Common Causes
The following could cause thrombocytopenic purpura:
- medications that prevent platelets from forming or that interfere with normal clotting
- drugs that cause the body to launch an immune reaction against platelets
- recent blood transfusions
- immune disorders such as idiopathic thrombocytopenic purpura
- an infection in the bloodstream
Related Conditions
Treatment
- Intravenous Immunoglobulin. If purpura is due to severe bleeding, intravenous immunoglobulin (IVIG) may be given. ...
- Other Therapies. Promacta (eltrombopag) and Nplate (romiplostim) are the latest medications used for the treatment of low platelet count in people who have chronic idiopathic thrombocytopenic purpura (ITP).
- Splenectomy. ...
What drugs can cause purpura?
They may also go away as you treat the underlying condition causing the spots. The time it takes for the petechiae to fade can vary based on the cause. For example, if you have Henoch-Schölein purpura, you may have the condition for about a month, and the spots will fade during that time.
How to treat purpura rash?
- Research health conditions
- Check your symptoms
- Prepare for a doctor's visit or test
- Find the best treatments and procedures for you
- Explore options for better nutrition and exercise
Does purpura go away?
How to get rid of senile purpura?
How long does it take for thrombocytopenia to go away?
Why are platelets important?
What is the most common cause of vasculitic purpura?
What is the cause of a fever in a child?
What is DIC in biology?
What is a professional reference?
What is a coagulation screen?
See 4 more
About this website

What is the most common cause of purpura?
Common causes of thrombocytopenic purpura are: Drugs or medications that affect platelet function or clotting. Immune disorders such as idiopathic thrombocytopenic purpura (ITP) or immune thrombocytopenia. Infections in your bloodstream.
When should I be concerned about purpura?
Patients who experience purpura with any of the following symptoms should seek medical treatment: low platelet count, which may lead to increased bleeding after an injury, bleeding gums or nose, or blood in urine or bowel movements. sore, swollen joints, particularly in the ankles and knees.
What does purpura rash look like?
Check if you or your child has HSP The main symptom of HSP is a rash of raised red or purple spots. The spots look like small bruises or blood spots.
How long does a Purpuric rash last?
Skin rash (palpable purpura) – This purple or red rash is palpable, which means you can feel it with your fingers. It usually appears on the legs and buttocks. You might also see it in other areas, such as the face and stomach. This rash usually goes away in about a week, but sometimes it can last as long as one month.
What is the fastest way to cure purpura?
How is purpura treated?Corticosteroids. Your doctor may start you on a corticosteroid medication, which can help increase your platelet count by decreasing the activity of your immune system. ... Intravenous immunoglobulin. ... Other drug therapies. ... Splenectomy.
What medications can cause purpura?
Drug-induced thrombocytopenic purpura is a skin condition result from a low platelet count due to drug-induced anti-platelet antibodies caused by drugs such as heparin, sulfonamines, digoxin, quinine, and quinidine.
How do you treat Purpuric rash?
How is purpura treated?Corticosteroids. Your doctor may start you on a corticosteroid medication, which can help increase your platelet count by decreasing the activity of your immune system. ... Intravenous immunoglobulin. ... Other drug therapies. ... Splenectomy.
Is purpura an emergency?
Purpura fulminans is a rare, life-threatening disease state, classically defined as a cutaneous marker of disseminated intravascular coagulation, which can be present in both infective and non-infective disease states [1].
Can purpura be caused by stress?
Psychogenic purpura (also referred to as Gardner-Diamond syndrome, autoerythrocyte sensitization, or painful bruising syndrome) is a rare and poorly understood clinical presentation in which patients develop unexplained painful bruises, mostly on the extremities and/or face, during times of stress.
What does a rash from Covid look like?
Coronavirus rash appears in many ways Hives-like rash: Dermatologists are seeing patients with COVID-19 who develop a rash that looks like hives. Symptoms: Some rashes itch. Treatment: Some rashes require medical treatment. Rash on COVID-19 patient's thigh: This rash could also be mistaken for hives.
Do kidney problems cause skin rashes?
When kidneys cannot remove waste from your body, a rash can develop. One rash that occurs in people who have end-stage kidney disease causes small, dome-shaped, and extremely itchy bumps. As these bumps clear, new ones can form. Sometimes, the small bumps join together to form rough, raised patches.
What does a vascular rash look like?
It's thought to be triggered by the body reacting to an infection. It can cause: a rash that looks like small bruises or reddish-purple spots.
Is purpura an emergency?
Purpura fulminans is a rare, life-threatening disease state, classically defined as a cutaneous marker of disseminated intravascular coagulation, which can be present in both infective and non-infective disease states [1].
How long do purpura spots last?
Most purpuric lesions last between one and three weeks, though the discoloration may be permanent after they fade. You can talk to your dermatologist about how to reduce their appearance.
What are the signs and symptoms of purpura?
SymptomsRash (purpura). Reddish-purple spots that look like bruises develop on the buttocks, legs and feet. ... Swollen, sore joints (arthritis). People with Henoch-Schonlein purpura often have pain and swelling around the joints — mainly in the knees and ankles. ... Digestive tract symptoms. ... Kidney involvement.
Can purpura be caused by stress?
Psychogenic purpura (also referred to as Gardner-Diamond syndrome, autoerythrocyte sensitization, or painful bruising syndrome) is a rare and poorly understood clinical presentation in which patients develop unexplained painful bruises, mostly on the extremities and/or face, during times of stress.
Purpura: Causes, Types, and Symptoms - Verywell Health
Senile (or solar) purpura: This affects older people with thinner skin and more fragile blood vessels.It causes ecchymoses on the hands and forearms that look concerning, but is usually mild and resolves on its own. Some types of vasculitis: Vasculitis may cause purpura through inflammation of the blood vessels in the skin, gastrointestinal tract, and kidneys.
What is the best treatment for low platelet count?
The latest drugs used to treat low platelet count in people with chronic immune (idiopathic) thrombocytopenic purpura (ITP) are romiplostim (Nplate) and eltrombopag (Promacta). These medications cause bone marrow to produce more platelets, which reduces the risk of bruising and bleeding.
What is purpura in blood?
There are two kinds of purpura: nonthrombocytopenic and thrombocytopenic. Nonthrombocytopenic means that you have normal platelet levels in your blood. Thrombocytopenic means that you have a lower than normal platelet count.
How long does it take for a child to recover from thrombocytopenic purpura?
Most children with thrombocytopenic purpura fully recover within several months of the disorder’s onset. However, in adults, the causes for purpura are usually chronic and require treatment to help manage symptoms and keep platelet counts within a healthy range.
What is the treatment for purpura?
They may also give you IVIG if you need to increase your platelet count rapidly before surgery. This treatment is usually effective in increasing your platelet count , but the effect is usually only in the short term. It can cause side effects such as headache, nausea, and fever.
What is purpura on the inside of the mouth?
What is purpura? Purpura, also called blood spots or skin hemorrhages, refers to purple-colored spots that are most recognizable on the skin. The spots may also appear on organs or mucous membranes, including the membranes on the inside of the mouth. Purpura occurs when small blood vessels burst, causing blood to pool under the skin.
What causes nonthrombocytopenic purpura?
The following could cause nonthrombocytopenic purpura: disorders that affect blood clotting. certain congenital disorders, present at or before birth, such as telangiectasia (fragile skin and connective tissue) or Ehlers-Danlos syndrome. certain medications, including steroids and those that affect platelet function.
Why do you need a spleenectomy?
Removing the spleen is a fast way of increasing your platelet count. This is because the spleen is the main body part responsible for eliminating platelets.
What are the symptoms of purpura?
The rash looks like little red spots on the skin. It's easy to recognise because - unlike other spotty rashes - the spots don't fade when you press them. The best way to do this is with a drinking glass or other see-through object like a plastic ruler.
What causes purpura?
There are many different causes of purpuric rashes. Several of them can be grouped into those caused by lack of platelets and those in which the platelets are present in normal numbers. Conditions in which the platelet numbers are normal are called non-thrombocytopenic. Those in which the platelet numbers are low are called thrombocytopenic.
How is purpura diagnosed?
The doctor will need to ask you questions about the rash and your general health (take a history), examine you and do some tests.
Will I need any tests?
There are a huge number of tests which could be arranged, but hopefully by the time the doctor has taken your history and examined you they will have a reasonable idea as to which are the most important. Most tests can be done on blood samples and may include:
How is a purpura treated?
Leaflets on the specific conditions mentioned in the Causes section will give you more details. If your platelet count is very low, the first treatment you will receive will be a platelet transfusion.
What is the condition of the elastic tissue of the blood vessels?
Pseudoxanthoma elasticum (a condition affecting the elastic tissue of the blood vessels and other parts of the body).
What is the cause of aplastic anemia?
Aplastic anaemia (anaemia caused by problems with production of the platelets and other blood cells by the bone marrow). Myeloma. Cancer deposits replacing the bone marrow. Medicines such as co-trimoxazole (an antibiotic) and chemicals.
What causes a purpuric rash in meningococcal septicaemia?
The purpuric rash in meningococcal septicaemia is a result of vasculitis (inflammation of the blood vessels).
What is a photodistributed purpuric eruption associated with visible light phototherapy?
A photodistributed purpuric eruption associated with visible light phototherapy has been described in children with severe hyperbilirubinemia as a result of ABO or Rh incompatibility receiving exchange transfusions. Areas that are covered by monitoring leads, diapers, or clothing are spared ( Figure 9-12 ). It is thought that accumulation of porphyrin metabolites (such as coproporphyrin and protoporphyrin) from erythrocyte breakdown causes a transitory porphyrinemia and associated photosensitivity. Once the phototherapy is discontinued, the condition resolves spontaneously within a week.
Why are purpuric lesions elevated?
Lesions in DIC may be flat or elevated. Those that are elevated are so because of edema that acutely accompanies necrosis.
Where are petechial rash found?
Petechiae are found in the skin, mucous membranes, and conjunctivae but not in the nail beds.
What causes purpura fulminans?
Diffuse thrombosis, including stroke, retinal infarcts, limb gangrene, and DIC, can occur in purpura fulminans. Causes include severe protein C, protein S, or AT deficiency, either acquired as a complication of sepsis or inherited as homozygous or compound heterozygous conditions. Some infants with severe protein C deficiency do not develop TE until adulthood, suggesting that additional factors influence the neonatal presentation. Treatment with heparin and replacement with protein C concentrate or FFP are indicated. Long-term anticoagulation is often needed. 33
What are the symptoms of gastrointestinal disease?
Gastrointestinal disease occurs in 65 to 76% of patients. 1,6 Edema and hemorrhage of the bowel wall lead to severe colicky abdominal pain. The ultrasound correlation of uncomplicated pain shows mural thickening and hemorrhage. Plain films may show dilated thickened bowel loops. 7 Contrast radiology, when used, shows thickened mucosal folds and small barium flecks, presumably in small ulcers ( Figure 50-2 ). Endoscopic findings include ulceration, erythema, edema, hematoma-like protrusions, and petechiae. 8,9 In 14 to 36% of patients, the rash may occur later in the course than the GI manifestations, leading to diagnostic difficulties. Pain consistent with appendicitis can occur before the rash and lead to “unnecessary” appendectomy. Vasculitis and hemorrhage of the abdominal wall musculature can occur, leading to severe pain that can be difficult to diagnose. 7
What is the rapid onset of widespread truncal redness with thousands of pinpoint (0.1 mm) pus?
A rapid onset of widespread truncal redness with thousands of pinpoint (0.1 mm) pustules, followed by waves of desquamation, characterizes the distinct, uncommon reaction pattern of acute generalized erythematous pustulosis (AGEP) ( Fig. 20.20 ). 1,31–33 It may begin within hours of starting the drug and certainly within a few days. 31,32 The child appears toxic and may have fever. Rapid reversal occurs with discontinuation of the drug. AGEP is particularly associated with amoxicillin, macrolide antibiotics, and anticonvulsants ( Box 20.7 ).
What are the symptoms of nonthrombocytopenic purpura?
Senile purpura is characterized by ecchymoses on the hands and forearms, while symptoms of IgA vasculitis include a skin rash and joint pain.
How are purpura and thrombocytopenic purpura classified?
They are classified by whether platelets are involved. Platelets are cells in the bloodstream that work to clot blood and prevent bleeding. Thrombocytopenic purpura is caused by low platelet counts, while nonthrombocytopenic purpura is not related to the number of platelets in your blood.
How to treat thrombocytopenic purpura?
In children with ITP, the disease usually goes away on its own without treatment, but some may require medical interventions. Adults are usually started on a steroid medicine, prednisone or dexamethasone, and may need to have their spleens removed through a splenectomy to increase platelet levels. If your platelet count is dangerously low, your healthcare provider may recommend a platelet or blood transfusion as well.
Why does IgA cause purpura?
IgA vasculitis leads to purpura because of inflammation. When blood vessels experience inflammation, they become damaged and red blood cells leak out, causing the fine rash. IgA vasculitis usually occurs after a respiratory illness, such as strep throat, but the exact cause is still unknown.
What is the name of the condition that causes inflammation of the blood vessels in the skin, gastrointestinal tract, and kidney?
Vasculitis is a condition characterized by inflammation of the blood vessels in the skin, gastrointestinal tract, and kidneys. 3 IgA vasculitis, previously known as Henoch-Schönlein purpura, and leukocytoclastic vasculitis are among the subsets of this condition that can cause purpura.
How to tell if you have DIC?
Other signs of DIC include fever, hypotension, shortness of breath, and confusion. Heparin-induced thrombocytopenia causes purpura, pain, and redness. You may also see redness or a rash at the site where the heparin was administered. Later signs include numbness and weakness.
What causes purpura in the body?
Amyloidosis is a rare medical condition that causes abnormal proteins to build up in the body’s organs and tissues. This buildup of proteins leads to inflammation, which can cause purpura.
What are purpura rash patches?
Some people develop larger patches of 1 centimeter or greater. These are called ecchymoses. Sometimes the spots can appear on mucous membranes, for instance, inside the mouth.
What are the symptoms of purpura?
Patients who experience purpura with any of the following symptoms should seek medical treatment: Low platelet count, which may lead to increased bleeding after an injury, bleeding gums or nose, or blood in urine or bowel movements. Sore, swollen joints, particularly in the ankles and knees.
How to treat purpura?
This can include options such as chemotherapy, antiviral drugs, steroid medications, antibiotics, and surgery. Corticosteroids – these can help increase platelet count by reducing the activity of the immune system.
What is purpura in medical terms?
Purpura, also known as skin hemorrhages or blood spots, can signal a number of medical problems, ranging from minor injuries to life-threatening infections. Purpura is a symptom rather than a disease in itself, and there are a number of potential causes.
What is the cause of a lack of vitamin C?
A lack of vitamin C, also known as scurvy. Infectious or inflammatory diseases that affect the blood vessels. Some drugs, such as steroids and sulfonamides. Purpura with a lowered platelet count (thrombocytopenia) has a number of potential causes: drugs that reduce platelet count. recent blood transfusions.
What causes purpura?
Purpura that does not lower platelet levels (nonthrombocytopenia) has a range of causes and risk factors, including: Disorders and infections present from birth that cause abnormalities in blood vessels or blood production, such as Ehlers-Danlos syndrome and rubella.
How to treat Henoch-Schönlein purpura?
Treatment for Henoch-Schönlein purpura focuses on improving the symptoms. Doctors may recommend non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDS) to reduce inflammation and pain. Steroid treatment can reduce kidney damage and abdominal pain. If kidney damage is severe, doctors may prescribe drugs to suppress the immune system.
What are purpura?
Purpura are purple or red spots on the skin or mucus membranes. Purpura happen when blood leaks from blood vessels and collects under the skin or mucus membrane.
What increases my risk for purpura?
Any condition or medicine that causes low platelet levels can increase your risk for purpur a. Your risk is also increased if you have a condition, or take medicine, that prevents platelets from working correctly.
How is the cause of purpura diagnosed?
Your healthcare provider will examine you and ask about your symptoms. Tell him about any health condition you have that causes bleeding. Also tell him what medicines or supplements you take. You may need blood tests to count your platelets or time how fast your blood clots. You may also need blood tests to check for infection or other conditions that cause purpura.
How is purpura treated?
If you have a large amount of bleeding, you may need a blood transfusion, medicines, or surgery to stop the bleeding.
What can I do to manage my symptoms?
Do not take NSAIDs, aspirin, or blood thinner medicine. These medicines can make purpura worse. Ask your healthcare provider how long you need to stop these medicines.
When should I seek immediate care?
You have bleeding that does not stop or a bruise that suddenly gets bigger.
How to stop bleeding from nose?
Apply firm, steady pressure to cuts or scrapes. If possible, elevate the area above the level of your heart. If your nose bleeds, pinch the upper part of your nose and hold a tissue at the opening. Do this until the bleeding stops.
What is the mechanism of thrombocytopaenic purpura?
Thrombotic thrombocytopaenic purpura has a very specific mechanism where an antibody to ADAMTS-13 (A Disintegrin And Metalloprotease with a ThromboSpondin type motif member 13) forms which cleaves a clotting factor (Von Willibrand) leading to uncontrolled clotting. Thrombotic thrombocytopaenic purpura can be linked to a wide range of conditions, including HIV and systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE), and there is a very specific test for diagnosing it that assesses the levels of ADAMTS13 protein. Treatment include immunotherapy and plasmapheresis.
What is purpura fulminans?
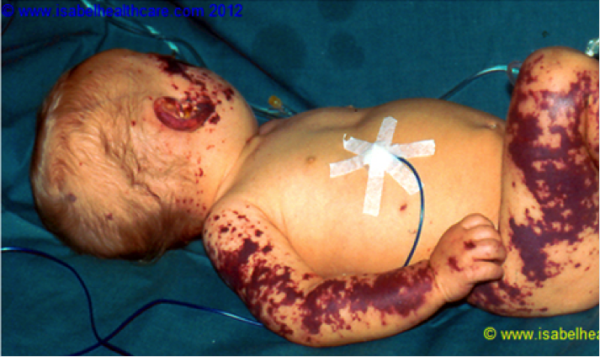
The first of these is purpura fulminans, a rare and severe complication of meningococcal septicaemia which is caused by Neisseria meningitidis. Although far more common in tropical countries than in North America, when meningococcal septicaemia does occur, it carries a high mortality-largely because it is not recognized until it’s too late. The bacteria latch on to the endothelial lining of blood vessels and activate the immune system, causing huge inflammation and massive leakage of vascular contents.
What is the cause of hemolytic uraemic syndrome?
Haemolytic uraemic syndrome is generally triggered by E coli infection. E coli shiga toxin binds to ceramide trihexoside on endothelial cells leading to platelet and clotting activation and the condition presents as bleeding and bruising, bloody diarrhoea, vomiting and abdominal pain and renal failure.
What is purpura in medical terms?
Purpura occurs when blood escapes from the vascular system into the skin. It can manifest in various ways from very small petechiae to large bruises, but despite its presentation, “they are all manifestations of the same problem. Although, the more most severely affected you are, the greater the leak is likely to be,” said Dr. Hay, of King’s College Hospital in London.
Why does the website store cookies?
This website stores data such as cookies to enable essential site functionality, as well as marketing, personalization, and analytics. Cookie Policy
How do you know if you're getting sick?
The warning signs of the patient getting really ill are largely relate to shock . The rash often becomes widespread, so for example conjunctiva can occur as well as pinpointing on the skin, and in more severe cases the mucosal surfaces may bleed. Other signs include worsening abdominal pain, increased vomiting, liver enlargement, high haematocrit with low platelet count, lethargy or restlessness.
Can meningococcal septicaemia cause fever?
These include limb pain, cold hands and feet, pale or mottled skin. People affected are likely to also have non-specific symptoms such as fever, drowsiness, rapid or laboured breathing, sometimes diarrhoea, and possibly thirst in older children.
How long does it take for thrombocytopenia to go away?
It is due to the production of an antibody to a specific platelet antigen that the woman normally lacks. The patient normally recovers within 1 to 3 weeks but the condition can be lethal and may need treatment with plasmapheresis or intravenous (IV) immunoglobulins.
Why are platelets important?
Platelets help maintain the integrity of the capillary lining as well as being important in the clotting process. As a general rule, purpura indicates a problem of the platelet system whilst a deficiency of clotting factors will cause haematomas or haemarthrosis as in haemophilia.
What is the most common cause of vasculitic purpura?
Allergic vasculitic purpura. This is caused by inflammation and infiltration of the blood vessel wall as an anaphylactic reaction to a number of physical and chemical stimuli, including infections. Henoch-Schönlein purpura (HSP) is one of the most common.
What is the cause of a fever in a child?
It is often preceded by an upper respiratory tract infection due to beta-haemolytic streptococcal infection. It can occur in epidemics in young children with a fever followed by a purpuric rash which may be slightly raised. Typically, it affects the fronts of the legs and the buttocks.
What is DIC in biology?
With DIC there is massive ecchymosis with sharp, irregular borders of deep purple colour and an erythematous halo. It can evolve to haemorrhagic bullae and blue-black gangrene. These appear as multiple lesions, often symmetrically involving distal extremities, areas of pressure and lips, ears, nose and trunk.
What is a professional reference?
Professional Reference articles are designed for health professionals to use. They are written by UK doctors and based on research evidence, UK and European Guidelines. You may find the Skin Rashes article more useful, or one of our other health articles.
What is a coagulation screen?
A coagulation screen will screen for clotting factor deficiencies.