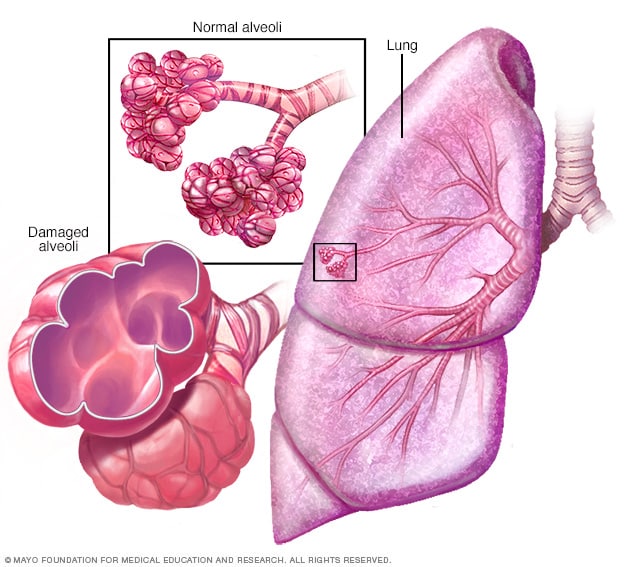
What is thought to be the cause of collapsed alveoli?
Without normal surfactant, the tissue surrounding the air sacs in the lungs (the alveoli) sticks together (because of a force called surface tension) after exhalation, causing the alveoli to collapse. Beside above, what prevent alveoli from collapsing?
Why do alveoli do not collapse?
Alveoli do not readily collapse into one another because they are suspended in a matrix of connective tissue “cables” and share common, often perforated walls, so there can be no pressure differential across them. Surfactant has important functions along planar surfaces of the alveolar wall and in mitigating the forces that tend to close ...
What would happen if your alveoli collapsed?
- aspiration pneumonia
- congestive heart failure
- destructive diseases such as cancer
What is the collapse of one or more alveoli called?
It is a condition where the alveoli are deflated down to little or no volume, as distinct from pulmonary consolidation, in which they are filled with liquid. It is often called a collapsed lung, although that term may also refer to pneumothorax.

Why would alveoli collapse without surfactant?
Without normal surfactant, the tissue surrounding the air sacs in the lungs (the alveoli) sticks together (because of a force called surface tension) after exhalation, causing the alveoli to collapse.
How is the collapse of alveoli in human lungs avoided?
For gas exchange to occur, the small air sacs within the lungs (alveoli) must remain open and filled with air. Alveoli are kept open by the elastic structure of the lung and by a liquid lining called surfactant. Surfactant counters the natural tendency of the alveoli to close (collapse).
What is alveoli collapse called?
A pneumothorax (noo-moe-THOR-aks) is a collapsed lung. A pneumothorax occurs when air leaks into the space between your lung and chest wall. This air pushes on the outside of your lung and makes it collapse.
What happens if the alveoli collapse?
The blood delivers the oxygen to organs and tissues throughout your body. When air sacs become deflated because of atelectasis, they cannot inflate properly or take in enough air and oxygen. If enough of the lung is affected, your blood may not receive enough oxygen, which can cause health problems.
What can damage alveoli?
One cause of damaged alveoli is pulmonary emphysema, a form of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD). About 14 million people in the United States have it. COPD is an umbrella term for health conditions that limit airflow in the lungs and damage lung tissue and alveoli.
Can you repair alveoli?
Alveolar regeneration after an acute lung injury has been observed in many mammals. Results in animal models have shown that alveolar type II (AT2) cells function as resident alveolar stem cells that can proliferate and differentiate into alveolar type I (AT1) cells to build new alveoli after lung injury.
Can you fix a collapsed lung?
Lung surgery may be needed to treat collapsed lung or to prevent future episodes. The area where the leak occurred may be repaired. Sometimes, a special chemical is placed into the area of the collapsed lung.
How painful is a collapsed lung?
A collapsed lung feels like a sharp, stabbing chest pain that worsens on breathing or with deep inspiration. This is referred to as "pleuritic" because it comes from irritation of nerve endings in the pleura (inner lining of the rib wall).
Can a collapsed lung repair itself?
Depending on the cause and the size of the leak, the lung can often heal itself, but in order to do so, the extra air in the pleura space needs to be removed to reduce the pressure so the lung can re-expand.
Can vaping cause a collapsed lung?
Smoking — and now vaping — are associated with an increased risk of bursting these blisters, leading to lung collapse.
Can you cough up an alveoli?
According to Tufts Medical Center, despite the old phrase, it's physically impossible to "cough up a lung." However, if a coughing fit is severe or lasts for an extended period of time, parts of the respiratory system and other areas of the body can be damaged.
Can you breathe with a collapsed lung?
Pneumothorax Treatment They treat a collapsed lung by getting rid of the pressure outside the lung so it can inflate again. In minor cases without symptoms, the lung can expand again on its own. You may need to breathe oxygen from a container for a short time to help.
How do you improve gas exchange in the lungs?
Improvements in gas exchange occur via several mechanisms: alterations in the distribution of alveolar ventilation, redistribution of blood flow, improved matching of local ventilation and perfusion, and reduction in regions of low ventilation/perfusion ratios.
How does exercise help your lungs?
When you are physically active, your heart and lungs work harder to supply the additional oxygen your muscles demand. Just like regular exercise makes your muscles stronger, it also makes your lungs and heart stronger.
Which of the following factors keeps the alveoli expanded?
alveolar ventilation. Which of the following factors keeps the alveoli expanded? decreasing the surface tension between water molecules on the lining of the alveoli.
What reduces the tension of the alveoli and allows them to maintain their shape?
Type 2 alveoli cells are smaller and responsible for producing the surfactant that coats the inside surface of the alveolus and helps reduce surface tension. The surfactant helps keep the shape of each alveolus when you breathe in and out.
What is the condition where fluid collects in the alveoli and causes respiratory failure?
Pulmonary edema is a condition caused by excess fluid in the lungs. This fluid collects in the alveoli and can cause respiratory failure. Respiratory failure is when your blood does not get enough oxygen.
What is the role of alveoli in the respiratory system?
Alveoli are an important part of the respiratory system whose function it is to exchange oxygen and carbon dioxide molecules to and from the bloodstream.
What is the fluid layer that lines the alveoli?
Alveoli are lined by a fluid layer known as a surfactant which maintains the shape and surface tension of the air sac.
How does CO2 get out of the body?
CO2 is a byproduct of the process in cells that uses oxygen to produce energy. As oxygen moves out of the alveolus , CO2 molecules pass into it. They are then breathed out of the body through the nose or mouth.
What is the purpose of surfactant in the lungs?
Pulmonary surfactant is a fluid made of phospholipids and proteins that lines the alveoli in the lungs. It helps air sacs maintain their shape and allows oxygen and carbon dioxide to pass through. 4
How many alveoli are there in the human lung?
One cubic millimeter of lung tissue contains around 170 alveoli. While the total number can vary from one person to the next, there are literally millions within the human lungs spanning a surface area of roughly 70 square meters.
Where does the air go when you inhale?
Alveoli are the endpoint of the respiratory system which starts when we inhale air into the mouth or nose. The oxygen-rich air travels down the trachea and then into one of the two lungs via the right or left bronchus. From there, the air is directed through smaller and smaller passages, called bronchioles, past the alveolar duct, until it finally enters an individual alveolus.
What causes a lung to collapse?
Air leaks into the space between your lungs and chest wall, indirectly causing some or all of a lung to collapse. Scarring of lung tissue. Scarring could be caused by injury, lung disease or surgery. Tumor. A large tumor can press against and deflate the lung, as opposed to blocking the air passages.
What is the term for a complete collapse of the lung?
Atelectasis (at-uh-LEK-tuh-sis) is a complete or partial collapse of the entire lung or area (lobe) of the lung. It occurs when the tiny air sacs (alveoli) within the lung become deflated or possibly filled with alveolar fluid.
How to prevent atelectasis in children?
Prevention. Atelectasis in children is often caused by a blockage in the airway. To decrease atelectasis risk, keep small objects out of reach of children. In adults, atelectasis most commonly occurs after major surgery. If you're scheduled for surgery, talk with your doctor about strategies to reduce your risk.
What is the most common respiratory complication after surgery?
Atelectasis is one of the most common breathing (respiratory) complications after surgery. It's also a possible complication of other respiratory problems, including cystic fibrosis, lung tumors, chest injuries, fluid in the lung and respiratory weakness. You may develop atelectasis if you breathe in a foreign object.
Why does atelectasis occur after heart surgery?
A mucus plug is a buildup of mucus in your airways. It commonly occurs during and after surgery because you can't cough.
What causes nonobstructive atelectasis?
Possible causes of nonobstructive atelectasis include: Injury. Chest trauma — from a fall or car accident, for example — can cause you to avoid taking deep breaths (due to the pain), which can result in compression of your lungs. Pleural effusion.
How to reduce the risk of atelectasis?
Some research suggests that certain breathing exercises and muscle training may lower the risk of atelectasis after certain surgeries. By Mayo Clinic Staff.
What causes a lung to collapse?
A collapsed lung is often the result of pressure on an airway from outside - a swollen lymph node or fluid between the lining of the lungs and the chest wall , for example - can also cause a lung to collapse. When the airway is blocked, the blood absorbs the air inside the air sacs (alveoli). Without more air, the sac shrinks.
How to treat a collapsed lung?
For example: If the lung has collapsed because of a blockage, the blockage can be removed by coughing, suctioning the airways or bronchoscopy. Antibiotics can be given to treat an infection.
How long before lung surgery should you stop smoking?
Preventing a collapsed lung is as important as treating one. These help avoid a collapsed lung: Patients who smoke should stop six to eight weeks before surgery. After surgery, patients should breathe deeply, cough regularly and move about as soon as possible.
What happens when the airway is blocked?
When the airway is blocked, the blood absorbs the air inside the air sacs (alveoli). Without more air, the sac shrinks. The space where the lung was before the collapse fills up with blood cells, fluids and mucus. It may then become infected.
What is the best way to help with shallow breathing?
Patients with a deformed chest or nerve condition that causes shallow breathing might need help breathing. Continuous positive airway pressure delivers oxygen through the nose or a facemask. This ensures the airways do not collapse even during the pause between breaths. Sometimes a mechanical ventilator is needed.
What causes scarring and shrinking of the membranes that cover the lungs and line the inside of the chest?
Scarring and shrinking of the membranes that cover the lungs and line the inside of the chest, which can occur as a result of exposure to asbestos. Smoking. Surgery, especially involving the chest or abdomen. Tight bandages.
What tests are done to determine if a lung is collapsed?
Other tests that may be performed include: Bronchoscopy. Chest X-rays, which may or may not show the airless area of the lung.
What is it called when your alveoli don't fill with air?
In order to do this, your alveoli must fill with air. When some of your alveoli don’t fill with air, it’s called “atelectasis. ”.
What causes atelectasis in the lung?
Atelectasis that affects most of your lung or happens quickly is almost always caused by a life-threatening condition , such as blockage of a major airway or when a large amount or fluid or air is compressing one or both lungs. Last medically reviewed on July 6, 2018.
What happens if you have low oxygen?
Having low blood oxygen can lead to: trouble breathing. sharp chest pain, especially when taking a deep breath or coughing. rapid breathing. increased heart rate. blue-colored skin, lips, fingernails, or toenails. Sometimes, pneumonia develops in the affected part of your lung.
Why do pleural effusions separate?
A pleural effusion causes the linings to separate and lose contact with each other. This allows the elastic tissue in your lung to pull inward, driving air out of your alveoli.
What causes obstructive atelectasis?
Causes of obstructive atelectasis. Obstructive atelectasis happens when a blockage develops in one of your airways. This prevents air from getting to your alveoli, so they collapse. Things that can block your airway include: inhalation of a foreign object, such as a small toy or small pieces of food, in an airway.
What is the difference between atelectasis and collapsed lung?
Depending on the underlying cause, atelectasis can involve either small or large portions of your lung. Atelectasis is different from a collapsed lung (also called pneumothorax ). A collapsed lung happens when air gets stuck in the space between the outside of your lung and your inner chest wall. This causes your lung to shrink or, eventually, ...
How to remove fluid from atelectasis?
If your atelectasis is due to pneumothorax or pleural effusion, your doctor may need to drain air or fluid from your chest. To remove fluid, they’ll likely insert a needle through your back, between your ribs, and into the pocket of fluid.
Why does my lungs collapse?
It can occur due to abnormal air sacs in the lungs that break apart and release air. Secondary spontaneous pneumothorax: Several lung diseases may cause a collapsed lung. These include chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD), cystic fibrosis and emphysema.
What are the factors that contribute to a collapsed lung?
Stab wound. Lifestyle factors associated with collapsed lung are: Drug use, especially inhaled drugs. Flying that involves drastic changes in air pressure. Scuba or deep-sea diving. Smoking. People with certain other risk factors may be more likely to have a collapsed lung. These are: Family history of pneumothorax.
How to prevent lung from collapsing again?
Your provider makes an incision and inserts a tube. Then your provider uses chemicals (such as doxycycline or talc) to attach the lung to the chest cavity, eliminating extra space in the chest cavity.
What is a collapsed lung?
A collapsed lung occurs when air enters the pleural space, the area between the chest wall and the lung. Air in the pleural space can build up and press against the lung, causing it to collapse partially or fully. Also called a deflated lung or pneumothorax, a collapsed lung needs immediate medical care.
What is the condition where the lung collapses?
Endometrial tissue lines the uterus. With endometriosis, it grows outside the uterus and attaches to an area inside the chest. The endometrial tissue forms cysts that bleed into the pleural space, causing the lung to collapse.
What is the condition where the chest is hard to breathe?
A collapsed lung occurs when air gets inside the chest cavity (outside the lung) and creates pressure against the lung. Also known as pneumothorax, collapsed lung is a rare condition that may cause chest pain and make it hard to breathe. A collapsed lung requires immediate medical care.
How to prevent a collapsed lung?
Anyone can take steps to reduce your chances of collapsed lung: Stop smoking. Avoid or limit activities with drastic changes in air pressure ( scuba diving and flying).

What The Alveoli Do
Structure of The Alveoli
- Alveoli are the smallest structures in the respiratory system. They are arranged in clusters throughout the lungs at the ends of the branches of your respiratory tree, which is the tree-like structure of passageways that brings air into the lungs. The walls of the alveoli are very thin. This lets oxygen and CO2 pass easily between the alveoli and capillaries, which are very small blood …
What Causes Damage to The alveoli?
- The alveoli will only work correctly if their tissue is healthy. Certain medical conditions can negatively impact alveoli by causing inflammation, scarring, infection, and fluid (water, pus, or blood) build-up. Known as alveolar lung diseases, these include: 1. Pneumonia 2. Emphysema 3. Tuberculosis 4. Alveolar proteinosis 5. Bronchioloalveolar car...
Summary
- The alveoli are an important part of the respiratory system. They are responsible for moving oxygen into, and CO2 out of, the bloodstream. Diseases that affect the alveoli can cause serious health problems. These include chronic lung conditions like emphysema and tuberculosis. Certain cancers can also begin in the alveoli. Other diseases, like pneumonia, are short-term but still seri…
A Word from Verywell
- The alveoli perform one of the body's most important functions. They are the gateway through which oxygen enters the bloodstream. They are also the primary way that the waste product carbon dioxide exits the body. Diseases that damage the alveoli affect the entire body. Damaged alveoli deliver less oxygen to tissues. This is called hypoxia. Hypoxia can cause damage to ever…
Overview
- Atelectasis (at-uh-LEK-tuh-sis) is a complete or partial collapse of the entire lung or area (lobe) of the lung. It occurs when the tiny air sacs (alveoli) within the lung become deflated or possibly filled with alveolar fluid. Atelectasis is one of the most common breathing (respiratory) complications after surgery. It's also a possible complicati...
Symptoms
- There may be no obvious signs or symptoms of atelectasis. If you do have signs and symptoms, they may include: 1. Difficulty breathing 2. Rapid, shallow breathing 3. Wheezing 4. Cough
Causes
- Atelectasis occurs from a blocked airway (obstructive) or pressure from outside the lung (nonobstructive). General anesthesia is a common cause of atelectasis. It changes your regular pattern of breathing and affects the exchange of lung gases, which can cause the air sacs (alveoli) to deflate. Nearly everyone who has major surgery develops some amount of atelectasi…
Risk Factors
- Factors that make you more likely to develop atelectasis include: 1. Older age 2. Any condition that makes it difficult to swallow 3. Confinement to bed with infrequent changes of position 4. Lung disease, such as asthma, COPD, bronchiectasis or cystic fibrosis 5. Recent abdominal or chest surgery 6. Recent general anesthesia 7. Weak breathing (respiratory) muscles due to mus…
Complications
- A small area of atelectasis, especially in an adult, usually is treatable. The following complications may result from atelectasis: 1. Low blood oxygen (hypoxemia).Atelectasis makes it more difficult for your lungs to get oxygen to the air sacs (alveoli). 2. Pneumonia.Your risk for pneumonia continues until the atelectasis goes away. Mucus in a collapsed lung may lead to infection. 3. Re…
Prevention
- Atelectasis in children is often caused by a blockage in the airway. To decrease atelectasis risk, keep small objects out of reach of children. In adults, atelectasis most commonly occurs after major surgery. If you're scheduled for surgery, talk with your doctor about strategies to reduce your risk. Some research suggests that certain breathing exercises and muscle training may low…