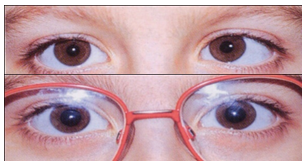
What is accommodative esotropia?
What is accommodative esotropia? Accommodative esotropia, or refractive esotropia, is one of the most common forms of esotropia (crossed eye), which is a type of strabismus, or eye misalignment. It refers to eye crossing that is caused by the focusing efforts of the eyes as they try to see clearly.
What is refractive esotropia and what causes it?
It refers to eye crossing that is caused by the focusing efforts of the eyes as they try to see clearly. Patients with refractive esotropia are typically farsighted (hyperopic).
How does esotropia affect the brain?
In esotropia, one eye may become turned in. When the eye is turned in, the brain typically suppresses or ignores the image the eye sees. Otherwise, the person with esotropia would see double constantly.
What is the disease entity of esotropia?
Disease Entity. It is usually found in patients with moderate amounts of hyperopia. As the patient accommodates or focuses the eyes, the eyes converge. The over-convergence associated with the accommodation to overcome a hyperopic refractive error can cause a loss of binocular control and lead to the development of esotropia.

What is esotropia caused by?
Esotropia is caused by a lack of coordination of your eye muscles. Usually, your eye muscles work together, as a binocular system (“seeing with two eyes”). You can tell how close you are to something. It's important for eyes to work together while you're riding a bicycle or driving a car or reading.
How common is accommodative esotropia?
The College of Optometrists in Vision Development (COVD), reports that up to 1 in 50 children have esotropia. A sudden eye turn at ages 2-3 can be very concerning, but might be due to a common and easily treated eye condition, accommodative esotropia.
Does accommodative esotropia go away?
Yes, children can outgrow accommodative esotropia. This usually happens during the grade school and adolescent years as a child becomes less farsighted. It is difficult to predict early in childhood whether any given child will outgrow their need for glasses.
Is accommodative esotropia genetic?
Accommodative esotropia is an esodeviation due to normal accommodation in uncorrected hyperopia. It is often hereditary, occasionally occurs with diplopia, and is sometimes brought on by trauma or illness.
What age does accommodative esotropia occur?
However, in some children who are farsighted, this accommodative effort is associated with a reflex crossing of the eyes. Hence the term, “accommodative esotropia.” Accommodative esotropia can begin anywhere from 4 months to 6 years of age. The usual age of onset is between 2 and 3 years of age.
Does esotropia get worse with age?
Without treatment, esotropia will continue to get worse. Children with any form of this condition should see a doctor or eye specialist, especially if they develop symptoms after age 3 or 4. Esotropia that isn't corrected before age 9 can cause permanent vision loss.
How long does it take to correct esotropia?
Sometimes esotropia isn't present from birth. A child's eyes might be fine up to age 3 or 4 years but then suddenly start to cross. If we catch that crossing early and straighten the eyes with surgery within three to six months, the 3D vision starts to work again.
Is esotropia a disability?
Entitlement to an increased disability rating for large angle esotropia (previously known as small angle esotropia), currently rated as 30 percent disabling.
Can patching help esotropia?
We frequently see patients who come for a second opinion or because they're new to the area, and their parents tell us something like, "He patched for a few months, but it didn't help, the eye was still crossed in." Patching doesn't help straighten the eyes; it's done to help the non-patched eye develop better vision, ...
Can esotropia be fixed with glasses?
People with acquired esotropia can often successfully treat the condition with glasses and vision therapy, although surgery may be necessary for some.
Is esotropia the same as lazy eye?
The most common of these misalignments is esotropia, commonly called “crossed eyes” and sometimes referred to as “lazy eye” or “squint.” About 1 to 2 percent of children will have esotropia.
Can Lasik fix accommodative esotropia?
In conclusion, LASIK appears to be effective and relatively safe to treat accommodative esotropia, even in young children, by reducing their hyperopic refractive error and eliminating the need for spectacle or contact lens correction.
Can Lasik fix accommodative esotropia?
In conclusion, LASIK appears to be effective and relatively safe to treat accommodative esotropia, even in young children, by reducing their hyperopic refractive error and eliminating the need for spectacle or contact lens correction.
What does fully accommodative esotropia mean?
A fully accommodative esotropia is a type of squint that is fully corrected with longsighted glasses and will allow your child to appreciate 3D vision when they wear the glasses. However, when the glasses are taken off you will still notice an esotropia as your child will automatically over focus to see clearly.
Is esotropia a disability?
Entitlement to an increased disability rating for large angle esotropia (previously known as small angle esotropia), currently rated as 30 percent disabling.
What is esotropia?
Esotropia is a form of eye turn, when one eye looks ‘cross-eyed’ as it points more inwards (towards the nose) than the other.
What is accommodative esotropia?
One of the most common forms of esotropia (crossed eye), which is a type of strabismus (eye turn) is accommodative esotropia.
What to do if your child has an eye turn?
If you notice your child has an eye turn, schedule an appointment with an eye doctor near you who can help manage and treat your accommodative esotropia, as well as any other underlying conditions.
What is vision therapy?
Vision therapy is a customized program that retrains the eyes and brain to work together. It consists of eye exercises, to help strengthen eye function and the muscles around the eye to improve vision.
How many children have esotropia?
The College of Optometrists in Vision Development (COVD), reports that up to 1 in 50 children have esotropia.
What is the focusing system?
The focusing system keeps the objects a person is looking at clear and focused. When a person sees an object clearly at a distance, the eye uses less focusing power.
Can glasses be used for farsightedness?
This is often the first option for treatment. Eye misalignment or farsightedness can be corrected using prescription glasses. If a person’s eyes continue to cross while wearing glasses, a bifocal lens may be required.
What is the greatest risk of binocular vision loss?
The greatest risk is development of amblyopia and loss of binocular visual development. Deterioration of control of esotropia is greater in patients with a high AC/A ratio, earlier age of onset, and amblyopia. Delay in treatment and noncompliance with treatment can result in loss of binocular potential.
What is the angle of esotropia?
The angle of the esotropia is often between 20 and 40 prism diopters and usually smaller than congenital esotropia. A cycloplegic refraction should be done. Most often a mixture of 1% cyclopentolate and 2.5% phenylephrine is used.
What is the most common type of strabismus?
Disease Entity. Accommodative esotropia is one of the most common types of strabismus in childhood. The incidence is estimated at 2% of the population. It is usually found in patients with moderate amounts of hyperopia. As the patient accommodates or focuses the eyes, the eyes converge.
What causes accomodative esotropia?
Accommodative esotropia is caused by accommodative convergence associated with hyperopia. As infants, the eyes are straight, but as they learn to accommodate to see clearly, the fusional divergence is not adequate and the child develops esotropia.
What is accommodation in hyperopia?
A patient with hyperopia must accommodate to clear a blurred image. Accommodation will stimulate convergence. If fusional divergence is insufficient to compensate for this, an esotropia will develop.
When does esotropia occur?
Esotropia occurs when focusing on an accommodative target.
How old do you have esotropes?
This condition may present anytime from infancy to late childhood, but most often between two and four years of age with no sexual or race predilection. Most accommodative esotropes are moderate hyperopes. Extreme hyperopes often remain orthotropic, preferring blurred vision rather than the constant accommodative effort.
What is the average cycloplegic refractive error?
The average cycloplegic refractive error in refractive accommodative esotropia is +4.75 D, 3 but ranges between + 1.5 and +7.0 D. The hypermetropia is predominantly axial in nature. 4 Special mention has to be made of the need for accurate cycloplegic refraction, especially in young children, where measurements are often difficult. Cyclopentolate is the standard cycloplegic; however, atropine, which has longer-acting cycloplegic effect, may be required in patients with dark irides to maximize the cycloplegic effect.
How old do you have to be to get off spectacles?
Lambert and colleagues at Emory University, USA, found that 60% of children with fully accommodative esotropia and baseline refractive errors of +1.50 to +5.00 D were successfully weaned off spectacles starting at a mean age of 8 years. Lower levels of baseline hyperopia of < 3 diopters were associated with higher success rates. 13
What causes esotropia in the retina?
The mechanism involves 3 factors: (1) uncorrected hyperopia, (2) accommodative convergence, and (3) poor fusional divergence. Due to uncorrected high hyperopia, the accommodative drive to produce a clear retinal image leads to increased convergence. If the patient’s fusional divergence is poor and easily overcome, esotropia occurs. Poor fusional divergence may occur if fusional divergence amplitudes are small, or motor fusion is altered by sensory factors. Patients with significant anisometropia are also at risk of developing refractive accommodative esotropia, even though they have lower levels of hyperopia. 2
What is accommodation esotropia?
Accommodative esotropia is defined as a convergent deviation of the eyes associated with activation of the accommodation reflex. It comprises more than 50% of all childhood esotropias 1 and can be classified into 3 forms: (1) refractive, (2) non-refractive, and (3) partially accommodative or decompensated.
Why do ophthalmologists observe binocular fusion near?
Some ophthalmologists would observe the excess esotropia at near because it generally improves with age, However, studies to date have not demonstrated a long-term benefit of observation, compared to surgery or bifocals. 22,23 Pratt-Johnson and colleagues found that bifocals allow more comfortable binocular fusion for near, but they are not strictly required to preserve overall fusion and stereopsis. 22
How old is a child when they have esotropia?
Although this usually occurs in a child between 2 and 3 years of age, children younger than 1 year may sometimes present with all the features of refractive accommodative esotropia.
Why is fusional divergence poor?
Poor fusional divergence may occur if fusional divergence amplitudes are small, or motor fusion is altered by sensory factors. Patients with significant anisometropia are also at risk of developing refractive accommodative esotropia, even though they have lower levels of hyperopia. 2.
What is it called when the angle of the esotropia is not fully corrected with glasses?
If the angle of the strabismus is not fully corrected with glasses, it is called a partially accommodative esotropia.
How long does it take for strabismus to go away?
Most babies outgrow intermittent strabismus by the age of 3 months, and there is no need for treatment. When the problem doesn't go away on its own, it can be treated with the following: Glasses or contact lenses : Accommodative esotropia due to farsightedness is often resolved with glasses or contact lenses.
What is the name of the eye that turns inward?
Esotropia is a type of strabismus (crossed eyes) characterized by one or both eyes turning inward, toward the nose. It is estimated that 4% of the U.S. population has strabismus, 1 and it can appear at any stage of life. It is the most common form of strabismus in infants. In some cases, such as those occurring in infants less than 20 weeks old, the misalignment is small and intermittent and goes away on its own, while other cases are more severe and require treatment. 2 Esotropia can be a sign of a serious medical condition such as thyroid eye disease and stroke .
What is the angle of deviation of infantile esotropia?
The misalignment in infantile esotropia has a large angle of deviation (>30 PD) and is constant. Transient misalignment of the eyes is common up to 3 months old, and should not be confused with infantile esotropia.
How old is accomodative esotropia?
All three forms have an age of onset between 6 months and 7 years. 7 It is frequently associated with amblyopia (lazy eye, or low vision due to abnormal visual development).
How old is a baby when it has misalignment?
In some cases, such as those occurring in infants less than 20 weeks old, the misalignment is small and intermittent and goes away on its own, while other cases are more severe and require treatment. 2 Esotropia can be a sign of a serious medical condition such as thyroid eye disease and stroke .
What is the term for the eye crossing caused by the focusing efforts of the eyes?
Accommodative Esotropia. Accommodative esotropia, also known as refractive esotropia, refers to eye crossing that is caused by the focusing efforts of the eyes as they try to see clearly. The focusing effort is called accommodation.
What Causes Esotropia?
Esotropia is a result of problems with the eye muscles, nerves that send information to those muscles, or the part of your brain that controls eye movements. It can also occur after an eye injury.
Are There Risks of Esotropia?
Without treatment, esotropia will continue to get worse. Children with any form of this condition should see a doctor or eye specialist, especially if they develop symptoms after age 3 or 4. Esotropia that isn't corrected before age 9 can cause permanent vision loss.
How early can you see with congenital esotropia?
Congenital esotropia usually appears very early between 2 to 4 months and the size of the deviation or eye turn tends to be very large. Often, infants with congenital esotropia do not have a large amount of farsightedness or nearsightedness. It is instead caused by an abnormal development of the binocular system.
What is the name of the abnormal brain development in infants?
Congenital esotropia: Congenital esotropia is a type of esotropia that infants are born with. 4 It usually caused by an abnormal wiring of the nerves or abnormal development in the motor areas of the brain. Congenital esotropia usually appears very early between 2 to 4 months and the size of the deviation or eye turn tends to be very large.
Why do we have accomodative esotropia?
It is usually caused by a problem with the two systems that control our eye muscles and the amount our eyes focus. The accommodative system (focusing system) allows our eyes to change power and focus so that objects remain clear no matter the distance.
What is it called when one eye is not seeing?
Amblyopia : Amblyopia is a common developmental problem associated with esotropia. Amblyopia is a condition that occurs when one or both eyes never see a clear image. 6 If the image is never seen clearly for a long enough period of time, permanent vision loss may develop. In esotropia, one eye may become turned in.
Why do humans have no depth perception?
Lack of true depth perception: 1 Humans and animals have depth perception because they have two eyes. The further apart an animal’s eyes are, the better depth perception is. When one eye is turned in or being suppressed, the person with esotropia only sees with one eye.
What does it mean when your eyes cross inward?
However, constant crossing of the eyes may be a concern. When an eye crosses inward it is termed esotropia. Esotropia is a type of strabismus. 1 “Eso” means to turn inward toward the nose. An esotropia can occur in just one eye or alternate between both eyes. It is rare for both eyes to cross in at the same time.
How old is too old to get vision back?
The human neurologic system is very “plastic” up until age 7 and some researchers say until age 14. After age 14, the brain and nervous system become hard-wired and it is difficult to improve vision back to normal. Therefore, early treatment is critical.
