Is glycerol the same thing as glycerin?
The main difference between glycerol and glycerin is glycerol is a pure form on the other hand glycerin contains 95% glycerol. Although that chemical formula is the same they cannot be used interchangeably especially when purity is preferred. It is a simple polyol compound, which is pure form.
How does glycerol become glucose?
Glycerol can be converted to dihydroxyacetone phosphate that can be converted to glucose through the gluconeogenic pathway. Glycerol kinase converts glycerol to glycerol-3-phosphate that, in turn, can be converted to dihydroxyacetone phosphate by cytosolic (and/or mitochondrial) glycerol 3-phosphate dehydrogenase.
Can oxaloacetate be converted to glucose?
Under some circumstances (such as starvation) oxaloacetate is drawn out of the citric acid cycle for use in synthesizing glucose. When the oxaloacetate concentration is very low, little acetyl-CoA enters the cycle, and ketone body formation is favored.
Can glucose-6-phosphate be converted back to glucose?
In mammals, glucose-6-phosphate (G6P) is formed by a kinase acting on glucose. It plays several roles and has its fate determined accordingly. It can get converted back to glucose by a phosphatase enzyme. It can pass into glycogen, or enter into the energy-yielding Embden-Meyerhof path or into the 6-phosphogluconate pathway.
What is the product of glycerol?
Glycerol, or also commonly known as glycerine in the oleochemical industry, is obtained as a co-product of fat splitting or transesterification. It can also be produced synthetically from propylene via epichlorohydrin.
Can glycerol be converted to ATP?
1 Oxidation of Glycerol. Glycerol may react with ATP under the catalytic influence of glycerol kinase to form glycerol-3-phosphate which is then oxidized in the presence of glycerol-3-phosphate dehydrogenase and NAD+ to produce dihydroxyacetone phosphate and enters into glycolysis.
Can glycerol be converted to fat?
In biochemistry, lipogenesis is the conversion of fatty acids and glycerol into fats, or a metabolic process through which acetyl-CoA is converted to triglyceride for storage in fat.
Can glycerol be converted to glucose in the body?
Glycerol derived from triacylglycerol in adipose tissue, and taken up by the liver is also converted to glucose via gluconeogenesis.
Can glycerol be converted to pyruvate?
Free glycerol is in equilibrium with triose phosphates and can be metabolized to pyruvate, oxaloacetate, phosphoenolpyruvate, and gluconeogenesis.
How is ATP formed from glycerol?
Glycerol. The anaerobic reactions of glycolysis accept glycerol as 3-phosphoglyceraldehyde, which then degrades to pyruvate to form ATP by substrate-level phosphorylation. Hydrogen atoms pass to NAD+, and the Krebs cycle oxidizes pyruvate.
How is glycerol broken down?
Lipolysis is the breakdown of triglycerides into glycerol and fatty acids, making them easier for the body to process.
Can humans turn fat into sugar?
The Bottom Line. Your body cannot convert fats directly into muscle-ready glycogen. However, through a series of metabolic processes that result from conditions of depleted carbohydrates, it is possible for stored fats to be broken down into glucose, which can then be converted into glycogen.
What happens to glycerol in metabolism?
Serum glycerol is mainly metabolized by the liver and kidneys. During the process glycerol kinase (GK) catalyzes glycerol into G3P, which can be used for lipid synthesis or enters glycolytic pathway after being oxidized into DHAP by FAD-dependent GPDH.
Can glycerol be used in glycolysis?
Glycerol is also a good substrate for energy, since it can be rapidly incorporated into the glycolytic pathway22.
Can the body convert fatty acids to glucose?
Glucose cannot be synthesized from fatty acids, since they are converted by β-oxidation into acetyl coenzyme A (CoA), which subsequently enters the citric acid cycle and is oxidized to CO2.
Which of the following can be converted to glucose?
CardsTerm Series of chemical reations that break down a large compound into smaller units is called:Definition CatabolismTerm Which of the following can be converted to glucose? Fatty acids Carbohydrate Alcohol ProteinDefinition Carbohydrate46 more rows•Nov 16, 2016
Can glycerol be oxidized?
The glycerol partial oxidation in the liquid phase can lead to various products such as aldehydes (glyceraldehyde), ketones (dihydroxyacetone), and carboxylic acids (glyceric acid, tartronic acid, glycolic acid, etc.)
How is glycerol metabolized?
Abstract. Glycerol is metabolized predominantly in the liver, the first step presumably being phosphorylation to α-glycerophosphate. When ethanol is present in the blood the rate of glycerol uptake by the splanchnic organs is reduced to about one-third of the control value.
What are the two fates of glycerol after it has been converted to a glycolysis intermediate?
Glycerol can be converted to glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate, an intermediate of glycolysis, and continue through the remainder of the cellular respiration breakdown pathway.
How many ATP are in lipids?
The last reaction is readily reversible if glycerol is needed for the synthesis of a lipid. The hydroxyacetone, obtained from glycerol is metabolized into one of two possible compounds....StepATP produced8 Acetyl CoA = 8 turns C.A.C.8 x 12 = 96 ATPFatty Acid Spiral34 ATPGRAND TOTAL130 ATP1 more row
Is glycerol converted to glucose in the liver?
The liver preferentially uses lactate, glycerol, and glucogenic amino acids (especially alanine) while the kidney preferentially uses lactate, glutamine and glycerol. The liver uses both glycogenolysis and gluconeogenesis to produce glucose, whereas the kidney only uses gluconeogenesis.
Does the liver convert glycerol?
During short-term fasting periods, the liver produces and releases glucose mainly through glycogenolysis. During prolonged fasting, glycogen is depleted, and hepatocytes synthesize glucose through gluconeogenesis using lactate, pyruvate, glycerol, and amino acids (Fig. 1).
How does glycerol enter glycolysis?
Glycerol enters gluconeogenesis, or glycolysis, depending on the cellular energy charge, as dihydroxyacetone phosphate or DHAP, whose synthesis occurs in two steps. Glycerol 3-phosphate is then oxidized to dihydroxyacetone phosphate, in the reaction catalyzed by glycerol 3-phosphate dehydrogenase (EC 1.1. 1.8).
Does the liver need glucose?
The liver produces, stores and releases glucose depending on the body’s need for glucose, a monosaccharide. This is primarily indicated by the hormones insulin – the main regulator of sugar in the blood – and glucagon.
Can Fats Be Turned Into Glycogen For Muscle?from diabetestalk.net
It is not possible for fats to be converted directly into glycogen because they are not made up glucose, but it is possible for fats to be indirectly broken down into glucose, which can be used to create glycogen. Relationship Between Fats and Glycogen Fats are a nutrient found in food and a compound used for long-term energy storage in the body, while glycogen is a chain of glucose molecules created by the body from glucose for short-term energy storage and utilization. Dietary fats are used for a number of functions in the body, including maintaining cell membranes, but they are not used primarily as a source of fast energy. Instead, for energy the body relies mostly on carbohydrates, which are converted into glucose that is then used to form glycogen. Turning Fats Into Glucose Excess glucose in the body is converted into stored fat under certain conditions, so it seems logical that glucose could be derived from fats. This process is called gluconeogenesis, and there are multiple pathways the body can use to achieve this conversion. Gluconeogenesis generally occurs only when the body cannot produce sufficient glucose from carbohydrates, such as during starvation or on a low-carbohydrate diet. This is less efficient than producing glucose through the metabolizing of carbohydrates, but it is possible under the right conditions. Turning Glucose Into Glycogen Once glucose has been obtained from fats, your body easily converts it into glycogen. In gl Continue reading >>
What is the purpose of protein catabolism?from diabetestalk.net
HEIMBURGER MD, in Handbook of Clinical Nutrition (Fourth Edition) , 2006 The major aim of protein catabolism during a state of starvation is to provide the glucogenic amino acids (especially alanine and glutamine) that serve as substrates for endogenous glucose production (gluconeogenesis) in the liver. In the hypometabolic/starved state, protein breakdown for gluconeogenesis is minimized, especially as ketones become the substrate preferred by certain tissues. In the hypermetabolic/stress state, gluconeogenesis increases dramatically and in proportion to the degree of the insult to increase the supply of glucose (the major fuel of reparation). Glucose is the only fuel that can be utilized by hypoxic tissues (anaerobic glycolysis), by phagocytosing (bacteria-killing) white cells, and by young fibroblasts. Infusions of glucose partially offset a negative energy balance but do not significantly suppress the high rates of gluconeogenesis in the catabolic patient. Hence, adequate supplies of protein are needed to replace the amino acids utilized for this metabolic response. In summary, the two physiologic states represent different responses to starvation. The hypometabolic patient, who conserves body mass by reducing the metabolic rate and using fat as the primary fuel (rather than glucose and its precursor amino acids), is adapted to starvation. The hypermetabolic patient also uses fat as a fuel but rapidly breaks down body protein to produce glucose, the fuel of reparation, thereby causing loss of muscle and organ tissue and endangering vital body functions. Joerg Klepper*, in Handbook of Clinical Neurology , 2013 Gluconeogenesis, predominantly in the liver, generates glucose from noncarbohydrate substrates such as lactate, glycerol, and glucogenic amino acid Continue reading >>
What is the process of glucose production?from diabetestalk.net
Gluconeogenesis (abbreviated GNG) is a metabolic pathway that results in the generation of glucose from non-carbohydrate carbon substrates such as lactate, glycerol, and glucogenic amino acids. It is one of the two main mechanisms humans and many other animals use to keep blood glucose levels from dropping too low (hypoglycemia). The other means of maintaining blood glucose levels is through the degradation of glycogen (glycogenolysis). Gluconeogenesis is a ubiquitous process, present in plants, animals, fungi, bacteria, and other microorganisms. In animals, gluconeogenesis takes place mainly in the liver and, to a lesser extent, in the cortex of kidneys. This process occurs during periods of fasting, starvation, low-carbohydrate diets, or intense exercise and is highly endergonic. For example, the pathway leading from phosphoenolpyruvate to glucose-6-phosphate requires 6 molecules of ATP. Gluconeogenesis is often associated with ketosis. Gluconeogenes is is also a target of therapy for type II diabetes, such as metformin, which inhibits glucose formation and stimulates glucose uptake by cells. Lactate is transported back to the liver where it is converted into pyruvate by the Cori cycle using the enzyme lactate dehydrogenase. Pyruvate, the first designated substrate of the gluconeogenic pathway, can then be used to generate glucose. All citric acid cycle intermediates, through conversion to oxaloacetate, amino acids other than lysine or leucine, and glycerol can also function as substrates for gluconeogenesis.Transamination or deamination of amino acids facilitates entering of their carbon skeleton into the cycle directly (as pyruvate or oxaloacetate), or indirectly via the citric acid cycle. Whether fatty acids can be converted into glucose in animals has been a longst Continue reading >>
What is the process of synthesis of glucose?from diabetestalk.net
The literal meaning of Gluconeogenesis is GLUCO – glucose; NEO – new; GENESIS – creation. Thus Gluconeogenes is is a biochemical term that describes the synthesis of glucose or glycogen from substances which are not carbohydrates. Gluconeogenesis is the procedure that generates the energy giving fuel ’ glucose’ from substances other than carbohydrates, which are stored in the body , when the carbohydrate substrates are not sufficiently available as in starvation or when they are of great demand as in intense physical exertion. [1,2,3,4] Gluconeogenesis Pathway Basically Gluconeogenesis is the reversal of Glycolysis which is the process of breaking down of glucose to produce energy. [1]Glycolysis proceeds to another energy cycle called Citric acid cycle by forming a substance called pyruvate. So, Gluconeogenesis is just the reversal of Glycolysis – starting with pyruvate. The substrates get converted to pyruvate or other intermediates of the Citric acid cycle by various chemical reactions from which Gluconeogenesis begins. Which way does the process go if all the set of enzymes are same for both glucose synthesis and breakdown? This conflict is overcome by the 3 key steps in Gluconeogenesis which cannot occur with enzymes of Glycolysis. So these 3 steps are circumvented by another set of enzymes to form glucose at the end. Substrates of Gluconeogenesis Glucogenic amino acids like alanine and glutamine Lactate which is produced as a byproduct of glycolysis in muscles, red blood cells etc Glycerol, which is a part of triacylglecerol molecule in adipose tissue Fatty acid Citric acid cycle intermediates through oxaloacetic acid Glucogenic amino acids Glucogenic amino acid undergoes transamination which causes change in the carbon skeleton and directly gets convert Continue reading >>
What is the mechanism of glucose metabolism?from diabetestalk.net
Gluconeogenesis is one of several main mechanisms used by humans and many other animals to maintain blood glucose levels, avoiding low levels (hypoglycemia). Other means include the degradation of glycogen (glycogenolysis) [1] and fatty acid catabolism.
What are the substrates of glucogenic amino acids?from diabetestalk.net
From breakdown of proteins, these substrates include glucogenic amino acids (although not ketogenic amino acids); from breakdown of lipids (such as triglycerides), they include glycerol (although not fatty acids); and from other steps in metabolism they include pyruvate and lactate.
How does fat become glycogen?from diabetestalk.net
The amount of fat in the average diet and the amount of stored fat in the average body make the notion of converting that fat into usable energy appealing. Glycogen, a form of energy stored in muscles for quick use, is what the body draws on first to perform movements, and higher glycogen levels result in higher usable energy. It is not possible for fats to be converted directly into glycogen because they are not made up glucose, but it is possible for fats to be indirectly broken down into glucose, which can be used to create glycogen. Relationship Between Fats and Glycogen Fats are a nutrient found in food and a compound used for long-term energy storage in the body, while glycogen is a chain of glucose molecules created by the body from glucose for short-term energy storage and utilization. Dietary fats are used for a number of functions in the body, including maintaining cell membranes, but they are not used primarily as a source of fast energy. Instead, for energy the body relies mostly on carbohydrates, which are converted into glucose that is then used to form glycogen. Turning Fats Into Glucose Excess glucose in the body is converted into stored fat under certain conditions, so it seems logical that glucose could be derived from fats. This process is called gluconeogenesis, and there are multiple pathways the body can use to achieve this conversion. Gluconeogenesis generally occurs only when the body cannot produce sufficient glucose from carbohydrates, such as during starvation or on a low-carbohydrate diet. This is less efficient than producing glucose through the metabolizing of carbohydrates, but it is possible under the right conditions. Turning Glucose Into Glycogen Once glucose has been obtained from fats, your body easily converts it into glycogen. In gl Continue reading >>
How is glycerin made?
Glycerin is a sugar alcohol derived from animal products, plants or petroleum. ... Vegetable glycerin is made by heating triglyceride-rich vegetable fats — such as palm, soy and coconut oils — under pressure or together with a strong alkali, such as lye.
What is glycerol an example of?
Overview. Glycerol is one of the sugar alcohols. Sugar alcohols belong to a class of polyols characterized by being white, water-soluble, organic compounds with a general chemical formula of (CHOH) n H 2. Sugar alcohols may be produced by the hydrogenation of sugars.
How is glycerol metabolized?
Serum glycerol is mainly metabolized by the liver and kidneys. During the process glycerol kinase (GK) catalyzes glycerol into G3P, which can be used for lipid synthesis or enters glycolytic pathway after being oxidized into DHAP by FAD-dependent GPDH.
What is glycerol Brainly?
Answer: Glycerol Definition. ... Glycerol is a sweet, syrupy fluid substance obtained from animal fats and oils or by the fermentation of glucose. It is used as a solvent, sweetener, and antifreeze and in making explosives and soaps.
Is glycerol a sugar?
Glycerin belongs to a special category of carbohydrates called polyols, which also includes sugar alcohols like sorbitol and erythritol. Like sugar alcohols, which I've talked about before, glycerin tastes sweet but it is not metabolized as sugar in the body and doesn't cause a rise in blood sugar.
What is glycerol in biology class 11?
Glycerol was first discovered in 1779 by Carl Scheele who is more famous for the discovery of oxygen. ... Glycerol also helps in production of dynamite. Structurally, glycerol is the trihydroxy sugar alcohol when three carbon atoms and three hydroxyl groups. Structure of glycerol is shown below.
What is glycerol in biology?
Glycerol is a colorless, odorless liquid with a sweet taste. ... Glycerol is seen in biological systems as an intermediate in carbohydrate and lipid metabolism because surplus carbohydrate can be converted into long chain fatty acids and esterified with the three hydroxyl groups.
Which valve controls the movement of food between the esophagus and stomach?
The pyloric sphincter serves as a valve that controls the movement of food between the esophagus and stomach.
How many teeth are in the small intestine?
Label the layers of the digestive tract wall and the associated structures. A set of primary teeth consists of 20 teeth, whereas a set of secondary teeth consists of 32 teeth. mucosa, submucosa, muscular layer, serosa.
Where is the hepatic portal triad located?
Three main vessels make up the hepatic portal triad. These structures are found on the inferior side of the liver. Blood arrives at the liver through two circulatory vessels. Blood from the digestive tract is diverted to the liver via the hepatic portal vein, which carries nutrient-rich, oxygen-poor blood to the liver.
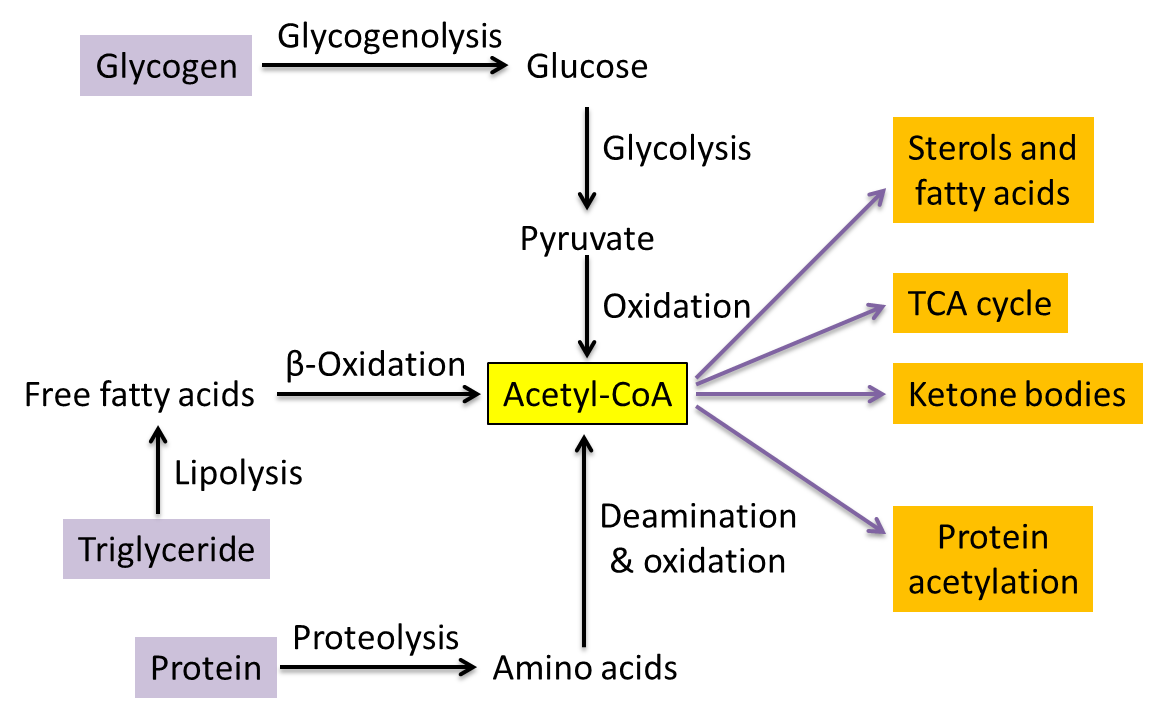
What are the steps of lipid metabolism?
Complete the sentences, then put the steps of lipid metabolism in order. Stored triglycerides are hydrolyzed to form glycerol and fatty acids. Glycerol can (1) be converted to glucose, (2) be used to re-form triglycerides, or (3) enter the cellular respiration pathway to produce ATP.
How are fatty acids broken down?
The fatty acids are further broken down into 2-carbon units by the process of beta oxidation. The 2-carbon units enter the respiratory pathway as aceytl CoA molecules. Place each image into the correct box, indicating whether the individual is in a positive nitrogen balance or a negative nitrogen balance.
What happens if a child has a few T lymphocytes?
The child will possess very few T lymphocytes and will be immunocompromised.
What is DiGeorge syndrome?
DiGeorge syndrome is a chromosomal disorder in which the thymus never develops/barely develops due to a deletion in a chromosome. Which of the following complications would you expect a child with DiGeorge syndrome to encounter?