
Symptoms
Untreated, impetigo often clears up on its own after a few days or weeks, Smith says. The key is to keep the infected area clean with soap and water and not to scratch it. The downside of not treating impetigo is that some people might develop more lesions that spread to other areas of their body.
Causes
Impetigo Home Treatment
- Foods that can help cure Impetigo. How to treat Impetigo fast with garlic? ...
- Herbal treatments for curing Impetigo. How to get rid of Impetigo with Aloe Vera? ...
- Essential oils for getting rid of Impetigo. How to use Tea Tree Oil for Impetigo Treatment? ...
- Home Remedies for curing Impetigo. ...
- Natural Treatments for healing Impetigo. ...
Prevention
In respect to this, how quickly does impetigo clear up? Impetigo isn't usually serious and often clears up without treatment after two to three weeks. Treatment is often recommended as it can help clear up the infection in around seven to 10 days and reduce the risk of the infection being passed on to others.
Complications
Impetigo is a highly contagious bacterial skin infection. It's caused by the Staphylococcus aureus bacteria and most commonly affects young children, although anyone can get it if infected.
Will impetigo go away on its own?
How to treat impetigo naturally without antibiotics?
How long does it take for impetigo to heal?
What is the pathogen that causes impetigo?
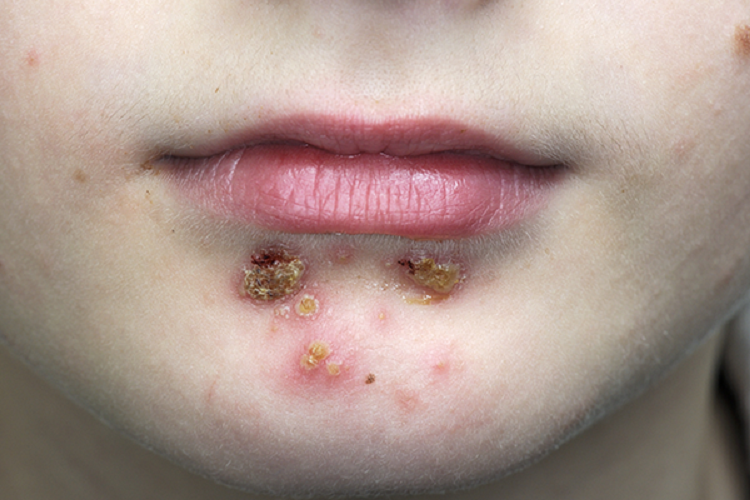
Which bacteria is the most common cause of impetigo?
Impetigo is a skin infection caused by one or both of the following bacteria: group A Streptococcus and Staphylococcus aureus. This page focuses on impetigo caused by group A Streptococcus (group A strep). In addition to impetigo, group A strep cause many other types of infections.
Can impetigo be caused by Streptococcus?
Impetigo is a superficial bacterial skin infection that is highly contagious. Impetigo can be caused by Streptococcus pyogenes and Staphylococcus aureus. This page focuses on infections caused by S. pyogenes, which are also called group A Streptococcus or group A strep.
What causes impetigo to flare up?
Causes of impetigo Impetigo occurs when the skin becomes infected with bacteria, usually either Staphylococcus aureus or Streptococcus pyogenes. These bacteria can infect the skin in two ways: through a break in otherwise healthy skin, such as a cut, insect bite or other injury – this is known as primary impetigo.
What are the 3 types of impetigo?
There are 3 kinds of impetigo:Nonbullous impetigo. This is the most common form in adults. It causes thick, honey-colored crusts.Bullous impetigo. This causes large blisters on the skin.Ecthyma. This is a more serious form that often results from untreated impetigo.
Is impetigo staph or strep?
Impetigo is a common bacterial skin infection caused by Group A Streptococcus (GAS) or "strep."
What is the difference between strep and staph?
Strep is most commonly found in the mouth and throat. Hence the relatively common condition strep throat. The infection is often accompanied by an extremely sore throat with white patches, difficulty swallowing, and a fever. Meanwhile, staph is a skin infection that is most often the result of surgery or an open wound.
Is impetigo from being dirty?
Impetigo is very contagious. The bacteria are easily passed to new areas of the skin by scratching or touching the sore. It can be passed to other people by unwashed hands, dirty fingernails, and clothing or other objects that have touched the sores.
Does impetigo stay in your system forever?
Impetigo will go away within a few weeks on its own. (6) A doctor might prescribe an antibiotic for 7 to 10 days, though you will likely see a response within 72 hours, Oza says.
Is impetigo caused by poor hygiene?
Impetigo is made worse by poor hygiene and warm temperatures. What are the symptoms of impetigo? Impetigo starts as a small vesicle or fluid-filled lesion. The lesion then ruptures and the fluid drains, leaving areas that are covered with the honey-colored crusts.
What is the best antibiotic for impetigo?
Topical antibiotics such as mupirocin (Bactroban) and fusidic acid (not available in the United States) are the preferred first-line therapy for impetigo involving limited body surface area.
What is best treatment for impetigo?
Impetigo is treated with prescription mupirocin antibiotic ointment or cream applied directly to the sores two to three times a day for five to 10 days. Before applying the medicine, soak the area in warm water or apply a wet cloth compress for a few minutes.
Can you get impetigo twice?
Anyone can get impetigo — and more than once, Smith says. Although impetigo is a year-round disease, it occurs most often during the warm weather months.
Overview
Symptoms
Causes
Risk Factors
Complications
- Impetigo (im-puh-TIE-go) is a common and highly contagious skin infection that mainly affects infants and young children. It usually appears as reddish sores on the face, especially around the nose and mouth and on the hands and feet. Over about a week, the sores burst and develop honey-colored crusts. Treatment with antibiotics can limit the spread of impetigo to others. Kee…
Prevention
- The main symptom of impetigo is reddish sores, often around the nose and mouth. The sores quickly rupture, ooze for a few days and then form a honey-colored crust. Sores can spread to other areas of the body through touch, clothing and towels. Itching and soreness are generally mild. A less common form of the condition called bullous impetigo causes larger blisters on the …
Etiology
- Impetigo is caused by bacteria, usually staphylococci organisms. You might be exposed to the bacteria that cause impetigo when you come into contact with the sores of someone who's infected or with items they've touched — such as clothing, bed linen, towels and even toys.
Clinical Features
- Factors that increase the risk of impetigo include: 1. Age.Impetigo occurs most commonly in children ages 2 to 5. 2. Close contact.Impetigo spreads easily within families, in crowded settings, such as schools and child care facilities, and from participating in sports that involve skin-to-skin contact. 3. Warm, humid weather.Impetigo infections are more common in warm, humid weathe…
Transmission
- Impetigo typically isn't dangerous. And the sores in mild forms of the infection generally heal without scarring. Rarely, complications of impetigo include: 1. Cellulitis.This potentially life-threatening infection affects the tissues underlying the skin and eventually may spread to the lymph nodes and bloodstream. 2. Kidney problems.One of the types of bacteria that cause impe…
Incubation Period
- Keeping skin clean is the best way to keep it healthy. It's important to wash cuts, scrapes, insect bites and other wounds right away. To help prevent impetigo from spreading to others: 1. Gently wash the affected areas with mild soap and running water and then cover lightly with gauze. 2. Wash an infected person's clothes, linens and towels every day with hot water and don't share th…
Risk Factors
- Impetigo can be bullous or non-bullous. Toxin-producing S. aureus cause bullous impetigo. S. aureus, S. pyogenes, or both cause non-bullous impetigo, which is also called “impetigo contagiosa.” S. pyogenes are gram-positive cocci that grow in chains (see Figure 1). They exhibit β-hemolysis (complete hemolysis) when grown on blood agar plates. They ...
Diagnosis and Testing
- Streptococcal impetigo, or non-bullous impetigo, begins as papules. The papules evolve to pustules and then break down to form thick, adherent crusty lesions (Figure 2). The crusts are typically golden or “honey-colored.” These lesions usually appear on exposed areas of the body, most commonly the face and extremities, but can occur anywhere on the body. Multiple lesions …
Treatment
- Streptococcal impetigo is most commonly spread through direct contact with other people with impetigo, including through contact with drainage from impetigo lesions. Lesions can be spread (by fingers and clothing) to other parts of the body. People with impetigo are much more likely to transmit the bacteria than asymptomatic carriers. Crowding, such as found in schools and dayc…
Prognosis and Complications
- The incubation period of impetigo, from colonization of the skin to development of the characteristic lesions, is about 10 days.1 It is important to note not everyone who becomes colonized will go on to develop impetigo.
Prevention
- Impetigo can occur in people of all ages, but it is most common among children 2 through 5 years of age. Scabies infections and activities that result in cutaneous cuts or abrasions increase the risk of impetigo. Poor personal hygiene, including lack of proper hand, face, or body hygiene, can increase someone’s risk of impetigo. Impetigo can occur in any climate and at any time of year, …
Epidemiology
- Impetigo is diagnosed by physical examination, but physical examination cannot reliably differentiate between streptococcal and staphylococcal non-bullous impetigo.1Gram stain or culture of the exudate or pus from an impetigo lesion can identify the bacterial cause; however, laboratory testing is not necessary nor routinely performed in clinical practice.