
Causes
The time that it will take for an individual to completely recover from a Pneumothorax depends on the type of injury that caused it. In cases where a car accident or a penetrating injury such as a gunshot or a stab wound caused the Pneumothorax, then it may take anywhere from four to Eight weeks after treatment of the underlying cause for an individual to completely recover from a Pneumothorax.
Symptoms
What Causes A Tension Pneumothorax?
- Penetrating Injury To The Chest. Most common cause of tension pneumothorax is penetrating injury (trauma) to the chest. ...
- Closed Pneumothorax. ...
- Spontaneous Pneumothorax. ...
- Iatrogenic Lung Injuries. ...
- Positive pressure ventilation. ...
Prevention
The symptoms of pneumothorax can vary from mild to life-threatening and may include:
- shortness of breath
- chest pain, which may be more severe on one side of the chest
- sharp pain when inhaling
- pressure in the chest that gets worse over time
- blue discoloration of the skin or lips
- increased heart rate
- rapid breathing
- confusion or dizziness
- loss of consciousness or coma
Complications
WebMD adds: “It usually takes one or two weeks to recover from pneumothorax.” However, the website states the recovery period can be longer depending on the severity of the condition. What we know about CJ McCollum’s condition
How long does it take to recover from a pneumothorax?
What is the most common cause of pneumothorax?
What are the signs and symptoms of pneumothorax?
What is the recovery time for pneumothorax?
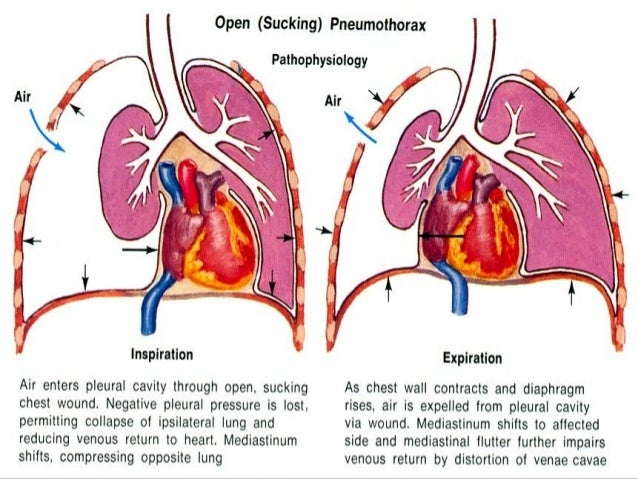
What is the difference between a simple pneumothorax and a tension pneumothorax?
Pneumothoraces can be classified as “simple” or “tension.” A simple pneumothorax is non-expanding. In a tension pneumothorax, a “one way valve” defect allows air into but not out of the pleural space. If left untreated, increasing pressure starts to collapse vascular structures within the mediastinum.
What is the most common cause of spontaneous pneumothorax?
Spontaneous means the pneumothorax was not caused by an injury such as a rib fracture. Primary spontaneous pneumothorax is likely due to the formation of small sacs of air (blebs) in lung tissue that rupture, causing air to leak into the pleural space.
Can a pneumothorax occur spontaneously?
Pneumothorax is defined as air or gas accumulated in the pleural cavity. A pneumothorax can occur spontaneously or after trauma to the lung or chest wall. Pneumothorax can also be divided into tension and non-tension.
Is simple pneumothorax a type of pneumothorax?
Depending on the cause, pneumothorax can be classified as spontaneous or traumatic. Spontaneous or simple pneumothorax can be further subdivided into primary spontaneous pneumothorax (in absence of an underlying lung disease) or secondary spontaneous pneumothorax (if resultant from an underlying lung disease).
What are 3 signs and symptoms of a pneumothorax?
What are the Symptoms of Pneumothorax?Sharp, stabbing chest pain that worsens when trying to breath in.Shortness of breath.Bluish skin caused by a lack of oxygen.Fatigue.Rapid breathing and heartbeat.A dry, hacking cough.
Who is at risk for pneumothorax?
In around 10% of cases, secondary spontaneous pneumothorax is fatal. The risk is higher if you have HIV or COPD. The risk of this type recurring within 5 years is around 43 percent , and the risk increases each time it happens.
Can a small pneumothorax heal itself?
A small pneumothorax may go away on its own over time. You may only need oxygen treatment and rest. The provider may use a needle to allow the air to escape from around the lung so it can expand more fully. You may be allowed to go home if you live near the hospital.
How is simple pneumothorax treated?
Treatment options may include observation, needle aspiration, chest tube insertion, nonsurgical repair or surgery. You may receive supplemental oxygen therapy to speed air reabsorption and lung expansion.
How is a small pneumothorax treated?
Most patients with secondary spontaneous pneumothorax (SSP) are treated with supplemental oxygen and removal of air from the pleural space, typically by chest tube thoracostomy. Patients also typically undergo a definitive procedure to prevent recurrence during the same hospitalization.
Is a pneumothorax life threatening?
If air continues to get into the pleural space as you breathe, this can start to squash organs like your other lung and heart. This is called a tension pneumothorax and can be life-threatening. Emergency treatment is needed to release the trapped air.
What are the three types of pneumothorax?
Pneumothorax is when air gets into the pleural cavity, often leading to a fully or partially collapsed lung. There are four types of pneumothorax....They are:traumatic pneumothorax. ... tension pneumothorax. ... primary spontaneous pneumothorax. ... secondary spontaneous pneumothorax.
Can vaping cause spontaneous pneumothorax?
Conclusion. Smoking is a well-known risk factor for primary spontaneous pneumothorax. There has been evidence that vaping has also been a risk factor and not a safer alternative to traditional smoking. Cessation is always advised with anyone at risk for spontaneous pneumothorax.
How common is spontaneous pneumothorax?
Primary spontaneous pneumothorax mostly occurs in 20-30 years of age. The incidence of PSP in the United States is 7 per 100,000 men and 1 per 100,000 women per year[5]. The majority of recurrence occurs within the first year, and incidence ranges widely from 25% to 50%.
Can spontaneous pneumothorax heal itself?
A small pneumothorax may go away on its own over time. You may only need oxygen treatment and rest. The provider may use a needle to allow the air to escape from around the lung so it can expand more fully. You may be allowed to go home if you live near the hospital.
How long does a spontaneous pneumothorax take to heal?
If your pneumothorax is caused by an underlying lung condition or chest trauma, you are more likely to need treatment. If the pneumothorax is small, the leak usually heals itself and the trapped air is gradually absorbed by your body. This normally takes 1-2 weeks.
What do you do for a spontaneous pneumothorax?
Treatment options may include observation, needle aspiration, chest tube insertion, nonsurgical repair or surgery. You may receive supplemental oxygen therapy to speed air reabsorption and lung expansion.
How do doctors measure pneumothorax?
The size of the pneumothorax is usually measured as the space between the lung and chest wall.
What causes a broken bone in the chest?
Other causes include sports injuries, car accidents, and puncture or stab wounds. A traumatic pneumothorax can occur even if there is no noticeable wound on the chest.
Why does a pneumothorax turn into tension?
Any of these types of pneumothorax can turn into a tension pneumothorax. This is caused by a leak in the pleural space that resembles a one-way valve. As a person inhales, the air leaks into the pleural space and becomes trapped. It cannot be released during an exhale.
What is the cause of PSP?
A primary spontaneous pneumothorax (PSP) occurs when the person has no known history of lung disease. The direct cause of PSP is unknown. At-risk groups for primary spontaneous pneumothorax include: tobacco or cannabis smokers. tall men. people ages 15-34.
How do you know if you have pneumothorax?
The symptoms of pneumothorax can vary from mild to life-threatening and may include: shortness of breath. chest pain, which may be more severe on one side of the chest. sharp pain when inhaling. pressure in the chest that gets worse over time. blue discoloration of the skin or lips. increased heart rate.
Which is more serious, SSP or PSP?
SSP carries more serious symptoms than PSP, and it is more likely to cause death. Lung diseases that may increase the risk of developing pneumothorax include: chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) cystic fibrosis. severe asthma. lung infections, such as tuberculosis and certain forms of pneumonia. sarcoidosis.
What causes pneumothorax?
The causes of pneumothorax are categorized as either primary spontaneous, secondary spontaneous, or traumatic.
What is the name of the disease that occurs when a person has no lung disease?
There are two major types of spontaneous pneumothorax: primary and secondary. Primary spontaneous pneumothorax (PSP) occurs in people who have no known lung disease, often affecting young males who are tall and thin.
What is the term for a lung injury that causes air to leak into the pleural space?
Traumatic pneumothorax. Traumatic pneumothorax occurs after some type of trauma or injury has happened to the chest or lung wall. It can be a minor or significant injury. The trauma can damage chest structures and cause air to leak into the pleural space.
What is pneumothorax in medical terms?
What is a pneumothorax? “Pneumothorax” is the medical term for a collapsed lung. Pneumothorax occurs when air enters the space around your lungs (the pleural space).
What are some examples of traumatic pneumothorax?
Examples of injuries that can cause a traumatic pneumothorax include: trauma to the chest from a motor vehicle accident. broken ribs. a hard hit to the chest from a contact sport, such as from a football tackle. a stab wound or bullet wound to the chest.
How many cases of secondary spontaneous pneumothorax are fatal?
In around 10% of cases, secondary spontaneous pneumothorax is fatal. The risk is higher if you have HIV or COPD. The risk of this type recurring within 5 years is around 43 percent, and the risk increases each time it happens.
How long does a chest tube stay in place?
This allows air to drain and the lung to reinflate. The chest tube may remain in place for several days if a large pneumothorax exists.
How do you know if you have a pneumothorax?
The onset of symptoms for a spontaneous pneumothorax normally occurs at rest. A sudden attack of chest pain is often the first symptom. Other symptoms may include: a steady ache in the chest. shortness of breath, or dyspnea. breaking out in a cold sweat. tightness in the chest. turning blue, or cyanosis.
How to prevent lung from collapsing again?
Your provider makes an incision and inserts a tube. Then your provider uses chemicals (such as doxycycline or talc) to attach the lung to the chest cavity, eliminating extra space in the chest cavity.
What is a collapsed lung?
A collapsed lung occurs when air enters the pleural space, the area between the chest wall and the lung. Air in the pleural space can build up and press against the lung, causing it to collapse partially or fully. Also called a deflated lung or pneumothorax, a collapsed lung needs immediate medical care.
What is the condition where the lung collapses?
Endometrial tissue lines the uterus. With endometriosis, it grows outside the uterus and attaches to an area inside the chest. The endometrial tissue forms cysts that bleed into the pleural space, causing the lung to collapse.
What is the condition where the chest is hard to breathe?
A collapsed lung occurs when air gets inside the chest cavity (outside the lung) and creates pressure against the lung. Also known as pneumothorax, collapsed lung is a rare condition that may cause chest pain and make it hard to breathe. A collapsed lung requires immediate medical care.
Why do you put a tube in your chest?
Chest tube drainage: If you have a larger pneumothorax, your provider may put a hollow tube in your chest to reduce the air in the pleural space. As the air pressure decreases, the lung re-expands and heals. You may have this tube in place for a couple of days or longer.
How long do you stay in the hospital after a lung transplant?
After treatment, you may be in the hospital for a couple of days or longer. This allows your provider to check your progress and give you oxygen, if necessary. You will make an appointment for follow-up visits. You should contact your provider if symptoms of collapsed lung return.
What are the factors that contribute to a collapsed lung?
Stab wound. Lifestyle factors associated with collapsed lung are: Drug use, especially inhaled drugs. Flying that involves drastic changes in air pressure. Scuba or deep-sea diving. Smoking. People with certain other risk factors may be more likely to have a collapsed lung. These are: Family history of pneumothorax.
How many cases of secondary spontaneous pneumothorax are there in a 100,000 patient population?
Secondary spontaneous pneumothorax is more seen in old age patients 60-65 years. The incidence of SSP is 6.3 and 2 cases for men and women per 100,000 patients, respectively. The male to female ratio is 3:1. COPD has an incidence of 26 pneumothoraces per 100,000 patients.[6] The risk of spontaneous pneumothorax in heavy smokers is 102 times higher than non-smokers.
How does air accumulate in the pleural space?
It occurs when air accumulates between the parietal and visceral pleurae inside the chest. The air accumulation can apply pressure on the lung and make it collapse. The degree of collapse determines the clinical presentation of pneumothorax. Air can enter the pleural space by two mechanisms, either by trauma causing a communication through ...
How long does it take to discharge a patient with a pneumothorax?
An asymptomatic small primary spontaneous pneumothorax (depth less than 2cm) patient is usually discharged with follow up in outpatient after 2-4 weeks. If the patient is symptomatic or depth/size is more than 2cm needle aspiration is done, after aspiration, if the patient improves and residual depth is less than 2cm then the patient is discharged otherwise tube thoracostomy is done.
What are the two subtypes of atraumatic pneumothorax?
The two subtypes of atraumatic pneumothorax are primary and secondary. A primary spontaneous pneumothorax (PSP) occurs automatically without a known eliciting event, while a secondary spontaneous pneumothorax (SSP) occurs subsequent to an underlying pulmonary disease.
What is an open pneumothorax?
Open pneumothorax is an open wound in the chest wall through which air moves in and out .[1][2][3][4] A pneumothorax is defined as a collection of air outside the lung but within the pleural cavity. It occurs when air accumulates between the parietal and visceral pleurae inside the chest. The air accumulation can apply pressure on ...
What is traumatic pneumothorax?
A traumatic pneumothorax can be the result of blunt or penetrating trauma. Pneumothoraces can be even further classified as simple, tension, or open. A simple pneumothorax does not shift the mediastinal structures, as does a tension pneumothorax. Open pneumothorax is an open wound in the chest wall through which air moves in and out.[1][2][3][4] ...
How does pressure change in a pneumothorax?
The pressure gradient inside the thorax changes with a pneumothorax. Normally the pressure of the pleural space is negative when compared to atmospheric pressure. When the chest wall expands outwards, the lung also expands outwards due to surface tension between parietal and visceral pleurae. Lungs have a tendency to collapse due to elastic recoil. When there is communication between the alveoli and the pleural space, air fills this space changing the gradient, lung collapse unit equilibrium is achieved, or the rupture is sealed. Pneumothorax enlarges, and the lung gets smaller due to this vital capacity, and oxygen partial pressure decreases. Clinical presentation of a pneumothorax can range anywhere from asymptomatic to chest pain and shortness of breath. A tension pneumothorax can cause severe hypotension (obstructive shock) and even death. An increase in central venous pressure can result in distended neck veins, hypotension. Patients may have tachypnea, dyspnea, tachycardia, and hypoxia.
How does pneumothorax develop?
A pneumothorax can develop when fluid begins to build up between the pleura and chest wall as a result of the quantity of fluid present inside of the lung tissues. When the pressure in the pleural space around the patient's lung becomes more than that of the air entering the air sacs in the lungs, the organ can collapse in on itself.
How many mutations are there in the FLCN gene?
Currently, eight different mutations in the FLCN gene are known to increase an individual's chances of a primary spontaneous pneumothorax. The FLCN gene is responsible for providing an individual's body with the encoded instructions for how to make a protein referred to as folliculin.
How to treat a small pneumothorax?
A small pneumothorax may be treated with observation. For a larger pneumothorax, medical personnel will perform a needle aspiration. In this procedure, excess air is removed through the insertion of a catheter between the ribs. If necessary, doctors may also need to insert a chest drain.
What is a pneumothorax?
Also known as a collapsed lung, a pneumothorax is generally considered a medical emergency. It can include a partial or complete collapse of the lung. As air leaks into the space between the lungs and the chest wall, it places pressure on the lung, leading to collapse. Symptoms of a pneumothorax include sudden onset chest pain and shortness ...
Which type of fibrosis has the highest rate of pneumothorax recurrence?
The highest rate of pneumothorax recurrence is in cystic fibrosis patients. Some researchers have established an association between the presence of air blebs that have been precipitated by inflammation and the development of a pneumothorax recurrence in most patients who have previously had one.
How old is too old to get a pneumothorax?
A primary spontaneous pneumothorax is most prevalent among individuals between fifteen and thirty-four years old. Children under ten years old can be at a greater risk of developing a pneumothorax if they are affected by certain conditions that include echinococcosis, foreign object inhalation, measles, and certain congenital malformations. A child may also be at an increased risk of developing a pneumothorax if they have a family member who has had a pneumothorax previously.
What are air blisters?
Air blisters, also known as blebs, may sometimes form at the top of the lungs. If these rupture, air could leak into the surrounding space, triggering a pneumothorax. Ruptured air blisters occur most frequently in men between the ages of twenty and forty, particularly in those who are taller than average and underweight. Air blisters are also common in patients who have emphysema. To treat air blisters, doctors may need to perform surgery. Using general anesthesia, surgeons can carry out a bleb resection, which is typically performed with a thoracoscope, a small camera that enables visual inspection of the inside of the chest.
What causes pneumothorax?
Pneumothorax can be caused by a number of diseases and conditions. There are two general types: Spontaneous pneumothorax occurs spontaneously, without prior lung disease. It occurs as a result of having an underlying lung disease, such as COPD, cystic fibrosis, emphysema, asthma, tuberculosis, or whooping cough.
What is pneumothorax in lung?
A pneumothorax is an accumulation of air or gas in the space between the lung and the chest wall that occurs when a hole develops in the lung that allows air to escape. This causes the lung to partially or completely collapse, hence the condition's other name: collapsed lung.
How long after a pneumothorax can you fly?
You also should not fly or scuba dive for two weeks following discharge from a hospital after being treated.
What test is used to determine if you have pneumothorax?
Tests that support a diagnosis of pneumothorax include: Arterial blood gas testing, which measures blood oxygen and carbon dioxide levels 1 .
How long does a chest tube stay in place?
A chest (thoracostomy) tube may then be inserted and will stay in place for several days while you recover in the hospital. If the pneumothorax recurs, video-assisted thoracic surgery may be required. Inserting the tube or needle can be painful, so you may receive painkillers by IV or regional anesthesia.
How to tell if you have a large pneumothorax?
Symptoms of a large pneumothorax include: 1 . Sharp chest pain that gets worse when coughing or taking a deep breath and that may radiate to the shoulder, arm, or back. Shortness of breath ( dyspnea) or shallow breathing. Chest tightness. Being easily fatigued.
How many people are treated for collapsed lung?
This causes the lung to partially or completely collapse, hence the condition's other name: collapsed lung. In the United States, 5 million people are treated for it each year. Jackyenjoyphotography / Getty Images. In the past, it occurred most frequently in conjunction with tuberculosis.
What is a spontaneous pneumothorax?
A spontaneous pneumothorax is a collapsed lung. Part or all of the lung may collapse. Air collects in the pleural space (the space between the lungs and chest wall). The trapped air prevents your lung from filling, and the lung collapses. A spontaneous pneumothorax can happen in one or both lungs. A primary spontaneous pneumothorax occurs in a person with no known lung problems. A secondary spontaneous pneumothorax occurs in a person who has a known lung disease or medical condition.
What is the difference between a primary and secondary pneumothorax?
A primary spontaneous pneumothorax occurs in a person with no known lung problems. A secondary spontaneous pneumothorax occurs in a person who has a known lung disease or medical condition.
Why does air leak out of the pleural space?
This allows air to leak out and become trapped in the pleural space. Air may also enter the pleural space if your lung tissue is damaged.
What does a chest x-ray show?
Chest x-ray: This is a picture of the bones, lungs, and other tissues in your chest. Healthcare providers use chest x-rays to see if you have broken ribs. These x-rays may show your healthcare provider how large your pneumothorax is. Chest x-rays may also show fluid around the heart and lungs.
What is the procedure used to irritate the walls of the pleural space?
Pleurodesis is a procedure used to irritate the walls of your pleural space. This causes the walls to close so air can no longer be trapped.
What is the name of the test that shows fluid around the heart and lungs?
Chest x-rays may also show fluid around the heart and lungs. CT scan: This test is also called a CAT scan. An x-ray machine uses a computer to take pictures of your chest and lungs. Healthcare providers check for a pneumothorax that did not show up on a chest x-ray.
What happens when you have a tension pneumothorax?
With a tension pneumothorax, the injured lung and trapped air push against your uninjured lung. A tension pneumothorax can lead to low blood pressure, decreased oxygen in your blood, and heart problems. Treatments that require cuts in your skin to reach your lung may lead to an infection in the lung area.
What causes tension pneumothorax?
However, it is most commonly seen after a traumatic chest injury or in individuals breathing through mechanic al ventilation .
What are the symptoms of pneumothorax tension?
Additional signs can include tracheal deviation away from the pneumothorax, distended neck veins, and decreased or absent breath sounds upon auscultation.
What happens when you have a pneumothorax?
When there's damage to the pleura, either due to lung disease or trauma to the chest wall, air from the outside or from the lungs can flow freely into the pleural space, but cannot leave. The accumulated air in the pleural space puts positive pressure on the lung and prevents it from expanding properly, which causes respiratory distress. As the air continues to accumulate, the trachea and other structures of the chest can be pushed away from the pneumothorax, leading to increased difficulty breathing. Additionally, the increased pressure inside the chest can compress the heart and lead to a collapse of the blood vessels that drain to the heart, in turn decreasing venous return and cardiac output. If left untreated, tension pneumothorax can rapidly progress to cardiovascular collapse, which ultimately leads to cardiac arrest.
What are the symptoms of a collapsed lung?
Upon physical examination, common findings include tracheal deviation away from the affected side, decreased or absent breath sounds upon lung auscultation, hyperresonant chest percussion, and asymmetrical expansion of the chest due to the collapsed affected lung. In severe cases, individuals can present blue discoloration of the skin due to decreased oxygen levels in the blood, and distended neck veins as a result of the collapsed blood vessels that should return blood to the heart.
What happens after a chest tube is placed?
After placing the chest tube, a chest X-ray is usually obtained to check the location of the tube and the successful re-expansion of the lung.
Can air enter the pleural space during inspiration?
As a result, air can enter the pleural space during inspiration, but is unable to escape during expiration. The accumulated air in the pleural space compresses the lungs, blood vessels, and other structures of the chest cavity. Tension pneumothorax can lead to significant respiratory distress and hemodynamic instability.
Can a tension pneumothorax be transferred to a critical care unit?
This procedure can be life-saving, especially in the prehospital setting, as transport to the hospital can delay treatment. Individuals with a tension pneumothorax should be transferred to a critical care unit, where they can be monitored for their vital signs and administered high-concentration supplemental oxygen.
What is an occult pneumothorax?
An occult pneumothorax refers to one missed on initial imaging, usually a supine /semierect chest radiograph 24. For those pneumothoraces occurring in neonates see the article on neonatal pneumothorax. On this page:
How old is a person when they have a pneumothorax?
There are many causes of pneumothorax which makes it impossible to generalize the epidemiology. However, primary spontaneous pneumothoraces occur in younger patients (typically less than 35 years of age) whereas secondary spontaneous pneumothoraces occur in older patients (typically over 45 years of age) 4 .
What does pneumothorax mean?
Pneumothorax is derived from two Greek words, πνευμα (pneumα) meaning breath and θωραξ (thorax) meaning breastplate. The synonym, aerothorax, which is rarely, if ever, seen in modern medicine also has Greek roots, from αερος (aero) meaning air 22,23.
What is a pneumothorax on a chest radiograph?
Plain radiograph. A pneumothorax is, when looked for, usually easily appreciated on erect chest radio graphs. Typically they demonstrate: visible visceral pleural edge is seen as a very thin, sharp white line. no lung markings are seen peripheral to this line.
What is M mode ultrasound?
Ultrasound. M-mode can be used to determine movement of the lung within the rib-interspace. Small pneumothoraces are best appreciated anteriorly in the supine position (gas rises) whereas large pneumothoraces are appreciated laterally in the mid-axillary line. See: ultrasound for pneumothorax.
What is a primary spontaneous pneumothorax?
Primary spontaneous. A primary spontaneous pneumothorax is one which occurs in a patient with no known underlying lung disease. Tall and thin people are more likely to develop a primary spontaneous pneumothorax. There may be a familial component, and there are well-known associations 10: Marfan syndrome.
What is the term for the presence of air in the pleural space?
Pneumothorax, sometimes abbreviated to PTX, (plural: pneumothoraces) refers to the presence of gas (often air) in the pleural space. When this collection of gas is constantly enlarging with resulting compression of mediastinal structures, it can be life-threatening and is known as a tension pneumothorax ...
