A Depression and a panic in 1893 crippled the U.S. economy and exacerbated the argument over bimetallism, which came to be seen by some as the solution to all of the United States’ economic troubles. The drama peaked during the 1896 presidential election.
What is bimetallism?
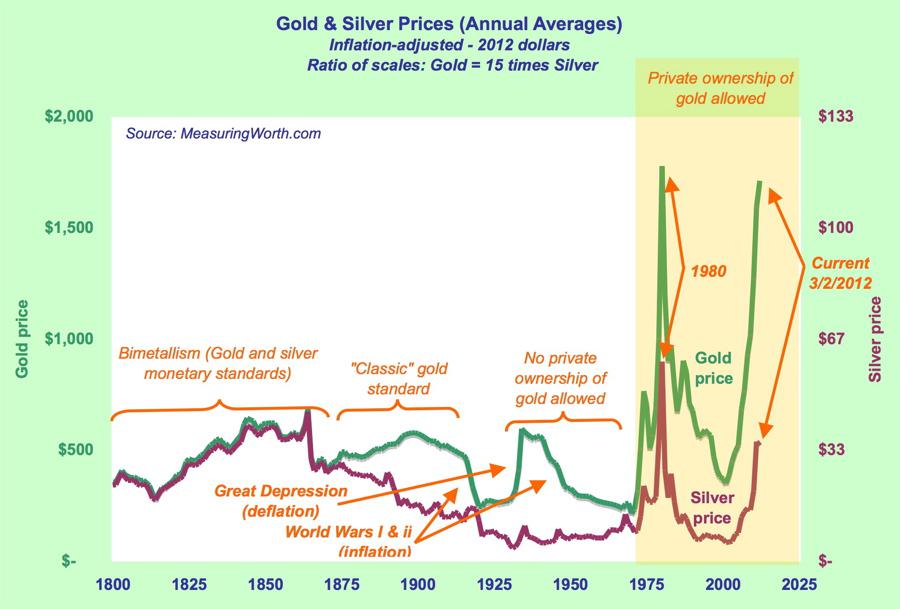
Bimetallism is a monetary standard in which the value of the monetary unit is defined as equivalent to certain quantities of two metals, typically gold and silver, creating a fixed rate of exchange between them.
When did bimetallism come to an end?
Ultimately, bimetallism drained the federal gold reserves and weakened the economy and bimetallism came to an end before the turn of the 20th century. Bimetallism is a monetary system that's based on the value of two metals, usually gold and silver. Bimetallism was very popular during the early and late 1800's.
What are the disadvantages of bimetallism?
Bimetallism is very unstable. Due to the fluctuation of the commercial value of the metals, the metal with a commercial price less than the legally-fixed price will be used as money and the other metal will be withdrawn from circulation as money.
Why did farmers support bimetallism?
Bimetallism. Farmers, especially in the wheat and cotton belts, supported bimetallism because they felt it was inflationary and advantageous to them and the economy; silver miners in the western United States supported bimetallism to ensure the value of silver.

Why was bimetallism created?
Bimetallism was intended to increase the supply of money, stabilize prices, and facilitate setting exchange rates.
When was the bimetallism created?
The bimetallic standard was first used in the United States in 1792 as a means of controlling the value of money. For example, during the 18th century in the United States, one ounce of gold was equal to 15 ounces of silver.
Who did bimetallism benefit?
Farmers, populists, and unions advocated for bimetallism because it would help them sell their goods at a higher price and lift them out of debt. The United States used bimetallism in the late 1800s and passed the Bland-Allison Act and the Sherman Silver Purchase Act to purchase a set number of silver each month.
Why did farmers support bimetallism?
Why did farmers support bimetallism or free silver? with more money in circulation prices for crops increased.
What was the significance of the cross of gold speech?
The Cross of Gold speech was delivered by William Jennings Bryan, a former United States Representative from Nebraska, at the Democratic National Convention in Chicago on July 9, 1896. In the address, Bryan supported bimetallism or "free silver", which he believed would bring the nation prosperity.
How does bimetallism cause inflation?
The Free Silver Movement was a political movement that proposed returning to “bimetallism”: Those in the movement wanted money backed by silver to be added to the money supply, which was backed by gold. Adding to the money supply would have ended the deflation and created the possibility of inflation.
Why did people oppose bimetallism?
Arguments advanced against bimetallism are: (1) it is practically impossible for a single nation to use such a standard without having international cooperation; (2) such a system is wasteful in that the mining, handling, and coinage of two metals is more costly; (3) because price stability is dependent on more than ...
What did William Jennings Bryan support?
After leaving office, Bryan retained some of his influence within the Democratic Party, but he increasingly devoted himself to Prohibition, religious matters, and anti-evolution activism. He opposed Darwinism on religious and humanitarian grounds, most famously in the 1925 Scopes Trial.
Why did populists support bimetallism?
Populist party calls for bimetallism, govt ownership of banks and railroads, lower interest rates on loans, and free coinage of silver. These people economically wanted an increase in the money supply, so they'd receive more money for their goods, income tax, & a federal loan program.
Who does free silver benefit?
farmersSupporters of free silver included owners of silver mines in the West, farmers who believed that an expanded currency would increase the price of their crops, and debtors who hoped it would enable them to pay their debts more easily.
What is the problem with bimetallism?
A major problem in the international use of bimetallism was that, with each nation independently setting its own rate of exchange between the two metals, the resulting rates often differed widely from country to country. In an attempt to establish the bimetallic system on an international scale, France, Belgium, Italy, ...
When was the bimetallic standard voted for?
The future of the bimetallic standard apparently had been sealed at an international monetary conference held in Paris in 1867, when most of the delegates voted for the gold standard. Supporters of bimetallism offer three arguments for it: (1) the combination of two metals can provide greater monetary reserves;
Definition
Do you know what the value of a dollar is? You might only have an idea of what you can buy with it - a stick of gum, or a candy bar maybe. But two hundred years ago, the value of that dollar was equal to a certain amount of gold or silver.
How the System Works
Of the two metals, gold is considered to be more valuable. In a bimetallic system, the value of gold and silver is tied to each other. For example, the value of one ounce of gold might be worth 15 ounces of silver. The value ratio of the two would be 1 to 15.
Bimetallism in the United States
The U.S. government adopted a bimetallic system in 1791 and began minting gold and silver coins. After just 15 years of minting silver coins, President Thomas Jefferson ended their use because most of the coins were being used in other countries, not the United States.
What is the problem with bimetallism?
One problem with bimetallism occurs when the face value of a coin is lower than the actual value of the metal it contains. A one-dollar silver coin, for example, might be worth $1.50 on the silver market. These value disparities resulted in a severe silver shortage as people stopped spending silver coins and opted instead to sell them ...
When was bimetallism first introduced?
History of Bimetallism. From 1792, when the U.S. Mint was established, until 1900, the United States was a bimetal country, with both silver and gold recognized as legal currency; in fact, you could bring silver or gold to a U.S. mint and have it converted into coins.
What is bimetallism in monetary policy?
Bimetallism is a monetary policy wherein the value of a currency is linked to the value of two metals, usually (but not necessarily) silver and gold. In this system, the value of the two metals would be linked to each other—in other words, the value of silver would be expressed in terms of gold, and vice versa —and either metal could be used as ...
Why is bimetallism unstable?
Due to the fluctuation of the commercial value of the metals, the metal with a commercial price less than the legally-fixed price will be used as money and the other metal will be withdrawn from circulation as money. (The general principle which governs this is called Gresham's Law .)
Why did farmers support bimetallism?
Farmers, especially in the wheat and cotton belts, supported bimetallism because they felt it was inflationary and advantageous to them and the economy ; silver miners in the western United States supported bimetallism to ensure the value of silver.
Why did silverites make a major effort to reestablish gold?
Because it became cheaper and cheaper in terms of gold, silverites made a major effort to reestablish it, in order to cause inflation and damage the financiers who supposedly monopolized gold. Silverites manages to force the U.S. Treasury to buy silver, but their efforts to make it currency failed.
What did the Silverites believe?
The "silverites" argued that using silver would inflate the money supply and mean more cash for everyone, which they equated with prosperity. The gold advocates said silver would permanently depress the economy, but that sound money produced by a gold standard would restore prosperity.
What was the silverite stance in the 1890s?
Heavy production of silver moved the ratio to 35:1 in the mid 1890s. The silverites in 1894 argued that gold enabled the bankers of London and New York (especially Jews like the Rothschilds) to have a stranglehold on honest people. from Harvey, Coin's Financial School (1894), the most popular silverite tract.

Overview
United States
In 1792, Secretary of the Treasury Alexander Hamilton proposed fixing the silver to gold exchange rate at 15:1, as well as establishing the mint for the public services of free coinage and currency regulation "in order not to abridge the quantity of circulating medium." With its acceptance, Sec.11 of the Coinage Act of 1792 established: "That the proportional value of gold to silver in all coins whic…
Historical creation
From the 7th century BCE, Asia Minor, especially in the areas of Lydia and Ionia, is known to have created a coinage based on electrum, a natural occurring material that is a variable mix of gold and silver (with about 54% gold and 44% silver). Before Croesus, his father Alyattes had already started to mint various types of non-standardized electrum coins. They were in use in Lydia and surro…
Argentina
In 1881, a currency reform in Argentina introduced a bimetallic standard, which went into effect in July 1883. Units of gold and silver pesos would be exchanged with paper peso notes at given par values, and fixed exchange rates against key international currencies would thus be established. Unlike many metallic standards, the system was very decentralized: no national monetary authority existed, and all control over convertibility rested with the five banks of issue. This conv…
France
A French law of 1803 granted anyone who brought gold or silver to its mint the right to have it coined at a nominal charge in addition to the official rates of 200 francs per kilogram of 90% silver, or 3100 francs per kilogram of 90% fine gold. This effectively established a bimetallic standard at the rate which had been used for French coinage since 1785, i.e. a relative valuation of gold to silver of 15.5 to 1. In 1803 this ratio was close to the market rate, but for most of the next half cen…
Latin Monetary Union
The national coinages introduced in Belgium (1832), Switzerland (1850), and Italy (1861) were based on France's bimetallic currency. These countries joined France in a treaty signed on 23 December 1865 which established the Latin Monetary Union (LMU). Greece joined the LMU in 1868 and about twenty other countries adhered to its standards. The LMU effectively adopted bimetallism by allowing unlimited free coinage of gold and silver at the 15.5 to 1 rate used in Fra…
United Kingdom
Medieval and early modern England used both gold and silver, at fixed rates, to provide the necessary range of coin denominations; but silver coinage began to be restricted in the 18th century, first informally, and then by an Act of Parliament in 1774. After the suspension of metal convertibility from 1797 to 1819, Peel's Bill set the country on the gold standard for the remainder of the century; however advocates of a return to bimetallism did not cease to appear. After the cras…
See also
• "Crime of 1873"
• Free silver
• Gold and Silver as an investment
• Gold and Silver standard
• Gresham's law