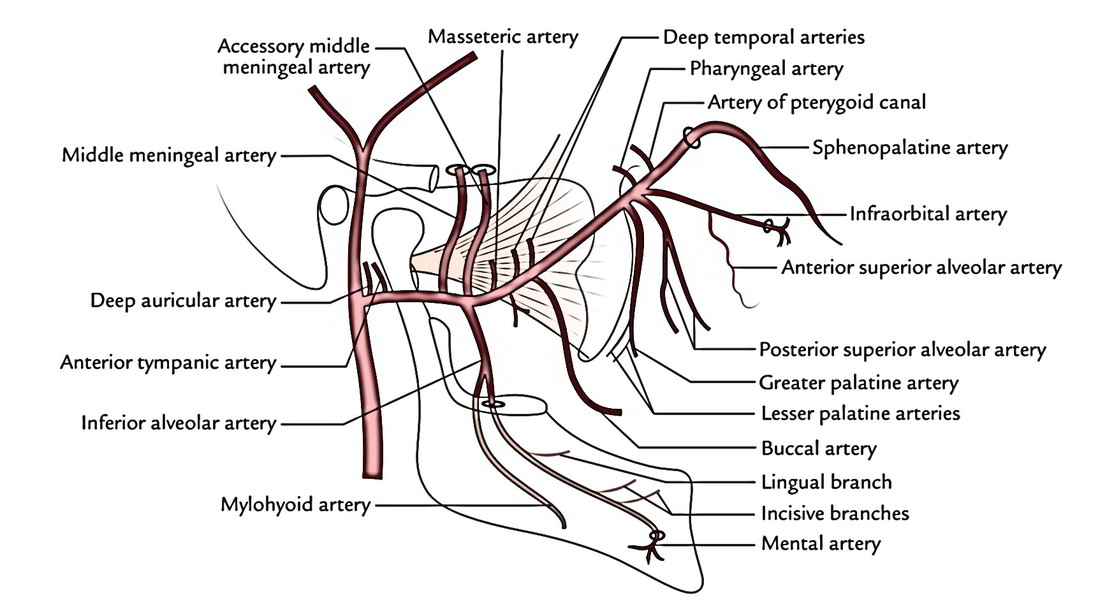
Where does the blood supply to the muscles of mastication originate?
Its blood supply is derived from the masseteric artery, which emerges from the maxillary artery.
Which of these nerves supplies the muscles of mastication?
the trigeminal nerve17 The muscles of mastication are innervated by the mandibular branch of the trigeminal nerve (CN V) except for the caudal belly of the digastricus muscle, which is innervated by the facial nerve (CN VII).
What artery supplies the medial pterygoid muscle?
maxillary arteryThe medial pterygoid muscle receives vascular supply from the maxillary artery through its pterygoid branches and by the facial artery through its muscular branches. The pterygoid branches of the maxillary artery are 2 or 3 in number.
Which nerve innervates the muscles of mastication quizlet?
The muscles of mastication are innervated by the mandibular division of cranial nerve V (trigeminal).
Which nerve innervates the muscles of mastication and facial sensation?
trigeminal nervesSensation on the face is innervated by the trigeminal nerves (V) as are the muscles of mastication, but the muscles of facial expression are innervated mainly by the facial nerve (VII) as is the sensation of taste.
What are the four muscles of mastication?
MusclesTemporalis Muscle. The temporalis muscle is a fan-shaped muscle with anterior fibers that have a vertical orientation, mid fibers have an oblique orientation, and posterior fibers have a more of a horizontal orientation. ... Medial Pterygoid. ... Lateral Pterygoid. ... Masseter. ... Accessory Muscles of Mastication.
What nerve Innervates Pterygoid muscle?
the trigeminal nerveThe lateral pterygoid muscle receives innervation from the mandibular branch of the trigeminal nerve. The main trunk of the mandibular nerve divides into the anterior and the posterior division.
What Innervates Pterygoid muscle?
The medial pterygoid muscle is innervated by the medial pterygoid branch of the mandibular division of the trigeminal nerve (CN V3). It receives blood supply from the pterygoid branches of the maxillary artery. The bilateral contraction of this muscle elevates the mandible and closes the mouth.
Which cranial nerve innervates the muscles of mastication?
Mandibular Nerve (V3) The mandibular nerve is the only branch of the trigeminal nerve that has both sensory and motor components. The motor component innervates all of the muscles of mastication (enumerated below).
What are the muscles of mastication quizlet?
There are four muscles of mastication - the masseter, temporalis, medial pterygoid and lateral pterygoid.
What are the trigeminal nerves?
The trigeminal nerve is the part of the nervous system responsible for sending pain, touch and temperature sensations from your face to your brain. It's a large, three-part nerve in your head that provides sensation. One section called the mandibular nerve involves motor function to help you chew and swallow.
Where is the mandibular nerve located?
The mandibular nerve is the only branch of the trigeminal nerve that contains a motor root. In the infratemporal fossa, near the skull base, the main trunk immediately gives off the sensory meningeal branch and motor muscular branches to the medial pterygoid, tensor tympani, and tensor veli palatini muscles.
What are the muscles of mastication?
The muscles of mastication are a group of muscles responsible for the chewing movement of the mandible at the temporomandibular (TMJ) joint , they enhance the process of eating, they assist in grinding food, and also function to approximate the teeth. The four main muscles of mastication originate from the surface of the skull and they attach onto the rami of the mandible at the TMJ. The movement performed by these muscles are elevation, depression, protrusion, retraction, and side to side movement. Three out of the main muscles are responsible for adduction of the mandible and one helps in the abduction of the mandible.
What is masticatory myofascial pain?
Masticatory Myofascial pain- Mastication muscle pain disorders are similar to other skeletal muscle disorders in other parts of the body. It is characterized by a dull regional ache with the presence of trigger points when palpated which produces referred pain, that increases during the function.
What muscle is responsible for depression of the mandible?
Its blood supply is from the pterygoid branch of 2nd part of the maxillary artery. Function[edit| edit source] The lateral pterygoid muscle functions as the sole muscle of mastication to causes depression of the mandible. This being the case, depression of the mandible is largely the result of gravity.
How to test masseter?
Masseter can be easily tested by having the patient clench the jaw and evaluating the volume and firmness of the muscles. The other muscle of mastication supplied by the trigeminal nerve, the pterygoids are examined by having the patient move the jaw from the side against resistance, and protrude the jaw.
What muscles are involved in the abduction of the mandible?
The movement performed by these muscles are elevation, depression, protrusion, retraction, and side to side movement . Three out of the main muscles are responsible for adduction of the mandible and one helps in the abduction of the mandible.
Which muscle of mastication is examined by having the patient move the jaw from the side against resistance?
The other muscle of mastication supplied by the trigeminal nerve, the pterygoids are examined by having the patient move the jaw from the side against resistance, and protrude the jaw. Contraction of each muscle causes deviation of the jaw to the opposite side so that the weakness of the pterygoid muscles would cause deviation of the open jaw to the ipsilateral side .
Which nerve innervates the muscles of facial expression?
Unlike the muscles of facial expression that are innervated by the facial nerve(CN VII), the muscles of mastication are innervated by motor branches of the mandibular division of the trigeminal nerve(CNV3), while the main arterial supply is derived from branches of the maxillary artery. Description[edit| edit source]
Which artery supplies the muscles of mastication?
Blood Supply and Lymphatics. The arterial supply to the muscles of mastication is via the maxillary artery, a branch of the external carotid artery. Nerves. The four main muscles of mastication are all innervated by the anterior trunk of the mandibular nerve, which is the third division of the trigeminal nerve (CN V3).
What muscles are involved in mastication?
The primary muscles of mastication (chewing food) are the temporalis, medial pterygoid, lateral pterygoid, and masseter muscles. The four main muscles of mastication attach to the rami of the mandible and function to move the jaw (mandible). The cardinal mandibular movements of mastication are elevation, depression, protrusion, retraction, ...
What muscle is used during mastication in macaques?
Jaw muscle function and wishboning of the mandible during mastication in macaques and baboons. [Am J Phys Anthropol. 1994]
What are the primary and accessory muscles of mastication?
Muscles. The primary and accessory muscles of mastication work in a coordinated fashion to produce mandibular movement for chewing food. The accessory muscles of mastication are the buccinator, suprahyoid muscles (digastric muscle, mylohyoid muscle, and geniohyoid muscle), and infrahyoid muscles (the sternohyoid, sternothyroid, ...
Which muscle receives innervation from the mandibular nerve?
The temporalis muscle receives innervation by deep temporal branches of the mandibular nerve. The medial pterygoid muscle receives innervation from the medial pterygoid nerve, a division of the mandibular nerve.
Where does the lateral pterygoid muscle get its nerve supply?
The lateral pterygoid muscle gets its nerve supply from the lateral pterygoid nerves, divisions of the mandibular nerve. The masseter muscle receives nerve input from the masseteric nerve, a division of the mandibular nerve. [2] Muscles. The primary and accessory muscles of mastication work in a coordinated fashion to produce mandibular movement ...
What muscles are used to raise the hyoid bone?
The strap muscles are composed of the suprahyoid, and infrahyoid muscles are located on the side of the neck bilaterally. The strap muscles primarily function to raise and depress the hyoid bone and larynx. The strap muscles also assist with depression of the mandible when opening the mouth against an opposing force. The buccinator is a facial expression muscle that helps in mastication by keeping food pushed back within the oral cavity. [1][3]
What muscles are used in mastication?
The Lateral Pterygoid, Masseter muscle, Medial Pterygoid and the Temporalis are the main muscles taking part in the process of mastication.
Which muscle is occupied by the medial pterygoid muscle?
Medial Pterygoid Muscle. The infratemporal fossa is occupied by the medial and lateral pterygoid muscles. A portion of the ramus of the mandible has to be removed to see them. The medial pterygoid muscle and the masseter muscle are exactly similar.
What muscle is the ramus of the mandible?
A majority of the the ramus of the mandible is covered by this quadrilateral muscle. As a single anterior border, this muscle is a blend of a superficial and a deep portion.
Which muscle inserts into the medial aspect of the mandible’s the coronoid process?
The temporalis muscle inserts into the medial aspect of the mandible’s the coronoid process.
Where does the medial pterygoid originate?
Origin of Medial Pterygoid. The medial pterygoid muscles originate from the lateral pterygoid plate of sphenoid bone with few of its fibers arising from the maxillary tuberosity.
Where does the superficial portion of the muscle originate?
The superficial portion of the muscle originates from the the zygomatic process of the maxilla and the deep portion originates from the the zygomatic arch.
Where are the fibers inserted in the mandibular ramus?
The fibers are inserted into the mandibular ramus while running downward, backward and even slightly laterally.
Masseter
This muscle composes of two main parts: the deep and superficial heads.¹
Temporalis
This large, fan-shaped muscle is located on the lateral aspect of the skull.
Lateral pterygoid
This muscle lies mostly superficial to the medial pterygoid and comprises of superior and inferior sections .¹
Which muscles assist in mastication?
Buccinator and suprahyoid muscle s assist in mastication and are termed as accessory muscles of mastication.
What are the main muscles of mastication?
There are 4 pairs of main muscles of mastication viz. Temporalis. Medial pterygoid. Lateral pterygoid. Masseter. All the main muscles of mastication are attached to the ramus of mandible are main muscles of mastication.
What is the name of the branch of the mandibular nerve that supplies the nerves?
Nerve supply: Is by deep temporal branches of anterior division of mandibular nerve.
What is the name of the branch from the mandibular nerve?
Nerve Supply: By nerve to medial pterygoid, a branch from trunk of mandibular nerve.
Which muscle produces side to side movement of the mandible?
Action: It depresses and protrudes the mandible. Along with medial pterygoid muscle produces side to side movement of mandible. Nerve Supply: It is supplied by a branch from anterior division of mandibular nerve.
Which muscle is supplied by the mandibular nerve?
All the main muscles are supplied by branches of mandibular nerve. Medial pterygoid is supplied by a branch from the trunk of mandibular nerve and others are supplied by branches from the anterior division of mandibular nerve. Buccinator and suprahyoid muscles assist in mastication and are termed as accessory muscles of mastication.
Where is the insert on the mandible?
Insertion: It is inserted on rough area on the medial surface of angle of mandible.

Introduction and Overview
- The muscles of mastication are a group of muscles responsible for the chewing movement of the mandible at the temporomandibular (TMJ) joint, they enhance the process of eating, they assist in grinding food, and also function to approximate the teeth. The four main muscles of mastication originate from the surface of the skull and they attach onto t...
Muscles of Mastication
- The muscles of mastication can be divided into the primary muscles and secondary or accessory muscles . 1. The primary muscles include: 1.1. Masseter 1.2. Temporalis 1.3. Lateral pterygoid 1.4. Medial pterygoid 2. The secondary or accessory muscles are: 2.1. Buccinator 2.2. Suprahyoid muscles (digastric muscle, mylohyoid muscle, and geniohyoid muscle) 2.3. Infrahyoid muscles(t…
Masseter
- It is a rectangular muscle that covers most of the lateral aspect of the ramus. It consists of three layers that blend anteriorly: the superficial layer, intermediate layer, and deep layer.
Temporalis
- It is a fan-shaped muscle that fills the temporal fossa, with anterior fibres that have a vertical orientation, mid fibres have an oblique orientation, and posterior fibres have more of a horizontal orientation.
Medial Pterygoid
- The medial pterygoid muscle is a thick rectangular muscle with a superficial head and a deep head. The deep head of the medial pterygoid is larger than the superficial head.
Clinical Relevance
- Masticatory Myofascial pain- Mastication muscle pain disorders are similar to other skeletal muscle disorders in other parts of the body. It is characterized by a dull regional ache with the presen...
Assessment
- Evaluation of the muscles of mastication forms part of the assessment of the trigeminal nerve (CN III).
- Masseter can be easily tested by having the patient clench the jaw and evaluating the volume and firmness of the muscles.