What is the anatomy of the tubal tonsils?
The tubal tonsils refer to lymphoid tissue around the opening of the Eustachian tube in the lateral wall of the nasopharynx. They form the lateral aspect of the Waldeyer’s ring. The epithelial covering of the tubal tonsils is ciliated pseudostratified epithelium. The neurovascular supply is similar to other structures in the nasopharynx.
What is the medical term for tonsils?
Anatomical terminology. [edit on Wikidata] The tonsils are a set of lymphoid organs facing into the aerodigestive tract, which is known as Waldeyer's tonsillar ring and includes the adenoid tonsil, two tubal tonsils, two palatine tonsils, and the lingual tonsils.
What are the tonsils of the torus tubaris called?
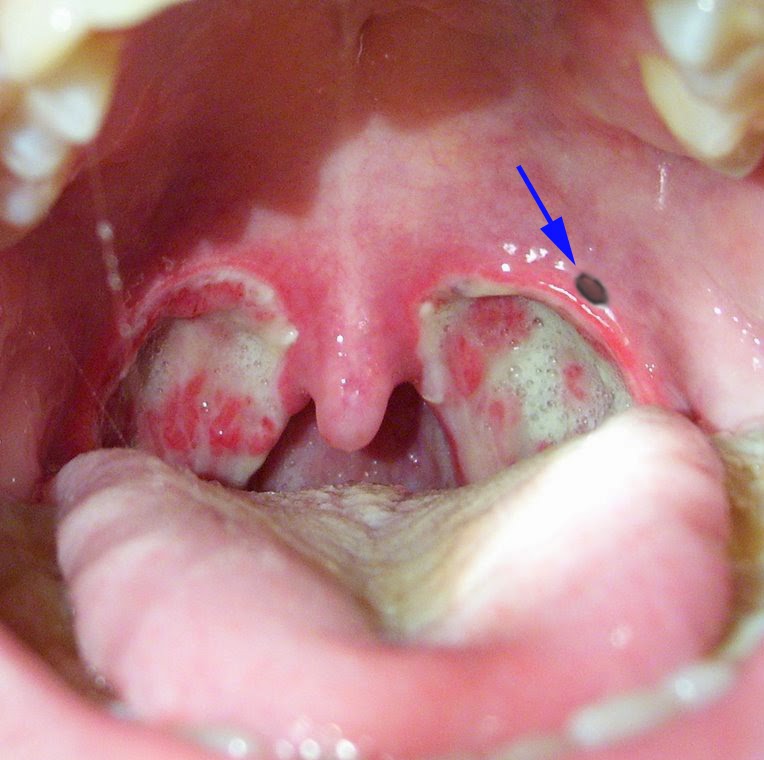
Tubal Tonsils (Gerlach’s Tonsils) The tubal tonsils are also located in the roof of the nasopharynx. They are bilateral and posterior to the torus tubaris, in the fossa of Rosenmüller (pharyngeal recess). Due to the relative closeness of the tubal tonsils to the torus tubaris, it is sometimes referred to as “the tonsils of the torus tubaris”.
What are tonsils made of?
[edit on Wikidata] Tonsils are collections of lymphoid tissue facing into the aerodigestive tract. The set of lymphatic tissue known as Waldeyer's tonsillar ring includes the adenoid tonsil, two tubal tonsils, two palatine tonsils, and the lingual tonsil.

What is the function of the tubal tonsils?
The current findings suggest that the tubal tonsils possess abilities of active transportation of foreign antigens, and will act as inductive and effector sites in the mucosal immune system.
Where is tubal tonsils located?
nasopharynxEach tubal tonsil is located posterior to the opening of the Eustachian tube on the lateral wall of the nasopharynx. It is one of the four main tonsil groups forming Waldeyer's tonsillar ring. This ring also includes the palatine tonsils, the lingual tonsils, and the adenoid.
How many tubal tonsils do we have?
two tubal tonsilsHumans are born with four types of tonsils: the pharyngeal tonsil, two tubal tonsils, two palatine tonsils and the lingual tonsils.
What are the 4 types of tonsils?
Tonsils are fleshy masses of lymphatic tissue found in the throat, or pharynx. There are four different types of tonsils: palatine, pharyngeal (commonly referred to as the adenoid), lingual and tubal. Together these four types of tonsils make up what is called Waldeyer's ring.
Can you see tubal tonsils?
They are found beneath the mucosa of the eustachian tube and the torus tubarius and within Rosenmüller fossa. The tubal tonsils are often not seen as a distinct entity on nasopharyngeal examination until after the adenoid has been removed.
Which tonsils are removed in a tonsillectomy?
There are several types of tonsils. The palatine tonsils are removed in a tonsillectomy. Palatine tonsils are collections of lymph tissue on the right and left side of the upper throat (also called the oropharynx). Tonsils are largest in 3-6 year olds and smallest in teen and adult years.
Why do people get their tonsils removed?
There are two main reasons it may be time to undergo a tonsillectomy (removal of the tonsils): You have chronic sleep apnea or snoring that disrupts your sleep. You experience recurrent tonsillitis (inflammation of the tonsils) caused by strep throat or other infections.
Can your tonsils grow back?
It is possible for tonsils to partially grow back. During a tonsillectomy, most of the tonsils are removed. However, some tissue often remains, so tonsils occasionally can regenerate (regrow) — although they probably won't grow back completely or to their original size.
Do you need your tonsils?
Tonsils are an essential part of the immune system, preventing germs from entering the mouth or nose. The tonsils typically shrink with age; but for some people, this does not happen. As a result, the tonsils can become overwhelmed and infected.
Is a tonsil a lymph node?
Causes. The tonsils are lymph nodes in the back of the mouth and top of the throat. They help to filter out bacteria and other germs to prevent infection in the body.
What's another name for tonsils?
The palatine (or faucial) tonsils, commonly referred to as tonsils, are bundles of lymphatic tissue located in the lateral oropharynx.
How are tonsils removed?
The surgeon may cut out the tonsils using a blade (scalpel) or a specialized surgical tool that uses heat or high-energy heat or sound waves to remove or destroy tissues and stop bleeding.
Where are tonsils and adenoids located?
The tonsils (located in the back of the throat) and adenoids (high in the throat, behind the nose and soft palate) work together to protect the body from illness – but sometimes fall prey themselves.
What are the signs and symptoms of tonsillitis?
Tonsillitisa sore throat.problems swallowing.a high temperature of 38C or above.coughing.a headache.feeling sick.earache.feeling tired.
Does tonsillitis go away on its own?
Tonsillitis usually improves on its own after around a week. It's most often caused by a virus, so antibiotics won't help. Even if it's a bacterial infection, it will often settle without antibiotics. You can ease your symptoms with self-help measures and over-the-counter medicines.
How many types of tonsils are there?
Technically, there are three sets of tonsils in the body: the pharyngeal tonsils, commonly known as adenoids, the palatine tonsils and the lingual tonsils, which are lymphatic tissue on the surface tissue of the base of the tongue, according to Encyclopedia Britannica.
What is the tubal tonsil?
The tubal tonsil (tonsilla tubaria) is a paired, aggregate of lymphoid tissue in the form of an interrupted plate in the thickness of the mucous membrane of the tube roller, in the region of the pharyngeal opening and the cartilaginous part of the auditory tube. The amygdala consists of diffuse lymphoid tissue and a few lymphoid nodules. The mucous membrane above the amygdala is covered with ciliated (multicellular ciliated) epithelium. Pipe tonsil is fairly well expressed in a newborn (its length is 7.0-7.5 mm), and its greatest development reaches 4-7 years. Children on the surface of the mucous membrane in the area of the tubal tonsil are seen small tubercles, under which there are accumulations of lymphoid tissue - lymphoid nodules. Lymphoid nodules and breeding centers in them appear on the 1st year of the child's life. The age-old involution of the tubal tonsil begins in adolescence and adolescence.
When does the tubal tonsil develop?
The development of the tubal tonsil begins at the 7-8th month of the fetal life in the thickness of the mucous membrane around the pharyngeal opening of the auditory tube. First, separate clusters of the future lymphoid tissue appear, from which the tubular tonsil forms later.
Where does blood flow to the tubal amygdala?
Blood to the tubal amygdala flows along the branches of the ascending pharyngeal artery. Venous blood from the amygdala flows into the veins of the pharyngeal plexus. Nerve fibers come in the composition of the branches of the facial, glossopharyngeal and vagus nerves, as well as from the periarterial sympathetic plexuses.
What is the tubal tonsil?
The tubal tonsils refer to lymphoid tissue around the opening of the Eustachian tube in the lateral wall of the nasopharynx. They form the lateral aspect of the Waldeyer’s ring. The epithelial covering of the tubal tonsils is ciliated pseudostratified epithelium.
What is the lingual tonsil covered by?
Like the rest of the tongue, the lingual tonsil is covered by a stratified non-keratinised squamous epithelium.
How to treat tonsillitis?
A complication of bacterial tonsillitis is a peritonsillar abscess (quinsy); a collection pus in the peritonsillar space. All quinsies will require drainage. There are two techniques adopted for this: 1 Needle aspiration following topical local anaesthetic. 2 Incision and drainage, with further opening via use of Magill forceps.
What is the role of palatine tonsils?
They have an important role in fighting infection – the first line of defence against pathogens entering through the nasopharynx or oropharynx.
Where are the palatine tonsils located?
The palatine tonsils are commonly referred to as ‘ the tonsils ‘. They are located within the tonsillar bed of the lateral oropharynx wall – between the palatoglossal arch ( anteriorly) and palatopharyngeal arch (posteriorly). They form the lateral part of the Waldeyer’s ring. Each tonsil has free medial surface which projects into the pharynx.
Which nerves are involved in the pharyngeal tonsil?
The pharyngeal tonsil receives nerve fibres from the vagus and glossopharyngeal cranial nerves.
Which tonsil receives arterial supply from several vessels?
The pharyngeal tonsil receives arterial supply from several vessels:
Where are tonsils found?
The tonsils are part of MALT ( mucosa associated lymphoid tissue ). MALT can also be found in the bowel, in Peyer’s patches. In general MALT is relatively undeveloped at birth with low cellularity. Tonsils start to develop around 14-15th week of embryonic life, while germinal cenres are absent at this stage. Palatine tonsils and tonsillar fossa are believed to be the derivatives of the 2nd pharyngeal pouch. The epithelial lining proliferates and forms buds, which form the primordium of the palatine tonsil.
What is the germinal center of a tonsil?
In addition, the center of each of these nodules is densely packed with lymphocytes , and is referred to as the germinal center. The tonsillar crypts (except the pharyngeal tonsil) will penetrate from the surface, almost down to the very center of the tonsil follicle. The luminal surfaces of the tonsils are coated in non-keratinizing stratified squamous epithelium, which is the same tissue of the surrounding oropharynx.
What is the role of tonsils in the immune system?
They act as the first line of defense against ingested or inhaled pathogens. Four types of tonsils are arranged into a ring around the pharynx ( oropharynx and nasopharynx ), known as Waldeyer’s ring of lymphoid tissue.
How many crypts are in the tonsil?
The tonsil is penetrated by 15-20 crypts. The lumen of the crypts contain lymphocytes, bacteria and desquamated epithelial cells. The palatine tonsils receive their blood supply from the tonsillar branches of five arteries: Ascending palatine branch of the facial artery. Tonsillar branch of the facial artery.
What is the palatine tonsil?
Palatine tonsils and tonsillar fossa are believed to be the derivatives of the 2nd pharyngeal pouch. The epithelial lining proliferates and forms buds, which form the primordium of the palatine tonsil.
How many tonsils are there in the human body?
There are four types of tonsils in humans; palatine, pharyngeal, lingual and tubal. To quickly remember this, you can use the following mnemonic: " PPL have T onsils", standing for P alatine, P haryngeal, L ingual, T ubal.
Where do tonsillar crypts penetrate?
The tonsillar crypts (except the pharyngeal tonsil) will penetrate from the surface, almost down to the very center of the tonsil follicle. The luminal surfaces of the tonsils are coated in non-keratinizing stratified squamous epithelium, which is the same tissue of the surrounding oropharynx.
What is the function of tonsils?
The tonsils are immunocompetent organs which serve as the immune system's first line of defense against ingested or inhaled foreign pathogens, and as such frequently engorge with blood to assist in immune responses to common illnesses such as the common cold.
How many tonsils are there in the human body?
Humans are born with four types of tonsils: the pharyngeal tonsil, two tubal tonsils, two palatine tonsils and the lingual tonsils.
What is the Waldeyer's tonsilar ring?
FMA. 9609. Anatomical terminology. The tonsils are a set of lymphoid organs facing into the aerodigestive tract, which is known as Waldeyer's tonsillar ring and consists of the adenoid tonsil, two tubal tonsils, two palatine tonsils, and the lingual tonsils. These organs play an important role in the immune system.
What is the best treatment for tonsillitis?
The most common way to treat tonsillitis is with anti-inflammatory drugs such as ibuprofen, or if bacterial in origin, antibiotics, e.g. amoxicillin and azithromycin. Surgical removal ( tonsillectomy) may be advised if the tonsils obstruct the airway or interfere with swallowing, or in patients with severe or recurrent tonsillitis. However, different mechanisms of pathogenesis for these two subtypes of tonsillar hypertrophy have been described, and may have different responses to identical therapeutic efforts. In older patients, asymmetric tonsils (also known as asymmetric tonsil hypertrophy) may be an indicator of virally infected tonsils, or tumors such as lymphoma or squamous cell carcinoma .
How big is a palatine tonsil?
In adults, each palatine tonsil normally measures up to 2.5 cm in length, 2.0 cm in width and 1.2 cm in thickness. The adenoid grows until the age of 5, starts to shrink at the age of 7 and becomes very small in adulthood.
What is the substance that accumulates on the palatine tonsil?
A tonsillolith (also known as a “tonsil stone”) is material that accumulates on the palatine tonsil. This can reach the size of a peppercorn and is white or cream in color. The main substance is mostly calcium, but it has a strong unpleasant odor because of hydrogen sulfide and methyl mercaptan and other chemicals.
Where are the palatine tonsils located?
When used unqualified, the term most commonly refers specifically to the palatine tonsils, which are two lymphoid organs situated at either side of the back of the human throat. The palatine tonsils and the adenoid tonsil are organs consisting of lymphoepithelial tissue located near the oropharynx and nasopharynx (parts of the throat).
Where are the tubal tonsils located?
The tubal tonsils are also located in the roof of the nasopharynx. They are bilateral and posterior to the torus tubaris, in the fossa of Rosenmüller (pharyngeal recess). Due to the relative closeness of the tubal tonsils to the torus tubaris, it is sometimes referred to as “the tonsils of the torus tubaris”.
What is the pharyngeal tonsil lined with?
The pharyngeal tonsil is lined by pseudo-stratified ciliated columnar epithelium (respiratory epithelium). Unlike the other tonsils, there are no crypts (invaginations in the surface of the tonsil) present in this tonsil. Blood supply to the pharyngeal tonsil arise from the: ascending pharyngeal and palatine arteries.
What arteries supply blood to the pharyngeal tonsil?
Blood supply to the pharyngeal tonsil arise from the: ascending pharyngeal and palatine arteries. tonsillar branch of the facial artery. pharyngeal branch of the maxillary artery. artery of the pterygoid canal. basosphenoid artery.
What is the palatine tonsil covered by?
Unlike the adenoids, the palatine tonsils are covered by stratified non-keratinized squamous epithelium. They also have many invaginations to increase the probability of exposure of foreign antigens to the lymphatic tissue present in the crypts. The tonsils receive arterial blood via the following arteries: tonsillar.
Which tonsil is responsible for screening air?
Pharyngeal tonsil (adenoids) Situated superior-posteriorly to the torus tubaris (elevation around the pharyngeal opening of the Eustachian tube), in the roof of the nasopharynx, the pharyngeal tonsil is primarily responsible for ‘screening’ the air that enters through the nostrils.
What is the roof of the nasopharynx covered with?
In the roof of the nasopharynx. Covered with respiratory epithelium. Tubal tonsils. In the roof of the nasopharynx. Covered with respiratory epithelium. Palatine tonsils. In the oropharynx. Covered with stratified non-keratinized squamous epithelium. Lingual tonsils.
Where are the palatine tonsils?
These bilateral lymphoid aggregates each rest within a tonsillar cleft, bordered anteriorly by the palatoglossal arch and posteriorly by the palatopharyngeal arch.
