The aggregate expenditure (AE) curve is drawn on the basis of given a given constant price level. Changes in price level cause shifts in AE curve. A rise in prices of goods and services causes a downward shift in the AE curve while a fall in price leads to upwards shift of the curve.
How do autonomous aggregate expenditures affect the aggregate demand curve?
An increase in autonomous aggregate expenditures shifts the aggregate demand curve to the right; a reduction shifts it to the left. There will be a different aggregate expenditures curve for each price level.
How does the aggregate expenditures curve change over time?
Changes in Aggregate Expenditures: The Multiplier. In the aggregate expenditures model, equilibrium is found at the level of real GDP at which the aggregate expenditures curve crosses the 45-degree line. It follows that a shift in the curve will change equilibrium real GDP.
What causes the aggregate demand curve to shift?
Any aggregate economic phenomena that cause changes in the value of any of these variables will change aggregate demand. If aggregate supply remains unchanged or is held constant, a change in aggregate demand shifts the AD curve to the left or to the right.
How can fiscal policy shift aggregate demand to the left?
Shifting AD to the Left. Demand might remain unchanged if those extra savings become loans to businesses and then total business spending on capital goods increases. Contractionary fiscal policy can shift aggregate demand to the left. The government might decide to raise taxes and/or decrease spending to fix a budget deficit.

What causes aggregate expenditure to fall?
Higher inflation will eventually cause aggregate expenditures to decrease, because higher prices reduces the wealth of consumers, thus leading to lower spending. This is particularly true for poorer consumers, since they tend to spend all the money that they have, to pay for essentials.
What are the 4 main things that can cause aggregate demand to shift?
The aggregate demand curve, or AD curve, shifts to the right as the components of aggregate demand—consumption spending, investment spending, government spending, and spending on exports minus imports—rise.
What affects aggregate expenditure?
Aggregate expenditures will vary with the price level because of the wealth effect, the interest rate effect, and the international trade effect. The higher the price level, the lower the aggregate expenditures curve and the lower the equilibrium level of real GDP.
What factors cause shifts in aggregate supply?
The aggregate supply curve shifts to the right as productivity increases or the price of key inputs falls, making a combination of lower inflation, higher output, and lower unemployment possible.
What would cause aggregate supply to shift left?
Increases in the price of such inputs represent a negative supply shock, shifting the SRAS curve to shift to the left. This means that at each given price level for outputs, a higher price for inputs will discourage production because it will reduce the possibilities for earning profits.
How do you explain aggregate expenditure?
In economics, aggregate expenditure is the current value of all the finished goods and services in the economy. It is the sum of all the expenditures undertaken in the economy by the factors during a specific time period. The equation for aggregate expenditure is: AE = C + I + G + NX.
How is aggregate expenditure related to GDP?
Each level of real GDP will result in a particular amount of aggregate expenditures. If aggregate expenditures are less than the level of real GDP, firms will reduce their output and real GDP will fall. If aggregate expenditures exceed real GDP, then firms will increase their output and real GDP will rise.
Does government spending affect aggregate expenditure?
Investment spending and government spending are fixed amounts; thus, adding the investment and government spending functions shifts the aggregate expenditure line up, parallel to the consumption function.
What shifts aggregate demand quizlet?
The aggregate-demand curve might shift to the left when something (other than a rise in the price level) causes a reduction in consumption spending (such as a desire for increased saving), a reduction in investment spending (such as increased taxes on the returns to investment), decreased government spending (such as a ...
Which of the following are the four components or determinants of aggregate demand?
Aggregate demand is the sum of four components: consumption, investment, government spending, and net exports.
What causes aggregate demand to increase?
Aggregate demand increases when the components of aggregate demand–including consumption spending, investment spending, government spending, and spending on exports minus imports–rise.
Which of these factors cause a movement along the aggregate demand curve?
In general, a change in the price level, with all other determinants of aggregate demand unchanged, causes a movement along the aggregate demand curve. A movement along an aggregate demand curve is a change in the aggregate quantity of goods and services demanded.
What is aggregate expenditure?
Aggregate expenditures equal the sum of consumption C and planned investment IP. The aggregate expenditures function is the relationship of aggregate expenditures to the value of real GDP. It can be represented with an equation, as a table, or as a curve.
What are the components of aggregate expenditures?
To develop a simple model, we assume that there are only two components of aggregate expenditures: consumption and investment. In the chapter on measuring total output and income, we learned that real gross domestic product and real gross domestic income are the same thing. With no government or foreign sector, gross domestic income in this economy and disposable personal income would be nearly the same. To simplify further, we will assume that depreciation and undistributed corporate profits (retained earnings) are zero. Thus, for this example, we assume that disposable personal income and real GDP are identical.
What is the slope of aggregate expenditures curve?
The slope of the aggregate expenditures curve, given by the change in aggregate expenditures divided by the change in real GDP between any two points, measures the additional expenditures induced by increases in real GDP. The slope for the aggregate expenditures curve in Figure 28.8 “Plotting the Aggregate Expenditures Curve” is shown for points B and C: it is 0.8.
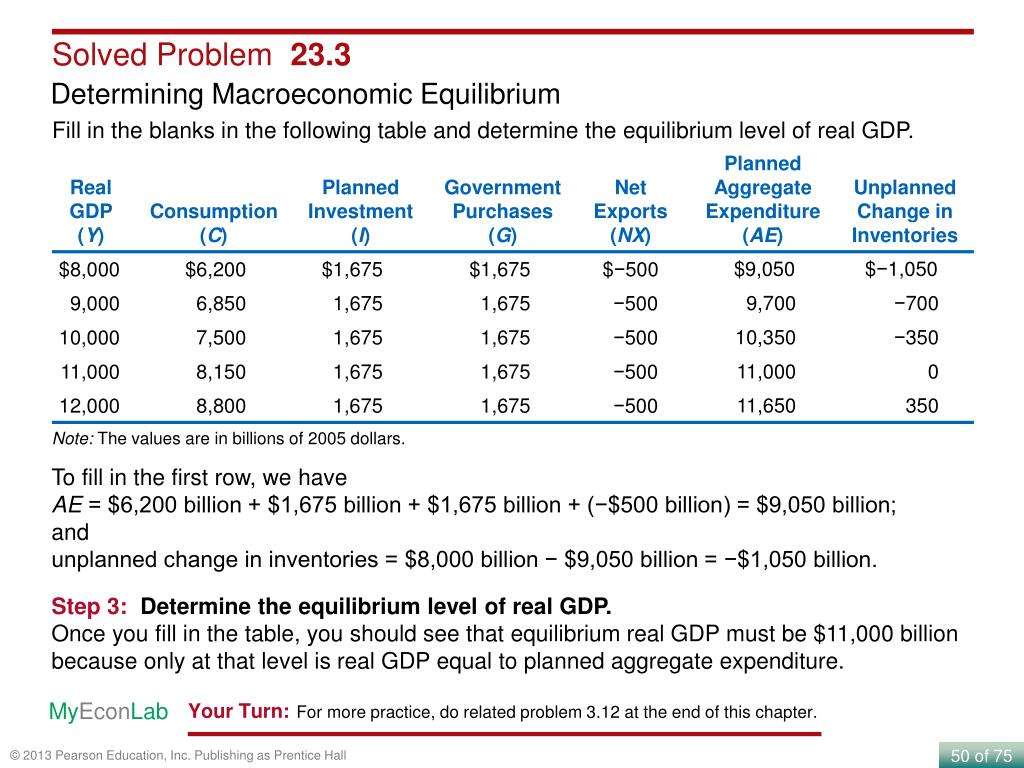
How to find equilibrium level of real GDP?
The equilibrium level of real GDP is $7,500. It can be found by determining the intersection of AE1 and the 45-degree line. At Y = $7,500, AE1 = $5,300 + 1,000 + 1,400 − 200 = $7,500.
How much does a 300 billion increase in planned investment increase GDP?
The $300 billion increase in planned investment results in an increase in equilibrium real GDP of $1,500 billion.
Where is equilibrium found in aggregate expenditures?
In the aggregate expenditures model, equilibrium is found at the level of real GDP at which the aggregate expenditures curve crosses the 45-degree line. It follows that a shift in the curve will change equilibrium real GDP. Here we will examine the magnitude of such changes.
Which investment plays a key role in aggregate expenditures?
We shall find that planned and unplanned investment play key roles in the aggregate expenditures model.
What is the shift in autonomous aggregate expenditures?
A change in autonomous aggregate expenditures shifts the aggregate expenditures curve for each price level. That shifts the aggregate demand curve by an amount equal to the change in autonomous aggregate expenditures times the multiplier.
Why do aggregate expenditures vary with the price level?
Aggregate expenditures will vary with the price level because of the wealth effect, the interest rate effect, and the international trade effect. The higher the price level, the lower the aggregate expenditures curve and the lower the equilibrium level of real GDP.
How does an increase in autonomous aggregate expenditures shift the aggregate demand curve?
An increase in autonomous aggregate expenditures shifts the aggregate demand curve to the right; a reduction shifts it to the left.
How does a $1,000 billion increase in net exports affect aggregate expenditures?
A $1,000-billion increase in net exports shifts each of the aggregate expenditures curves up by $1,000 billion, to AE ′ P=1.0 and AE ′ P=1.5. That changes the equilibrium real GDP associated with each price level; it thus shifts the aggregate demand curve to AD2 in Panel (b). In the aggregate expenditures model, equilibrium real GDP changes by an amount equal to the initial change in autonomous aggregate expenditures times the multiplier, so the aggregate demand curve shifts by the same amount. In this example, we assume the multiplier is 2. The aggregate demand curve thus shifts to the right by $2,000 billion, two times the $1,000-billion change in autonomous aggregate expenditures.
What is aggregate expenditure curve?
An aggregate expenditures curve assumes a fixed price level. If the price level were to change, the levels of consumption, investment, and net exports would all change, producing a new aggregate expenditures curve and a new equilibrium solution in the aggregate expenditures model.
Why is there a different level of equilibrium real GDP for each price level?
More generally, there will be a different level of equilibrium real GDP for every price level; the higher the price level, the lower the equilibrium value of real GDP. Because there is a different aggregate expenditures curve for each price level , there is a different equilibrium real GDP for each price level.
How does a higher price level affect the real quantity of money?
Similarly, a higher price level reduces the real quantity of money , raises interest rates, and reduces investment. This is called the interest rate effect. Finally, a change in the domestic price level will affect exports and imports.
What causes aggregate demand to shift left?
A decline in exports causes aggregate demand to shift left. If your currency becomes weaker, then countries are able to purchase more of your goods because they are relatively cheaper. This increases exports, and net exports, and therefore shifts aggregate demand right.
What factors can shift the aggregate demand curve?
The factors that can shift the aggregate demand curve can be summarized as: 1) A change in expectations for either firms or households. 2) A change in government policy. 3) A change in international variables. Below is a table that shows some different examples that will cause shifts in the aggregate demand curve:
What happens to the aggregate demand curve when the government raises taxes?
If the government raises taxes, or reduces government spending, then the aggregate demand curve shifts left (contractionary policy). If the government lowers taxes, or increases government spending, we will see the AD shift right (expansionary policy). Monetary policy is the result of the federal reserve (at least in the United States) ...
What happens to GDP if it rises faster?
However, if the rest of the world’s GDP is rising faster, then they will begin purchasing more of your goods, increasing exports for your country. This will shift aggregate demand to the right.
What does it mean when a consumer shifts the AD curve right?
A change in consumer confidence, meaning that consumers are more confident/worried and this causes them to buy more/less which shifts the AD curve right/left.
What happens to the economy when the federal reserve raises interest rates?
Monetary policy is the result of the federal reserve (at least in the United States) manipulating interest rates in the economy. If the federal reserve raises interest rates, then we will see aggregate demand decrease or shift left because it has become more expensive to finance investment. Alternatively, if the federal reserve decreases interest rates, we will see investment increase, and aggregate demand will shift right.
What happens when currency becomes weaker?
A decline in exports causes aggregate demand to shift left. If your currency becomes weaker, then countries are able to purchase more of your goods because they are relatively cheaper. This increases exports, and net exports, and therefore shifts aggregate demand right.
How does consumption increase with the level of national income?
In the expenditure-output model, how does consumption increase with the level of national income? Output on the horizontal axis is conceptually the same as national income, since the value of all final output that is produced and sold must be income to someone, somewhere in the economy. At a national income level of zero, $600 is consumed. Then, each time income rises by $1,000, consumption rises by $800, because in this example, the marginal propensity to consume is 0.8.
What happens when marginal propensity to consume changes?
A change in the marginal propensity to consume will change the slope of the consumption function. An increase in the MPC steepens the consumption function; a decrease in the MPC flattens it.
What does Keynes say about consumption expenditure?
Keynes observed that consumption expenditure depends primarily on personal disposable income, i.e. one’s take home pay. Let’s examine this relationship in more detail. People can do two things with their income: they can consume it or they can save it. (For the moment, let’s ignore the need to pay taxes with some of it).
Does consumption increase with income?
First, consumption expenditure increases as income does. For every increase in income, consumption increases by the MPC times that increase in income. Thus, the slope of the consumption function is the MPC. Second, at low levels of income, consumption is greater than income.