What causes necrotizing skin infections?
Several different bacteria, such as Streptococcus and Clostridia, may cause necrotizing skin infections, but in many people the infections are caused by a combination of bacteria. The necrotizing skin infection caused by streptococci in particular has been termed “flesh-eating disease” by the lay press, but it differs little from the others.
What types of bacteria are involved in necrotizing infections?
However, more often, many different types of bacteria are involved in a necrotizing infection including: Anaerobic and gram negative bacteria such as E. coli It can take time to find out which bacteria are present. For this reason, your healthcare providers may recommend a treatment that can fight many different infections.
What bacteria causes necrotizing fasciitis?
Sometimes a necrotizing infection can be caused by a bacteria called Streptococcus, the same bacteria that causes strep throat. However, more often, many different types of bacteria are involved in a necrotizing infection including: Anaerobic and gram negative bacteria such as E. coli
What causes necrosis in the lungs?
Caseous necrosis is another type of necrosis that typically happens as a result of a bacterial or fungal infection. The most common cause of caseous necrosis is tuberculosis —a bacterial disease that leads to caseous necrosis in the lungs. 2 Caseous necrotic tissue has a cheese-like appearance.

What infections cause necrosis?
However, more often, many different types of bacteria are involved in a necrotizing infection including:Enterococci.Staphylococcus aureus.Clostridium perfringens.Anaerobic and gram negative bacteria such as E. coli.
What causes necrotic tissue?
Necrosis can be caused by a number of external sources, including injury, infection, cancer, infarction, poisons, and inflammation. Black necrotic tissue is formed when healthy tissue dies and becomes dehydrated, typically as a result of local ischemia.
Is necrosis a bacterial infection?
The word necrotizing comes from the Greek word "nekros." It means "corpse" or "dead." A necrotizing infection causes patches of tissue to die. These infections are the result of bacteria invading the skin or the tissues under the skin. If untreated, they can cause death in hours.
What are the first signs of necrosis?
The first symptoms of necrotizing fasciitis may not seem serious. Your skin may become warm and red, and you may feel as if you've pulled a muscle. You may even feel like you simply have the flu. You can also develop a painful, red bump, which is typically small.
What are the 4 types of necrosis?
These are coagulative, liquefactive, caseous, gangrenous which can be dry or wet, fat and fibrinoid. Necrosis can start from a process called “oncosis”.
What is the most common bacterial skin infection?
Staph bacteria are one of the most common causes of skin infections in the U.S. Most of these skin infections are minor (such as pimples and boils), are not spread to others (not infectious), and usually can be treated without antibiotics.
How do you get rid of necrosis?
There are several methods to remove necrotic tissue: Autolytic debridement: Autolytic debridement leads to softening of necrotic tissue. It can be accomplished using dressings that add or donate moisture. This method uses the wound's own fluid to break down necrotic tissue.
How fast does necrosis spread?
The affected area may also spread from the infection point quickly, sometimes spreading at a rate of an inch an hour. If NF progresses to show advanced symptoms, the patient will continue to have a very high fever (over 104 degrees Fahrenheit) or may become hypothermic (low temperature) and become dehydrated.
Can necrosis be reversed?
Necrosis cannot be reversed. When large areas of tissue die due to a lack of blood supply, the condition is called gangrene. Meningococcemia is a life-threatening infection that occurs when the bacteria, Neisseria meningitidis, invades the blood stream.
What happens if necrosis is left untreated?
Untreated, avascular necrosis worsens. Eventually, the bone can collapse. Avascular necrosis also causes bone to lose its smooth shape, possibly leading to severe arthritis.
How do you know if a tissue is necrotic?
Necrotic wounds will lead to discolouration of your skin. It usually gives a dark brown or black appearance to your skin area (where the dead cells are accumulated). Necrotic tissue color will ultimately become black, and leathery.
How do you get rid of necrosis?
There are several methods to remove necrotic tissue: Autolytic debridement: Autolytic debridement leads to softening of necrotic tissue. It can be accomplished using dressings that add or donate moisture. This method uses the wound's own fluid to break down necrotic tissue.
How do you know if a tissue is necrotic?
Necrotic wounds will lead to discolouration of your skin. It usually gives a dark brown or black appearance to your skin area (where the dead cells are accumulated). Necrotic tissue color will ultimately become black, and leathery.
How long does it take for necrotic tissue to form?
Soft tissue necrosis usually begins with breakdown of damaged mucosa, resulting in a small ulcer. Most soft tissue necroses will occur within 2 years after radiation therapy. Occurrence after 2 years is generally preceded by mucosal trauma.
Can necrosis be cured?
Treatment can slow the progress of avascular necrosis, but there is no cure. Most people who have avascular necrosis eventually have surgery, including joint replacement. People who have avascular necrosis can also develop severe osteoarthritis.
What is necrosis in a cell?
The cellular mechanism that leads to necrosis is the loss of cell membrane integrity as a result of exposure to a noxious stimulus; this allows extracellular ions to move inside the cell, followed by fluid leading to eventual swelling of the cell and its organelles. Another cellular mechanism is the disruption of the lysosomal membrane, which leads to the release of proteolytic enzymes into the cell, such as proteases, RNAase, DNAases, and phosphatases. These, when activated in the cytosol, leading to damage to DNA, RNA, and proteins.[8] These enzymes cause the digestion of the cellular components causing cell destruction. Both these mechanisms lead to disruption of the plasma membrane leading to the spilling of intracellular contents into the surrounding tissue. [1]
What are some examples of necrosis?
Various drugs have been linked to kidney injury including phenylbutazone, ibuprofen, and mefenamic acid.[22] Similarly, alcohol consumption has been studied to lead to hepatic inflammation, necrosis, and steatosis. inflammation has been proposed to be a progression event in the development of alcoholic steatohepatitis. [23][24] Ischemia of the heart leading to myocardial injury, ischemia of the brain leading to stroke, and ischemia of the limbs leading to gangrene are all clinical examples of necrosis. Necrosis hence helps to describe the pathological mechanism of most commonly encountered diseases. [25]
What causes necrotic death?
Necrotic death is almost always associated with an inflammatory response . Necrotic cells release factors like high mobility group box 1 protein (HMGB1), and hepatoma-derived growth factor (HDGF). [18][19] These factors are sensed by a nod-like receptor protein 3 (NLRP3), which is a core protein of the inflammasome.[20] This results in inflammasome activation and causes the release of the pro-inflammatory cytokine IL1β. NLRP3 inflammasome activation is triggered mainly through ATP produced by mitochondria released from damaged cells.[21] Necrosis does not typically correlate with activation of caspases, and it appears that it causes cell demise in response to damage or pathology, but not during normal development. Despite this, it turns out that a programmed form of necrotic death (termed necroptosis) is very common in vivo, mainly in diverse forms of neurodegeneration and death inflicted by ischemia or infection. Unlike unordered necrosis, necroptosis is a more physiological and programmed type of necroptotic death and shares several key processes with apoptosis. It occurs due to the activation of the kinase domain of the receptor-interacting protein 1 (RIP1) and the assembly of the RIP1/RIP3-containing signaling complex. It is triggered by tumor necrosis factor (TNF) family members, needs caspase 8 inhibition, and assembly of necrosome(RIPK1-RIPK3 complex IIb). [9][19]
What type of necrosis occurs in blood vessels due to the deposition of immune complexes in blood vessel walls?
6) Fibrinoid necrosis: This type of necrosis occurs in blood vessels due to the deposition of immune complexes in blood vessel walls leading to leakage of fibrin. This observed staining appears as a bright pink amorphous material. [16]
What is gangrenous necrosis?
4) Gangrenous necrosis: This is not a morphological pattern but rather a clinical term for ischemic necrosis of the limbs. It has two types i) dry (ischemia leading to coagulative necrosis), and ii) wet (ischemia with superimposed bacterial infection leading to liquefactive necrosis). [14]
Why is necrosis important?
Identifying the various types of necrosis and the underlying cause of necrosis can help to target treatment for multiple diseases. Most of the time, identifying the cause of necrosis and treating it is more important than removing the dead tissue. In the case of myocardial infarction, we are aware that necrosis occurs due to hypoxia due to the occlusion of coronary vessels. Therefore treatment is targeted at opening the coronary vessels either by thrombolysis or PCI to restore blood supply. [25]
What is the term for a necrotic area?
This necrosis takes place in tuberculous infection, and the necrotic area is referred to as a granuloma.
What causes a cut to be necrotizing?
But, many types of bacteria can invade an open wound, even a small cut. Sometimes a necrotizing infection can be caused by a bacteria called Streptococcus, the same bacteria that causes strep throat. However, more often, many different types of bacteria are involved in a necrotizing infection including: Enterococci. Staphylococcus aureus.
What does it mean when a person dies from a necrotizing infection?
The word necrotizing comes from the Greek word "nekros", which means "corpse" or "dead". A necrotizing infection causes patches of tissue to die. These infections are the result of bacteria invading the skin or the tissues under the skin. If untreated, they can cause death in a matter of hours. Fortunately, such infections are very rare.
What is necrotizing soft tissue infection?
A necrotizing soft tissue infection is a serious, life-threatening condition that requires immediate treatment to keep it from destroying skin, muscle, and other soft tissues. The word necrotizing comes from the Greek word "nekros", which means "corpse" or "dead". A necrotizing infection causes patches of tissue to die.
How to tell if a wound is necrotizing?
These are the most common symptoms of a necrotizing soft tissue infection. See your healthcare provider right away for any of these symptoms: Pain that hurts more than you think it should, based on the size of the wound or sore. A wound accompanied by a fever (higher than 100.4°F or 38°C) and a rapid heartbeat (usually more than 100 beats a minute) ...
Can you get a red spot from a skin infection?
If you have a skin infection with a warm, red area, you should use a marker or pen and outline the red area so that you and the healthcare provider can see how far and how quickly it spreads outside the line.
Can salt water cause necrotizing?
If you've been exposed to slightly salty (brackish) water or saltwater. If you've developed a necrotizing soft tissue infection as a result of surgery, it may be slower moving and your skin at the wound site may even look normal at first.
Can a virus spread from the original site?
Fortunately, such infections are very rare. They can quickly spread from the original infection site, so it's important to know the symptoms.
What is Bacterial Necrosis?
Saguaro cactus can live for 200 years and grow up to 60 feet in height. These monstrous desert dwellers look imposing and impervious but can actually be brought down by a tiny bacteria. Saguaro cactus necrosis can invade the plant in a number of ways. It eventually creates necrotic pockets in the flesh which will spread. These necrotic areas are dead plant tissue and, if left unchecked, can eventually kill these regal plants. Treating bacterial necrosis in saguaro in the early stages can give the plant an 80 percent chance of survival.
What is the name of the cacti that fall prey to bacterial necrosis?
Saguaro are one of the most stately and statuesque of the cacti. They are also fall prey to a nasty infection called bacterial necrosis of saguaro. What is bacterial necrosis?
How to cut a saguaro cactus?
Excise at least ½ inch of the surrounding healthy tissue as well. As you cut, dip the knife into a 1:9 ratio solution of bleach and water to sanitize between cuts. As you make your cuts, angle them so any water will drain out of the cactus.
What is the necrosis of a saguaro cactus?
Saguaro cactus necrosis starts out as dark spots in the flesh, which is soft and smelly. Eventually, the disease progresses to rotten lesions that exude dark, smelly fluid. Saguaro cactus necrosis may also develop into a corky patch where the plant is trying to heal itself. Any breach of the corked area will release the bacteria and infect more ...
Can you kill saguaro necrosis?
Bacterial necrosis of saguaro treatment is mostly manual, as there are no approved chemicals to combat the bacteria. The infected material needs to be removed from the plant and the area cleaned to prevent the spread of the disease. Infected material must be destroyed and not added to the compost bin. Immediately doing “surgery” on your plant may or may not save it, however, as the bacteria lives in the soil or in dead plant matter on the ground.
Can a cactus be destroyed?
In rare cases, a cactus has been entirely girdled by the disease and, sadly, the plant needs to be removed and destroyed.
Can you put bacteria in compost?
Infected material must be destroyed and not added to the compost bin. Immediately doing “surgery” on your plant may or may not save it, however, as the bacteria lives in the soil or in dead plant matter on the ground. Any future injury or even the tunneling of larvae into the plant will leave it open to re-infection.
What bacteria cause necrotizing?
But many different types of bacteria can cause a necrotizing infection. Some of these are: Enterococci. Staphylococcus aureus. Clostridium perfringens and other anaerobic bacteria. Gram negative bacteria such as Escherichia coli (E. coli) It can take time to find out which bacteria are present.
What causes a wound to become necrotizing?
But many types of bacteria can invade an open wound, even a small cut. Most commonly, a necrotizing infection is caused by bacteria called Streptococcus. This is the same bacteria that causes strep throat. But many different types of bacteria can cause a necrotizing infection. Some of these are:
What is a necrotizing soft tissue infection?
A necrotizing soft tissue infection is a serious, life-threatening condition. It requires treatment right away to keep it from destroying skin, muscle, and other soft tissues. The word necrotizing comes from the Greek word "nekros." It means "corpse" or "dead." A necrotizing infection causes patches of tissue to die.
What are possible complications of a necrotizing soft tissue infection?
A necrotizing soft tissue infection can destroy skin , muscle , and other soft tissues. If untreated , it may lead to amputation of major parts of the body and sometimes death.
What does necrotizing mean?
The word necrotizing comes from the Greek word "nekros.". It means "corpse" or "dead.". A necrotizing infection causes patches of tissue to die. These infections are the result of bacteria invading the skin or the tissues under the skin. If untreated, they can cause death in hours.
How to reduce the risk of a peripheral artery infection?
Lifestyle habits such as heavy alcohol use and IV drug use can raise your risk, too. Manage your risk factors to reduce the risk of infection. For example, control your diabetes well. Or if you drink a lot, cut back on alcohol.
Can a virus spread from the original site?
Fortunately, such infections are very rare. They can quickly spread from the original infection site. So it's important to know the symptoms.
What bacteria can cause necrotizing fasciitis?
Bacteria that live in water, including Vibrio vulnificus, can also cause necrotizing fasciitis. Learn about Vibrio wound infections. There are many types of bacteria that can cause the “flesh-eating disease” called necrotizing fasciitis. Public health experts believe group A Streptococcus (group A strep) are the most common cause ...
What is necrotizing fasciitis?
Necrotizing fasciitis is a very serious illness that requires care in a hospital. Antibiotics and surgery are typically the first lines of defense if a doctor suspects a patient has necrotizing fasciitis. Since necrotizing fasciitis can spread so rapidly, patients often must get surgery done very quickly.
How many people die from necrotizing fasciitis and streptococcal toxic shock syndrome at the same?
Six out of every 10 people who get both necrotizing fasciitis and streptococcal toxic shock syndrome at the same time die from their infections. Streptococcal toxic shock syndrome is another very serious illness caused by group A strep.
What is the difference between fasciitis and necrotizing?
Necrotizing means causing the death of tissues. Fasciitis means inflammation of the fascia (the tissue under the skin that surrounds muscles, nerves, fat, and blood vessels).
How does necrotizing fasciitis affect the body?
Necrotizing fasciitis can lead to sepsis, shock, and organ failure. It can also result in life-long complications from loss of limbs or severe scarring due to surgically removing infected tissue. Even with treatment, up to 1 in 3 people with necrotizing fasciitis die from the infection.
What is the name of the bacterial infection that spreads quickly in the body and can cause death?
Necrotizing fasciitis (NECK-re-tie-zing FASH-e-i-tis) is a rare bacterial infection that spreads quickly in the body and can cause death. Accurate diagnosis, rapid antibiotic treatment, and prompt surgery are important to stopping this infection.
Why can't antibiotics be given to all infected areas?
Sometimes, however, antibiotics cannot reach all of the infected areas because the bacteria have killed too much tissue and reduced blood flow. When this happens, doctors have to surgically remove the dead tissue. It is not unusual for someone with necrotizing fasciitis to end up needing multiple surgeries.
Why does necrotic tissue die?
Dead tissue is termed necrotic. Because the body's immune defenses that travel through the bloodstream (such as white blood cells and antibodies) can no longer reach this area , the infection spreads rapidly and may be difficult to control.
How to treat necrotizing fasciitis?
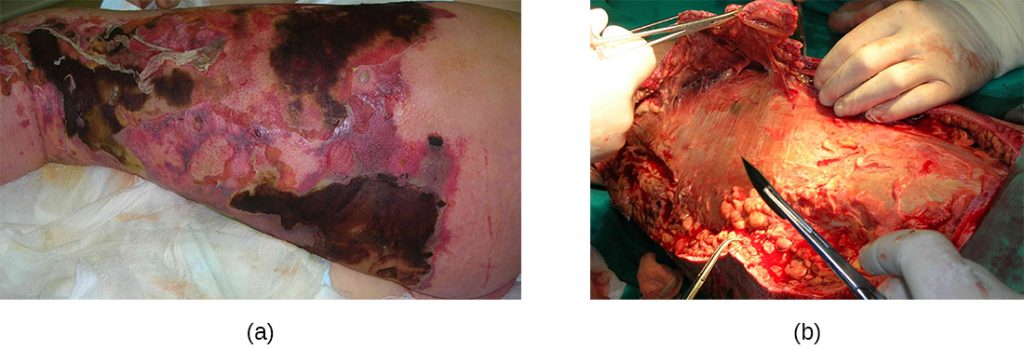
The treatment of necrotizing fasciitis is surgical removal of the dead tissue plus antibiotics given by vein (intravenously). Large amounts of skin, tissue, and muscle must often be removed, and in some cases, an affected arm or leg may have to be removed (amputated).
How do you know if you have a necrotizing skin infection?
Symptoms of necrotizing skin infections often begin just as for a common skin infection, cellulitis. The skin may look pale at first but quickly becomes red or bronze and warm to the touch and sometimes swollen. Later, the skin turns violet, often with the development of large fluid-filled blisters (bullae). The fluid from these blisters is brown, watery, and sometimes foul smelling. Areas of dead skin turn black ( gangrene ). Some types of infection, including those caused by Clostridia and mixed bacteria, produce gas. The gas creates bubbles under the skin and sometimes in the blisters themselves, causing the skin to feel crackly when pressed. Initially the infected area is extremely painful, but as the skin dies, the nerves stop working and the area loses sensation. The muscles may be affected as the infection worsens.
Why does my skin turn black?
Some types of infection, including those caused by Clostridia and mixed bacteria, produce gas. The gas creates bubbles under the skin and sometimes in the blisters themselves, causing the skin to feel crackly when pressed.
What is the term for a skin infection that spreads deep in the skin?
Some necrotizing skin infections spread deep in the skin along the surface of the connective tissue that covers muscle (fascia) and are termed necrotizing fasciitis. Other necrotizing skin infections spread in the outer layers of skin and are termed necrotizing cellulitis. Several different bacteria, such as Streptococcus and Clostridia, ...
How do bacteria spread to the skin?
The bacteria may initially create an abscess (a pocket of pus) in the abdominal cavity and spread directly outward to the skin, or they may spread through the bloodstream to the skin and other organs.
Where do necrotizing wounds start?
Some necrotizing skin infections begin at puncture wounds or lacerations, particularly wounds contaminated with dirt and debris. Other infections begin in surgical incisions or even healthy skin. Sometimes people with diverticulitis, intestinal perforation, or tumors of the intestine develop necrotizing infections of the abdominal wall, ...
What bacteria are responsible for necrotizing fasciitis?
But, several types of bacteria, such as staphylococcus and others, have also been linked to the disease. Necrotizing fasciitis happens when these types of bacteria infect the superficial fascia, a layer of connective tissue below the skin.
What Is Flesh-Eating Bacteria (Necrotizing Fasciitis)?
Flesh-eating bacteria ( necrotizing fasciitis) is a rare infection of the skin and tissues below it. It can be deadly if not treated quickly.
What is the term for the bacteria that infect the superficial fascia?
Necrotizing fasciitis happens when these types of bacteria infect the superficial fascia, a layer of connective tissue below the skin.
How does a syphilis infection begin?
In some cases, it is unknown how the infection began. Once it takes hold, the infection rapidly destroys muscle, skin, and fat tissue.
Should you test for necrotizing fasciitis?
Household members and others who have had close contact with someone with necrotizing fasciitis should be tested for the disease if they have symptoms of an infection.