
Some of the key concepts of allocative efficiency include:
- 1. Society’s preferences dictate how resources are allocated The producer of a commodity allocates the scarce resources depending on what consumers prefer. ...
- 2. The market must be efficient For a market to be allocatively efficient, it must be informationally and transactionally efficient. ...
- 3. One party does not benefit at the expense of another
When does allocative efficiency take place?
When does allocative efficiency take place? when the ideal quantities of goods and services are produced. What is the reason behind why monopolies are allocatively inefficient? the price at the profit-maximizing level of output is greater than marginal cost.
Why are monopolies inefficient 3 reasons?
What are two reasons why monopolies are bad?
- Higher prices than in competitive markets – Monopolies face inelastic demand and so can increase prices – giving consumers no alternative.
- A decline in consumer surplus.
- Monopolies have fewer incentives to be efficient.
- Possible diseconomies of scale.
Why is P MC allocative efficiency?
The Allocative Inefficiency of Monopoly. Allocative Efficiency requires production at Qe where P = MC. A monopoly will produce less output and sell at a higher price to maximize profit at Qm and Pm. Thus, monopolies don’t produce enough output to be allocatively efficient.
Is monopolistic competition allocatively efficient?
A monopolistically competitive firm is not allocatively efficient because it does not produce where P =MC, but instead produces where P > MC A profit-maximizing monopolistic competitor will seek out the quantity where
How does allocative efficiency occur?
Allocative efficiency occurs when one party does not derive the benefits of a commodity at the expense of another party. Each person must be willing to exchange the commodity with another person in order for both parties to benefit.
What might help achieve allocative efficiency?
Allocative efficiency can only occur when the marginal utility of a good or service is the same for both the buyer and seller. Such efficiency is most likely to occur in a competitive market.
At what point does allocative efficiency occur?
Allocative efficiency would occur at the point where the MC cuts the Demand curve so Price = MC. The area of deadweight welfare loss shows the degree of allocative inefficiency in the economy.
What shows allocative efficiency?
Allocative efficiency looks at the marginal benefit of consumption compared to the marginal cost. Allocative efficiency will occur at an output when marginal benefit (price) = marginal cost. We can say: Allocative efficiency occurs where price = marginal cost (MC)
What causes allocative inefficiency?
Allocative inefficiency occurs when the consumer does not pay an efficient price. An efficient price is one that just covers the costs of production incurred in supplying the good or service. Allocative efficiency occurs when the firm's price, P, equals the extra (marginal) cost of supply, MC.
How is allocative efficiency achieved perfectly competitive?
In the argument for why perfect competition is allocatively efficient, the price that people are willing to pay represents the gains to society and the marginal cost to the firm represents the costs to society.
What is allocative efficiency quizlet?
What is allocative efficiency? A situation in which resources are allocated such that the last unit of output produced provides a marginal benefit to consumers equal to the marginal cost of producing it.
Which statement about allocative efficiency is true?
The given statement is true Allocative efficiency is concerned with the most efficient allocation of goods or it might be services. Allocative efficiency, at its most fundamental level, means that the producers provide the amount of every product that customers want.
Under what circumstances will a resource allocation be efficient?
– An efficient allocation of resources occurs when we produce the goods and services that people value most highly. – Resources are allocated efficiently when it is not possible to produce more of a good or service without giving up some other good or service that is valued more highly.
Why allocative efficiency is important?
Operating under allocative efficiency ensures the correct resource allotment in terms of consumer needs and desires. Virtually all resources (i.e., factors of production) are limited; therefore, it is essential to make the right decisions regarding where to distribute resources in order to maximize value.
What is allocative efficiency quizlet?
What is allocative efficiency? A situation in which resources are allocated such that the last unit of output produced provides a marginal benefit to consumers equal to the marginal cost of producing it.
What does allocative efficiency refer to quizlet?
Allocative Efficiency means that. every good or service is produced up to the point where marginal benefit is equal to marginal cost.
How is efficiency achieved in terms of allocating resources to produce goods and services?
Efficiency in Production, Allocation, and Distribution To do this, they choose the combination of inputs that minimize their costs while producing as much output as possible. By doing so, they operate efficiently; when all firms in the economy do so, it is known as productive efficiency.
What is allocative efficiency?
Definition of allocative efficiency. This occurs when there is an optimal distribution of goods and services, taking into account consumer’s preferences. A more precise definition of allocative efficiency is at an output level where the Price equals the Marginal Cost (MC) of production.
Why are firms in perfect competition said to produce at an allocative efficient level?
Firms in perfect competition are said to produce at an allocative efficient level because at Q1, P=MC
Why is monopoly inefficient?
Monopoly sets a price of Pm. This is allocatively inefficient because at this output of Qm, price is greater than MC.
When is optimal distribution achieved?
Therefore the optimal distribution is achieved when the marginal utility of the good equals the marginal cost.
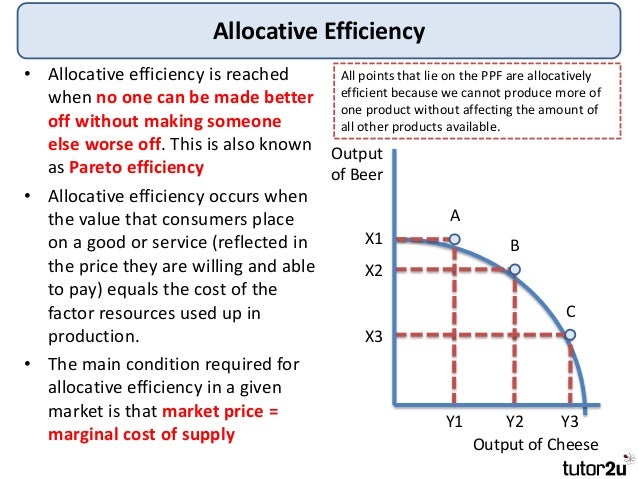
Is PPF allocatively efficient?
This occurs on the production possibility frontier (PPF). (Note producing on the production possibility frontier is not necessarily allocatively efficient because a PPF only shows the potential output. Allocative efficiency is concerned with the distribution of goods and this requires the addition of indifference curves.
Key Takeaways
Allocative efficiency is the output level at which a good or service’s cost (P) and the marginal cost of production (MC) are equal (P=MC).
Allocative Efficiency Explained
You are free to use this image on your website, templates, etc, Please provide us with an attribution link
Formula
There is no particular formula to derive allocative efficiency. It is, however, represented as P=MC, where P is the price of goods and services and MC is the marginal cost. Marginal cost describes the rise or fall in price associated with producing or providing services to an additional consumer. It is also referred to as incremental cost.
Example
Suppose ABC ltd wants to produce shoes; the output of 10 shoes has a marginal cost of $50. However, the consumer is willing to pay a high amount of $150 for good-quality shoes. Here, the marginal utility derived by the consumers is higher than the company’s marginal cost.
When does it occur?
Allocative efficiency occurs when the production costs of output are equal to the value of marginal cost. The determination happens when businesses try to meet future demands using demand projections.
Allocative efficiency vs. Productive efficiency
Allocative efficiency vs. productive efficiency is a misunderstood concept. Even though they are both concerned with utilizing resources in the optimum way possible, they are different concepts. Productive efficiency concerns the best way to produce commodities and how to do so efficiently.
Recommended Articles
This is a guide to Allocative efficiency and its meaning. We discuss formula, chart graphs, example and its comparison with productive efficiency. You can learn more from the following articles –
What is allocative efficiency?from economicshelp.org
Definition of allocative efficiency. This occurs when there is an optimal distribution of goods and services, taking into account consumer’s preferences. A more precise definition of allocative efficiency is at an output level where the Price equals the Marginal Cost (MC) of production.
How can a market be allocatively efficient?from corporatefinanceinstitute.com
For a market to be allocatively efficient, it must be informationally and transactionally efficient. By informationally efficient, we mean that all the necessary data about the market must be easily available and accessible to the consumers and stakeholders. A transactionally efficient market is one where the transaction costs for goods and services are not only fair but also fair to all parties. If the cost is too expensive for one party, then it will be impossible to achieve an allocatively efficient market.
Why is monopoly inefficient?from economicshelp.org
Monopoly sets a price of Pm. This is allocatively inefficient because at this output of Qm, price is greater than MC.
What is transactionally efficient market?from corporatefinanceinstitute.com
A transactionally efficient market is one where the transaction costs for goods and services are not only fair but also fair to all parties. If the cost is too expensive for one party, then it will be impossible to achieve an allocatively efficient market. 3. One party does not benefit at the expense of another.
When is optimal distribution achieved?from economicshelp.org
Therefore the optimal distribution is achieved when the marginal utility of the good equals the marginal cost.
Why are firms in perfect competition said to produce at an allocative efficient level?from economicshelp.org
Firms in perfect competition are said to produce at an allocative efficient level because at Q1, P=MC
What is the marginal benefit of the office staff?from corporatefinanceinstitute.com
The marginal benefit (benefit of the office staff) is equal to the marginal cost (cost incurred by the clothing manufacturer to produce an additional unit of production), that is, the amount they will pay to buy the navy blue suit.
How does allocative efficiency work?
When the market is allocatively efficient, the producer will continue to produce more and more up till the point where marginal cost is equal to price. In other words, where it no longer makes a profit. This is where the cost to make an additional good is equal to the price that it sells that good for. This may be due to a number of factors which make the good more expensive to produce as production increases (also known as diseconomies of scale).
What is allocation efficiency?
So what is meant by Allocative Efficiency? Allocative efficiency occurs when consumer demand is completely met by supply. In other words, businesses are providing the exact supply that consumers want.
Why can allocative efficiency only exist under perfect competition?
True allocative efficiency can only exist under perfect competition. This is because perfectly competitive firms are profit maximizers. They must operate under strong competition which brings marginal revenue in line with marginal costs. In turn, this creates an environment that maximizes the consumer’s utility.
What is an allocatively efficient market?
In an allocatively efficient market, this would be where marginal cost equals marginal utility. This is also known as the equilibrium point – marked up as 2 below. If the producer produces at a lower quantity, there will be excess demand — meaning it is not allocatively efficient from the consumers side.
When is a market allocatively efficient?
From the consumer’s perspective, a market is allocatively efficient when the price reflects the maximum they are willing to pay. In other words, allocative efficiency is where the consumers satisfaction is maximized in relation to cost. For instance, the consumer may be willing to spend a maximum of $5 on a bagel.
What happens to utility as the price increases?
As the price increases, the level of utility or satisfaction decreases. For instance, few would enjoy a croissant if they had to pay $50 for it. So allocative efficiency is where consumers maximize their utility, but also the price they pay.
What is the condition for allocative efficiency?
Where externalities exist the condition for allocative efficiency is that price = social marginal cost = social marginal benefit i.e. the price must equal the true marginal cost of production to society as a whole, rather than just the private marginal cost.
How do externalities affect allocative efficiency?
Given the existence of perfect competition, allocative efficiency would automatically occur where price equals marginal cost in all markets, assuming that neither negative nor positive externalities are present.
What would happen if the production of a good conferred net positive externalities on society?
Conversely, if the production of a good conferred net positive externalities on society, then there would be under-production and under-consumption at the free market price and again a misallocation of resources. This is illustrated in Figure 2 below.
What would happen if the firm's production decisions were to generate positive externalities?
Similarly, if the firm's production decisions were to generate positive externalities, such as the beneficial effects arising from the provision of employment, then there would be a divergence between private and social benefit.
What would happen if a company dumping waste into a river?
However, the dumping of waste into a river imposes an external cost on society as a whole, for which the firm would not have to pay . Clearly, if the firm had to pay the full social cost of its production activities, the additional cost would shift the supply curve, or private marginal cost curve, to the left.
Allocative Efficiency Explained
Formula
- There is no particular formula to derive allocative efficiency. It is, however, represented as P=MC, where P is the price of goods and services and MC is the marginal cost. Marginal cost describes the rise or fall in price associated with producing or providing services to an additional consumer. It is also referred to as incremental cost. One should consider certain when calculating allocatio…
Example
- Suppose ABC ltd wants to produce shoes; the output of 10 shoes has a marginal cost of $50. However, the consumer is willing to pay a high amount of $150 for good-quality shoes. Here, the marginal utilityderived by the consumers is higher than the company’s marginal cost. When the optimal output level changes to 20, the marginal cost equals marginal utility. This is because out…
When Does It occur?
- Allocative efficiency occurs when the production costs of output are equal to the value of marginal cost. The determination happens when businesses try to meet future demands using demand projections. It enables enterprises to choose the most effective ways to distribute resources like labor and raw materialsto maximize customer benefits based on t...
Allocative Efficiency vs. Productive Efficiency
- Allocative efficiency vs. productive efficiency is a misunderstood concept. Even though they are both concerned with utilizing resources in the optimum way possible, they are different concepts. Productive efficiency concerns the best way to produce commodities and how to do so efficiently. The most effective distribution of goods and services is what allocation efficiency is.
Recommended Articles
- This is a guide to Allocative efficiency and its meaning. We discuss formula, chart graphs, example and its comparison with productive efficiency. You can learn more from the following articles – 1. Welfare Economics 2. Supply-Side Economics 3. Managerial Economics