaks?
Should the lysosome rupture or leak, the acidic fluid is rapidly neutralized, and the lysosomal enzymes and other digesting chemicals will no longer be effective and will not attack healthy cell structures. Maintaining the acidic pH inside the lysosome is therefore critical for its function and for cell protection.
How does the lysosome maintain pH?
The lysosome accomplishes this by using chemical reactions with proton pumps on its surface and inside the membrane to transfer hydrogen ions or protons across the membrane and into the interior.
What is a lysosome?
Lysosomes are like small cell stomachs: they digest waste and superfluous cell fragments.
What breaks down large structures and molecules into simple components?
The digestive enzymes of their acidic interior break down large structures and molecules into simple components, and they then return the products to the cell for further use or disposal.
How do the Lysosome function?
The key function of lysosomes is digestion and removal of waste. Cellular debris or foreign particles are pulled in to the cell through the process of endocytosis. The process of endocytosis happens when the cell membrane falls in on itself (invagination), creating a vacuole or a pouch around the external contents and then bringing those contents into the cell.
How do lysosomes work?
As stated before, lysosomes work as the waste discarding structures of the cell by processing undesirable materials and degrading them, both from the exterior of the cell and waste constituents inside the cell.
Where are Lysosomal Enzymes made?
Lysosomes comprise of over 50 different enzymes. They are synthesized in the rough endoplasmic reticulum.
What causes a cell to die?
But sometimes, the digestive enzymes may end up damaging the lysosomes themselves, and this can cause the cell to die. This is termed as autolysis, where “ auto ” means “ self ” and “ lysis ” means “ the disintegration of the cell by the destruction of its cell membrane “. Hence, lysosomes are known as “Suicidal Bags” of the cell.
What is the process of removing waste from the cell?
On the other hand, discarded wastes and other substances originating from within the cell is digested by the process of autophagocytosis or autophagy. The process of autophagy involves disassembly or degradation of the cellular components through a natural, regulated mechanism.
How big are lysosomes?
The sizes of lysosomes vary, with the largest ones measuring in more at than 1.2 μm.
Where are lysosomes found?
Lysosomes are predominantly found in eukaryotic animal cells and are responsible for breaking down cellular debris. In plants, the role of lysosomes is undertaken by the vacuoles as traditional cell biology dictates.
What are the functions of lysosomes?
Some of the main functions of Lysosomes are as follows: 1. Intracellular digestion: The word lysosome is derived from (lyso lytic or digestive; and soma body) thus helping in digestion. Pinocytic vacuoles formed as a result of absorption of fluid substance into cell or phagocytic vacuoles formed by absorption of solid particles into cell, ...
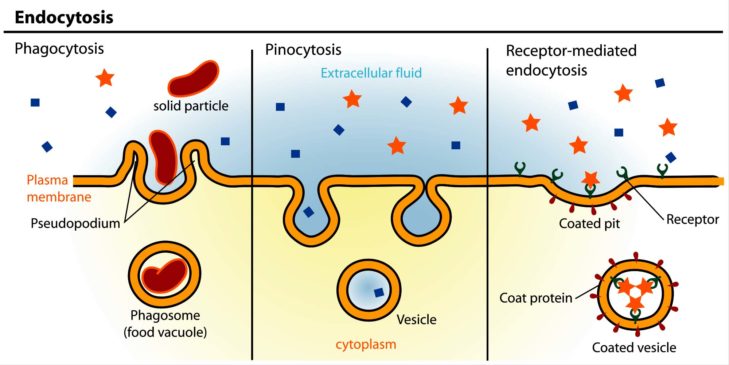
What happens to the plasma membrane during endocytosis?
In endocytosis contraction of microfilaments of actin and myosin present in the peripheral cytoplasm occurs. It causes plasma membrane to invaginate and form the endocytic vacuole. Ingested particles enclosed in membranes derived from the plasma membrane and forming vacuoles are sometimes celled phagosomes. After the entrance of a particle ...
What happens after endocytosis?
Within this vacuole the lysosomal enzymes begin the process of digestion of the foreign material.
What is the function of mitochondria in the ER?
The digestion of mitochondria or other cell structures, such as elements of ER, provides a source of energy for these cells. After the digestion of cell structure, the autophagic vacuoles may become residual bodies.
What is the mechanism of phagocytosis?
Phagocytosis and pinocytosis are active mechanisms in which cell requires energy for their operation. During phagocytosis by leucocytes oxygen consumption, glucose uptake and glycogen breakdown all increase significantly.
Where does the digestion of proteins end?
Digestion of proteins usually ends at the level of dipeptide, which can pass through the membrane and be further digested into amino acids.
Which organelle is surrounded by smooth endoplasmic reticulum?
Cytoplasmic organelles become surrounded by membranes of smooth endoplasmic reticulum, forming vacuoles, then lysosomal enzymes are discharged into autophagic vacuoles and the organelles are digested. Autophagy is a general property of eukaryotic cells.
What are the two parts of a lysosome?
Each lysosome consists of mainly two parts- a limiting membrane and an inner dense mass or matrix.
Where do lysosomes occur?
Lysosomes occur mainly in most animal and few plant cells (e.g.-Onion seeds, Barley seeds, Corn seedlings, Yeast, and Neurospora). They are absent in bacteria and mature mammalian erythrocytes. Leukocytes, especially granulocytes are rich in lysosomes. Few lysosomes occur in muscle cells or in acinar cells of the pancreas.
What are the substances that cause instability of the lysosomal membrane?
Significantly in the presence of certain substances (Vitamin A, Vitamin B, Vitamin K, Progesterone, Testosterone, etc.) called labializes, cause instability of the lysosomal membrane. Other substances (cholesterol, cortisol, phenothiazine, etc.) called stabilizers, help to maintain the stability of the membrane.
How big are lysosomes?
Morphologically they can be compared with Amoeba and white blood cells (W.B.C.). Lysosomes are normally 0.2 to 0.5 um in size. Since the size and shape of lysosomes vary from cell to cell and time to time (polymorphic nature), their identification becomes difficult.
Is the lysosomal membrane semi-permeable?
The lysosomal membrane functions as a semi-permeable membrane (the lysosomal membrane is impermeable to the substrate of the enzymes contained in the lysosome). As a result, the substrate of the lysosomal enzymes (the enzymes present in the lysosome) cannot enter the lysosome.
