There are several mechanisms that can produce a pyroclastic flow:
- Fountain collapse of an eruption column from a Plinian eruption (e.g. ...
- Fountain collapse of an eruption column associated with a Vulcanian eruption (e.g., Montserrat 's Soufrière Hills volcano has generated many of these deadly pyroclastic flows and surges). ...
- Frothing at the mouth of the vent during degassing of the erupted lava. ...
What type of surge is caused by pyroclastic flows?
Pyroclastic flows may generate surges. For example, the city of Saint-Pierre in Martinique in 1902 was overcome by one. Pyroclastic surge include 3 types, which are base surge, ash-cloud surge, and ground surge.
What causes a pyroclastic flow to increase in size?
This rapid heating of air causes the flow to increase in size and speed, hurling fragmented materials forward at an even faster rate than before. Pyroclastic flows can even move over water.
How many types of pyroclastic surge are there?
Pyroclastic surge include 3 types, which are base surge, ash-cloud surge, and ground surge. First recognized after the Taal Volcano eruption of 1965 in the Philippines, where a visiting volcanologist from USGS recognized the phenomenon as congruent to base surge in nuclear explosions.
What is an example of a Cold pyroclastic surge?
Cold pyroclastic surges can occur when the eruption is from a vent under a shallow lake or the sea. Fronts of some pyroclastic density currents are fully dilute; for example, during the eruption of Mount Pelée in 1902, a fully dilute current overwhelmed the city of Saint-Pierre and killed nearly 30,000 people.

How a pyroclastic is formed?
Most pyroclastic flows form by collapse of an eruption column, collapse of a dense slug of debris erupted just a few hundred meters above a vent, or collapse of the toe of a lava flow or dome growing on a steep slope.
What is the difference between a pyroclastic flow and a pyroclastic surge?
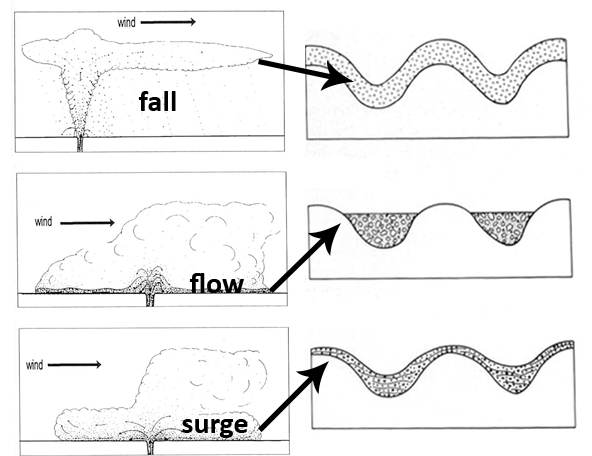
The difference between a pyroclastic flow and a pyroclastic surge is one of degree:- ❑ Flows are more dense than surges, consequently they tend to follow topography along predictable paths. Surges are less dense, they move more quickly and can surmount topography such as hills and ridges.
What are the 3 ways that a pyroclastic flow can form?
Pyroclastic flows and surges form in several ways: (1) gravitational collapse of a vertical eruption column (Sparks et al., 1978), (2) the "boiling-over" of a highly gas-charged magma from a crater (Taylor, 1958), (3) inclined blasts from the base of an emerging spine or dome (Lacroix, 1904), (4) lateral blasts ...
Where do pyroclastic flows occur?
Pyroclastic flows contain a high-density mix of hot lava blocks, pumice, ash and volcanic gas. They move at very high speed down volcanic slopes, typically following valleys.
Can you outrun a pyroclastic flow?
The first thing you should know if you want to escape from a pyroclastic flow is that you can't outrun them. They can reach speeds of up to 300 mile/hour; if you are in their path there is no escape.
Can you survive a pyroclastic flow?
1:415:54How to Survive a Pyroclastic Flow - YouTubeYouTubeStart of suggested clipEnd of suggested clipThey use flame resistant kevlar and breathable fabric wearing this will help you withstand theMoreThey use flame resistant kevlar and breathable fabric wearing this will help you withstand the incredibly hot temperatures number three seek shelter.
How does an explosive eruption produce a pyroclastic flow?
How does an explosive eruption produce pyroclastic flow? It builds up pressure and blows the top of, and it breaks lava into fragments that cool quickly and harden.
When was the last pyroclastic flow?
Fuego volcano: the deadly pyroclastic flows that have killed dozens in Guatemala. Dozens of people have been killed, and with many more missing, after Volcán de Fuego (Fuego) in Guatemala erupted on June 3 2018.
Do pyroclastic flows form during explosive or nonexplosive eruptions?
Do pyroclastic flows form during explosive or nonexplosive eruptions? These flows form during explosive eruptions because they are composed of ash and dust which is the material found in explosive eruptions.
What type of volcanoes produce pyroclastic flows?
Stratovolcanoes show inter-layering of lava flows and pyroclastic material, which is why they are sometimes called composite volcanoes. Pyroclastic material can make up over 50% of the volume of a stratovolcano.
How can you prevent pyroclastic flows?
Protecting yourself during ashfallStay inside, if possible, with windows and doors closed.Wear long-sleeved shirts and long pants.Use goggles to protect your eyes. ... Exposure to ash can harm your health, particularly the respiratory (breathing) tract. ... Keep your car or truck engine switched off.
How hot are pyroclastic flows?
These heavier-than-air flows race down the sides of a volcano much like an avalanche. Reaching speeds greater than 100 kilometers per hour (60 miles per hour) and temperatures between 200° and 700° Celsius (392°and 1292° Fahrenheit), pyroclastic flows are considered the most deadly of all volcano hazards.
What is the difference between pyroclastic flow and lava flow?
The difference between lava and pyroclastic flows lies on its speed. Lava creeps slowly and burns everything in its path but pyroclastic flows destroys nearly everything by land and air, its speed is usually greater than 80 km per hour, but it can reach 400 km per hour.
What are the different types of pyroclastic flows?
In general, there are two end-member types of flows:NUÉE ARDENTES -- these contain dense lava fragments derived from the collapse of a growing lava dome or dome flow, and.PUMICE FLOWS -- these contain vesiculated, low-density pumice derived from the collapse of an eruption column.
What are pyroclastic flows for kids?
A pyroclastic flow (also known as a pyroclastic density current or a pyroclastic cloud) is a fast-moving current of hot gas and volcanic matter (collectively known as tephra) that moves away from a volcano about 100 km/h (62 mph) on average but is capable of reaching speeds up to 700 km/h (430 mph).
What is a volcano surge?
A pyroclastic surge is a fluidized mass of turbulent gas and rock fragments that is ejected during some volcanic eruptions.
What is a pyroclastic surge?
From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia. Jump to navigation Jump to search. A pyroclastic surge is a fluidized mass of turbulent gas and rock fragments that is ejected during some volcanic eruptions. It is similar to a pyroclastic flow but it has a lower density or contains a much higher ratio of gas to rock, which makes it more turbulent ...
What are the three types of pyroclastic surges?
Pyroclastic surge include 3 types, which are base surge, ash-cloud surge, and ground surge.
How do base surges form?
They develop from the interaction of magma (often basaltic) and water to form thin wedge-shaped deposits characteristic of maars.
Where is ground surge found?
Ground surge. These deposits are often found at the base of pyroclastic flows. They are thinly bedded, laminated and often cross-bedded. Typically they are about 1 m. thick and consist mostly of lithic and crystal fragments (fine ash elutriated away).
What is base surge?
First recognized after the Taal Volcano eruption of 1965 in the Philippines, where a visiting volcanologist from USGS recognized the phenomenon as congruent to base surge in nuclear explosions. Very similar to the ground-hugging blasts associated with nuclear explosions, these surges are expanding rings of turbulent mixture of fragments and gas that surge outward at the base of explosion columns. Base surges are more likely generated by the interaction of magma and water or phreatomagmatic eruptions. They develop from the interaction of magma (often basaltic) and water to form thin wedge-shaped deposits characteristic of maars.
How does a pyroclastic form?
Some pyroclastic forms develop after an eruption collapse s a volcano’s hardened lava dome, whose dense rock then avalanches down the volcano. Within seconds, a faster-moving cloud of ash expands above and in front of the tumbling blocks of rock. These flows are known as “block-and-ash” flows because of their dual composition.
What is the Greek word for a pyroclastic flow?
The world pyroclast is derive d from the Greek pyr, meaning “fire”, and klastos, meaning “broken in pieces.”. A pyroclastic flow’s “broken pieces” consist of volcanic glass, crystal s, and rock s such as pumice or scoria. These solids have been heated and fragmented by an explosive eruption. Heavier fragments roll downward along ...
What is the name of the liquid landslide that occurs when pyroclastic flows mix with water
When pyroclastic flows mix with water, they create dangerous liquid landslide s called lahar s. The 1985 eruption of Nevado del Ruiz in Colombia caused pyroclastic flows to mix with melted snow and flow down into the surrounding river valleys.
How many people died in the eruption of Mount Vesuvius?
The famous 79 CE eruption of Mount Vesuvius buried the nearby cities of Pompeii and Herculaneum, Italy, in pyroclastic fallout, killing about 13,000 people.
How deep is the pyroclastic flow?
The 1991 eruption of Mount Pinatubo, Philippines, filled the Marella River valley with a pyroclastic flow 200 meters (656 feet) deep, more than the height of the Washington Monument.
Why do pumice flows cover larger areas?
The higher the volcanic debris is thrust into the air, the further it will fall by force of gravity, gaining momentum along the way. For this reason, pumice flows are able to cover larger areas faster than block-and-ash flows.
What is Andrews' method of simulated pyroclastic flows?
Andrews simulates pyroclastic flows using baby powder, walnut shells, and glass beads. Lasers allow him to study the dust currents left by the simulated flows, which helps other volcanologists estimate the paths or behavior of pyroclastic flows. to move forward or progress.
Why are pyroclastic surges so low density?
The reason they are low density is because they lack a high concentration of particles and contain a lot of gases. These flows are very turbulent and fast. They overtop high topographic features and are not confined to valleys.
How far can a pyroclastic surge travel?
Pyroclastic surges can travel up to at least 10 kilometers from the source (Scott, 1989). There are three types of pyroclastic surges: 1) base surge, 2) ash cloud surge, and 3) ground surge. A base surgeis usually formed when the volcano initially starts to erupt from the base of the eruption column as it collapses.
Can pyroclastic surges be dangerous?
Such deposits can be formed before, after, and during, the formation of pyroclastic flows (Francis, 1989). Pyroclastic surges are very hazardous. Such surges can bury, burn, and destroy things upon impact. These surges contain lots of gases that can asphyxiate people. Many people have been killed by pyroclastic surges.
What is a cold pyroclastic surge?
Cold pyroclastic surges can occur when the eruption is from a vent under a shallow lake or the sea. Fronts of some pyroclastic density currents are fully dilute; for example, during the eruption of Mount Pelée in 1902, a fully dilute current overwhelmed the city of Saint-Pierre and killed nearly 30,000 people.
What is a pyroclast?
The word pyroclast is derived from the Greek πῦρ, meaning "fire", and κλαστός, meaning "broken in pieces".
How far can pyroclastic flows travel?
Most pyroclastic flows are around 1 to 10 km 3 (about ¼ to 2½ cubic miles) and travel for several kilometres.
What is a fast moving current of hot gas and volcanic matter that moves away from a volcano?
Pyroclastic flows sweep down the flanks of Mayon Volcano, Philippines, in 1984. A pyroclastic flow (also known as a pyroclastic density current or a pyroc lastic cloud) is a fast-moving current of hot gas and volcanic matter (collectively known as tephra) ...
What is the name of the rock that is formed by the lava vents?
Frothing at the mouth of the vent during degassing of the erupted lava. This can lead to the production of a rock called ignimbrite. This occurred during the eruption of Novarupta in 1912.
What is the name of the directional blast that occurs when a volcano collapses?
The directional blast (or jet) when part of a volcano collapses or explodes (e.g., the eruption of Mount St. Helens on May 18, 1980 ).
Can pyroclastic flows cross water?
Interaction with water. Testimonial evidence from the 1883 eruption of Krakatoa, supported by experimental evidence, shows that pyroclastic flows can cross significant bodies of water. However, that might be a pyroclastic surge, not flow, because the density of a gravity current means it cannot move across the surface of water.
