- Structure. Because of their features type IIa fibers are often labelled as the intermediate muscle fibers. ...
- Function. Considering their structure, It will come as no surprise to hear that type IIa fibers produce more force than type I fibers but less than type IIb fibers.
- Impact on performance. Given their position as an intermediary, type IIa fibers are able to bridge the gap between aerobic and high-intensity exercise.
What are the different types of muscle fibers?
Three types of fibers are defined by this classification scheme are:
- Slow oxidative (SO)
- Fast oxidative (FO)
- Fast glycolytic (FG)
What exercise is best for Type IIB fiber?
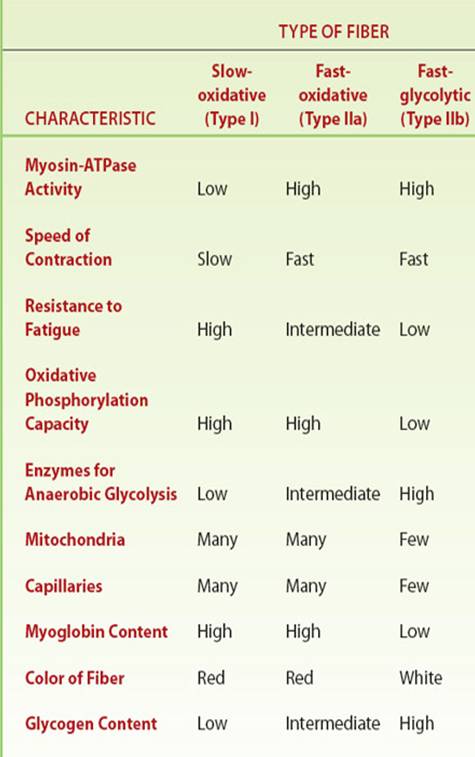
Type I fibers use oxygen to create energy for lower-intensity, long-term, endurance-oriented activities like walking, running, swimming, cycling or standing for extended periods of time. Type IIB fibers are known as anaerobic muscle fibers. Type IIB fibers store energy that is released for short, explosive, extremely high-intensity activities.
What are Type 1 muscle fibres?
- Type 1. These fibers utilize oxygen to generate energy for movement. Type 1 fibers have a higher density of energy-generating organelles called mitochondria. ...
- Type 2A. Like type 1 fibers, type 2A fibers can also use oxygen to generate energy for movement. ...
- Type 2B. Type 2B fibers don’t use oxygen to generate energy. ...
What are types of fibers?
Inorganic fibers
- Glass fibers
- Man-made rubber. This is a combination of man made and synthetic rubber.
- Rayon fibers. These are beautiful silk-like fibers made from cotton linters / wooden pulp (cellulose). The drapeability of rayon fabrics make them a favorite in making clothes.
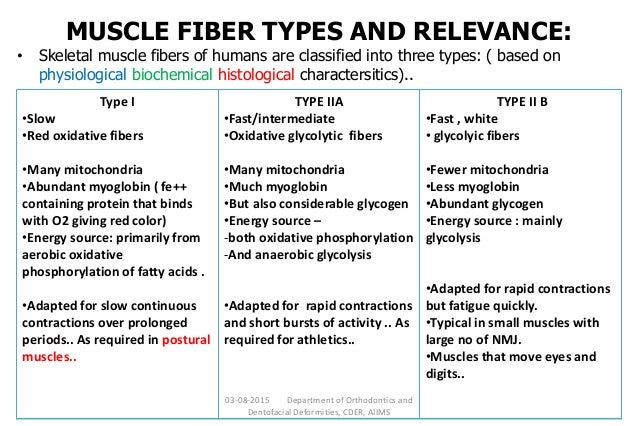
What is type 2 muscle fiber used for?
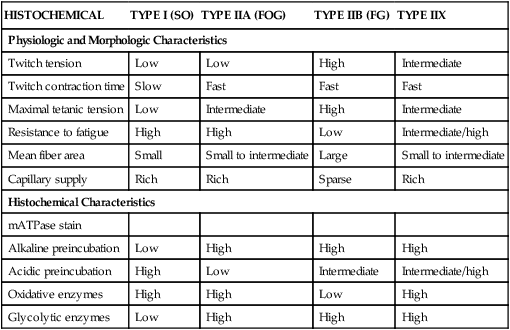
Type 2 A: Fast oxidative (FO) fibers have fast contractions and primarily use aerobic respiration, but because they may switch to anaerobic respiration (glycolysis), can fatigue more quickly than SO fibers.
What are type I and Type II muscle Fibres?
Skeletal muscle fibers can be categorized into two types: slow-twitch (Type I) and fast-twitch (Type II). Type I muscle fibers are more efficient over long periods of time. They are mainly used for postural maintenance (such has holding the head upright), or endurance exercises (like marathon running).
Which is a characteristic of Type IIA muscle fibers?
Type IIA fibers have high myosin ATPase activity (pH 9.4), are fast twitch, have high oxidative and glycolytic capacity, and are relatively resistant to fatigue.
What are type 2A and 2B muscle fibers?
Intermediate-twitch type-2A: used when moving a semi-heavy object. Fast-twitch type-2B: the largest fibres, called into action when all-out effort is required (fight or flight). They contract many times faster than slow-twitch fibres and with much greater force, but they fatigue quickly.
Where are type 2A muscle fiber found?
the armsSuch fibres are found in large numbers in the muscles of the arms.
How do you get type 2 muscle fibers?
Heavy Squats, Deadlifts and Bench Presses are good ways to increase Type II fibers. So is running sprints, agility drills and med ball training. Plyometric training and Olympic lifting are also effective fast-twitch fiber recruiters.
What is a characteristic of a type II muscle fiber quizlet?
Type II- fast twitch muscle fibers are "fast" or quick to fatigue due to having fewer capillaries, mitochondria, myoglobin, and decreased oxygen delivery. They also produce more force and power with their short term contractions.
What is a characteristic of a type II muscle fiber Nasm quizlet?
Type II muscle fiber characteristics. 1) Fast twitch or "white" fibers. 2) less oxygen delivery. 3) more anaerobic.
Which of the following is a characteristic of fast twitch Type 2 fibers?
Fast-twitch muscle fibers provide bigger and more powerful forces, but for shorter durations and fatigue quickly. They are more anaerobic with less blood supply, hence they are sometimes referred to as white fibers or type II.
What basic characteristics differ between type I and type II muscle fibers?
The key difference between type 1 and type 2 muscle fibers is that the type 1 muscle fibers contract slowly while the type 2 muscle fibers contract rapidly. Moreover, type 1 muscle fibers depend on aerobic respiration while type 2 muscle fibers depend on anaerobic respiration.
How many types of muscle fibers are there?
There are three main types of muscle fiber:
What are the fibers of skeletal muscle?
Each muscle is wrapped in a thick connective tissue called the epimysium. Within this is a number of muscle fibers which are bundled together to form a fascicle, which are held in place by the perimysium.
What is your muscle type?
As we have shown, muscle fiber types are varied between individuals, so it is highly likely that you show differences between your friends and family. Sadly, the only true way of finding out what your muscle fiber types is through a muscle biopsy – this involves taking away a tiny portion of the muscle for testing in the labs.
Why do muscle fibers change shape?
This is because muscle fibers are plastic, meaning they are capable of changing their size and shape. Even more interesting is the fact that they can also convert from one type to another! These changes to muscle fibers are due to a number of factors, these include your age but also your activity level.
What is the skeletal muscle made of?
Skeletal muscle is therefore made up of hundreds, if not thousands of muscle fibers. These fibers are singular protein dense cells which contain many nuclei, mitochondria and endoplasmic reticulum. Each fiber is surrounded by a plasma membrane called the sarcolemma, and inside this sits the sarcoplasm, a gelatin-like substance which separates ...
What is the smallest connective tissue?
Within each muscle fiber we have a number of myofibrils which are aligned in parallel, each individual fiber is surrounded by endomysium – the smallest of the connective tissue.
Which muscle fibers produce the most force?
Type IIb muscle fibers are without doubt the most powerful, they produce the most force and are faster at getting to their peak force. However, they are easily fatiguable, meaning this high-level of force cannot be sustained for as long as type I fibers.
What is type 2 muscle fiber?
Type II muscle fiber is also known as fast twitch muscle fiber. Muscle fiber types can be broken down into two main types: slow twitch ( Type I) muscle fibers and fast twitch (Type II) muscle fibers . These fast twitch fibers can be further categorized into Type IIa and Type IIb fibers, which are also known as "fast twitch oxidative" and "fast twitch glycolytic," respectively. Type I fibers are characterized by low force/power/speed production and high endurance, Type IIB fibers are characterized by high force/power/speed production and low endurance, while Type IIA fall in between the two.
What type of fibers are red?
Type II A fibers are red, unlike Type II B fibers, which are white. Type IIA fibers have a very high capacity for generating ATP by oxidative metabolic processes, and split ATP at a very rapid rate. They have a fast contraction velocity and are more resistant to fatigue than Type IIB.
What type of fiber is used for sprints?
Type IIb fast-twitch fibers, or fast glycolytic fibres (also known as Type IIx), are recruited for very short-duration high-intensity bursts of power such as maximal and near-maximal lifts and short sprints.
Can you change from type IIB to type IIA?
It is possible that a fiber might be transformed from Type IIB to Type IIAB to Type IIA with exercise training. Furthermore, researchers at Boston University School of Medicine have found that increasing the mass or size of type II muscle fibers will lead to a significant decrease in fat mass or the amount of fat in the body.
What are the tubular fibers in skeletal muscle?
Each skeletal muscle consists of thousands of tubular muscle fibers called myocytes that run through the length of a muscle. These muscle fibers are a combination of thousands of myofibrils that are bundled together into fascicles and connected via a thin layer of connective tissue, called the fascia. Myofibrils are composed of repeating sections ...
How many muscle fibers do athletes have?
An average adult has roughly the same amount of both fast and slow-twitch muscle fibers, whereas some elite athletes may have up to 70% of a specific muscle fiber type. For example, sprinters and weightlifters may have a greater amount of fast-twitch muscle fibers while endurance athletes have more slow-twitch fibers.
What physiological factors affect muscle fiber distribution?
The amount of different muscle fiber types is a combination of a few physiological factors, including genetics, sex, age and training background . Although different muscle fiber types have certain characteristics that may make them seemingly more suitable for certain sports, studies have shown that both fiber types adapt to the way you use them.
How does genetics affect muscle fibers?
Genetics can also have a significant impact on your muscle fiber proportion. On average, people tend to have roughly the same amount of both fast and slow-twitch muscle fibers. However, some elite athletes may have up to 80% of a specific muscle fiber type. For example, sprinters and weightlifters may have a greater amount of fast-twitch muscle fibers while endurance athletes have more slow-twitch fibers. These individual differences between muscle fiber proportions are a result of both hereditary factors and environmental variance.
Why are glycolytic fibers pale?
Because fast glycolytic muscle fibers do not primarily rely on aerobic energy production, they also have the smallest amount of capillaries, mitochondria and myoglobin of any muscle fiber type. As a result, type IIb/IIx fibers are pale and therefore often referred to as white muscle fibers.
What is the difference between slow and fast twitch muscle fibers?
You see, slow-twitch muscle fibers are specialized in energy- efficient contraction with relatively low force production. On the other hand, fast-twitch muscle fibers contract rapidly with a lot of force and relatively poor efficiency, making them more suitable for short and powerful performances.
Why are fast-twitch muscles activated?
Thus, they are only activated when slow-twitch muscle fibers aren’t able to produce enough force.
What are the two types of muscle fibers?
Types of Muscle Fiber. Muscle fiber types can be broken down into two main types: slow twitch ( Type I) muscle fibers and fast twitch ( Type II) muscle fibers. Type II fibers can subsequently be broken down into two types: type IIA, which is referred to as "fast twitch oxidative glycolytic", and type IIX, which is referred to as "fast twitch ...
What is a type 1 fiber?
Type I fibers are used in lower-intensity exercises such as very light resistance work aimed at muscular endurance and long-duration aerobic activities such as 5K and 10K runs. Type I fibers are identified by slow contraction times and a high resistance to fatigue.
What type of fiber is used for fast twitch?
Type IIx fast-twitch fibers (Fast twitch 2), or fast glycolytic fibres, are recruited for very short-duration high-intensity bursts of power such as maximal and near-maximal lifts and short sprints.
How to determine fiber type?
The only way to directly determine the fiber-type composition in an athlete is to perform an invasive muscle biopsy test. Since this is not always feasible, an indirect method that can be used to determine the fiber composition of a muscle group is to initially establish the athlete's 1RM.
How many repetitions are in a muscle group?
Fewer than seven repetitions and the muscle group is likely composed of more than 50% FT fibers. Greater than 12 and the muscle group has more than 50% ST fibers. If the athlete can do between 7 and 12 repetitions, then the muscle group probably has an equal proportion of fibers.
What is ST fiber used for?
ST fibers are predominantly used for aerobic activities requiring low-level force production, such as walking and maintaining posture, but are also the primary fiber type found in endurance athletes. Most activities of daily living use ST fibers
What is the difference between type IIa and type IIx?
“Type IIa muscle fibers are more fatigue-resistant than type IIx , but more fatigable than slow-twitch muscle fibers. They also produce more force than slow-twitch muscle fibers but less than type IIx,” he says.
What type of muscle fibers are in the triceps?
From your biceps and triceps to your quads and glutes, your skeletal muscles contain two different types of muscle fibers—slow-twitch (type I) and fast-twitch (type II)—which differ in the type of energy they produce. Here's what you need to know about your fast-twitch muscle fibers—including how to properly train them, ...
What are fast-twitch muscle fibers?
In the simplest terms, fast-twitch (type II) muscle fibers are built for short, powerful bursts of energy— that's in contrast to slow-twitch (type I) muscle fibers, which are built for endurance activities like long-distance running or biking. "Type II fibers are needed for high-intensity work, such as heavy lifting or sprinting," Dan Giordano, PT, DPT, CSCS, co-founder of Bespoke Treatments Physical Therapy in New York City, tells Health. "They contract and fatigue quickly, synthesizing energy through the anaerobic [without oxygen] process." That's different than slow-twitch muscles, which rely on aerobic [with oxygen] respiration, meaning through the steady intake of oxygen, exercise can be sustained for a longer amount of time.
How do you know if you have fewer fast-twitch muscle fibers?
Most people are born with 50% slow-twitch muscle fibers and 50% fast-twitch muscle fibers. “Only elite strength or power athletes might have 80% type II muscle fibers and endurance athletes have about 90% type I. They have more homogeneous fiber distributions from birth and that is what allows them to excel in their respective sports,” Sternlicht says.
What happens when a muscle fiber loses its nerve supply?
When a muscle fiber loses its nerve supply, Giordano says it goes through a process called apoptosis. Because of this, these fast-twitch muscle fibers start to receive nerve supply from different motor neurons, usually from slow-twitch muscle fibers, meaning they begin to take on characteristics of slow-twitch muscle fibers.
How long should I rest my muscle fibers?
It's also important to take your rest days when training fast-twitch muscle fibers, since high-intensity work can take a toll. “Take 48 to 72 hours in between training type II muscle fibers to allow for the repair phase of the muscle to recover,” Giordano says.
Why do muscles lose fibers?
Muscle fiber loss in general is due to a loss in motor neurons, or communication cells that send signals to muscles, making them perform. This results in the loss of nerve supply to the muscles, which is often referred to as denervation,” Giordano explains.