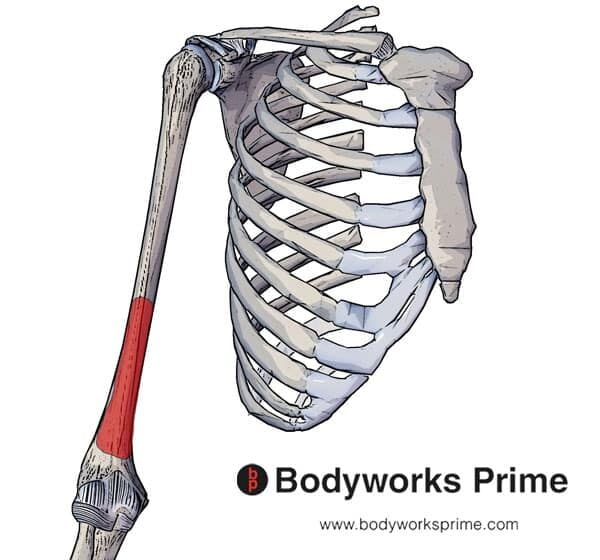
The Anatomy of the Brachialis Muscle
- Anatomy. The brachialis muscle originates from the front of your humerus, or upper arm bone. ...
- Function. The function of the brachialis is to flex your elbow especially when your forearm is in the pronated, or palm down, position.
- Associated Conditions. ...
- Rehabilitation. ...
- A Word From Verywell. ...
What is bone in the brachial region?
The Anatomy of the Brachial Artery
- Anatomy. The brachial artery is the main artery of the arm. ...
- Function. The brachial artery is primarily involved with providing oxygenated blood to the arm and hand. ...
- Clinical Significance. Because the brachial artery serves such an important role in providing blood to the upper limbs, it can be involved in a number of disorders or conditions.
What is the meaning of brachial?
Definition of brachial in English: brachial. adjective. 1 Anatomy Relating to the arm or to a structure resembling the arm. ‘the brachial artery’ ...
What body region is the brachial located?
The brachialis muscle is located in the upper arm. It lies underneath the biceps muscle. It acts as a structural bridge between the humerus, which is the bone of the upper arm, and the ulna, which is one of the forearm bones. The muscle is innervated by both the musculoskeletal nerve and the radial nerve.
Where is the brachial artery found?
The brachial artery is the major blood vessel of the (upper) arm. It is the continuation of the axillary artery beyond the lower margin of teres major muscle. It continues down the ventral surface of the arm until it reaches the cubital fossa at the elbow. It then divides into the radial and ulnar arteries which run down the forearm.

Where is your brachial region?
Brachial region - Regio brachii Located between the shoulder and the elbow, the brachial region (Regio brachialis) is much shorter in proportion in domestic Mammals, and especially in great Ungulates, than in the human species.
What is the bone in your arm called?
humerusYour arm is made up of three bones: the upper arm bone (humerus) and two forearm bones (the ulna and the radius).
How many bones make up the brachial region?
It extends from the shoulder joint to the fingers and contains 30 bones. It also consists of many nerves, blood vessels (arteries and veins), and muscles. The nerves of the arm are supplied by one of the two major nerve plexus of the human body, the brachial plexus.
What structure is in the brachial region?
Brachial artery: biceps brachii muscle, triceps brachii muscle, coracobrachialis muscle.
Is the humerus bone?
The humerus — also known as the upper arm bone — is a long bone that runs from the shoulder and scapula (shoulder blade) to the elbow.
What bone is the ulna?
1 Anatomy. The ulna is the longest, thinnest bone of the forearm. It articulates proximally with the trochlea of the humerus and with the head of the radius. Distally it articulates with the ulnar notch of the radius and with an articular disk that separates it from the carpal bones.
How many bones are found in the arm or brachial region quizlet?
Arms and forearms (6 bones) - Left and right humerus (2) (arm), ulna (2) and radius (2) (forearm).
What are the 5 parts of the brachial plexus?
The 5 terminal branches of the brachial plexus are the musculocutaneous, median, ulnar, axillary, and radial nerves.
What does the term brachial mean?
Definition of brachial : of, relating to, or situated in the arm or an armlike process the brachial artery of the upper arm.
Which muscles are found in the brachial region?
Biceps brachii. Biceps brachii is one of the three muscles found in the anterior compartment of the arm. ... Coracobrachialis. Coracobrachialis is the most medial muscle in the anterior compartment of the arm. ... Brachialis. Brachialis is the last of the three muscles forming the anterior compartment of the arm. ... Triceps brachii.
What region is the shoulder in?
the acromial region where the shoulders bones are found. the thoracic region is the upper part of the back (also chest) the lumbar region encompassing the lower back. the sacral region occurring at the end of the spine, directly above the buttocks.
What are the regions of the shoulder region?
In human anatomy, the shoulder joint comprises the part of the body where the humerus attaches to the scapula, and the head sits in the glenoid cavity. The shoulder is the group of structures in the region of the joint....ShoulderTA98A01.1.00.020TA2139FMA25202Anatomical terminology6 more rows
Where is the mandibular arch?
The mandibular arch lies between the first branchial groove and the stomodeum; from it are developed the lower lip, the mandible, the muscles of mastication, and the anterior part of the tongue. Its cartilaginous bar is formed by what are known as Meckel’s cartilages (right and left) (Fig. 43); above this the incus is developed.
What is the cartilage of the third arch?
The cartilage of the third arch gives origin to the greater cornu of the hyoid bone. The ventral ends of the second and third arches unite with those of the opposite side, and form a transverse band, from which the body of the hyoid bone and the posterior part of the tongue are developed.
What is the first arch of the aortic arch?
The first arch is named the mandibular, and the second the hyoid; the others have no distinctive names. In each arch a cartilaginous bar, consisting of right and left halves, is developed, and with each of these there is one of the primitive aortic arches. The mandibular arch lies between the first branchial groove and the stomodeum;
Which process forms the cheek and lateral part of the upper lip?
From the dorsal ends of the mandibular arch a triangular process, the maxillary process, grows forward on either side and forms the cheek and lateral part of the upper lip. The second or hyoid arch assists in forming the side and front of the neck.
What are the rounded lateral angles of the medial process?
The rounded lateral angles of the medial process constitute the globular processes of His. The olfactory pits form the rudiments of the nasal cavities, and from their ectodermal lining the epithelium of the nasal cavities, with the exception of that of the inferior meatuses, is derived.
Which cartilage is ossified to form the malleus?
The dorsal end of each cartilage is connected with the ear-capsule and is ossified to form the malleus; the ventral ends meet each other in the region of the symphysis menti, and are usually regarded as undergoing ossification to form that portion of the mandible which contains the incisor teeth.
Which direction is the flexor surface of the fore limb?
As a consequence of this rotation the preaxial (radial) border of the fore-limb is directed lateralward, and the preaxial (tibial) border of the hind-limb is directed medialward; thus the flexor surface of the fore-limb is turned forward, and that of the hind-limb backward.
What is the brachialis muscle?
The brachialis muscle is located in the upper arm. It lies underneath the biceps muscle. It acts as a structural bridge between the humerus, which is the bone of the upper arm, and the ulna, which is one of the forearm bones. The muscle is innervated by both the musculoskeletal nerve and the radial nerve. In some people, the muscle may appear doubled. Also called the brachialis anticus, its primary action is to flex the forearm muscles at the elbow. Due to its high contractile strength, the branchialis makes many arm and elbow movements possible. Such movements are important for the activities of daily life. Because movements involving the arms and elbows are almost always continuous, injuries to the brachialis muscle are quite common. They can be as subtle as muscle aches or as serious as muscle rupture and hematoma. The muscle can tear, lacerate or rupture with overextension of the elbow or when extreme force is exerted against surrounding structures.
Why is the branchialis important?
Due to its high contractile strength , the branchialis makes many arm and elbow movements possible. Such movements are important for the activities of daily life. Because movements involving the arms and elbows are almost always continuous, injuries to the brachialis muscle are quite common.
What nerve innervates the forearm?
The muscle is innervated by both the musculoskeletal nerve and the radial nerve. In some people, the muscle may appear doubled. Also called the brachialis anticus, its primary action is to flex the forearm muscles at the elbow. Due to its high contractile strength, the branchialis makes many arm and elbow movements possible.

Anatomy
Function
- The function of the brachialis is to flex your elbow especially when your forearm is in the pronated, or palm down, position. It has a large cross sectional area, and is able to produce more strength than the biceps brachii. Many people think the biceps brachii is a major flexor of your elbow; flexion is actually accomplished by the brachialis and brachioradialis muscles. The bicep…
Associated Conditions
- The brachialis muscle muscle may be injured if a forceful or repetitive strain is placed upon it, especially if your elbow is in a pronated position when the force is applied. Climbers, throwing athletes, and people who participate in racquet sports may suffer from a brachialis injury due to overuse or repetitive strain. Symptoms of brachialis injury may include: 1. Pain in the front of yo…
Rehabilitation
- If you have suffered an injury to your brachialis, you may benefit from a course of physical therapy (PT) to recover. Initial treatment of your brachialis injury may include the P.O.L.I.C.E. principle. This stands for protection, optimal loading, ice, compression, and elevation. Protection of your injured brachialis muscle may include wearing a sling or splintto allow your arm to rest and heal…
A Word from Verywell
- The brachialis is a muscle in the front of your elbow that flexes, or bends, the joint. It does this when your forearm is in a palm down, pronated, position. Injury to the muscle may cause pain and difficulty using your arm normally. By understanding the anatomy and function of the brachialis muscle, you can be sure to have a successful rehab process and quickly and safely return to you…