What is the conoid tubercle?
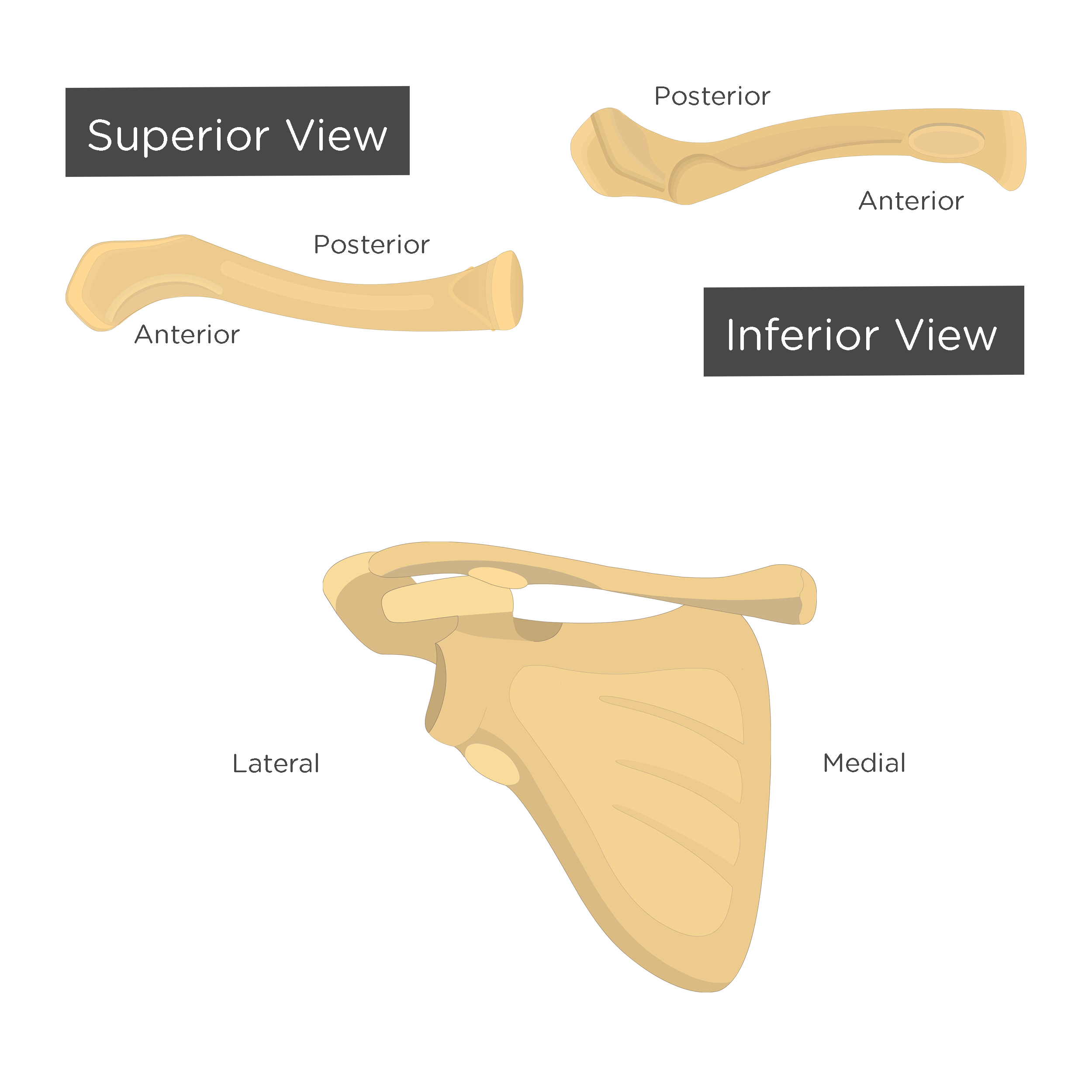
The conoid tubercle also known as the coracoid tuberosity (not to be confused with the coracoid process of the scapula) is a bony prominence on the inferior surface of the lateral third of the clavicle . It marks the insertion of the conoid ligament (which along with the trapezoid ligament) forms part of the coracoclavicular ligament complex.
What is the difference between conoid tubercle and costoclavicular ligament?
It is distinguished as a broad rough surface over 2 cm in length, and is the site where costoclavicular ligament attaches. The conoid tubercle, which is found more laterally towards the acromial end.
What attaches to the glenoid tubercles?
The glenoid tubercles serves as attachment points for the long heads of the biceps brachii and the triceps brachii muscles. What attaches to the greater tubercle of the humerus?
What is the conoid tuberosity of clavicle?
A.Prof Frank Gaillard ◉ ◈ et al. The conoid tubercle also known as the coracoid tuberosity (not to be confused with the coracoid process of the scapula) is a bony prominence on the inferior surface of the lateral third of the clavicle.
:watermark(/images/watermark_only.png,0,0,0):watermark(/images/logo_url.png,-10,-10,0):format(jpeg)/images/anatomy_term/conoid-tubercle/tajx3Q0ECs5DhflS9QkA_Conoid_tubercle_02.png)
What muscles attaches to the conoid tubercle?
triceps brachii muscle.anconeus muscle.articularis cubiti muscle.
What is the function of the conoid tubercle?
Conoid tubercle (tuberculum conoide-um) is a bump on the inferior surface of the bone, near the acromial end. It is an attachment point for the conoid ligament. The conoid ligament is a part of the coracoclavicular ligament, which attaches the clavicle to the coracoid process of the scapula.
Which bone contains the conoid tubercle?
The conoid tubercle is found on the lateral end (acromial extremity) of the clavicle, and is located posteriorly. It is the attachment point for the conoid ligament, which attaches to the coracoid process of the scapula and reinforces the joint between these two bones.
What attaches to the coracoid process?
The coracoid also serves as a critical anchor for many tendinous and ligamentous attachments. These include the tendons of the pectoralis minor, coracobrachialis, and short head of the biceps brachii muscles, and the coracoclavicular, coracohumeral, coracoacromial, and transverse scapular ligaments.
What attaches to greater tubercle of humerus?
The greater tuberosity is the prominent area of bone at the top of the humerus and is the attachment for the two large, powerful rotator cuff muscles - supraspinatus and infraspinatus.
Which muscles attach to clavicle?
The muscles that attach to the clavicle are respectively the pectoral muscle, the deltoid muscle, the subclavian muscle, the trapezoid and the sternocleidomastoid muscle.
Where does the collar bone attach?
The clavicle joins the scapula, or shoulder blade, and sternum to form two joints on either end of the bone, which are: Acromioclavicular (AC) joint: The acromioclavicular joint forms between the acromion of the scapula and clavicle at the top of the shoulder, held together by the acromioclavicular ligament.
What bone attaches to the right scapula?
The scapula is a flat, triangular-shaped bone (colloquially as the "shoulder blade"). It is located in the upper thoracic region on the dorsal surface of the rib cage. It connects with the humerus at the glenohumeral joint as well as the clavicle at the acromioclavicular joint to form the shoulder joint.
What is the clavicle bone connected to?
The clavicle is a sigmoid-shaped long bone with a convex surface along its medial end when observed from cephalad position. It serves as a connection between the axial and appendicular skeleton in conjunction with the scapula, and each of these structures forms the pectoral girdle.
What 3 muscles attach to the coracoid process?
The coracoid process serves as the attachment site for several muscles. The pectoralis minor is attached to the medial aspect of the coracoid. The coracobrachialis is attached to the tip of the process on the medial side, and the short head of the biceps is attached to the tip of the process on the lateral side.
What muscle originates at the coracoid process?
The coracobrachialis is a slender muscle that originates from the deep surface of the coracoid process of scapula. The muscle fibers run inferolaterally towards the humerus. They insert onto the anteromedial surface of the humeral shaft, between the brachialis muscle and the medial head of triceps.
What muscles attach to coronoid process of ulna?
MusclesPronator teres – the medial surface of the coronoid process.Flexor carpi ulnaris – olecranon process.Flexor digitorum superficialis – coronoid process.Flexor digitorum profundus – anteromedial surface.Pronator quadratus – distal anterior shaft.Extensor carpi ulnaris – posterior border.Supinator – proximal ulna.More items...•
What is a conoid process?
The ulna is one of two bones of the forearm, together with the radius. Its proximal end is larger and specialized for articulation with the humerus proximally and radius laterally in order to form the elbow joint. The coronoid process is the smaller of two projections located on the proximal end of the ulna.
What is the function of Costoclavicular ligament?
The costoclavicular ligament, also known as the rhomboid ligament or Halsted's ligament, is a ligament of the shoulder girdle. It is short, flat, and rhomboid in form. It is the major stabilizing factor of the sternoclavicular joint and is the axis of movement of the joint, especially during elevation of the clavicle.
What is the function of the Coracoacromial ligament?
The coracoacromial ligament (CAL) connects the acromion and coracoid process of the scapula, forming an osseoligamentous static restraint to superior humeral head displacement.
What is the Supraglenoid tubercle of scapula?
The supraglenoid tubercle is a region of the scapula from which the long head of the biceps brachii muscle originates. It is a small, rough projection superior to the glenoid cavity near the base of the coracoid process.
Which joint is formed by the acromial end of the clavicle and the acro?
Acromioclavicular joint. The first is the acromioclavicular joint, which is formed by the acromial end of the clavicle and the acromion of the scapula respectively. It enables slight gliding movement about the shoulder region.
What is the cartilage of the sternoclavicular joint?
Like the acromioclavicular joint, the sternoclavicular joint is surrounded by an articular cartilage capsule, but with a fibrocartilage articular disk inside that creates a clavicular and a sternal synovial cavity. Sternoclavicular joint ligaments stabilize the joint on its anterior and posterior surfaces.
What is the clavicle?
The clavicle is an elongated, S-shaped bone that rests horizontally at the sternum across the upper part of the ribcage, and the acromial end of the scapula . This bone is an important part of the skeletal system since it plays an essential role in everyday functional movement, serving as the connection between the axial skeleton and the pectoral girdle.
What is the lateral third of the clavicle?
The orientation of the clavicle can be distinguished by its ends: a broad, flat acromial end (referred to as the lateral third); and a round pyramidal-like sternal end (referred to as the medial two-thirds). Each end has unique bony landmarks, depending whether the superior or inferior surface of the bone is viewed.
Where is the acromial facet?
The superior surface of the clavicle has a smooth appearance. The acromial facet can be seen at the far posterior edge of the acromial end. It appears as a small flattened oval surface and enables the clavicle to articulate about the acromion of the scapula in the acromioclavicular joint.
Which ligament covers the superior surface of the joint?
The anterior interclavicular ligament, which covers the superior surface of the joint. This ligament is responsible for preventing dislocation of the clavicle upon shoulder depression.
Which muscle is attached along the posterior surface of the bone?
The trapezius muscle, which is attached along the posterior surface of the bone.
Where is the conoid tubercle?
The conoid tubercle also known as the coracoid tuberosity (not to be confused with the coracoid process of the scapula) is a bony prominence on the inferior surface of the lateral third of the clavicle.
What is a tubercle?
tubercle [Latin. tuberculum, small lump] (i) a smal rounded prominence, usually on bone. (ii) The specific lesion produced by the Mycobacterium tuberculosis.
Where is the supraglenoid tubercle located?
The supraglenoid tubercle is a region of the scapula from which the long head of the biceps brachii muscle originates. It is a small, rough projection superior to the glenoid cavity near the base of the coracoid process. The term supraglenoid is from the Latin supra meaning above and glenoid meaning socket or cavity.
What is Darwin's tubercle?
Darwin's tubercle (or auricular tubercle) is a congenital ear condition which often presents as a thickening on the helix at the junction of the upper and middle thirds.
Where is the alveolar sac located?
The alveolar sac is a small chamber of pulmonary tissue located at the end of the alveolar duct from which smaller sacs, called alveoli, project.
Is a tubercle a condyle?
A tubercle is also a projection, often smaller than a condyle which connects to muscles, ligaments/tendons.