How many arteries are in circle of Willis?
The circle of Willis is a group of blood vessels in the brain that connect with each other, forming a continuous structure that resembles a circle. These nine arteries supply blood to a large portion of the brain. Most of the time, blood can flow through the vessels of the circle of Willis without any interruption.
What structures form the circle of Willis?
The structure of the circle of Willis includes:left and right internal carotid arteries.left and right anterior cerebral arteries.left and right posterior cerebral arteries.left and right posterior communicating arteries.basilar artery.anterior communicating artery.
Which arteries form the circle of Willis quizlet?
The specialized collateral circulation of the brain is referred to as the cerebral arterial circle or circle of Willis. It is formed by anatomoses between the internal carotid arteries and the vertebral arteries.
Which two pairs of arteries bring blood to the circle of Willis?
At the base of the brain, the carotid arteries and vertebral arteries come together to form the Circle of Willis. This is a circle of arteries that pro- vide many paths for blood to supply oxygen and nutrients the brain. From the Circle of Willis, major arteries arise and travel to all parts of the brain.
Which arteries are not part of the circle of Willis?
The basilar artery and middle cerebral arteries, though they supply the brain, are not considered part of the circle.
Is middle cerebral artery part of circle of Willis?
The MCA is part of the circle of Willis anastomotic system within the brain, which forms when the anterior cerebral arteries anastomose anteriorly with each other through the anterior communicating artery and posteriorly with the two posterior communicating arteries bridging the MCA with the posterior cerebral artery ...
What makes up the circle of Willis quizlet?
What is the Circle of Willis? It is a network of arteries that supplies the brain ,brain stem, & the SC w/arterial blood. T or F, if an occlusion occurs w/n the Circle of Willis, the brain can still get blood.
Which of the following arteries supply blood to the brain quizlet?
Blood is supplied to the brain, face, and scalp via two major sets of vessels: the right and left common carotid arteries and the right and left vertebral arteries.
Why is the circle of Willis important quizlet?
The circle of willis is an important means of collateral circulation in the event of gradual obstruction of one of the major arteries forming the circle. Sudden occlusion, even in only partial, results in neurological deficits.
What are the 4 main arteries supplying the brain?
The brain receives blood from two sources: the internal carotid arteries, which arise at the point in the neck where the common carotid arteries bifurcate, and the vertebral arteries (Figure 1.20). The internal carotid arteries branch to form two major cerebral arteries, the anterior and middle cerebral arteries.
What are the two main arteries that supply the head?
Carotid Artery. There are two carotid arteries in the neck — one on either side. They supply essential blood and oxygen to the brain and head. Carotid artery disease is a common but serious condition affecting the carotid arteries.
How do you remember the circle of Willis?
0:003:08MNEMONIC Brain's Blood Supply: MEMORIZE in 3 Minutes - YouTubeYouTubeStart of suggested clipEnd of suggested clipOther blood vessels hence the Circle of Willis is the spirit bowl appearing on top of the meditatingMoreOther blood vessels hence the Circle of Willis is the spirit bowl appearing on top of the meditating cow's head as well as the meditating cows horns.
What two structure does circle of Willis surround?
The circle of Willis surrounds the optic tracts, pituitary stalk, and basal hypothalamus. It includes the three sets of paired cerebral arteries plus the anterior communicating artery, interconnecting the ACAs, and the posterior communicating arteries, interconnecting the MCAs and PCAs.
Why is the circle of Willis an important structure?
The circle of Willis acts to provide collateral blood flow between the anterior and posterior circulations of the brain, protecting against ischemia in the event of vessel disease or damage in one or more areas.
Is the circle of Willis in the subarachnoid space?
Circle of Willis lies in subarachnoid space within the deep interpeduncular cistern. Anterior communicating arteries in the circle of Willis is derived from Anterior cerebral artery.
What part of the circle of Willis is the most common site of aneurysm?
anterior communicating arteryMost cerebral aneurysms are found at predictable locations around the circle of Willis; the three most common are the junction of the anterior communicating artery with the anterior cerebral artery (30% to 35%), the posterior communicating artery at the junction with the internal carotid artery (30% to 35%), and the ...
Which arteries are not part of the circle of Willis?
Internal carotid artery (left and right) Posterior cerebral artery (left and right) Posterior communicating artery (left and right) The middle cerebral arteries, supplying the brain, are not considered part of the circle of Willis.
Which artery forms the anterolateral portion of the circle of Willis?
The anterior cerebral artery forms the anterolateral portion of the circle of Willis, while the middle cerebral artery does not contribute to the circle. The right and left posterior cerebral arteries arise from the basilar artery, which is formed by the left and right vertebral arteries. The vertebral arteries arise from the subclavian arteries .
What is the redundancy of the circle of Willis?
Subclavian steal syndrome. The redundancies that the circle of Willis introduce can also lead to reduced cerebral perfusion. In subclavian steal syndrome , blood is "stolen" from the circle of Willis to preserve blood flow to the upper limb.
Why is the circle of Willis important?
The arrangement of the brain's arteries into the circle of Willis is believe d to create redundancy (analogous to engineered redundancy) for collateral circulation in the cerebral circulation. If one part of the circle becomes blocked or narrowed ( stenosed) or one of the arteries supplying the circle is blocked or narrowed, blood flow from the other blood vessels can often preserve the cerebral perfusion well enough to avoid the symptoms of ischemia.
Which cerebral artery supplies the cerebrum?
In one common variation the proximal part of the posterior cerebral artery is narrow and its ipsilateral posterior communicating artery is large, so the internal carotid artery supplies the posterior cerebrum; this is known as a fetal posterior communicating cerebral artery.
Which artery connects the two anterior cerebral arteries?
The vertebral arteries arise from the subclavian arteries . The anterior communicating artery connects the two anterior cerebral arteries and could be said to arise from either the left or right side. All arteries involved give off cortical and central branches. The central branches supply the interior of the circle of Willis, more specifically, ...
What is the circle of Willis?
Anatomical terminology. The circle of Willis (also called Willis' circle, loop of Willis, cerebral arterial circle, and Willis polygon) is a circulatory anastomosis that supplies blood to the brain and surrounding structures in reptiles, birds and mammals, including humans.
What is the circle of Willis?
Cerebral arterial circle (Circulus arteriosus cerebri) The circle of Willis ( cerebral arterial circle or circulus arteriosus) is an anastomotic ring of arteries located at the base of the brain. This arterial anastomotic circle connects the two major arterial systems to the brain, the internal carotid arteries and the vertebrobasilar ...
Where is the circle of Willis located?
The circle of Willis is located on the inferior surface of the brain within the interpeduncular cistern of the subarachnoid space. It encircles various structures within the interpeduncular fossa (depression at the base of the brain) including the optic chiasm and infundibulum of the pituitary gland.
What is the posterior arc of the circle of Willis?
Posterior arc of the circle of Willis. The posterior arc of the circle of Willis is formed by the posterior cerebral arteries (PCA), on each side, and the posterior communicating arteries (PComm), which connect the posterior cerebral arteries to their ipsilateral internal carotid arteries.
Why is the circle of Willis restricted?
This is due to significant variations in the size of component arteries that limit the normal flow of blood through these regions.
Which arteries supply the occipital lobe of the brain?
The vertebral arteries, basilar artery, posterior cerebral arteries, together with the PComm form the posterior cerebral circulation. The posterior cerebral arteries through their central and cortical branches supply the occipital lobe of the brain, the inferior aspect of the temporal lobes , midbrain, thalamus and choroid plexus of the third and lateral ventricles.
Where are the perforated arteries located?
Several small perforating (central) arteries emerge from the circle of Willis, many of which pass into the brain through the anterior and posterior perforated substances, which are areas of grey matter located at the basal forebrain and the interpeduncular fossa respectively.
Which arteries are paired with the posterior cerebral arteries?
The basilar artery then bifurcates into the paired posterior cerebral arteries at the superior border of the pons . The vertebral arteries, basilar artery, posterior cerebral arteries, together with the PComm form the posterior cerebral circulation.
Which arteries run along the circle of Willis?
The left and right anterior cerebral arteries (ACAs): These vessels run along the sides of the circle of Willis. The left and right internal carotid arteries (ICAs): The ICAs travel in the front of the neck, through the carotid canal, to enter into the brain.
Where is the circle of Willis located?
Location. The circle of Willis is located deep in the center of the brain, near two other important structures—the pituitary gland and the optic chiasm. It's often described as being located at the base of the brain because it lies in the inferior (lower) surface of the brain.
Why is the circle of Willis shaped like a hexagon?
Although it has nine sides, the circle of Willis is shaped more like a hexagon because the ICAs are very short and the two PCAs are almost straight.
What is the effect of an aneurysm on the optic chiasm?
An aneurysm in the circle of Willis can impinge on the optic chiasm, which may impair vision in one or more visual fields. It can also place pressure on the pituitary stalk (a part of the pituitary gland), disturbing its function. 3
What is the unique feature of the circle of Willis?
One of the unique features of the circle of Willis is that its continuous structure creates a redundant blood supply in the brain. 2 What this means is that the ACOM and PCAs, which do not directly send blood to the brain, connect the ACAs and the ICAs—arteries that directly send blood to the brain.
What is the function of the circle of Willis?
Function. Associated Conditions. Rehabilitation. The circle of Willis is a group of blood vessels in the brain that connect with each other , forming a continuous structure that resembles a circle. These nine arteries supply blood to a large portion of the brain. Most of the time, blood can flow through the vessels of the circle ...
Which arteries provide blood to the brain?
Several of the arteries of the circle of Willis branch into smaller vessels that directly provide blood to the brain.
What are the arteries in the Circle of Willis?
The Circle of Willis is a wreath of interconnected arteries that surrounds the optic chiasm, the tuber cinereum, and the region between the cerebral peduncles at the ventral surface of the diencephalon. It is formed by anastomotic branches of the two ICAs, the horizontal (A1) segments of the ACAs, ACommA, the two PCommAs, the horizontal segments (P1) of both PCAs, and the BA (Figure 2 ). Penetrating vessels from the arteries of the Circle of Willis supply structures within its wreath, such as the optic chiasm and hypothalamus.
What is the circle of Willis?
The circle of Willis consists of an arterial network located at the skull base allowing arterial blood flow exchange between the anterior and the posterior circulation, and between the right and left hemispheres. Several imaging techniques may be useful to provide anatomical information of the main branches of the circle of Willis including digital subtraction angiography (DSA), Doppler ultrasound, magnetic resonance (MR) angiography, and computed tomography angiography. Each technique has its own advantages and limitations but due to the invasive nature of conventional angiography, which was the method of reference in the past, the current tendency is to combine several noninvasive imaging modalities such as Doppler ultrasound and MR angiography.
What is MR angiogram?
MR angiogram may depict the presence of a vessel segment with a diameter of at least 1 mm and is widely used for the detection of intracranial aneurysms of the circle of Willis.
Where are berry aneurysms most likely to occur?
The most likely site of these berry aneurysms is at the junctions of arteries in the circle of Willis.
What is the gold standard for vascular anatomy?
Conventional angiography is considered the gold standard for evaluating vascular anatomy ( Fig. 1 ). This technique requires anesthesia, a femoral arterial approach, a selective catheterism of supra-aortic vessels by using a catheter, and the administration of iodinated contrast material for each selective view.
What imaging techniques are used to determine the anatomical structure of the circle of Willis?
Several imaging techniques may be useful to provide anatomical information of the main branches of the circle of Willis including digital subtraction angiography (DSA), Doppler ultrasound, magnetic resonance (MR) angiography, and computed tomography angiography.
Which cerebral artery is associated with an aneurysm?
For example, atresia of one proximal anterior cerebral artery may be associated with an aneurysm on the opposite, or dominant, anterior cerebral artery. The most common sites are the anterior communicating, posterior communicating, and middle cerebral arteries, depending on the particular study population.
What vessels form the circle of Willis?
Vessels comprising the circle of Willis include: The basilar artery divides at the upper border of the pons to form the left and right PCAs. From each ICA, a PCOM arises at the anterior perforated substance and runs back through the interpeduncular cistern to join the ipsilateral PCA. Each ICA also gives off an ACA.
What is the circle of Willis?
The Circle of Willis is an arterial polygon (heptagon) formed as the internal carotid and vertebral systems anastomose around the optic chiasm and infundibulum of the pituitary stalk in the suprasel lar cistern. This communicating pathway allows equalization of blood-flow between the two sides of the brain, and permits anastomotic circulation, ...
Which artery supplies the brainstem and cerebellum?
It courses through the hypoglossal canal, parallel to the nerve, connecting the cervical ICA with the basilar artery. When present, it is functionally a single artery that supplies the brainstem and cerebellum (often associated with aneurysms). persistent otic (acoustic) artery. persistent proatlantal artery.
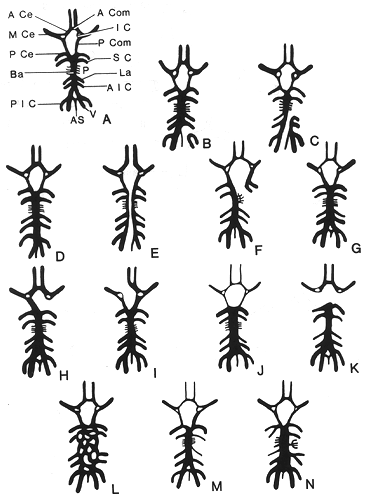
What percentage of individuals have a complete circle of Willis?
A complete circle of Willis (in which no component is absent or hypoplastic) is only seen in 20-25% of individuals. Posterior circulation anomalies are more common than anterior circulation variants and are seen in nearly 50% of anatomical specimens.
Which structures are supplied by the Branches of the Circle of Willis?
Branches of the circle of Willis also supply the optic chiasm and tracts, infundibulum, hypothalamus and other structures at base of brain:
Where is the Circulus Arteriosus Cerebri buried?
He died in 1675 from pleurisy and his remains are buried at Westminster Abbey in London, UK.
Who is the founder of the circle?
History and etymology. It is named after the English physician Thomas Willis (1621–1675), who first described the anatomy of his circle in 1664 in his book "Cerebri anatome: cui accessit nervorum descriptio et usus" (The Anatomy of the Brain and Nerves). He called his discovery the "circulus arteriosus cerebri".

Overview
Structure
The circle of Willis is a part of the cerebral circulation and is composed of the following arteries:
• Anterior cerebral artery (left and right)
• Anterior communicating artery
• Internal carotid artery (left and right)
Function
The arrangement of the brain's arteries into the circle of Willis is believed to create redundancy (analogous to engineered redundancy) for collateral circulation in the cerebral circulation. If one part of the circle becomes blocked or narrowed (stenosed) or one of the arteries supplying the circle is blocked or narrowed, blood flow from the other blood vessels can often preserve the cerebral perfusion well enough to avoid the symptoms of ischemia.
Clinical significance
The adaptive flow that the circle of Willis introduces can also lead to reduced cerebral perfusion. In subclavian steal syndrome, blood is "stolen" from the vertebral artery on the affected side to preserve blood flow to the upper limb. Subclavian steal syndrome results from a proximal stenosis (narrowing) of the subclavian artery, one of arteries originating off of the aortic arch. Subclavian steal syndrome has potential to affect flow in the circle of Willis.
Additional images
• Fetal ultrasound image at the level of circle of Willis, showing PCA, MCA and ACA
• Cerebral angiogram showing an anterior/posterior projection of the vertebrobasilar and posterior cerebral circulation, the posterior aspect of the circle of Willis, and one of its feeding vessels
• An anterior view of major cerebral and cerebellar arteries.
See also
• Cerebral circulation
• Leptomeningeal collateral circulation
External links
• Bergman, Ronald A.; Afifi, Adel K.; Miyauchi, Ryosuke. "Fourteen Variations of Circle of Willis and Related Vessels". Illustrated Encyclopedia of Human Anatomic Variation: Opus II: Cardiovascular System.