
What is the best city in the Bay Area?
103 rows · Today, the Bay Area is the home of Silicon Valley, Wine Country, and numerous companies, ...
What Bay Area city is America's hardest-working?
What Is Considered The Bay Area Of California? The San Francisco Bay Area: Breaking it Down. The San Francisco Bay is a large estuary that brings the flowing waters of California to the depths of ... Alameda County. Contra Costa County. Marin County. Napa County.
What cities are in the Bay Area?
Furthermore, what cities are considered the Bay Area? The region encompasses the major cities and metropolitan areas of San Jose, San Francisco, and Oakland, along with smaller urban and rural areas. The Bay Area's nine counties are Alameda, Contra Costa, Marin, Napa, San Francisco, San Mateo, Santa Clara, Solano, and Sonoma.
Why is the Bay area called the Bay Area?
Feb 20, 2022 · Although it doesn't have any firm boundaries, the Bay Area includes portions of nine counties: Marin, Sonoma, Napa, Solano, San Francisco, San Mateo, Contra Costa, Alameda, and Santa Clara. San Mateo and the northern part of Santa Clara counties comprise the Peninsula while Contra Costa and Alameda counties comprise the East Bay of the Bay Area.

What cities are considered part of the Bay Area?
- San Francisco.
- Palo Alto.
- San Jose.
- Mountain View.
- Sunnyvale.
- Santa Clara.
- Menlo Park.
- San Mateo.
What encompasses Bay Area?
What part of California is the Bay Area?
| San Francisco Bay Area | |
|---|---|
| Location of the Bay Area within California. The nine-county Bay Area. Additional counties in the larger fourteen-county combined statistical area. | |
| Country | United States |
| State | California |
| Subregions | East Bay North Bay Peninsula San Francisco South Bay |
Is the Bay Area considered Northern California?
What is considered South Bay in Northern California?
Why is Bay Area called Bay Area?
What's considered East Bay?
Is Santa Cruz considered the Bay Area?
How many times have the Bay Area voted for a Republican?
In U.S. Presidential elections since 1960, the nine-county Bay Area voted for Republican candidates only two times, in both cases voting for a Californian: in 1972 for Richard Nixon and again in 1980 for Ronald Reagan. The last county to vote for a Republican presidential candidate was Napa county in 1988 for George H. W. Bush. Since then, all nine Bay Area counties have voted consistently for the Democratic candidate. Currently, both of California's U.S. Senators are Democrats, and all twelve U.S. congressional districts located wholly or partially in the Bay Area are represented by a Democratic representative. Additionally, every Bay Area member of the California State Senate and the California State Assembly is a registered Democrat.
What is the East Bay?
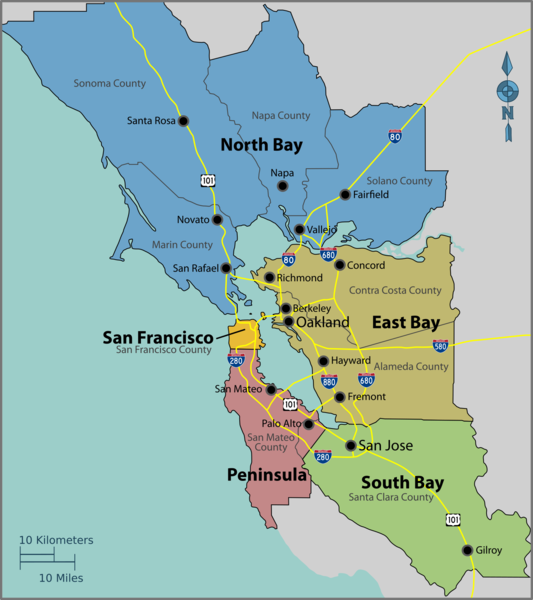
The " East Bay " is the densest region of the Bay Area outside of San Francisco and includes cities and towns in Alameda and Contra Costa counties, centered around Oakland. As one of the larger subregions, the East Bay includes a variety of enclaves, including the suburban Tri-Valley area and the highly urban western part of the subregion that runs alongside the bay. The " Peninsula " subregion includes the cities and towns on the San Francisco Peninsula, excluding the titular city of San Francisco. Its eastern half, which runs alongside the Bay, is highly populated, while its less populated western coast traces the coastline of the Pacific Ocean and is known for its open space and hiking trails. Roughly coinciding with the borders of San Mateo county, it also includes the northwestern Santa Clara county cities of Palo Alto, Mountain View, and Los Altos. The "South Bay" includes all of the rest of the cities in Santa Clara county, centered around San Jose, the largest city in Northern California. It is roughly synonymous with Silicon Valley due to its high concentration of tech companies, although the industry also has a significant presence in the rest of the Bay Area. The " North Bay " includes Marin, Sonoma, Napa, and Solano counties, and is the largest and least populated subregion. The western counties of Marin and Sonoma are encased by the Pacific Ocean on the west and the bay on the east and are characterized by its mountainous and woody terrain. Sonoma and Napa counties are known internationally for their grape vineyards and wineries, and Solano county to the east, centered around Vallejo, is the fastest growing region in the Bay Area.
How many major league teams are there in the Bay Area?
The Bay Area is home to six professional major league sports franchises: The San Francisco 49ers of the National Football League (NFL) in American football, the San Francisco Giants and Oakland Athletics of Major League Baseball (MLB), the Golden State Warriors of the National Basketball Association (NBA), the San Jose Sharks of the National Hockey League (NHL), and the San Jose Earthquakes of Major League Soccer (MLS).
What are the subregions of the Bay Area?
Among locals, the nine-county Bay Area can be further divided into five sub-regions: the East Bay, North Bay, South Bay, Peninsula, and the city of San Francisco. Although geographically located on the tip of the San Francisco Peninsula, the city of San Francisco is not considered part of the "Peninsula" subregion, but as a separate entity.
Why is the San Francisco Bay Area so dry?
The same location during the summer months. Because rain is rare in the San Francisco Bay Area during this time, the surrounding hills quickly become dry and golden-hued in grassy areas.
How many counties are there in the Bay Area?
A map of the locally accepted nine-county definition of the Bay Area. Also displayed are the five subregions of the Bay Area, which are divided along county lines except for the northwestern portion of Santa Clara county.
What is the area code of San Francisco?
Area codes. 408 / 669, 415 / 628, 510 / 341, 650, 707, 925. The San Francisco Bay Area, popularly referred to as the Bay Area, is a populous region surrounding the San Francisco, San Pablo, and Suisun Bay estuaries in Northern California. Although the exact boundaries of the region are variously defined, the Bay Area is defined by ...
How many counties are there in the Bay Area?
Many of the important factors that shape life in the Bay Area — including water and energy systems, development patterns, housing affordability, the transportation network and the economy — have never been entirely contained in nine counties. To reflect this larger geography, SPUR released a report on the Northern California megaregion in 2007. This first-ever report on the subject revealed a 21-county core area surrounded by an additional 20-county sphere of influence that extends from the Bay to Fresno and Reno.
What is Northern California?
The Northern California megaregion better captures our growing connection with places outside the Bay Area. It consists of the nine-county Bay Area, the six-county Sacramento region, the three-county Monterey Bay Area and three northern San Joaquin Valley counties.
What is the SPUR Regional Strategy?
SPUR has launched a multi-year project, the SPUR Regional Strategy, to develop a civic vision for the Bay Area over the next half-century. The goal is to collectively imagine what kind of region we want to be and develop an actionable set of strategies to get us there. Addressing many of our current regional challenges — such as job access, housing affordability and congestion — will require working at many scales: at the local level with cities, at the nine-county level with regional agencies and sometimes at the level of the Northern California megaregion.
What is the strongest way to track human-based geographies?
SPUR’s research and conversations with stakeholders showed that population and commute patterns are the strongest way to track human-based geographies. These patterns show that different areas are in fact economically interdependent: They demonstrate how people’s lives depend on their neighborhoods, their job locations and the connection between the two. Over time we can track these connections to either create new definitions of what constitutes an economically interdependent region or understand how important collaboration across regions could be.
What is SPUR gathered experts?
To answer these questions, SPUR gathered experts, looked to other efforts to define geographies, and studied maps and data to decide which scale (s) will work best for addressing the region’s greatest challenges.
What is goods movement?
The goods movement industry is set up to overcome distance and geography in service of connecting producers along supply chains and sellers with buyers, increasing the economic gains of all involved in these transactions and providing jobs across the state. The most heavily trafficked goods movement corridors in Northern California are mapped below, showing the importance of the Central Valley in this network and how the Bay Area seems to connect to it and Sacramento for some exchanges.
How many counties are there in San Francisco?
The San Francisco Bay Area has long been understood as a region made up of the nine counties that touch the Bay. This definition has a simplicity that other large metro areas lack; not all can be organized around a natural feature that is significant in geologic time and scale. But the nine -county border doesn’t always hold.
How much does a BART ticket cost?
BART is also useful for getting around within SF and Oakland. Ticket prices vary by distance travelled, but usually run about $2-5 one way and tickets can be purchased from vending machines at any station. You will need to insert your ticket into barriers when entering and exiting the system. Tickets hold a balance, deducting the appropriate price for each trip, so someone who plans to use the system several times can buy a $10 or $20 ticket and not worry about fares until the card is used up. Note that the BART vending machines accept any credit card only twice within any 24 hour period. Trains run about every 10-20 minutes starting around 6AM and closing just after midnight.
Why is the Bay Area so busy?
The Bay Area, partly because of it being nestled between hills and rugged terrain, has lots of major freeways and intersections in the busy and often congested parts of the area, especially in the East Bay, San Francisco, and the Peninsula. So, driving can often get confusing, the freeways and even the inner streets can get crowded, and many of the local drivers tend to be more aggressive. Thus, minor car crashes can be quite common, especially on the major bridges during rush hours. Remember to plan your route well and always drive defensively. The busy areas also often have police officers patrolling the freeways and intersections, and almost always give tickets to those who violate traffic laws.
What is Silicon Valley?
Silicon Valley — a shorthand for the computer industry as much as a meta-region within the Bay Area, comprising parts of the South Bay and southern Peninsula.
What cities are in the San Francisco Bay Area?
South of the Peninsula and the East Bay, includes most of Santa Clara County, and is anchored by the most populous city in the Bay Area, San Jose .
How hot is the East Bay?
The weather in the Bay Area is affected by microclimates, so certain parts of East Bay can be up to 15 degrees warmer than downtown San Francisco, and as much as 20 degrees warmer than the area around the Golden Gate bridge.
What is the Bay Area?
The Bay Area (more fully, the San Francisco Bay Area ), ringing the San Francisco Bay in northern California, is a geographically diverse and extensive metropolitan region that is home to over 7 million inhabitants in cities such as San Francisco, Oakland, and San Jose. Once a focus of Spanish missions and Gold Rush prospectors, ...
Where is Amtrak in California?
Amtrak, +1 800 872-7245, [1] serves the Bay Area with long-distance and intercity trains. Two long distance trains, the California Zephyr [2] to Chicago and the Coast Starlight [3] between Seattle and Los Angeles, serve the Bay Area with stations in Martinez and Emeryville, with the Coast Starlight also stopping at Oakland's Jack London Square Station and San Jose. From Emeryville, passengers may take an Amtrak California [4] Thruway bus over the Bay Bridge to San Francisco's Amtrak stop at 101 The Embarcadero (near the Ferry Building) and usually several other downtown destinations (note that Amtrak passengers are not subjected to any extra charge for the bus).
What is California cuisine?
You might think California cuisine - the organic, local, farm-to-table goods served at Chez Panisse or The French Laundry. Or you might think of dishes made by the many immigrant groups that have made this place home - lumpia, hand-pulled noodles, injera or tikka masala. Once you start to think about it, there is no one taste of the Bay Area. It’s our diversity that defines us.
How many counties are there in the Bay Area?
For now, easiest to stick with the nine county definition, but if we’re looking at the Bay Area as a cultural place it’s pretty hard to put a border on that.
What are the cities in the Bay Area?
Part of what makes the Bay Area hard to define is that we have three central cities -- Oakland, San Jose and San Francisco.
Where are the commuters in the Bay Area?
Looking at a map of Bay Area commutes, you’ll see well-worn commute routes extend ing to Stockton, Modesto, Santa Cruz and even Sacramento. Even if they don’t live within the traditional boundaries, these commuters are part of the Bay Area fabric.
When did San Francisco Bay Area start?
References to the term “The San Francisco Bay Area” first show up on maps in the early 1900s. But the borders weren’t consistent, and some references included Santa Cruz and San Joaquin counties.
Who is the Italian astronaut on the International Space Station?
An image of the San Francisco Bay Area taken by Samantha Cristoforetti, an Italian crew member aboard the International Space Station. ( Samantha Cristoforetti via Twitter)
Is everyone in the same step with the same values?
Of course, not everybody is in step with the same politics or environmental values.
What does SHADING mean in California?
NOTE: Shading represents the share of unregistered Californians who lean Democratic minus the share who lean Republican. Estimates come from multilevel regression and poststratification models as described in Technical Appendix A. Full model results can be found in Technical Appendix B.
Why are Californians not registered to vote?
Many California adults are not registered to vote, generally because they have not taken the necessary steps or because they are not citizens and so are not eligible . PPIC’s work on the “exclusive electorate” has shown that these unregistered Californians have different policy views than those who are part of the electorate, especially in favoring a larger and more active government (Baldassare et al. 2019). PPIC has asked unregistered Californians (including noncitizens who cannot legally register to vote) which party they lean toward, and they lean Democratic in virtually every part of the state (Figure 5).
What does the line above the unregistered mean?
Points below that line indicate places where the unregistered lean more Republican on average, and points above the line indicate places where the unregistered lean more Democratic on average.
How many people support gun control in California?
About two-thirds of Californians (68%) have supported stricter gun control laws over the past two years of PPIC Statewide Surveys. Figure 11 shows that this strong overall support masks an extremely sharp geographic divide. In the rural places in the far north and east of the state, support for stricter gun laws falls below 40 percent. In most of the remaining rural areas-along the north coast, the southern San Joaquin Valley, and the Mojave Desert, support falls short of a majority. But support is above 70 percent in most of the Bay Area and all of LA County, and it exceeds 80 percent in the three liberal enclaves of central LA, the East Bay, and San Francisco.
How many places are there in California?
We define the political geography of California through 46 “places’ (see technical appendix Figure A1 ). Most state representation is based in physical locations, so it matters how opinion differs from one location to the next. We can sometimes approximate opinion with government data; for instance, the Democratic share of the vote for president can indicate partisan lean in a particular location. However, there are many politically important questions that public government sources cannot answer.
What is public opinion?
Public opinion is about more than party support; a range of issues animates the state’s politics, and those issues may not link perfectly to party loyalties. A few issue questions have been asked often enough in recent PPIC Statewide Surveys to permit detailed mapping in our places. As with the questions about party strength, we draw on surveys from the last two years, but because these questions are not asked as often we generally have fewer surveys to work with.
What are the questions asked in the California debate?
These include three questions about the size and scope of government: opinions about one’s own tax burden, concern about the state budget, and favorability toward the Affordable Care Act (ACA). Three questions address immigration: abstract feelings about the value of immigrants to California, attitudes about whether California should take action to protect undocumented immigrants, and support for President Trump’s border wall with Mexico. Finally, we review two questions about issues at the top of public discussion: feelings about housing affordability and support for gun control. For our purposes, what is interesting about these questions is how they map onto the state’s geography. Some questions, such as gun control, produce sharp geographic divisions while others, such as feelings about one’s tax burden, do not.
Overview
Boundaries
The borders of the San Francisco Bay Area are not officially delineated, and the unique development patterns influenced by the region's topography, as well as unusual commutepatterns caused by the presence of three central cities and employment centers located in various suburban locales, has led to considerable disagreement between local and federal definitions of the area. …
History
The earliest archaeological evidence of human habitation of the Bay Area dates to around 10,000 B.C. (Coyote Hills Shell Mound) along the shores of the bay, with evidence pointing to even earlier settlement in Point Reyes in Marin County. The Miwokan and Costanoan Ohlone people, who were living in the Bay Area at the time of first European contact, were possibly descended from Siberiantribe…
Geography
The Bay Area is located in the warm-summer Mediterranean climate zone (Köppen Csb) that is a characteristic of California's coast, featuring mild to cool winters with occasional rainfall, and warm to hot, dry summers. It is largely influenced by the cold California Current, which penetrates the natural mountainous barrier along the coast by traveling through various gaps. In term…
Demographics
According to the 2010 United States Census, the population of the nine-county Bay Area was 7.15 million, with 49.6% male and 50.4% female. Of these, approximately 2.3 million (32%) are foreign born. In 2010 the racial makeup of the nine-county Bay Area was 52.5% White (42.4% were non-Hispanic and 10.1% were Hispanic), 23.3% Asian, 6.7% non-Hispanic Black or African American, 0.7% Native …
Economy
The three principal cities of the Bay Area represent different employment clusters and are dominated by different, but commingled, industries. San Francisco is home to the region's financial industry, tourism, and is host to numerous conventions. The East Bay, centered around Oakland, is home to heavy industry, metalworking, oil, and shipping, while San Jose is the heart of …
Housing
The Bay Area is the most expensive place to live in the United States. Strong economic growth has created hundreds of thousands of new jobs, but coupled with severe restrictions on building new housing units, has resulted in an extreme housing shortage. For example, from 2012 to 2017, the San Francisco metropolitan area added 400,000 new jobs, but only 60,000 new housing units…
Education
The Bay Area is home to a large number of colleges and universities. The three most notable universities are Stanford University, University of California, Berkeley, and University of California, San Francisco, all considered among the most prestigious universities in the world. The first institution of higher education in the Bay Area, Santa Clara University, was founded by Jesuitsin 18…
What’s Valuable About The Nine-County Definition of The Region?
What About Related Activity Outside The Nine Counties?
- Because many of the region’s patterns extend outside the nine counties, it’s important to look at what’s happening beyond this boundary. 1. The Bay Area is part of an emerging Northern California megaregion that combines several adjacent metropolitan regions. Many of the important factors that shape life in the Bay Area — including water and energy...
Should We Use Different Regional Geographies For Different Issues?
- As the following examples show, in some situations it’s critical to map complete systems, instead of using the data contained in a pre-ordained set of counties. 1. Commutes reveal the geographic spread of our economic patterns. SPUR’s research and conversations with stakeholders showed that population and commute patterns are the strongest way to track human-based geographies…
Conclusion
- The spatial patterns explored above extend — and have meaning — across different geographies. All represent systems that are regional in nature and critical to life in the Bay Area. With this understanding, SPUR arrived at the following decisions: 1. The SPUR Regional Strategy will focus most deeply on the nine-county Bay Area, which remains important for the region’s identity and g…