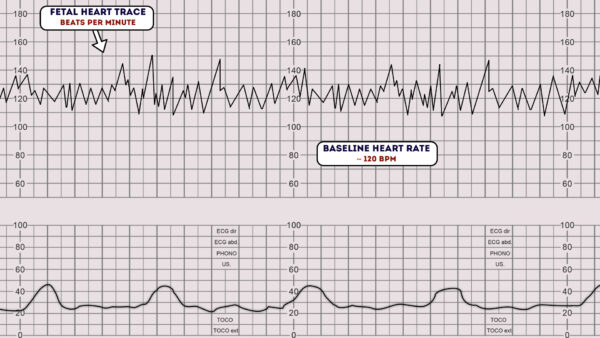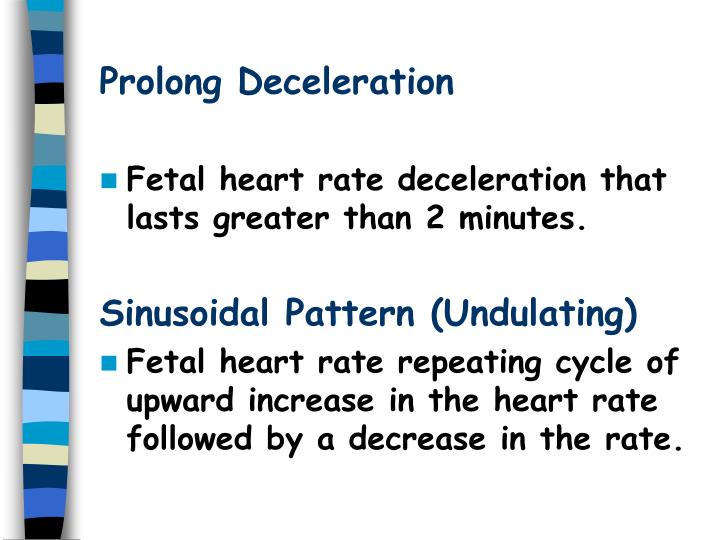
Prolonged Deceleration. Prolonged decelerations can be caused by any mechanism which normally may lead to periodic or episodic decelerations, but the return to baseline is delayed because the stimulus or mechanism causing the deceleration is not reversed. This often is associated with hypoxia.
What is prolonged deceleration?
Prolonged deceleration - finding (Concept Id: C0457246) A decrease in the fetal heart rate below baseline lasting 2 to less than 10 minutes with a decrease from baseline that is greater than or equal to 15 beats per minute. Prolonged deceleration - finding MedGen UID: 452559 •Concept ID: C0457246 Finding Synonyms:
What causes deceleration during pregnancy?
Deceleration has various causes, depending on the type. For example, late decelerations (a drop in the fetal heart rate after uterine contractions) are caused by a decrease in the placental blood flow. This results in insufficient oxygen supply to the fetus (uteroplacental insufficiency). 2
What is a variable deceleration?
A variable deceleration is a very quick decrease in fetal heart rate of 15 bpm or more, that lasts at least 15 seconds (but may last up to two minutes) before the heart rate returns to baseline. The onset of fetal slow heart rate, as well as the duration of the decelerations, varies with uterine contractions. What Causes Deceleration?
What are the complications of late deceleration?
Complications arising from repeated or prolonged late decelerations include: A low APGAR (i.e., appearance, pulse, grimace, activity, and respiration) score A multidisciplinary team of health care professionals manages the process of labor and delivery for you.

What does a prolonged deceleration mean?
Prolonged deceleration. A decrease in FHR below the baseline of 15 bpm or more, lasting at least 2 minutes but <10 minutes from onset to return to baseline. A prolonged deceleration of 10 minutes or more is considered a change in baseline.
What causes prolonged fetal heart rate deceleration?
Late decelerations are caused by uteroplacental insufficiency, which is a decrease in the blood flow to the placenta that reduces the amount of oxygen and nutrients transferred to the fetus. Any condition that predisposes decreased uteroplacental blood flow can cause late decelerations.
What are risk factors for late decelerations?
Causes of “late decelerations” or the drop in heart rate with uterine contraction are known to be : uteroplacental insuffiency ( not enough oxygen to the baby), amniotic fluid infection which can occur due to excessively long labor is permitted after the water has been broken, low maternal blood pressure, complications ...
What is the indication of late deceleration?
Late deceleration is defined as a visually apparent, gradual decrease in the fetal heart rate typically following the uterine contraction. The gradual decrease is defined as, from onset to nadir taking 30 seconds or more.
What are three 3 priority actions for late decelerations in the fetal heart rate?
Interventions for late decelerations are:Lower the head of the bed and turn the mom on her left side to take the pressure off the vena cava and allow blood flow to the heart and to the lungs. ... Re-oxygenation or the reintroduction of oxygen to the baby by giving oxygen to the mother.
What are the 4 types of fetal heart decelerations?
Decelerations are temporary drops in the fetal heart rate. There are three basic types of decelerations: early decelerations, late decelerations, and variable decelerations. Early decelerations are generally normal and not concerning. Late and variable decelerations can sometimes be a sign the baby isn't doing well.
Are late decelerations an emergency?
Specific patterns of deceleration, such as late deceleration, can be signs of fetal distress, which may require emergency interventions, such as a cesarean section delivery (C-section).
Are late decelerations common?
Late decelerations are relatively common and correlate with uteroplacental insufficiency.
How can late decelerations be prevented?
Also, you can take certain steps to treat late decelerations and improve fetal oxygen supply.Lie down in the left lateral, knee-chest, or right lateral position to relieve compression of the large vein (or vena cava) by your pregnant uterus. ... Your doctor might administer oxygen in response to late decelerations.More items...•
Can you have decelerations without contractions?
Variable decelerations have no fixed time relationship to uterine contractions. Therefore, the pattern of decelerations changes from one contraction to another. Variable decelerations are usually caused by compression of the umbilical cord and do not indicate the presence of fetal distress.
What heart rate is considered fetal distress?
The relation between fetal distress and the subsequent condition at birth was studied in 2791 pregnancies. Fetal distress was defined as a heart rate greater than 160 or less than 120/min between uterine contractions, with or without meconium-stained liquor.
What is the most common deceleration pattern encountered during labor?
VARIABLE DECELERATIONS They are the most commonly encountered patterns during labor and occur frequently in patients who have experienced premature rupture of membranes17 and decreased amniotic fluid volume. Variable decelerations are caused by compression of the umbilical cord.
What can cause a baby heart rate to drop?
A slow fetal heart rate is typically caused by problems with the heart's electrical system, which sends out electrical impulses that signal the heart muscles to contract or beat. The problem can occur in the sinus node, the heart's natural pacemaker, where these electrical impulses are generated.
What causes a baby heart rate to drop during labor?
Umbilical cord compression Sometimes the umbilical cord gets stretched and compressed during labor, leading to a brief decrease in blood flow to the fetus. This can cause sudden, short drops in fetal heart rate, called variable decelerations, which are usually picked up by monitors during labor.
Can uterine rupture cause prolonged decelerations?
Conclusions: The most common fetal heart rate abnormalities that occurred prior to uterine rupture were recurrent late decelerations and bradycardia. The appearance of recurrent late decelerations may be an early sign of impending uterine rupture.
What do early decelerations indicate?
Although the presence of early decelerations don't necessarily indicate fetal hypoxia, it does point to strong uterine contractions. That's why your doctor should carefully monitor your fetus' early decels as they're more likely to be receiving an insufficient amount of oxygen.
What is a fetal deceleration?
Fetal decelerations refer to temporary but distinct decreases of the fetal heart rate (FHR) identified during electronic fetal heart monitoring. El...
What causes decelerations in fetal heart rate?
The causes of fetal decelerations mainly depend on the types of decelerations.Early decelerations in FHR are caused by compression of the fetus’s h...
What do variable declarations indicate?
Variable decelerations usually indicate an obstruction to the fetal blood flow through the umbilical cord or compression of the umbilical vessels w...
What are the signs and symptoms of fetal deceleration?
The main sign of fetal decelerations is the decrease of fetal movements. Fetal movements are a sign of the fetus’s well-being and are typically fel...
How is fetal deceleration diagnosed?
Fetal decelerations are diagnosed based on FHR tracing. The FHR should be monitored throughout pregnancy, especially during every prenatal appointm...
How is fetal deceleration treated?
In order to treat fetal decelerations, immediate measures must be initiated to prevent fetal hypoxemia and decrease fetal morbidity and mortality....
What are the most important facts to know about fetal decelerations?
Fetal decelerations refer to short-term but clear decreases of the fetal heart rate (FHR) identified during fetal heart monitoring. They are classi...
What does prolonged deceleration mean?
A prolonged deceleration may signal danger—or reflect a perfectly normal fetal response to maternal pelvic examination. Because of the wide range of possibilities, this fetal heart rate pattern justifies close attention. For example, repetitive prolonged decelerations may indicate cord compression from oligohydramnios. Even more troubling, a prolonged deceleration may occur for the first time during the evolution of a profound catastrophe, such as amniotic fluid embolism or uterine rupture during vaginal birth after cesarean delivery (VBAC). In some circumstances, a prolonged deceleration may be the terminus of a progression of nonreassuring fetal heart rate (FHR) changes, and becomes the immediate precursor to fetal death ( TABLE 1 ). 1
Why do we differentiate between fetal bradycardia and prolonged deceleration?
In practice, we must differentiate these entities because underlying pathophysiologic mechanisms and clinical management may differ substantially.
Does amnioinfusion help with FHR decelerations?
Fetal bradycardias and prolonged decelerations are 2 distinct entities; the first usually does not warrant immediate intervention. Amnioinfusion for cord compression reduces variable FHR decelerations and the need for cesarean section.
What Causes Deceleration?
The cause of deceleration varies depending on the type. For example, early decelerations are caused by the compression of the baby’s head during uterine contractions. The compression causes vagal stimulation, which slows the fetal heart rate.
How long does a variable deceleration last?
A variable deceleration is a very quick decrease in fetal heart rate of 15 bpm or more, that lasts at least 15 seconds ( but may last up to two minutes) before the heart rate returns to baseline.
Why is my fetus decelerating?
Late decelerations may indicate that a fetus has high levels of acid in the blood (a condition called impending fetal academia), which is often caused by a lack of oxygen. 1
What does acceleration mean in fetal heart rate?
Accelerations are short-term increases in fetal heart rate by at least 15 beats per minute (bpm) that last at least 15 seconds. These accelerations occur at different times throughout labor and delivery and are a sign that the fetus has an adequate supply of oxygen.
How many types of deceleration are there in labor?
There are three types of deceleration that may occur during labor. Each type is categorized by the timing of the deceleration during uterine contractions. 1
When does FHR slow down?
The FHR begins to slow by midterm. By about 10 weeks of pregnancy, the FHR beings to slow to approximately twice the normal adult heart rate (which is about 60 to 100 bpm). The FHR can also slow down when the fetus is asleep.
What causes late deceleration?
Usually, any process that causes the following conditions is capable of inducing late decelerations: 1 Maternal low blood pressure (or hypotension) 2 Excessive activity in your uterus 3 Reduced oxygen supply to your placenta
What happens when you have late decels?
However, when late decels occur in more than 50 percent of the contractions of your uterus, then fetal hypoxia is a plausible explanation. Your doctor will then take action to prevent medical complications for your newborn.
Why is my placenta decelerating?
Reduced oxygen supply to your placenta. Two of the most common late deceleration causes include an overactive uterus and hypotension due to epidural analgesia. This is the injection of an anesthetic into your spinal epidural space to eliminate pelvic pain during labor and delivery.
What does it mean when your heart rate drops after labor?
Believed to be an abnormal FHR pattern, late decelerations indicate a reduction in heart rate, usually after a uterine contraction. Once deceleration starts, it takes about 20 to 30 seconds to reach its lowest point.
How long does it take for a deceleration to reach its lowest point?
Once deceleration starts, it takes about 20 to 30 seconds to reach its lowest point. When the timing of deceleration is delayed, it means that the lowest point is occurring past the peak of your uterine contraction. In the majority of cases, the beginning, low point, and recovery of late decelerations happen after the start, peak, ...
Is late deceleration dangerous?
One of many unusual FHR patterns observed during labor, late decelerations could be considered dangerous. They’re a sign of hampered blood flow to your placenta, which might trigger imminent fetal hypoxia (or a lack of oxygen for fetal tissues).
Can a doctor monitor late deceleration?
If your doctor identifies reversible causes, they’ll likely conduct other tests and closely monitor you. Also, you can take certain steps to treat late decelerations and improve fetal oxygen supply.
What is a fetal deceleration?
Fetal decelerations refer to temporary but distinct decreases of the fetal heart rate (FHR) identified during electronic fetal heart monitoring. Electronic fetal monitoring is used to record the heartbeat of the fetus and the contractions of the mother’s uterus before and during labor.
What causes decelerations in fetal heart rate?
The causes of fetal decelerations mainly depend on the types of decelerations.
What do variable declarations indicate?
Variable decelerations usually indicate an obstruction to the fetal blood flow through the umbilical cord or compression of the umbilical vessels within the cord.
What are the signs and symptoms of fetal deceleration?
The main sign of fetal decelerations is the decrease of fetal movements. Fetal movements are a sign of the fetus’s well-being and are typically felt by the mother around the 28th week of gestation.
How is fetal deceleration diagnosed?
Fetal decelerations are diagnosed based on FHR tracing. The FHR should be monitored throughout pregnancy, especially during every prenatal appointment. Additionally, the mother should note any changes in the fetal movements during the last few days in order to assess a decrease in fetal movements.
How is fetal deceleration treated?
In order to treat fetal decelerations, immediate measures must be initiated to prevent fetal hypoxemia and decrease fetal morbidity and mortality. All measures aim to restore efficient uteroplacental blood flow, increasing the oxygen transferred to the fetus.
What are the most important facts to know about fetal decelerations?
Fetal decelerations refer to short-term but clear decreases of the fetal heart rate (FHR) identified during fetal heart monitoring. They are classified into three categories according to their shape and timing related to uterine contractions: early, late, and variable decelerations.
What causes variable deceleration in a fetus?
Variable decelerations can be seen resulting from fetal movement if the fetus is premature.[4] In the term fetus, variable decelerations result from vagus nerve-mediated parasympathetic effects on the heart. There are several theories regarding the pathway that leads to this vagal stimulation.
How long does variable deceleration last?
Variable decelerations reaching a nadir of fewer than 60 beats per minute regardless of baseline and lasting longer than 60 seconds
What causes variable decelerations in fetal heart rate tracing?
Several aspects of the patient’s history are pertinent to the diagnosis of, or expectation for, variable decelerations. Small variable decelerations are often present in the fetal heart tracings of premature fetuses. In term fetuses, causes of low amniotic fluid are important to elicit. These include rupture of membranes and oligohydramnios (placental insufficiency, idiopathic, etc.). Other causes of umbilical cord compression may be implicated in the etiology of variable decelerations. For example, the presence of a nuchal cord may increase the risk of cord compression during uterine contractions. Monoamniotic twins are at risk of umbilical cord entanglement, which may manifest as fetal heart rate decelerations. Deep, recurrent variable decelerations may precede bradycardia in cases of uterine rupture. In a patient who presents in labor with an abnormal fetal heart rate tracing, a history of a prior classical cesarean section or previous uterine rupture would warrant immediate evaluation. Worrisome variable decelerations may also be present in cases of umbilical cord prolapse. A history of polyhydramnios, breech presentation, advanced cervical dilation, or high fetal station before the rupture of membranes may raise suspicion for a prolapsed umbilical cord.
Can pushing cause variable deceleration?
In the second stage of labor, maternal pushing efforts may also lead to variable decelerations with pushing. Depending on the presence or absence of other signs of reassuring fetal status, the patient might be directed not to push with every contraction to allow for adequate fetal recovery between pushes.
When does the nadir occur?
The nadir occurs at the same time as the peak of the contraction.
Does amnioinfusion reduce decelerations?
Initial management of recurrent variable decelerations should have a target of relieving potential cord compression.[8] Maternal repositioning is a reasonable first maneuver. Amnioinfusion, which reintroduces fluid into the uterine cavity, has also been shown to decrease decelerations and reduce the rate of cesarean delivery .[8] The 2012 Cochrane Review for amnioinfusion for umbilical cord compression showed not only an improvement in cesarean section and decelerations, but also in five-minute Apgar scores, postpartum endometritis, maternal hospital stay, and mean umbilical artery pH. [11]
What causes late deceleration?from flo.health
Usually, any process that causes the following conditions is capable of inducing late decelerations: 1 Maternal low blood pressure (or hypotension) 2 Excessive activity in your uterus 3 Reduced oxygen supply to your placenta
What does prolonged deceleration mean?from mdedge.com
A prolonged deceleration may signal danger—or reflect a perfectly normal fetal response to maternal pelvic examination. Because of the wide range of possibilities, this fetal heart rate pattern justifies close attention. For example, repetitive prolonged decelerations may indicate cord compression from oligohydramnios. Even more troubling, a prolonged deceleration may occur for the first time during the evolution of a profound catastrophe, such as amniotic fluid embolism or uterine rupture during vaginal birth after cesarean delivery (VBAC). In some circumstances, a prolonged deceleration may be the terminus of a progression of nonreassuring fetal heart rate (FHR) changes, and becomes the immediate precursor to fetal death ( TABLE 1 ). 1
Why is my placenta decelerating?from flo.health
Reduced oxygen supply to your placenta. Two of the most common late deceleration causes include an overactive uterus and hypotension due to epidural analgesia. This is the injection of an anesthetic into your spinal epidural space to eliminate pelvic pain during labor and delivery.
What does it mean when your heart rate drops after labor?from flo.health
Believed to be an abnormal FHR pattern, late decelerations indicate a reduction in heart rate, usually after a uterine contraction. Once deceleration starts, it takes about 20 to 30 seconds to reach its lowest point.
What happens when you have late decels?from flo.health
However, when late decels occur in more than 50 percent of the contractions of your uterus, then fetal hypoxia is a plausible explanation. Your doctor will then take action to prevent medical complications for your newborn.
How long does it take for a deceleration to reach its lowest point?from flo.health
Once deceleration starts, it takes about 20 to 30 seconds to reach its lowest point. When the timing of deceleration is delayed, it means that the lowest point is occurring past the peak of your uterine contraction. In the majority of cases, the beginning, low point, and recovery of late decelerations happen after the start, peak, ...
Why do we differentiate between fetal bradycardia and prolonged deceleration?from mdedge.com
In practice, we must differentiate these entities because underlying pathophysiologic mechanisms and clinical management may differ substantially.
What does decreased variability mean?
Decreased or absent variability therefore represents some dysfunction in one or both of these systems, or in increased and dominant tone of one system over the other , such as during sleep cycles or due to the effects of drugs.
Is FHR acceleration good or bad?
FHR accelerations and good (moderate) variability are closely associated and sometimes may be visually indistinguishable, though both are reflective of a well-oxygenated fetus.
Is a late deceleration the same as an early deceleration?
An early deceleration and a late deceleration may visually appear identical. Both are smooth and curvilinear and appear to be a mirror image of the contraction. The distinction between the two is based upon the relationship of the deceleration to the uterine contraction (UC).