Three Types of RNA | mRNA tRNA & rRNA
- Messenger RNA (mRNA)
- Transfer RNA (tRNA)
- Ribosomal RNA (rRNA)
What are two kinds of RNA and their jobs?
RNA Types. There are various types of RNA, out which most well-known and most commonly studied in the human body are : tRNA – Transfer RNA; The transfer RNA is held responsible for choosing the correct protein or the amino acids required by the body in-turn helping the ribosomes. It is located at the endpoints of each amino acid.
What three things are RNA composed of?
What 3 things is RNA made of? RNA consists of ribose nucleotides (nitrogenous bases appended to a ribose sugar) attached by phosphodiester bonds, forming strands of varying lengths. The nitrogenous bases in RNA are adenine, guanine, cytosine, and uracil, which replaces thymine in DNA.
What are the functions of each type of the RNA?
structural and functional components of the ribosome mRNA (messenger RNA) carries genetic code for proteins tRNA (transfer RNA) helps incorporate amino acids into polypepetide chain snRNA (Small Nuclear RNA) processing of pre-mRNA snoRNA (Small nucleolar RNA) processing and assembly of rRNA miRNA (microRNA) inhibits translation of mRNA
What are three ways that DNA are different from RNA?
RNA is different from DNA is three ways: (1) the sugar in RNA is ribose not dioxyribose; (2) RNA is generally single-stranded and not double-stranded; and (3) RNA contains uracil in place of thymine. DNA is the "master plan." RNA is the "disposable copy" or blueprint.

What are the 3 types of RNA and what does each one do?
There are three types of RNA: mRNA, tRNA, and rRNA. mRNA is the intermediary between the nucleus, where the DNA lives, and the cytoplasm, where proteins are made. rRNA and tRNA are involved in protein synthesis. Additional RNAs are involved in gene regulation and mRNA degradation.
Where are the 3 types of RNA made?
Three RNAsmessenger RNA (mRNA) carries the instructions from the nucleus to the cytoplasm. mRNA is produced in the nucleus, as are all RNAs.The other two forms of RNA, ribosomal RNA (rRNA) and transfer RNA (tRNA), are involved in the process of ordering the amino acid to make the protein.
What are types of RNA?
In both prokaryotes and eukaryotes, there are three main types of RNA – messenger RNA (mRNA), ribosomal RNA (rRNA), and transfer RNA (tRNA).
What is mRNA tRNA and rRNA and their functions?
Messenger RNA (mRNA) molecules carry the coding sequences for protein synthesis and are called transcripts; ribosomal RNA (rRNA) molecules form the core of a cell's ribosomes (the structures in which protein synthesis takes place); and transfer RNA (tRNA) molecules carry amino acids to the ribosomes during protein ...
Where is RNA produced?
It is produced in the nucleus, before moving out into the cytoplasm to bind with proteins and form a ribosome.
Where does the transcription take place?
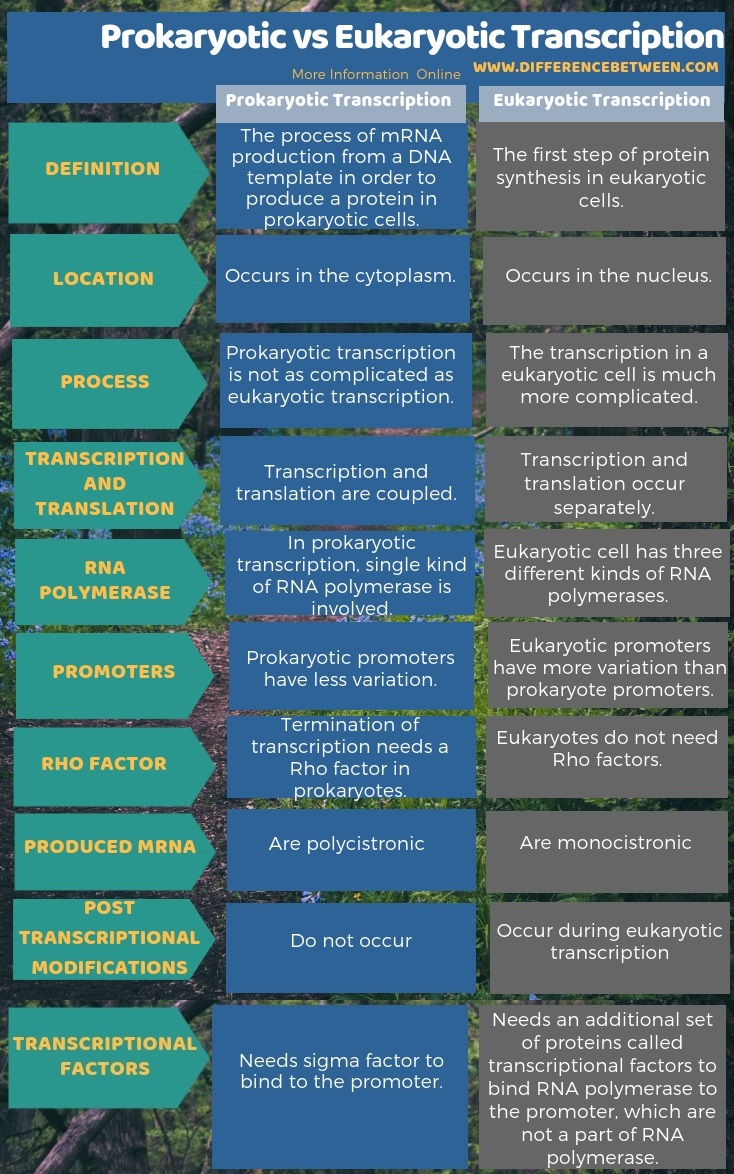
nucleusThe process of Transcription takes place in the cytoplasm in prokaryotes and in nucleus in eukaryotes. It uses DNA as a template to make an RNA (mRNA) molecule. During transcription, a strand of mRNA is made that is complementary to a strand of DNA .
Where is RNA found?
DNA vs. RNA – 5 Key Differences and ComparisonComparisonDNARNALocationDNA is found in the nucleus, with a small amount of DNA also present in mitochondria.RNA forms in the nucleolus, and then moves to specialised regions of the cytoplasm depending on the type of RNA formed.9 more rows
Where in the cell does transcription take place?
With the genes bound in the nucleus, transcription occurs in the nucleus of the cell and the mRNA transcript must be transported to the cytoplasm. The prokaryotes, which include bacteria and archaea, lack membrane-bound nuclei and other organelles, and transcription occurs in the cytoplasm of the cell.
What are the different types of RNA?
The types of RNA are: 1. Transfer RNA (tRNA) 2. Messenger RNA (mRNA) and 3. Ribosomal RNA (rRNA). RNA Type # 1. Transfer RNA (tRNA): It delivers amino acids to ribosome and decodes the information of mRNA. Each nucleotide triplet codon on mRNA represents an amino acid. The tRNA plays the role of an adaptor and matches each codon to its particular ...
How many base pairs does a tRNA have?
It has a seven base pairs stem formed by base pairing between 5′ and 3′ ends of tRNA. At 3′ end a sequence of 5′-CCA-3′ is added. This is called CCA arm or amino acid acceptor arm. Amino acid binds to this arm during protein synthesis.
What is the name of the tRNA that is charged with an amino acid?
The tRNA charged with an amino acid is called amino acyl tRNA.
What are the properties of tRNA?
The tRNA has two properties: ADVERTISEMENTS: (a) It represents a single amino acid to which it binds covalently. (b) It has two sites. One is a trinucleotide sequence called anticodon, which is complementary to the codon of mRNA. The codon and anticodon form base pairs with each other.
Why is tRNA a secondary structure?
The tRNA due to its property of having stretches of complementary base pairs forms secondary structure, which is in the form of a cloverleaf. Several regions of the single stranded molecule form double stranded stems or arms and single stranded loops due to folding of various regions of the molecule.
What is the tertiary structure of tRNA?
X-ray crystallographic analysis of tRNA shows three dimensional structure called tertiary structure. The molecule is folded and has two helical double stranded branches. One branch consists of acceptor arm and T ψ C arm. The other arm consists of DHU loop and anticodon arm with loop.
Where are RNA-RNA base pairs formed?
These snRNP molecules contain small RNA sequences which are complementary to the introns of mRNA and form RNA-RNA base pairs at 5′ and 3′ splice sites where actual splice reaction occurs.
What are the different types of RNA?
Types of RNA: mRNA, rRNA and tRNA. RNA or ribonucleic acid is a polymer of nucleotides that is made up of a ribose sugar, a phosphate, and bases such as adenine, guanine, cytosine, and uracil. It plays a crucial role in gene expression by acting as the intermediate between the genetic information encoded by DNA and proteins.
What is the most heterogeneous type of RNA?
Messenger RNA (mRNA) mRNA accounts for just 5% of the total RNA in the cell. mRNA is the most heterogeneous of the 3 types of RNA in terms of both base sequence and size. It carries complementary genetic code copied, from DNA during transcription, in the form of triplets of nucleotides called codons. Each codon specifies a particular amino acid, ...
What is the ribozyme that is involved in generating tRNA molecules from larger precursor RNAs?
One of the first ribozymes to be discovered was RNase P , a ribonuclease that is involved in generating tRNA molecules from larger, precursor RNAs. RNase P is composed of both RNA and protein; however, the RNA moiety alone is the catalyst.
What is the role of RNA in protein synthesis?
Beyond the primary role of RNA in protein synthesis, several varieties of RNA exist that are involved in post-transcriptional modification, DNA replication, and gene regulation. Some forms of RNA are only found in particular forms of life, such as in eukaryotes or bacteria.
What is the smallest RNA?
tRNA is the smallest of the 3 types of RNA, possessing around 75-95 nucleotides. tRNAs are an essential component of translation, where their main function is the transfer of amino acids during protein synthesis. Therefore, they are called transfer RNAs.
How is siRNA produced?
siRNA (20-25 nt) are often produced by breakdown of viral RNA, though there are also endogenous sources of siRNAs. They act similarly to miRNA. An mRNA may contain regulatory elements itself, such as riboswitches, in the 5' untranslated region or 3' untranslated region; these cis-regulatory elements regulate the activity of that mRNA.
Where is RNA found in the cell?
Ribosomal RNA (rRNA) rRNAs are found in the ribosomes and account for 80% of the total RNA present in the cell. Ribosomes are composed of a large subunit called the 50S and a small subunit called the 30S, each of which is made up of its own specific rRNA molecules. Different rRNAs present in the ribosomes include small rRNAs and large rRNAs, ...
How many nucleotides are in the small subunit of RNA?
The small subunit is made up of two short rRNA molecules that are less than 200 nucleotides in length (5S and 5.8S), and the large subunit which is made up of two large molecules that are longer, one which has over 5kb (28S) and a second one with 2kilobases (18S).
Where is RNA synthesized?
The rRNA is synthesized or transcribed in the cell nucleus, specifically in the nucleoli. The nucleoli play a major role in the biogenesis of ribosomes via the sequestration of ribosomal proteins.
What is the function of RNA polymerase?
RNA polymerase synthesizes RNA from DNA that is functionally for protein-coding (messenger RNA, mRNA) or non-coding (RNA genes). Because of these functions, RNA molecules are of following types: messenger RNA (mRNA) – It is the RNA that carries information from DNA to the ribosomes (site of protein synthesis) in the cell.
How many nucleotides are in ribosomal proteins?
The small subunit along with ribosomal proteins has a sedimentation rate of the 30S. This is paired with the larger subunit, having two RNA molecules – one that is nearly 3000 nucleotides (23S) in length and the other is a short sequence of 120 nucleotides (5S).
What type of mRNA is found in RBCs?
Some types of mRNA are specific for certain types of cells, which encode for the proteins that are needed for the function of that particular cell such as mRNA for hemoglobin is found in Red Blood Cells (RBCs). Figure: Prokaryotic and Eukaryotic Messenger RNA (mRNA). Image Source: ScienceDirect.
What is the mRNA code used for?
transfer RNA (tRNA) – It is used to transfer specific amino acids to growing polypeptide chains at the ribosomal site of protein synthesis during translation.
How many nucleotides are in a prokaryotic subunit?
The small subunits of the prokaryotes are made of an RNA molecule of about 1500 nucleotides in length with a Svedberg coefficient of 16S.
What are the three main types of RNA?
There are three main types of RNA, messenger, mRNA, transfer, tRNA, and ribosomal, rRNA. Each one plays a different role in the synthesis of proteins. mRNA is first transcribed from DNA by complementary base pairing in the nucleus of eucaryotic cells. With adenine binding to thymine, guanine binding to cytosine, and uracil binding to adenine.
What is the tRNA molecule?
Here, a tRNA molecule, with a three nucleotide anticodon sequence on one side and a specific amino acid on the other, binds to a complementary codon in the mRNA. The ribosome travels down the mRNA and the correct tRNAs are added sequentially.
What is the role of riboswitches in RNA?
Regulatory sequences in mRNA—called riboswitches—act as environmental sensors by detecting changes in temperature and nutrient levels. Riboswitch-based regulation depends on the formation of two mutually exclusive and stable conformations of the RNA secondary structure.
What is messenger RNA?
Messenger RNA (mRNA) is the protein-coding RNA. It consists of codons—sequences of three nucleotides that encode a specific amino acid. Transfer RNA (tRNA) and ribosomal RNA (rRNA) are non-coding RNA. tRNA acts as an adaptor molecule that reads the mRNA sequence and places amino acids in the correct order in the growing polypeptide chain.
What is the function of RNA in protein synthesis?
RNA Performs Diverse but Cooperative Functions During Protein Synthesis. The central dogma of molecular biology states that DNA contains the information that encodes proteins and RNA uses this information to direct protein synthesis. Different types of RNA are involved in protein synthesis.
What are the functions of ribosomes in translation?
During translation, ribosomes move along an mRNA strand where they stabilize the binding of tRNA molecules and catalyze the formation of peptide bonds between amino acids. Thus, different types of RNA perform specific but complementary functions during protein synthesis.
What is RNA in school?
This mRNA is then translated into a protein. It serves as the genetic template of a protein since the DNA can’t leave the nucleus.
Why is mRNA called mRNA?
Let’s start with mRNA or messenger RNA, so named because it acts as the messenger between the genes in DNA and protein production on ribosomes. And if you want to know the differences between RNA and DNA, I have a great video for that .
What is the role of tRNA in genetics?
RNA is generally single stranded, but tRNA actually folds back onto itself to form a distinct “t” shape. Without going to deep, transfer RNA is responsible for bringing amino acids together during translation to form the growing peptide chain that will become a protein.
What is the main component of ribosomes?
Last but not least is rRNA or Ribosomal RNA . This RNA is a main component of ribosomes, which I have discussed in a previous video on ribosomes. rRNA combines with special proteins to form ribosomes which then “read” mRNA to form proteins. There was a lot in that sentence, so feel free to go back and read it again if you need to. But essentially, ribosomes contain rRNA and help build proteins.
