Types of Synovial Joints.
- Planar Joints. Planar joints have bones with articulating surfaces that are flat or slightly curved faces. These joints allow for gliding movements, ...
- Hinge Joints.
- Pivot Joints.
- Condyloid Joints.
- Saddle Joints.
What are the five major features of synovial joints?
The bones in a synovial joint are connected by ligaments, which:
- are a type of connective tissue and are tough, fibrous and slightly elastic
- connect bone to bone and help keep the joint together
- stabilise the joints during movement and prevent dislocation by restricting actions outside the normal joint range
- can absorb shock because of their elasticity, which protects the joint
What are the six types of joints?
Classification of Joints
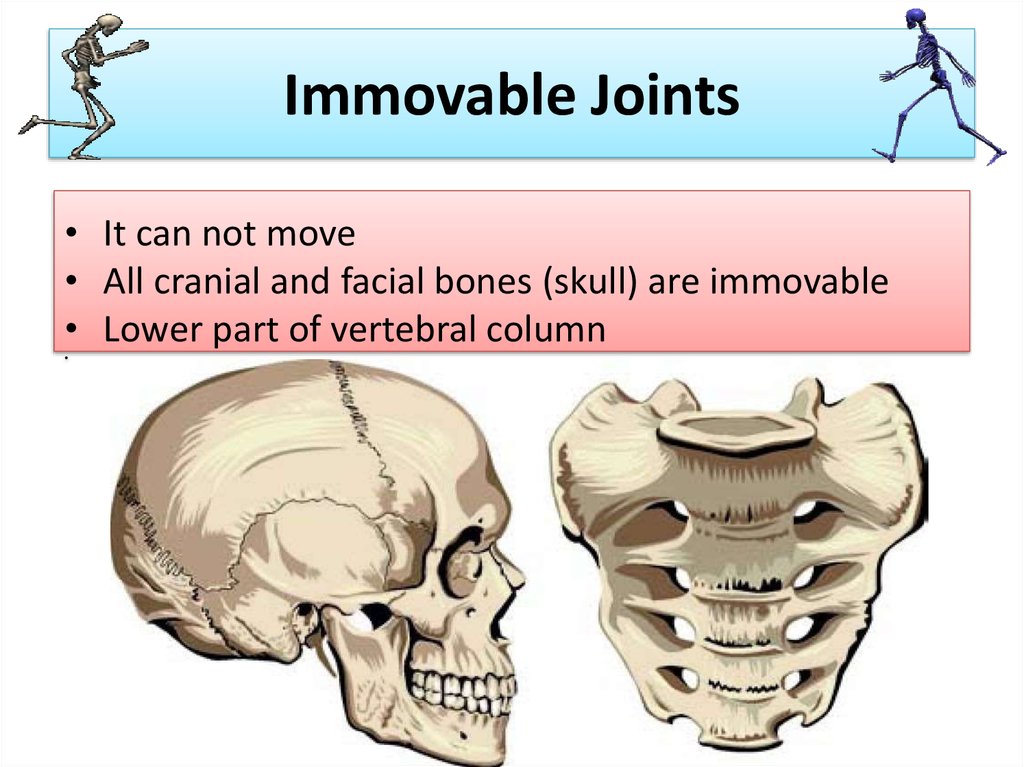
- Fibrous Joints. Fixed joints, also called immovable joints, are found where bones are not flexible. ...
- Cartilaginous Joints. Cartilaginous joints are partly movable joints comprising of symphysis or synchondrosis joints. ...
- Synovial Joints. ...
- Ball and Socket Joints. ...
- Pivotal Joints. ...
- Hinge Joints. ...
- Saddle Joints. ...
- Condyloid Joints. ...
- Gliding Joints. ...
What is the least stable type of joints?
Which joint is the least stable? Shoulder joint. ... Most common type degenerative joint disease-pitting and erosion of cartilage "wear and tear" Rheumatoid arthritis.
What are the four types of joints in your body?
What Are the Four Types of Movable Joints?
- Ball-and-socket. A ball-and-socket joint consists of one bone with a rounded end and and another cupped bone that it fits into, allowing a full range of motion.
- Hinge. Just like a door hinge, hinge joints in the human body facilitate a simple angular moment, allowing extension but not rotation.
- Pivot. ...
- Gliding. ...
- Other. ...

What are the main 2 types of joints?
Hinge joints, such as in the fingers, knees, elbows, and toes, allow only bending and straightening movements. Pivot joints. Pivot joints, such as the neck joints, allow limited rotating movements.
What are the types of synovial?
The six types of synovial joints are pivot, hinge, condyloid, saddle, plane, and ball-and socket-joints (Figure 9.4.
How many types of synovial are there?
There are five types of synovial joints. These are planar joints, hinge joints, condyloid joints, saddle joints and ball and socket joints. So, the correct answer is '5'.
What are the 3 types of joints and the type of synovial joints?
Joints are formed where bones come together. The six types of synovial joints are the pivot, hinge, saddle, plane, condyloid, and ball-and-socket joints. Pivot joints are found in your neck vertebrae, while hinge joints are located in your elbows, fingers, and knees. Saddle and plane joints are found in your hands.
What are synovial joints examples?
A synovial joint is the type of joint found between bones that move against each other, such as the joints of the limbs (e.g. shoulder, hip, elbow and knee). Characteristically it has a joint cavity filled with fluid.
What are synovial joints commonly known as?
A synovial joint, also known as diarthrosis, joins bones or cartilage with a fibrous joint capsule that is continuous with the periosteum of the joined bones, constitutes the outer boundary of a synovial cavity, and surrounds the bones' articulating surfaces.
How many synovial joints are there in the body?
six typesThe six types of synovial joints are pivot, hinge, condyloid, saddle, plane, and ball-and socket-joints ([link]). The six types of synovial joints allow the body to move in a variety of ways.
What is a ball-and-socket synovial joint?
The ball and socket joint (or spheroid joint) is a type of synovial joint in which the ball-shaped surface of one rounded bone fits into the cup-like depression of another bone.
What are the 7 synovial joints?
Planar, hinge, pivot, condyloid, saddle, and ball-and-socket are all types of synovial joints.
What are the 8 synovial joints?
These joints can be described as planar, hinge, pivot, condyloid, saddle, or ball-and-socket joints. Figure 19.26. Different types of joints allow different types of movement. Planar, hinge, pivot, condyloid, saddle, and ball-and-socket are all types of synovial joints.
What are the different types of synovial joints quizlet?
ball-and-socket, condyloid, gliding, hinge, pivot, and saddle.
What are types of joints?
The six types of freely movable joint include ball and socket, saddle, hinge, condyloid, pivot and gliding. Common causes of joint pain include inflammation (pain and swelling), infection and injury.
What are the 6 main types of synovial joints?
Synovial joints are often further classified by the type of movements they permit. There are six such classifications: hinge (elbow), saddle (carpometacarpal joint), planar (acromioclavicular joint), pivot (atlantoaxial joint), condyloid (metacarpophalangeal joint), and ball and socket (hip joint).
What are the 7 synovial joints?
Planar, hinge, pivot, condyloid, saddle, and ball-and-socket are all types of synovial joints.
What are the 4 main characteristics of synovial joints?
Synovial joints comprise most of the joints of the extremities and are the most accessible joints to direct inspection and palpation. Synovial joints share important structural components: subchondral bone, hyaline cartilage, a joint cavity, synovial lining, articular capsule, and supporting ligaments.
What are the 6 types of joints?
A joint is the part of the body where two or more bones meet to allow movement. Generally speaking, the greater the range of movement, the higher the risk of injury because the strength of the joint is reduced. The six types of freely movable joint include ball and socket, saddle, hinge, condyloid, pivot and gliding.
What are the different types of synovial joints?
Different types of joints allow different types of movement. Planar, hinge, pivot, condyloid, saddle, and ball-and-socket are all types of synovial joints.
What are saddle joints?
Saddle Joints. Saddle joints are so named because the ends of each bone resemble a saddle, with concave and convex portions that fit together. Saddle joints allow angular movements similar to condyloid joints but with a greater range of motion. An example of a saddle joint is the thumb joint, which can move back and forth and up and down, ...
What is a ball and socket joint?
Ball-and-socket joints possess a rounded, ball-like end of one bone fitting into a cuplike socket of another bone. This organization allows the greatest range of motion, as all movement types are possible in all directions. Examples of ball-and-socket joints are the shoulder and hip joints (Figure 7).
Where are planar joints found?
Planar joints are found in the carpal bones in the hand and the tarsal bones of the foot, as well as between vertebrae (Figure 2). Figure 2. The joints of the carpal bones in the wrist are examples of planar joints. (credit: modification of work by Brian C. Goss)
What is an example of a hinge joint?
Figure 3. The elbow joint, where the radius articulates with the humerus, is an example of a hinge joint. (credit: modification of work by Brian C. Goss)
What is hinge joint?
Hinge Joints. In hinge joints, the slightly rounded end of one bone fits into the slightly hollow end of the other bone. In this way, one bone moves while the other remains stationary, like the hinge of a door. The elbow is an example of a hinge joint. The knee is sometimes classified as a modified hinge joint (Figure 3).
Which joints allow abduction?
These biaxial joints allow abduction, adduction, or side to side and flexion extension movement, but not rotation. The wrist between the radius and carpals, and the knuckle between the metacarpals and phalanges contain ellipsoidal joints. Convex and concave areas form like a saddle to make saddle joints.
How many types of synovial joints are there?
What are the types of synovial joints? There are a total of 7 types of synovial joints in the human body. These joints allow movement which is why it is also known as movable joints. Actually, the articulating surface of this type of joint is filled with a special lubricating fluid known as synovial fluid. This fluid provides lubrication ...
Why are synovial joints called synovial joints?
They are called synovial joint because is filled with synovial fluid which acts as lubricants. It is also interesting to know that there are 6 types of synovial joints in our body. But our body also has numerous immovable joints which do not allow any movement. In this article, we are concerned about the movable joints / synovial joints, ...
What are some examples of plane joints?
So the plane joint permits gliding movement. The examples of plane joint are intercarpal joints, intertarsal joints, joints between articular processes of vertebrae.
What are the two types of joints?
Types of joints in human body. Whenever two or more bones meet they form a joint. The human body has broadly two types of joint, one is immovable joint and another is movable joint.
Why is cartilage smooth?
Smooth cartilage allows friction-less movement and this smoothness is further enhanced by body lubricants. Our movable joints are also lubricated and filled with fluid known as synovial fluid and this is why we call this joint as synovial Joint.
Which synovial joint is the most movable?
The last on the list of types of synovial joints is the most movable of all the types. As the name suggests the ball and socket joint consists of a ball that fits into the socket a cup-shaped socket. The spherical ball fits into the cup-shaped socket and that’s why it allows movement in almost all direction. It gives great freedom of movement.
What is the purpose of immovable joints?
However, there are other joints whose purpose is to maintain the structure of the body parts by not allowing movement, they are fixed and do not take part in any kind of movement. These are immovable joints.
What is the synovial joint?
Synovial joints, also termed diarthrotic joints, have a fibrous capsule that connects two bones or cartilage and connects to the periosteum of the two bones. This type of joint aids in the movement and cushioning of the two articulating bones as they glide past each other. In doing so, it prevents friction from building up that might impact each bone and erode away at the articular hyaline cartilage that is at the end of long bones, such as the femur and tibia.
Where is the compound joint located?
Compound: A compound joint is found in the knee joint (femur-tibia region and femur-patellar region). It allows for flexion and extension.
What is the articular cartilage of a dog?
Articular cartilage that is the end of the epiphyses of each articulating bone. It is hyaline cartilage, but in contrast to most hyaline cartilage, it lacks a perichondrium. Thus, the only mechanism it has to regenerate is through interstitial growth, which is slower than appositional growth via the perichondrium. The articular cartilage acts as a smooth and gliding surface to reduce friction and absorb shock and reduce friction during movement. In dogs and humans with degenerative joint disease (DJD), the articular cartilage wears away from the bone and can even break off into the joint where such pieces are called 'joint mice'. When this occurs, it results in bone rubbing on bone during movement, which results in friction and further wearing away at the remaining articular cartilage that is slow to repair. Mainstays of treatment for DJD include treating the associated pain with a non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drug (NSAID) and trying to rebuilding the matrix portion of the cartilage by hyaluronic acid and other glycosaminoglycan supplementation.
What is a fibrous joint capsule?
In synovial joints, also called diarthrotic joints, a fibrous joint capsule bridges two bones or cartilage. The location, structure, and function of this type of joint are discussed in this lesson. Updated: 01/06/2021
What is saddle joint?
Saddle: A saddle joint e.g. carpometacarpal region (thumb) gets this name as the concave portion of one bone opposes the convex region of another bone. Due to this arrangement, this type of joint permits greater range of movement than a condyloid joint.
What is the term for a disk that is composed of fibrocartilage?
Articular disks or menisci, which normally should be comprised of fibrocartilage.
What is the purpose of synovial joints?
Synovial joints allow for smooth movements between the adjacent bones. The joint is surrounded by an articular capsule that defines a joint cavity filled with synovial fluid. The articulating surfaces of the bones are covered by a thin layer of articular cartilage.
What is the most common type of joint in the body?
Synovial joints are the most common type of joint in the body (Figure 1). A key structural characteristic for a synovial joint that is not seen at fibrous or cartilaginous joints is the presence of a joint cavity. This fluid-filled space is the site at which the articulating surfaces of the bones contact each other.
What is the function of tendons and muscles in synovial joints?
At many synovial joints, additional support is provided by the muscles and their tendons that act across the joint. A tendon is the dense connective tissue structure that attaches a muscle to bone. As forces acting on a joint increase, the body will automatically increase the overall strength of contraction of the muscles crossing that joint, thus allowing the muscle and its tendon to serve as a “dynamic ligament” to resist forces and support the joint. This type of indirect support by muscles is very important at the shoulder joint, for example, where the ligaments are relatively weak.
Where are plane joints located?
Plane joints are found between the carpal bones (intercarpal joints) of the wrist or tarsal bones (intertarsal joints) of the foot, between the clavicle and acromion of the scapula (acromioclavicular joint), and between the superior and inferior articular processes of adjacent vertebrae (zygapophysial joints).
Which joint is a multiaxial joint?
Ball-and-socket joints are classified functionally as multiaxial joints. The femur and the humerus are able to move in both anterior-posterior and medial-lateral directions and they can also rotate around their long axis. The shallow socket formed by the glenoid cavity allows the shoulder joint an extensive range of motion. In contrast, the deep socket of the acetabulum and the strong supporting ligaments of the hip joint serve to constrain movements of the femur, reflecting the need for stability and weight-bearing ability at the hip.
Which type of joint allows only for bending and straightening motions along a single axis?
In a hinge joint, the convex end of one bone articulates with the concave end of the adjoining bone (see Figure 3b). This type of joint allows only for bending and straightening motions along a single axis, and thus hinge joints are functionally classified as uniaxial joints.
Which joint is the only ball and socket joint?
The hip joint and the glenohumeral (shoulder) joint are the only ball-and-socket joints of the body. At the hip joint, the head of the femur articulates with the acetabulum of the hip bone, and at the shoulder joint, the head of the humerus articulates with the glenoid cavity of the scapula.
What is the synovial capsule?
Synovial joints are surrounded by a synovial capsule that encloses the synovial cavity and joins the bones of the joint. Read on to learn more about them! Synovial joints provide a connection between two bones. They’re made up of a cartilage-lined cavity filled with fluid.
What are some examples of pivot joints?
One example is the elbow. Pivot joints allow movement around a shaft, meaning they regulate rotation movements. One example is the distal radioulnar joint. Compound or bicondyloid joints. These joints allow movement between an axis, with limited rotation in a second axis. They consist of two convex condyles.
Which membrane is highly vascularized and produces synovial fluid?
The synovial membrane is highly vascularized and produces synovial fluid. Then, this builds up in the joint cavity and lubricates the joint surfaces.
What are sacs in tendons?
This is where they form bursae or tendon sheaths. The sacs often form between structures such as tendons and joints, tendons and bone, or skin and bone and reduce friction when one structure moves over another. Also, tendon sheaths surround tendons and reduce friction.
Which joint allows flexion, extension, abduction, and adduction?
Condyloid joints allow movement within two perpendicular axes and passive or secondary movement on a third axis. Thus, they allow flexion, extension, abduction, and adduction movements (circumduction). This is the case of the wrist joint. Saddle joints.
Which joint allows adduction and flexion?
This is the case of the wrist joint. Saddle joints. These allow the same movements as the condyloid joints but allow greater movement. This name derives from their saddle shape. They provide flexion, extension, abduction, and adduction movements (circumduction). Ball joints allow all movements except gliding.
What would happen if we didn't have joints?
If we didn’t have joints, the bones of our body couldn’t move. Thanks to our joints, we can make different movements such as bending, rotating, and flexing our arms and legs!
Where is the synovial joint located?
synovial joint formed between the spherical end of one bone (the ball) that fits into the depression of a second bone (the socket); found at the hip and shoulder joints; functionally classified as a multiaxial joint. bursa.
What is the purpose of synovial joints?
Synovial joints allow for smooth movements between the adjacent bones. The joint is surrounded by an articular capsule that defines a joint cavity filled with synovial fluid. The articulating surfaces of the bones are covered by a thin layer of articular cartilage.
What is the most common type of joint in the body?
Synovial joints are the most common type of joint in the body ( [link] ). A key structural characteristic for a synovial joint that is not seen at fibrous or cartilaginous joints is the presence of a joint cavity. This fluid-filled space is the site at which the articulating surfaces of the bones contact each other.
Which joint allows the body to move?
The six types of synovial joints allow the body to move in a variety of ways. (a) Pivot joints allow for rotation around an axis, such as between the first and second cervical vertebrae, which allows for side-to-side rotation of the head. (b) The hinge joint of the elbow works like a door hinge.
Where are plane joints located?
Plane joints are found between the carpal bones (intercarpal joints) of the wrist or tarsal bones (intertarsal joints) of the foot, between the clavicle and acromion of the scapula (acromioclavicular joint), and between the superior and inferior articular processes of adjacent vertebrae (zygapophysial joints).
Which joint is a multiaxial joint?
Ball-and-socket joints are classified functionally as multiaxial joints. The femur and the humerus are able to move in both anterior-posterior and medial-lateral directions and they can also rotate around their long axis. The shallow socket formed by the glenoid cavity allows the shoulder joint an extensive range of motion. In contrast, the deep socket of the acetabulum and the strong supporting ligaments of the hip joint serve to constrain movements of the femur, reflecting the need for stability and weight-bearing ability at the hip.
Which joint has the greatest range of motion?
The joint with the greatest range of motion is the ball-and-socket joint. At these joints, the rounded head of one bone (the ball) fits into the concave articulation (the socket) of the adjacent bone (see [link] f ). The hip joint and the glenohumeral (shoulder) joint are the only ball-and-socket joints of the body.
What is the synovial joint?
A synovial joint is a connection between two bones consisting of a cartilage lined cavity filled with fluid, which is known as a diarthrosis joint. Diarthrosis joints are the most flexible type of joint between bones, because the bones are not physically connected and can move more freely in relation to each other.
What is the structure of a synovial joint?
Extending from the periosteum of the bone, an articular capsule made of cartilage and other fibers encapsulates the entire joint.
Why is synovial joint better than other joints?
1. One of the benefits of a synovial joint over other types of joints is the ability of the joint to recover after trauma. A synovial joint can undergo an event called dislocation, when the bones become misaligned. However, the bones can usually be forced back into place.
What is the term for a joint that is completely immobile?
Synarthrosis – A type of joint between bones which is completely immobile, such as those in the skull.
Which type of joint is found between bones and needs to move and flex a lot?
A is correct. Synovial joints are found between bones which need to move and flex a lot. More fixed connections, like those between ribs, are made with stronger and more durable joints containing more cartilage and tendons, and ligaments.
Which joint gives the greatest flexibility?
Some synovial joints, like the hip joint mentioned above, are meant to give the greatest flexibility around the joint. Other joints, like the joints found in the ankle, have a slightly more limited range of motion, but provide an enormous cushion for the repeated impacts from running and jumping. A synovial joint may vary slightly in function based ...
Which joint can only move in one direction?
A uniaxial joint can only move in one direction, such as the elbow. While this is slightly limited in range, it allows the muscles to make extremely powerful levers of the bones connected to these synovial joints. A biaxial joint can move in two directions, which is important for joints in the wrist and ankle.
