What factors force a shift in a demand curve?
There are five significant factors that cause a shift in the demand curve: income, trends and tastes, prices of related goods, expectations as well as the size and composition of the population.
What else can shift the demand or supply curve?
- More fuel-efficient cars means there is less need for gasoline. ...
- Cold weather increases the need for heating oil. ...
- A discovery of new oil will make oil more abundant. ...
- When an economy slows down, it produces less output and demands less input, including energy, which is used in the production of virtually everything. ...
What makes a shift in the aggregate demand curve?
Shifts in the aggregate demand curve . Graph to show increase in AD. An increase in AD (shift to the right of the curve) could be caused by a variety of factors. 1. Increased consumption: An increase in consumers wealth (higher house prices or value of shares) Lower Interest Rates which makes borrowing cheaper, therefore, people spend more on ...
What are the factors causing increase in demand?
Various factors responsible for increase in aggregate demand for goods and services are as follows. 1. Increase in Money Supply: An increase in the money supply leads to an increase in money income. The increase in money income raises the monetary demand for goods and services.
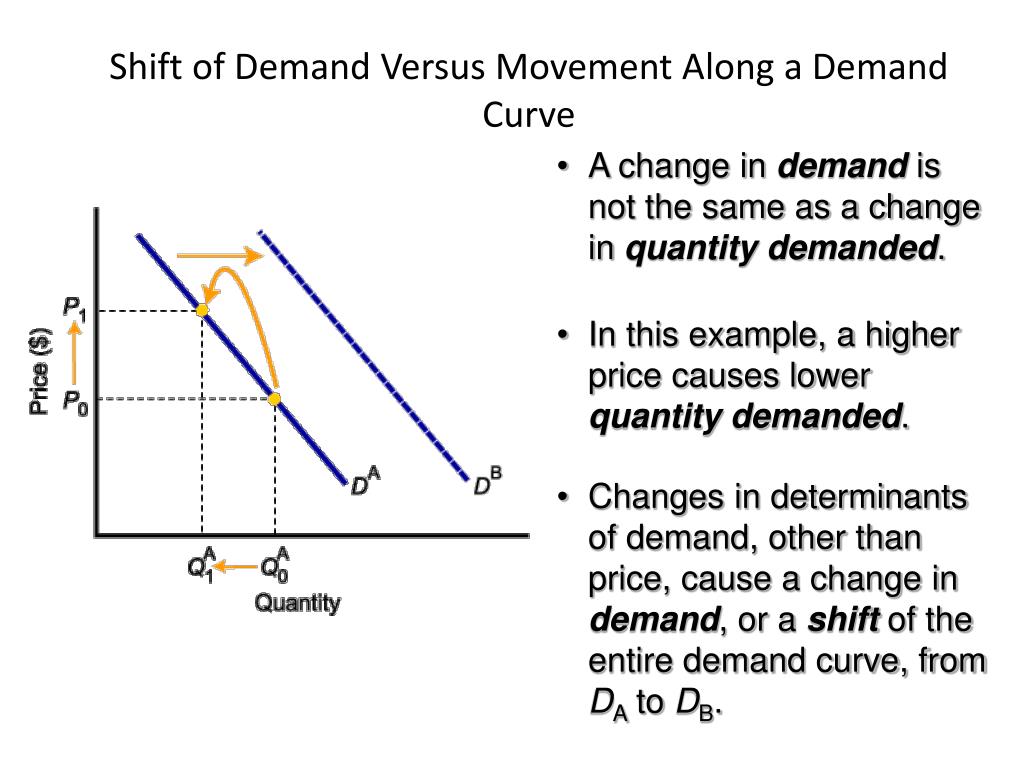
What could cause the demand curve shift to the right?
Increases in demand are shown by a shift to the right in the demand curve. This could be caused by a number of factors, including a rise in income, a rise in the price of a substitute or a fall in the price of a complement.
What are the 6 factors that can cause the demand curve to shift to the right?
6 Important Factors That Influence the Demand of GoodsTastes and Preferences of the Consumers:Income of the People:Changes in Prices of the Related Goods:Advertisement Expenditure:The Number of Consumers in the Market:
What are 3 things that will cause the demand curve to shift?
Other Factors That Shift Demand CurvesChanging Tastes or Preferences. ... Changes in the Composition of the Population. ... Changes in Expectations about Future Prices or Other Factors that Affect Demand.
What causes the demand curve to shift to the left?
A leftward shift in the demand curve indicates a decrease in demand because consumers are purchasing fewer products for the same price.
What are 5 things that will shift a supply curve to the right?
Supply shifters include (1) prices of factors of production, (2) returns from alternative activities, (3) technology, (4) seller expectations, (5) natural events, and (6) the number of sellers. When these other variables change, the all-other-things-unchanged conditions behind the original supply curve no longer hold.
What are the 4 main causes of demand changing?
The factors that may cause shifts in demand are: consumers' income, prices of related goods, consumers' tastes and preferences, expectations for the future, and changes in population.
What are the 5 factors that cause demand curve shifts?
5 Phenomenons That Cause a Shift in the Demand CurveChange in Taste and Preferences. ... Population Increase or Decrease. ... Price Change of a Related Good. ... Change in the Expected Future Prices. ... Change in the Income Level of Buyers.
Why does a demand fall from left to right?
Thus, when the quantity of goods is more, the marginal utility of the commodity is less. Thus, the consumer is not willing to pay more price for the commodity and its demand will decline. Also, when the price of the commodity is low, its demand increases. Hence, the demand curve slopes downwards from left to right.
What causes the demand curve to shift to the right to the left quizlet?
Any change that increases the demand shifts the demand curve to the right and is called an increase in demand. Any change that reduces the quantity demanded at every price shifts the demand curve to the left and is called a decrease in demand.
When the demand curve shifts to the right the equilibrium price?
If the demand curve shifts to the right, demand increases, leading to a higher equilibrium price. A shift to the right would result in a rise to the equilibrium, meaning higher prices.
What are the 6 demand shifters?
Demand shifters include preferences, the prices of related goods and services, income, demographic characteristics, and buyer expectations. Two goods are substitutes if an increase in the price of one causes an increase in the demand for the other.
What are the 6 major demand shifters?
Demand shifters include changes in any combination of the following factors:Consumer income.Styles, tastes, and habits.Prices or availability of related goods and services.Weather or season.Number of buyers.Expectations.Available credit or taxes.Consumer confidence in the health of the macroeconomy.
What causes the demand curve to shift to the right to the left quizlet?
Any change that increases the demand shifts the demand curve to the right and is called an increase in demand. Any change that reduces the quantity demanded at every price shifts the demand curve to the left and is called a decrease in demand.
What are the factors that cause a shift in the demand curve?
There are five significant factors that cause a shift in the demand curve: income, trends and tastes, prices of related goods, expectations as well as the size and composition of the population.
What is demand curve?
The demand curve tells us how much of a good or service people are willing to buy at any given price (see Law of Supply and Demand ). However, we know that demand is not constant over time. As a result, the demand curve constantly shifts left or right. Depending on the direction of the shift, this equals a decrease or an increase in demand. There are five significant factors that cause a shift in the demand curve: income, trends and tastes, prices of related goods, expectations as well as the size and composition of the population. We will look at each of them in more detail below.
How does income affect demand for goods?
By contrast, in the case of an inferior good, demand decreases as income grows. That means an increase in income shifts the demand curve to the left. This holds for goods that are usually replaced as income grows. A common example of an inferior good is bus rides. If people don’t have enough money to buy a car or pay for a taxi, they have to travel by bus. However, once their income allows them to buy a car, they don’t need bus rides anymore. Therefore, the demand for bus rides decreases as income increases and vice versa.
Why does demand increase with income?
In the case of a normal good, demand increases as the income grows. That is, an increase in income shifts the demand curve to the right. The reason for this is that with a higher salary, people can afford to buy more of any given good. And since people have unlimited wants, more is generally considered better.
What happens to the demand curve as the population grows?
As a result, the demand curve shifts to the right. For example, as the population grows, the demand for food increases as well, simply because there are more mouths to feed.
How does the population affect the demand curve?
This becomes apparent when we look at a simple example: Let’s say a country currently experiences a baby boom. As a consequence, the demand for diapers increases. Many years later, the population has grown old, and birthrates are down. Now, the demand for medical care and retirement homes is on the rise, while the demand for diapers decreases.
Which two types of related goods shift the demand curve in opposite directions?
There are two types of related goods, which shift the demand curve in opposite directions: substitutes and complements (see also Price Elasticity of Demand ).
Why does aggregate demand curve shift to the left?
The aggregate demand curve tends to shift to the left when total consumer spending declines. Consumers might spend less because the cost of living is rising or because government taxes have increased. Consumers may decide to spend less and save more if they expect prices to rise in the future.
What does it mean when the economy is right shift?
In macroeconomic models, right shifts in aggregate demand are typically viewed as a sign that aggregate demand increased or is growing —typically viewed as positive. Shifts to the left, a decrease in aggregate demand, mean that the economy is declining or shrinking—typically viewed as negative. However, this is not always the case.
What is demand shock?
According to macroeconomic theory, a demand shock is an important change somewhere in the economy that affects many spending decisions and causes a sudden and unexpected shift in the aggregate demand curve. Some shocks are caused by changes in technology.
How does contractionary fiscal policy affect aggregate demand?
Contractionary fiscal policy can also shift aggregate demand to the left. The government might decide to raise taxes or decrease spending to fix a budget deficit. Monetary policy has less immediate effects. If monetary policy raises the interest rate, individuals and businesses tend to borrow less and save more. This could shift AD to the left.
What happens to aggregate demand when aggregate supply remains unchanged?
If aggregate supply remains unchanged or is held constant, a change in aggregate demand shifts the AD curve to the left or to the right. The aggregate demand formula is identical to the formula for nominal gross domestic product.
What is aggregate demand?
Aggregate demand consists of the sum of consumer spending, investment spending, government spending, and the difference between exports and imports. When any of these aggregate demand inputs change, then there is a shift in aggregate demand.
What causes demand shocks?
In this case, the demand for total goods and services increases at the same time prices are falling. Diseases and natural disasters can cause demand shocks if they limit earnings and cause consumers to buy fewer goods. For example, Hurricane Katrina caused negative supply and demand shocks in New Orleans and the surrounding areas.

Income
Trends and Tastes
Prices of Related Goods
- There are two types of related goods, which shift the demand curve in opposite directions: substitutes and complements (see also Price Elasticity of Demand). We speak of substituteswhen a fall in the price of one good results in a decrease in the demand for another good. Thus, substitutes are goods that can be used to replace one another. The more closely related they ar…
Expectations
- People’s expectations about the future can have a significant impact on demand. Or, more specifically, their expectations of future prices or other factors that can change demand. If consumers expect prices to increase shortly, current demand often increases, i.e., the demand curve shifts to the right. For example, if consumers have reason to believe that the price of ice cr…
Size and Composition of The Population
- As a rule of thumb, a larger population results in a higher demand for most goods. As a result, the demand curve shifts to the right. For example, as the population grows, the demand for food increases as well, simply because there are more mouths to feed. In addition to that, the composition of the population also affects the demand curve. However...
Summary
- Demand for goods and services is not constant over time. As a result, the demand curve constantly shifts left or right. There are five significant factors that cause a shift in the demand curve: income, trends and tastes, prices of related goods, expectations as well as the size and composition of the population.