What cell produces aggrecan?
Aggrecan is a multimodular molecule expressed by chondrocytes. Its core protein is composed of three globular domains (G1, G2, and G3) and a large extended region (CS) between G2 and G3 for glycosaminoglycan chain attachment.
Where is aggrecan found?
Along with type-II collagen, aggrecan forms a major structural component of cartilage, particularly articular cartilage.
What does aggrecan contain?
The core protein of aggrecan consists of three disulfide-bonded globular regions (termed G1, G2 and G3) with intervening extended regions (Sandy et al. [1990]) (Figure 2). The G1 region resides at the amino terminus of the core protein and is responsible for the interaction with HA.
What is the aggrecan gene?
The ACAN gene provides instructions for making the aggrecan protein. Aggrecan is a type of protein known as a proteoglycan, which means it has several sugar molecules attached to it. It is the most abundant proteoglycan in cartilage, a tough, flexible tissue that makes up much of the skeleton during early development.
Is aggrecan found in bone?
Aggrecan is the major structural macromolecule of cartilage, which contributes to water retention and provides resistance to compression. Whereas cartilage is localized on the joint surface and help movement of individuals, it serves as a primodium of most bones during development.
What is aggrecan degradation?
Aggrecan degradation is the hallmark of cartilage degeneration in osteoarthritis (OA), though it is unclear whether a common proteolytic process occurs in all individuals.
Is aggrecan negatively charged?
Aggrecan is a high molecular weight, bottlebrush-shaped, negative-charged biopolymer that forms supermolecular complexes with hyaluronic acid.
Is aggrecan a CSPG?
CSPGs consist of a core protein covalently attached to long glycosaminoglycan (GAG) carbohydrate chains7. There are 16 different types of CSPGs, of which Neurocan, Brevican, Phosphacan, Aggrecan and Versican are most common within the nervous system7.
Is aggrecan in hyaline cartilage?
Hyaline cartilage contains five well-characterized proteoglycans in its extracellular matrix, and it is likely that others exist. The largest in size and most abundant by weight is aggrecan, a proteoglycan that possesses over 100 chondroitin sulfate and keratan sulfate chains.
Are proteins aggrecan?
Aggrecan is a proteoglycan, and in common with all proteoglycans it possesses a core protein with covalently attached sulfated glycosaminoglycan (GAG) chains. Aggrecan does not exist in isolation within the extracellular matrix, but occurs in the form of proteoglycan aggregates (Hascall, 1988; Watanabe et al. 1998).
Is aggrecan in the extracellular matrix?
Aggrecan is a large proteoglycan that forms giant hydrated aggregates with hyaluronan in the extracellular matrix (ECM).
What is gag in biology?
Glycosaminoglycans (GAGs), also known as mucopolysaccharides, are negatively-charged polysaccharide compounds. They are composed of repeating disaccharide units that are present in every mammalian tissue. [1] Their functions within the body are widespread and determined by their molecular structure.
Is aggrecan in hyaline cartilage?
Hyaline cartilage contains five well-characterized proteoglycans in its extracellular matrix, and it is likely that others exist. The largest in size and most abundant by weight is aggrecan, a proteoglycan that possesses over 100 chondroitin sulfate and keratan sulfate chains.
Is aggrecan in the extracellular matrix?
Aggrecan is a large proteoglycan that forms giant hydrated aggregates with hyaluronan in the extracellular matrix (ECM).
Where is glycosaminoglycan keratan sulfate found?
Keratan sulfate (KS), also called keratosulfate, is any of several sulfated glycosaminoglycans (structural carbohydrates) that have been found especially in the cornea, cartilage, and bone.
Where is dermatan sulfate found in the body?
Dermatan sulfate is found in the cornea and the sclera of the eye, which helps to maintain corneal transparency and the shape of the eye. Many other tissues in animals and humans also contain dermatan, such as blood vessel walls, heart valve, and the umbilical cord.
Why is Aggrecan important?
This causes discs to get stiffer and less resilient with age. Aggrecan also plays an important role in the organization of the extracellular spaces between neurons in the brain. Through interactions with link protein and tenascins, aggrecan binds to hyaluronan, forming large aggregated complexes at the cell surface.
What is the aggrecan family?
Along with type-II collagen, aggrecan forms a major structural component of cartilage, particularly articular cartilage . The aggrecan family includes other important members such as versican, also named PG-M, neurocan, brevican and the cell surface HA receptor CD44.
What is the name of the protein family that degrades aggrecans?
Proteases capable of degrading aggrecans are called aggrecanases, and they are members of the ADAM (A Disintegrin And Metalloprotease) protein family. Degenerative joint disease is a leading source of morbidity resulting in significant social and economic impact.
What is the role of Aggrecan in the extracellular matrix?
Functionally, the G1 domain interacts with hyaluronic acid and link protein, forming stable ternary complexes in the extracellular matrix. G2 is homologous to the tandem repeats of G1 and of link protein and is involved in product processing.
What is the globular domain of Aggrecan?
Aggrecan consists of two globular structural domains (G1 and G2) at the N-terminal end and one globular domain (G3) at the C-terminal end, separated by a large extended domain (CS) heavily modified with GAGs.
How many amino acids are in Aggrecan?
Aggrecan is a proteoglycan, or a protein modified with large carbohydrates; the human form of the protein is 2316 amino acids long and can be expressed in multiple isoforms due to alternative splicing.
What is the ACAN gene?
Aggrecan (ACAN), also known as cartilage-specific proteoglycan core protein (CSPCP) or chondroitin sulfate proteoglycan 1, is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ACAN gene. This gene is a member of the lectican ( chondroitin sulfate proteoglycan) family. The encoded protein is an integral part of the extracellular matrix in cartilagenous ...
What is the aggrecan protein?
It is also crucial in chondroskeletal morphogenesis during development. Aggrecan is a multimodular molecule expressed by chondrocytes. Its core protein is composed of three globular domains (G1, G2, and G3) and a large extended region (CS) between G2 and G3 for glycosaminoglycan chain attachment.
How many exons are in the aggrecan gene?
The mouse aggrecan gene spans at least 61 kb and contains 18 exons. Exon 1 encodes 5'-untranslated sequence and exon 2 contains a translation start codon. The coding sequence is 6545 bp for a 2132-amino-acid protein with calculated molecular weight of 259,131 Da, including an 18-amino acid signal peptide. There is a strong correlation between structural domains and exons. Notably, the chondroitin sulfate domain consisting of 1161 amino acids is encoded by a single exon of 3.6 kb.
What is the role of Aggrecan in articular cartilage?
Aggrecan is the major proteoglycan in the articular cartilage. This molecule is important in the proper functioning of articular cartilage because it provides a hydrated gel structure (via its interaction with hyaluronan and link protein) that endows the cartilage with load-bearing properties. It is also crucial in chondroskeletal morphogenesis ...
How many kDa are in Aggrecan?
There are fewer keratan sulfate chains (up to 60) and they are usually of smaller size (5-15 kDa). Aggrecan also contains a variable number of O- and N-linked oligosaccharides. The O-linked oligosaccharides have a linkage to protein similar to that of keratan sulfate.
Which proteoglycan is most important to the proper functioning of articular cartilage?
Among the cartilage proteoglycans, the most crucial to the proper functioning of articular cartilage is aggrecan, one of the large aggregating chondroitin sulfate proteoglycans. Aggrecan is a multimodular molecule and here, we will review the structures and functions of its modules.
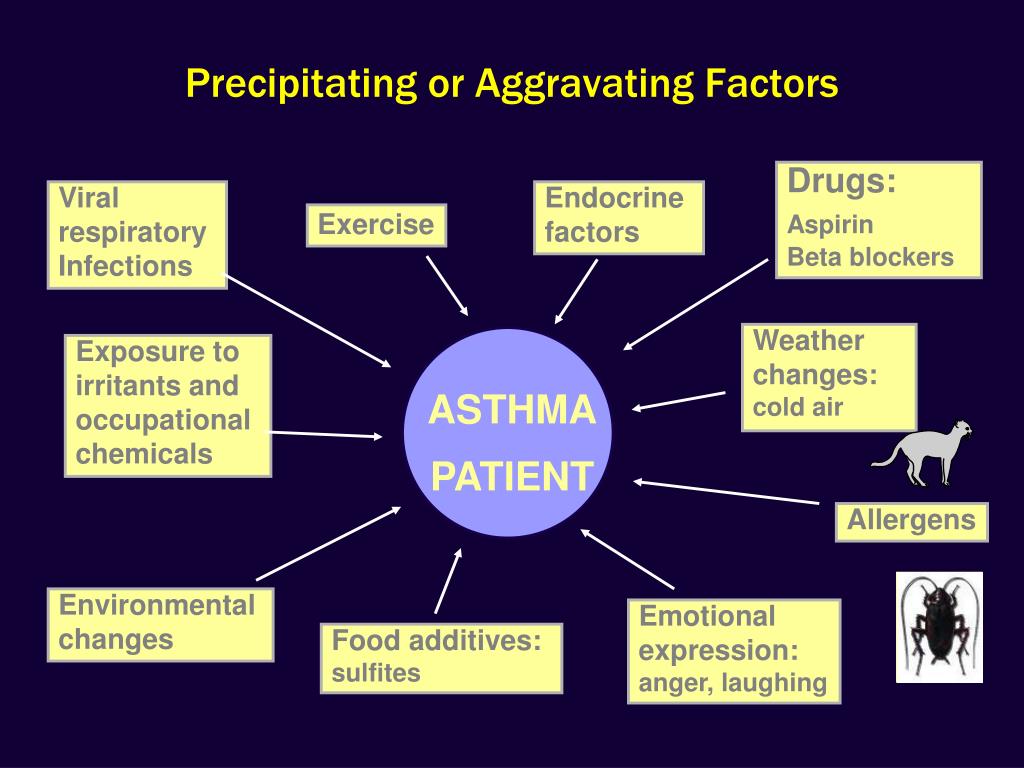
Why do people become angry?
Some people, however are quicker to anger, more prone to aggression, are less able to control their aggression, or are chronically unable to control their emotions effectively. When such negative behavior is pervasive, it may represent an underlying psychiatric or personality disorder. In the setting of other physical symptoms or illness, this may be representative of an illness negatively impacting brain function.
What causes aggression in the brain?
Dementia: Breakdown of certain parts of the brain, usually due to aging or genetic disease, can lead to changes in behavior, memory, and aggression. Brain lesions: Tumors or infections of the brain can lead to behavior changes.
Why do kids get irritable?
Most commonly, irritable or aggressive children may be missing sleep. Sleep deprivation can cause symptoms of depression or conduct disorders. Additionally, undiagnosed attention-deficit hyperactivity disorder can lead to aggression in some children, especially if they are under stress to perform well at school or at home.
How to deal with aggression at home?
If you're dealing with aggression, consider the following methods for calming yourself or another person down. Take a deep breath: Many people find it beneficial to take a deep breath before reacting impulsively to a situation.
What are the symptoms of aggression?
Aggression symptoms. As fallible human beings, we are all prone to a burst of aggression now and then. Friends don't get along, coworkers get into it, and families fight. Rage and aggression are never pleasant emotions, and most of us always reflect back negatively on when we "lost control" or yelled at another person.
What is it called when you feel an overwhelming urge to repeat certain rituals or behaviors?
To try to control the thoughts, one feels an overwhelming urge to repeat certain rituals or behaviors. These are called compulsions . Rarity: Rare. Top Symptoms: impaired social or occupational functioning, anxiety, aggression, anxiety resembling obsessive-compulsive disorder, repetitive patterns of behavior.
How to control anger and aggression?
If you are feeling angry or aggressive, consciously taking a moment to think can help control your emotions.
What is the function of aggrecan?
The function of aggrecan in articular cartilage. Proteoglycan aggregates are depicted as being entrapped by collagen fibrils. In the relaxed state the aggregates swell as the anionic chondroitin sulfate and keratan sulfate chains draw water into the tissue until an equilibrium is attained in which swelling is balance by tensile forces in the collagen fibrils. Under compression, water is displaced and the chondroitin sulfate and keratan sulfate chains are brought into closer proximity, so increasing their swelling potential and balancing the applied load. The increased swelling potential is dissipated upon removal of the load as the original equilibrium is restored.
How does aggrecan affect cartilage?
When aggrecan finds itself in an aqueous environment its swells as the sulfated GAG chains become hydrated in an attempt to expand their molecular domain and increase their separation from one another. Within the ECM, such swelling is resisted by the collagen fibrils that form the framework of the cartilage. If sufficient aggrecan is present, an equilibrium will be attained with the swelling of the aggrecan being balanced by the tensile forces that it induces upon stretching of the collagen fibrils (Figure 4). For optimal cartilage function it is essential that aggrecan concentration be high enough so that such an equilibrium be attained. Upon compressing articular cartilage, the equilibrium is perturbed. Compression displaces water and as the size of the proteoglycan aggregates limits their free diffusion within the tissue, the aggrecan at the site of compression is bought into closer proximity. This increases the swelling potential of the aggrecan, and upon removal of the compression the aggrecan will re-swell and restore the original equilibrium. Thus normal articular cartilage function requires a high concentration of aggrecan, a high degree of aggrecan sulfation, and the ability to form large aggregates. Each of these properties is impaired in the OA joint.
What is the structure of proteoglycan aggregates?
Structure of proteoglycan aggregates. The proteoglycan aggregate is depicted as a central hyaluronan (HA) filament with aggrecan and link proteins (LP) attached to it. The domains of the aggrecan core protein are indicated. G1, G2 and G3, globular regions; IGD, interglobular domain; KS, keratan sulfate-rich domain; CS1 and CS2, chondroitin sulfate-rich domains.
How many exons are in the aggrecan gene?
The human aggrecan gene consists of 19 exons. The G1 region is encoded by exons 3–6, with exon 3 encoding the A domain, exons 4 and 5 encoding the B domain and exon 6 encoding the B′ domain. The IGD is encoded by exon 7. The G2 region is encoded by exons 8–10, with exons 8 and 9 encoding the B domain and exon 10 encoding the B′ domain. The GAG attachment region is encoded by exons 11 and 12, with exon 11 encoding the first part of the KS-rich domain, and the large exon 12 encoding the remainder of the KS-rich domain plus the CS1 and CS2 domains. The hexapeptide repeats of the KS-rich region are encoded by exon 12. The G3 region is encoded by exons 13–19, with exons 13 and 14 each encoding an EGF-like domain, exons 15–17 encoding the lectin-like domain, and exon 18 encoding the CRP-like domain.
How many molecules are in a proteoglycan aggregate?
Mechanisms of proteoglycan aggregate degradation. A proteoglycan aggregate bearing five aggrecan molecules is depicted. Degradation is represented following proteolysis of the aggrecan core protein, non-enzymic glycation of the aggrecan core protein and link protein, and hyaluronidase or free radical cleavage of hyaluronan.
What is the function of Aggrecan?
Aggrecan is a large proteoglycan bearing numerous chondroitin sulfate and keratan sulfate chains that endow articular cartilage with its ability to withstand compressive loads. It is present in the extracellular matrix in the form of proteoglycan aggregates, in which many aggrecan molecules interact with hyaluronan and a link protein stabilizes ...
How does aggrecan affect cartilage?
If sufficient aggrecan is present, an equilibrium will be attained with the swelling of the aggrecan being balanced by the tensile forces that it induces upon stretching of the collagen fibrils (Figure 4 ). For optimal cartilage function it is essential that aggrecan concentration be high enough so that such an equilibrium be attained. Upon compressing articular cartilage, the equilibrium is perturbed. Compression displaces water and as the size of the proteoglycan aggregates limits their free diffusion within the tissue, the aggrecan at the site of compression is bought into closer proximity. This increases the swelling potential of the aggrecan, and upon removal of the compression the aggrecan will re-swell and restore the original equilibrium. Thus normal articular cartilage function requires a high concentration of aggrecan, a high degree of aggrecan sulfation, and the ability to form large aggregates. Each of these properties is impaired in the OA joint.
What is the structure of proteoglycan aggregates?
Structure of proteoglycan aggregates. The proteoglycan aggregate is depicted as a central hyaluronan (HA) filament with aggrecan and link proteins (LP) attached to it. The domains of the aggrecan core protein are indicated. G1, G2 and G3, globular regions; IGD, interglobular domain; KS, keratan sulfate-rich domain; CS1 and CS2, chondroitin sulfate-rich domains.
How many molecules are in a proteoglycan aggregate?
Mechanisms of proteoglycan aggregate degradation. A proteoglycan aggregate bearing five aggrecan molecules is depicted. Degradation is represented following proteolysis of the aggrecan core protein, non-enzymic glycation of the aggrecan core protein and link protein, and hyaluronidase or free radical cleavage of hyaluronan.
How long does the G1 fragment stay in the HA?
Following proteolytic cleavage of the aggrecan core protein at any site, two fragments are generated. One fragment will possess a G1 region and remain bound to HA, whereas the other is no longer able to interact with HA. This latter non-aggregating fragment is free to diffuse within the ECM and is rapidly lost into the synovial fluid. In contrast, fragments that remain bound to HA can reside in the tissue for many years (Maroudas et al. [ 1998 ]). It has been estimated that the G1 regions that form the end product of proteolytic truncation of the aggrecan core protein have a half-life of about 20 years. This can be viewed as an impediment to repair, as the G1 regions cannot participate in the load bearing function of the cartilage, yet they occupy space on the HA that could be used for binding newly synthesized aggrecan.
What is the role of Aggrecan in OA?
Aggrecan plays an essential role in the function of articular cartilage and is a central participant in its destruction in the OA joint. Agents that prevent aggrecan degradation and restore its production may play a future role in the treatment of early stage OA.
How many exons are in the aggrecan gene?
[ 1995 ]) (Figure 2 ). The human aggrecan gene consists of 19 exons. The G1 region is encoded by exons 3–6, with exon 3 encoding the A domain, exons 4 and 5 encoding the B domain and exon 6 encoding the B′ domain. The IGD is encoded by exon 7. The G2 region is encoded by exons 8–10, with exons 8 and 9 encoding the B domain and exon 10 encoding the B′ domain. The GAG attachment region is encoded by exons 11 and 12, with exon 11 encoding the first part of the KS-rich domain, and the large exon 12 encoding the remainder of the KS-rich domain plus the CS1 and CS2 domains. The hexapeptide repeats of the KS-rich region are encoded by exon 12. The G3 region is encoded by exons 13–19, with exons 13 and 14 each encoding an EGF-like domain, exons 15–17 encoding the lectin-like domain, and exon 18 encoding the CRP-like domain.
Which approach views aggression as an instinctive drive and ignores mediational processes like thought and memory?
The psychodynamic approach views aggression as an instinctive drive and ignores mediational processes like thought and memory. The cognitive approach, on the other hand, claims that aggression is learnt behavior and emphasizes the thought processes that contribute to learning it.
When one is disposed to aggression and capable of behaving aggressively, a specific situation must?
Even when one is disposed to aggression and capable of behaving aggressively, a specific situation must elicit the act. Thus, in order to fully understand the complicated nature of aggression, further research is required into both factors before drawing any final conclusion.
How does psychodynamic approach affect aggression?
For the psychodynamic approach, aggression can result from unresolved conflicts, while for the social cognitive approach, exposure to aggressive behavior, along with reinforcement, can encourage children to learn it.
Which approach views aggression as innate?
The psychoanalytic approach (which views aggression as innate),
Is aggression an instinctive drive?
According to his theory, human aggression is an instinctive drive, one that springs from the person rather than the situation, and is therefore an unavoidable part of human life (Glassman, 2004).
Can aggression be eliminated?
In short, nothing can be done to eliminate aggression; it can only be channeled. On the other hand, since a social cognitive approach sees aggression as learned behavior, it is not inevitable, and an individual is seen as actively involved in this process.
Is Aggression Innate or Learnt?
Aggression is behavior which causes intentional harm to another person (Anderson, 2002). More specifically, aggression is defined as "any sequence of behavior, the goal response to which is the injury of the person toward whom it is directed" (Dollard et al.,1939). Although some definitions emphasize the role of intention, most psychologists agree that it is the actual observable behavior causing harm that defines aggression.
Overview
Aggrecan (ACAN), also known as cartilage-specific proteoglycan core protein (CSPCP) or chondroitin sulfate proteoglycan 1, is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ACAN gene. This gene is a member of the lectican (chondroitin sulfate proteoglycan) family. The encoded protein is an integral part of the extracellular matrix in cartilagenous tissue and it withstands compression in ca…
Structure
Aggrecan is a high molecular weight (1x10 < M < 3x10 ) proteoglycan. It exhibits a bottlebrush structure, in which chondroitin sulfate and keratan sulfate glycosaminoglycan (GAG) chains are attached to an extended protein core.
Aggrecan has a molecular mass >2,500 kDa. The core protein (~300 kDa ) has around 100 GAG chains attached to it.
Function
Aggrecan is a critical component for cartilage structure and the function of joints.
Functionally, the G1 domain interacts with hyaluronic acid and link protein, forming stable ternary complexes in the extracellular matrix. G2 is homologous to the tandem repeats of G1 and of link protein and is involved in product processing. G3 makes up the carboxyl terminus of the core protein. It enhances glycosaminoglycan modification and product secretion. Aggrecan plays an i…
Clinical significance
The synthesis and degradation of aggrecan are being investigated for their roles in cartilage deterioration during joint injury, disease, and aging.
The linker domain between the N-terminal globular domains, called the interglobular domain, is highly sensitive to proteolysis. Such degradation has been associated with the development of arthritis. Proteases capable of degrading aggrecans are called aggrecanases, and they are memb…
Further reading
• Watanabe H, Yamada Y, Kimata K (1998). "Roles of aggrecan, a large chondroitin sulfate proteoglycan, in cartilage structure and function". J. Biochem. 124 (4): 687–93. doi:10.1093/oxfordjournals.jbchem.a022166. PMID 9756610.
• Fosang AJ, Neame PJ, Last K, Hardingham TE, Murphy G, Hamilton JA (1992). "The interglobular domain of cartilage aggrecan is cleaved by PUMP, gelatinases, and cathepsin B". J. Biol. Chem. 267 (27): 19470–4. doi:10.1016/…
External links
• Aggrecan at the US National Library of Medicine Medical Subject Headings (MeSH)
• Human ACAN genome location and ACAN gene details page in the UCSC Genome Browser.
• Overview of all the structural information available in the PDB for UniProt: P16112 (Human Aggrecan core protein) at the PDBe-KB.