How to treat adenoids naturally?
Preventing Enlarged Adenoids:
- Throat should be gargled with salt water (hot) this increases the circulation of blood in the throat. Alternate cold and hot water gargles should be done for best results.
- Diet rich in junk food and processed food which contains high carbohydrate and low protein may also cause this condition.
- Avoid people who smoke. ...
- Eat raw vegetables and fresh fruits. ...
Why are my adenoids swollen?
This procedure may be beneficial if one or more of the following problems are occurring:
- recurring ear infections that do not respond to antibiotics
- a buildup of fluid in the ear and earaches from adenoid swelling
- repeated infections of the adenoids that do not clear up with antibiotics
- excessive daytime sleepiness due to adenoids interfering with sleep
- behavior or learning issues as a result of poor quality sleep
What are the symptoms of adenoid problems?
Symptoms of Adenoids - Stuffy Nose, Snoring and Sleep Apnea, Sore throat, Troublesome swallowing, Swollen neck, Ear problems, Sinus symptoms.
What parents should know about adenoid removal?
What Parents Should Know About Tonsillectomy and Adenoidectomy
- Tonsil and adenoid response to infections. Tonsils are located on both sides of the back of the throat, and adenoids are located in the back of the nose.
- Common reasons for tonsil and adenoid surgeries. ...
- It’s important to prepare a child for these procedures. ...
- Recovering from surgery. ...
What causes adenoids to enlarge?
What causes enlarged tonsils and adenoids? Tonsils and adenoids can become enlarged for many different reasons, including exposure to viruses, bacteria, fungal, parasitic infections, and cigarette smoke. Common viruses include: adenovirus.
What causes inflammation of adenoids?
Because adenoids trap germs that enter the body, adenoid tissue sometimes temporarily swells (becomes enlarged) as it tries to fight an infection. Allergies also can make them get bigger. The swelling sometimes gets better. But sometimes, adenoids can get infected (this is called adenoiditis).
How do you treat enlarged adenoids?
Many people with enlarged adenoids have few or no symptoms and do not need treatment. Adenoids shrink as a child grows older. The provider may prescribe antibiotics or nasal steroid sprays if an infection develops. Surgery to remove the adenoids (adenoidectomy) may be done if the symptoms are severe or persistent.
Can enlarged adenoids go away?
The lymphatic system clears away infection and keeps body fluids in balance. The adenoids and tonsils work by trapping germs coming in through the mouth and nose. Adenoids usually start to shrink after about age 5. By the teenage years, they are almost completely gone.
How can I shrink my adenoids naturally?
A prescription steroid nasal spray may be able to decrease the size of the adenoids. Eating healthful foods, getting enough sleep, and drinking plenty of water can keep the immune system functioning well and help reduce the risk of enlarged adenoids. Also, good hygiene can help prevent infections.
What foods to avoid if you have adenoids?
Crunchy or harsh foods Crunchy, spicy, and hard foods may be difficult to consume even if they are healthy. As the throat is still healing from the surgery these foods may be too harsh on the throat. In addition to this, certain dry fruits and such may also cause an allergic reaction.
What problems can enlarged adenoids cause?
What Problems May Result from an Enlarged Adenoid? An enlarged adenoid may cause snoring, mouth breathing, persistent congestion, nasal drainage, ear problems, sinusitis, and “nasal” voice quality (the way you sound when you have a cold).
What happens if enlarged adenoids are not removed?
When a child's adenoids become enlarged, they can cause problems by partially blocking his or her airway. When this happens, children can have breathing problems, ear infections, or other complications, which can lead to snoring or more serious conditions such as sleep apnea (stopping breathing) at night.
What happens if adenoids are not treated?
It's important for the adenoids to be removed, especially if your child is experiencing repeated infections that lead to sinus and ear infections. Adenoids that are very badly swollen can also lead to infections or middle ear fluid, which can temporarily cause hearing loss.
Is adenoid removal painful?
Your child will be asleep through the surgery and not feel pain. The surgeon will remove extra adenoid tissue. The surgery usually lasts 20 to 30 minutes. Your child will stay in the recovery room until they are awake and can breathe easily, cough and swallow.
When should adenoids be removed?
A health care provider may recommend this procedure if: Enlarged adenoids are blocking your child's airway. Symptoms in your child can include heavy snoring, problems breathing through the nose, and episodes of not breathing during sleep.
Can allergies cause swollen adenoids?
Because adenoids trap germs that enter the body, adenoid tissue sometimes temporarily swells (becomes enlarged) as it tries to fight an infection. Allergies also can make them get bigger. The swelling sometimes gets better.
What problems can enlarged adenoids cause?
What Problems May Result from an Enlarged Adenoid? An enlarged adenoid may cause snoring, mouth breathing, persistent congestion, nasal drainage, ear problems, sinusitis, and “nasal” voice quality (the way you sound when you have a cold).
How do you tell if your adenoids are infected?
breathing through the mouth. speaking with a nasal sound, as if you are speaking with a pinched nose....Symptoms of adenoiditis can vary depending on what is causing the infection, but may include:sore throat.stuffy nose.swollen glands in the neck.ear pain and other ear problems.
What happens if adenoids are not treated?
Chronic (long-term) nasal drainage, congestion and sinus infections can also be seen. Enlarged adenoids can also affect the recurrence (return) of ear infections and chronic fluid in the ear, which can result in temporary hearing loss. Surgery to remove the glands is often needed.
What happens if enlarged adenoids are not removed?
Ongoing enlargement of the adenoids can block the eustachian tube, which connects the ears to the nose and drains fluid from the middle ear. This blockage causes fluid to build up in the ear, which can lead to repeated ear infections and potential hearing loss.
What Causes Enlarged adenoids?
Your child's adenoids can be enlarged, or swollen, for different reasons. It may just be that your child had enlarged adenoids at birth. Adenoids c...
What Problems Can Enlarged Adenoids Cause?
Enlarged adenoids can make it hard to breathe through the nose. Your child might end up breathing only through the mouth. This may cause 1. A dry m...
How Can Enlarged Adenoids Be Diagnosed
Your child's health care provider will take a medical history, check your child's ears, throat, and mouth, and feel your child's neck.Since the ade...
What Are The Treatments For Enlarged adenoids?
The treatment depends on what is causing the problem. If your child's symptoms are not too bad, he or she may not need treatment. Your child might...
What Is An Adenoidectomy and Why Might I My Child Need One?
An adenoidectomy is surgery to remove the adenoids. Your child might need it if 1. He or she has repeated infections of the adenoids. Sometimes the...
Why are my adenoids growing?
The adenoids can become enlarged due to an infection or may be enlarged from birth. The adenoids are glands that sit behind the nose above the roof of the mouth. When they grow large, they can cause snoring and breathing problems.
What happens when adenoids grow?
When they grow large, they can cause snoring and breathing problems. This article will describe the function of the adenoids, what causes them to become enlarged, and how to identify enlarged adenoids. We also look at various treatment options.
What are the risks of adenoidectomy?
An adenoidectomy is a simple surgery that is generally low-risk. The doctor may decide that surgery to remove the adenoids is appropriate if the child experiences: 1 recurrent infections of the adenoids, resulting in frequent sinus or ear infections 2 infections that do not go away with antibiotics 3 breathing problems, especially those that interfere with sleep
How long do adenoids shrink?
The size of the adenoids increases until a child is 6 years old, then they slowly shrink. The adenoids usually disappear by the time a person is 16. Enlarged adenoids are rare in adults.
Why do children need adenoidectomy?
A child may require an adenoidectomy if they have frequent infections. An adenoidectomy is a simple surgery that is generally low-risk. The doctor may decide that surgery to remove the adenoids is appropriate if the child experiences: recurrent infections of the adenoids, resulting in frequent sinus or ear infections.
How to prevent enlarged adenoids?
Eating healthful foods, getting enough sleep, and drinking plenty of water can keep the immune system functioning well and help reduce the risk of enlarged adenoids. Also, good hygiene can help prevent infections. In some cases, children need their adenoids removed.
How do doctors look at adenoids?
A doctor can look at the adenoids using a special mirror or lighted camera on the end of a flexible tube.
What are enlarged adenoids?
Enlarged adenoids are adenoids that are swollen. It is a common problem in children.
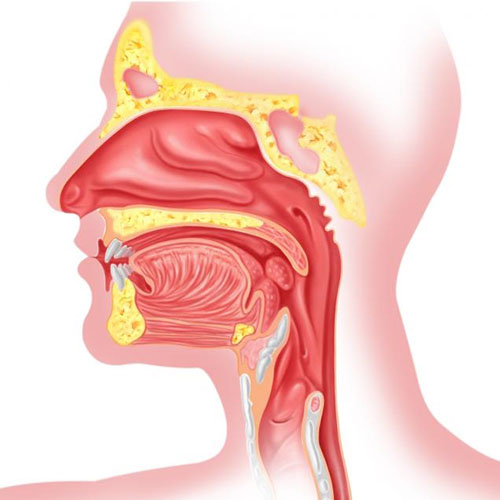
What are adenoids?
Adenoids are a patch of tissue that is high up in the throat, just behind the nose. They, along with the tonsils, are part of the lymphatic system. The lymphatic system clears away infection and keeps body fluids in balance. The adenoids and tonsils work by trapping germs coming in through the mouth and nose.
How can enlarged adenoids be diagnosed?
Your child's health care provider will take a medical history, check your child's ears, throat, and mouth, and feel your child's neck.
What is an adenoidectomy and why might I my child need one?
An adenoidectomy is surgery to remove the adenoids. The provider may recommend this surgery if:
How do tonsils and adenoids work?
The adenoids and tonsils work by trapping germs coming in through the mouth and nose. Adenoids usually start to shrink after about age 5. By the teenage years, they are almost completely gone. By then, the body has other ways to fight germs.
What are the complications of an adenoidectomy?
What is an adenoidectomy and why might I my child need one? 1 He or she has repeated infections of the adenoids. Sometimes the infections can also cause ear infections and fluid buildup in the middle ear. 2 Antibiotics can't get rid of a bacterial infection 3 The enlarged adenoids block the airways
Why is it so hard to breathe through your nose?
Enlarged adenoids can make it hard to breathe through the nose. Your child might end up breathing only through the mouth. This may cause. A dry mouth, which can also lead to bad breath. Cracked lips. A runny nose. Other problems that enlarged adenoids can cause include. Loud breathing. Snoring.
What is the term for inflammation of the adenoids caused by infection?
Adenoiditis is an inflammation of the adenoids caused by infection. Adenoids are masses of lymphatic tissue that help the body fight infection.
How to prevent adenoiditis?
There are a few things you can do to try to prevent adenoiditis. Eating healthy foods and drinking plenty of fluids is important. Also, getting enough sleep can help. Using good hygiene practices can minimize the chance of infection.
What are the risks of adenovirus?
Certain risk factors can make you susceptible to infections of the adenoidal tissues. These may include: 1 recurring infections in the throat, neck, or head 2 infections of the tonsils 3 contact with airborne viruses, germs, and bacteria
What is the cause of adenosis?
Adenoiditis can be caused by a bacterial infection, such as infection with the bacteria Streptococcus. It can also be caused by a number of viruses, including Epstein-Barr virus, adenovirus, and rhinovirus.
Why are children more susceptible to adenoiditis?
Children are more susceptible to adenoiditis. This is because adenoids progressively shrink through childhood. By the time you reach your late teen years, your adenoids are generally gone.
How long does it take for adenosis to go away?
Adenoiditis caused by a virus generally resolves on its own, and may take up to 2 to 3 weeks to fully resolve.
What to do if you have adenoids?
If a bacteria caused your adenoiditis, your doctor may prescribe antibiotics. The use of antibiotics often proves successful in treating inflamed adenoidal tissue. If a virus caused your adenoiditis, your doctor will put you on a treatment plan that’s specific to the virus.
How to see adenoids?
The health care provider can see them by using a special mirror in the mouth or by inserting a flexible tube (called an endoscope) placed through the nose.
Why do adenoids grow bigger?
They may grow bigger when the baby grows in the womb. The adenoids help the body prevent or fight infections by trapping bacteria and germs. Infections can cause the adenoids to become swollen. The adenoids may stay enlarged even when you are not sick. Maybe your child snores a lot. Maybe your child gets a lot of ear infections or has a lot ...
How to treat adenoids in a child?
Your child may also need an x-ray. Your child's doctor may try to treat the chronic swelling with medications such as antibiotics. If that doesn't work, your child may need surgery to remove the adenoids.
Where are adenoids located in a child?
Let's talk about enlarged adenoids. The adenoids are glands located between the airway your child breathes into through their nose and the back of your child's throat. Like your child's tonsils, the adenoids can often become swollen.
When to do adenoidectomy?
Surgery to remove the adenoids ( adenoidectomy) may be done if the symptoms are severe or persistent.
Can enlarged adenoids cause sleep problems?
Enlarged adenoids may also cause sleep problems. A child may:
Can adenoids shrink?
Many people with enlarged adenoids have few or no symptoms and do not need treatment. Adenoids shrink as a child grows older. The provider may prescribe antibiotics or nasal steroid sprays if an infection develops. Surgery to remove the adenoids ( adenoidectomy) may be done if the symptoms are severe or persistent.
What Are Adenoids?
Adenoids are a mass of tissue that, along with your tonsils, help keep you healthy by trapping harmful germs that pass through the nose or mouth. Your adenoids also produce antibodies to help your body fight infections. Unlike tonsils, which can be easily seen by opening your mouth, you cannot see the adenoids. A doctor has to use a small mirror or special instrument with a light to see the adenoids. Sometimes X-rays may be taken to see them more clearly.
What Are the Symptoms of Adenoiditis?
Symptoms of adenoiditis can vary depending on what is causing the infection , but may include:
How Is Adenoiditis Treated?
Adenoiditis is treated with antibiotics. However, if your child has frequent infections, including ear and sinus infections, or antibiotics do not help, or if your child has ongoing breathing problems, their doctor may refer them to a specialist who can discuss surgery to remove the adenoids. This procedure is called an adenoidectomy.
What is an adenoidectomy?
An adenoidectomy is performed by a doctor who specializes in ear, nose, and throat surgery. It occurs in a hospital or outpatient surgical center under general anesthesia, meaning your child is put to sleep. The tonsils and/or adenoids can be removed through the mouth so no additional incisions are made except for where the tissues are removed.
Why are adenoids less important?
While adenoids play an important role in keeping a person healthy, as you get older, adenoids become less important, because your body is able to fight infection in other ways. In fact, adenoids often get smaller around age 5 or 6 and virtually disappear by the teen years.
How long does it take for a child to feel nauseous after adenoidectomy?
After surgery, your child may feel nauseous until the anesthesia completely wears off. In the week following the adenoidectomy, your child may experience the following: Sore throat: Your child's throat may be sore for seven to ten days following the procedure and eating can be uncomfortable.
Where are the adenoids located?
Adenoids, located higher up in the mouth -- behind the nose and roof of the mouth -- can also get infected. Enlarged and inflamed adenoids -- called adenoiditis -- can make breathing difficult and lead to recurring respiratory infections.
Why do adenoids swell?
The severity of symptoms may vary with the degree of infection and inflammation. An infection of adenoids in adults results in its swelling. As the adenoids are located in the airway, such inflammation obstructs air passage and cause problems with breathing through the nose. The following are some of the swollen adenoid symptoms.
What is a swollen adenoid?
Swollen adenoids in adults can cause severe discomfort and lead to various health problems. Read on... Adenoids are clusters of lymphoid tissues , located in the back of the throat. Swollen adenoids in adults can cause severe discomfort and lead to various health problems. Read on….
What is adenoids in adults?
Swollen adenoids in adults can cause severe discomfort and lead to various health problems. Read on…. Just like tonsils, adenoids are also lymphoid tissues, assigned with the task of aiding the immune system in fighting infections. While tonsils are like two masses of tissues, located on either side of the back of the throat, ...
How to tell if adenoids are swollen?
The following are some of the swollen adenoid symptoms. Snoring, Noisy breathing. Blocked nose . Breathing through the mouth. Nasal speech. Dry or sore throat in the morning.
Why do adenoids cause inflammation?
Adenoids produce antibodies and white blood cells to destroy these germs. While carrying out this function, the adenoids are exposed to the risk of getting infected. This leads to inflammation of the adenoids, which can cause further complications. During birth, babies may not have visible adenoids and tonsils.
Why do tonsils get enlarged?
Even if the adenoids diminish in size, as the child reaches adulthood, they may get enlarged once again due to primary or reactivation of certain bacterial or viral infections. One such example is Epstein Barr Virus infection.
What are the functions of adenoids?
Functions and Growth of Adenoids. Adenoids, along with tonsils, help the body fight infections. While breathing, air-borne disease-causing germs enter the mouth and get trapped by the sticky mucus and the hair. Adenoids produce antibodies and white blood cells to destroy these germs.
What happens when adenoids are enlarged?
When adenoids become enlarged, your child may experience: Difficulty breathing through the nose. Bad breath and dry lips from breathing through the mouth. Sounding as if the nose is pinched or stuffed. Frequent sinus symptoms. Snoring. Restless sleep or disruptive sleep apnea.
What are the symptoms of enlarged adenoids?
Frequent sinus symptoms. Snoring. Restless sleep or disruptive sleep apnea. Ongoing middle ear infections or fluid build-up in school age. If your doctor suspects enlarged adenoids, he or she may perform a basic physical examination of the nose, throat, ears and feeling the neck along the jaw in order to diagnose.
How long does it take to remove adenoids?
Adenoidectomy is the removal of the adenoids via surgery through the open mouth, with your child under general anesthesia for around 30 minutes. It is an outpatient procedure that is may be done at the same time as a tonsillectomy. Your doctor may want to perform an adenoidectomy if your child: 1 Has multiple episodes of adenoid infection and subsequent middle ear infections or fluid build-up in the ear. 2 Shows no improvement of bacterial infection while taking an antibiotic. 3 Suffers from airway blockage. 4 Develops obstructive sleep apnea. 5 Has recurrent episodes of sinusitis.
Why are adenoids important?
Like tonsils, the adenoids do important work for babies and young children, as the adenoids are one of the first lines of defense when harmful bacteria and viruses are inhaled or swallowed. As your child ages, the adenoids lose significance as the body learns how to fight infection. Adenoids begin to shrink in childhood.
How to treat enlarged adenoids in children?
Treatment of Enlarged Adenoids. If your child has minimal symptoms, no treatment is typically needed. Your doctor may recommend a nasal spray to help reduce swelling and potentially an antibiotic if the infection is bacterial. Another treatment for more severe cases is an adenoidectomy.
Can adenoidectomy be done at the same time as tonsillectomy?
It is an outpatient procedure that is may be done at the same time as a tonsillectomy. Your doctor may want to perform an adenoidectomy if your child: Has multiple episodes of adenoid infection and subsequent middle ear infections or fluid build-up in the ear.
Do adenoids grow back?
Adenoids do not typically grow back, although that is not always the case. Symptoms of Enlarged Adenoids. Because they are on the front line of a body's defenses, it's possible that the adenoids may swell temporarily as they fight off infections.
Why do Adenoids Swell?
However, due to various reasons such as trapping of food or infection, these tissues swell or enlarge. When someone is allergic to particular food items, the adenoids can swell. Moreover, children can also be born with swollen glands and continue to stay enlarged until late childhood.
How to identify Swollen Adenoids?
It is very easy to identify swollen adenoids. Here are signs and symptoms that can help identify-
What is the best treatment for swollen adenoids?
Rather than looking for the ‘best’ treatment for swollen adenoids, the patient should look for a treatment option that offers the most-effective results.
What to do for swollen adenoids?
Thyme tea for Swollen Adenoids. Thyme is a kitchen spice that can help in dealing with swollen adenoids. This has a wide range of antibacterial effects. A hot cup of thyme tea can help with the symptom of the drippy nose due to swollen adenoids.
Where are the adenoids located?
Adenoids are glands that are located in the roof of the mouth. Similar to tonsils, adenoids also trap pathogens that enter through the nose or mouth. Under normal conditions, these tissues are invisible to the eye.
Can adenoids be removed?
As mentioned earlier, these home remedies work only if the swelling of the adenoids is not very severe. There are several possible treatment options for adenoids. If the condition gets serious and home remedies don’t work, then ENT doctors suggest adenoidectomy. It is simply the removal of the adenoids. Didn’t find what you are looking for? Drop a query in the comment section.
Can swelling of adenoids cause sleep apnea?
The swelling of the adenoids also leads to snoring and in some cases, sleep apnea.
