
Causes
- Angina tends to radiate, causing referred pain all around the shoulder and neck.
- Anxiety chest pains/hyperventilation tend to be more localized near the heart.
- Anxiety chest pains are usually sharper, although not always. Many people with angina experience more of a dull discomfort than a pain, while anxiety tends to be more of a ...
Symptoms
Usually, angina becomes more stable within eight weeks. In fact, people who are treated for unstable angina can live productive lives for many years. Coronary artery disease can be very difficult to deal with emotionally. Both you and your loved one may feel a loss of control, as if something had taken over your lives.
Prevention
They are as follows:
- Anginal pain is precipitated or aggravated by effort, emotional stress, or heavy meals and relieved by rest or nitroglycerin.
- It feels as if pressure is exerted on the chest, or a burning sensation in the middle of the chest, or even a squeezing or a choking sensation.
- Pain is usually localized just beneath the breast bone. ...
Complications
Angina may feel like pressure in your chest. This pain can also occur in shoulders, arms, neck, back or jaw. It must be noted that an angina pain may even feel like indigestion. Angina is not a disease; rather it is a symptom of an underlying heart problem.
How to tell if you have angina?
How long can a person live with angina?
What are signs of angina?
What does angina feel like?

What is the main cause of angina?
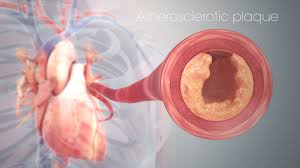
Angina is usually caused by the arteries supplying blood to the heart muscles becoming narrowed by a build-up of fatty substances. This is called atherosclerosis. Things that can increase your risk of atherosclerosis include: an unhealthy diet.
How do you stop angina chest pain?
You can reduce or prevent angina by reducing your heart disease risks factors, including:Smoking. If you smoke, stop. ... Poor diet. Eat a healthy diet with limited amounts of saturated fat, trans fat, salt and sugar. ... Lack of physical activity. ... Excess weight. ... Medical conditions. ... Stress.
What does an angina attack feel like?
Chest pain feels tight, dull or heavy – although some people (especially women) may have sharp, stabbing pain. spreads to your arms, neck, jaw or back. is triggered by physical exertion or stress. stops within a few minutes of resting.
What is the fastest way to cure angina?
If you need immediate relief from your angina:Stop, relax, and rest. Lie down if you can. ... Take nitroglycerin.If the pain or discomfort doesn't stop a few minutes after taking nitroglycerin or if your symptoms become more severe, call 911 or let someone know that you need immediate medical assistance.
Does drinking water help angina?
Angina pectoris tends to be accompanied by thrombosis [18]. Therefore, drinking an adequate amount of water may help reduce blood coagulation and result in a lower OR for angina pectoris.
Does angina show up on ECG?
You may have tests to check if you have angina and assess your risk of more serious problems like heart attacks or stroke. You may have: an electrocardiogram (ECG) – a test to check your heart's rhythm and electrical activity.
How are you checked for angina?
Blood tests check the level of cardiac troponins. Troponin levels can help doctors tell unstable angina from heart attacks. Your doctor may also check levels of certain fats, cholesterol, sugar, and proteins in your blood. Chest X-ray looks for lung disorders and other causes of chest pain not related to heart disease.
Is angina considered a heart attack?
Angina is the specific type of pain you experience when the heart is in trouble. Heart attacks, on the other hand, occur when the narrowing is severe or causes a blockage, leading to actual damage to the heart muscle. In other words, a heart attack is an actual medical condition and angina is a symptom.
How long does an angina attack lasts?
Usually lasts 5 minutes; rarely more than 15 minutes. Triggered by physical activity, emotional stress, heavy meals, extreme cold or hot weather. Relieved within 5 minutes by rest, nitroglycerin or both. Pain in the chest that may spread to the jaw, neck, arms, back or other areas.
Where is angina pain located?
Angina is chest pain or discomfort caused when your heart muscle doesn't get enough oxygen-rich blood. It may feel like pressure or squeezing in your chest. The discomfort also can occur in your shoulders, arms, neck, jaw, abdomen or back.
What age does angina occur?
Angina affects both men and women, but at different ages based on men and women's risk of developing coronary heart disease. In men, heart disease risk starts to increase at age 45. Before age 55, women have a lower risk for heart disease than men. After age 55, the risk rises in both women and men.
How can I fix my angina naturally?
Here are best foods to eat and lifestyle changes to reverse angina.Stop smoking. Smoking cigarettes is detrimental to cardiovascular health and efforts should be made to stop.Work towards a healthier body weight. ... Consume omega-3 fats (EPA+DHA) ... Eat more plants. ... Reduce intake of bad fats and sugar. ... Exercise regularly.
How long does chest pain last with angina?
The chest pain typically lasts a short time, perhaps five minutes or less. Unstable angina (a medical emergency). Unstable angina is unpredictable and occurs at rest. Or the angina pain is worsening and occurs with less physical effort.
How long does it take for angina pain to go away?
Stable angina Usually lasts 5 minutes; rarely more than 15 minutes. Triggered by physical activity, emotional stress, heavy meals, extreme cold or hot weather. Relieved within 5 minutes by rest, nitroglycerin or both.
How long does it take for angina to go away?
Angina attacks usually last a few minutes. If it has been triggered by exertion, it usually subsides within a few minutes as you rest. When such pain lasts more than 10 minutes, it could indicate a heart attack. If you have this type of pain and it lasts more than 10 minutes, call 9-1-1.
Does angina pain go away on its own?
If it's angina, your symptoms usually ease or go away after a few minutes' rest, or after taking the medicines your doctor or nurse has prescribed for you, such as glyceryl trinitrate medicine (GTN). If you're having a heart attack, your symptoms are less likely to ease or go away after resting or taking medicines.
What causes chest pain?
Other conditions also can cause chest pain, such as: Pulmonary embolism (a blockage in a lung artery) Aortic dissection (tearing of a major artery) A lung infection. Aortic stenosis (narrowing of the heart’s aortic valve) Hypertrophic cardiomyopathy (heart muscle disease)
What are the different types of angina?
There are many types of angina, including microvascular angina, Prinzmetal's angina, stable angina, unstable angina and variant angina. View an animation of angina. . This usually happens because one or more of the coronary arteries is narrowed or blocked, also called ischemia.
What to do if you have chest pain?
All chest pain should be checked out by a healthcare provider. If you have chest pain, your doctor will want to find out whether it's angina and if it is, whether the angina is stable or unstable. If it's unstable, you may need emergency medical treatment to try to prevent a heart attack.
What tests are done for unstable angina?
If your doctor thinks that you have unstable angina or that your angina is related to a serious heart condition, they may recommend the following tests and procedures: EKG (Electrocardiogram) Stress Testing. Blood Tests. Chest X- Rays. Coronary Angiography and Cardiac Catheterization. Computed Tomography Angiography.
What to do if your heart is unstable?
If it's unstable, you may need emergency medical treatment to try to prevent a heart attack. Your doctor will most likely perform a physical exam, ask about your symptoms, and ask about your risk factors for and your family history of heart disease and other cardiovascular conditions.
Is heart disease a risk factor for angina?
If you’re at risk for heart disease or coronary artery disease, you’re also at risk for angina. The major risk factors for heart disease and coronary artery disease include:
Is angina a disease?
The discomfort also can occur in your shoulders, arms, neck, jaw, or back. Angina pain may even feel like indigestion. But, angina is not a disease. It is a symptom of an underlying heart problem, usually coronary heart disease (CHD).
What causes angina in the heart?
When you climb stairs, exercise or walk, your heart demands more blood, but narrowed arteries slow down blood flow. Besides physical activity, other factors such as emotional stress, cold temperatures, heavy meals and smoking also can narrow arteries and trigger angina.
Why is my angina unstable?
Unstable angina can also be caused by blood clots that block or partially block your heart's blood vessels. Unstable angina worsens and isn't relieved by rest or your usual medications. If the blood flow doesn't improve, your heart is starved of oxygen and a heart attack occurs.
What is the pain in the chest called?
Overview. Angina is a type of chest pain caused by reduced blood flow to the heart. Angina (an-JIE-nuh or AN-juh-nuh) is a symptom of coronary artery disease. Angina, also called angina pectoris, is often described as squeezing, pressure, heaviness, tightness or pain in your chest. Some people with angina symptoms say angina feels like ...
How does stress affect your heart?
Stress. Stress can increase your risk of angina and heart attacks. Too much stress, as well as anger, also can raise your blood pressure. Surges of hormones produced during stress can narrow your arteries and worsen angina.
What is the risk of heart attacks and angina?
Cholesterol is a major part of the deposits that can narrow arteries throughout your body, including those that supply your heart. A high level of low-density lipoprotein (LDL) cholesterol, also known as "bad" cholesterol, increases your risk of angina and heart attacks. A high level of triglycerides, a type of blood fat related to your diet, also is unhealthy.
What is it called when your heart is narrowed?
Your heart (coronary) arteries can become narrowed by fatty deposits called plaques. This is called atherosclerosis. During times of low oxygen demand — when you're resting, for example — your heart muscle may still be able to function on the reduced amount of blood flow without triggering angina symptoms.
What happens if you have a family history of heart disease?
Family history of heart disease. If a family member has coronary artery disease or has had a heart attack, you're at a greater risk of developing angina.
What is the cause of angina in men?
Angina is a sign of an underlying heart problem, such as: Coronary artery disease (CAD): CAD is the top cause of angina in men and women. It occurs when deposits called plaques build up in the arteries that supply blood to the heart. The arteries narrow or harden ( atherosclerosis ), reducing blood flow to the heart.
What does it mean when you have angina?
Unstable angina: This type comes on without warning, often when you’re resting. A blood clot in an artery is often the cause. Unstable angina can indicate a heart attack. It is a medical emergency.
What is the name of the heart disease that causes chest pain?
Angina . Angina — chest pain or pressure — is a sign of coronary artery disease or another type of heart disease. Stable angina comes and goes during physical exertion and stress. Treatments for heart disease can relieve angina . Unstable angina happens suddenly.
How long does angina last?
These sensations may last a few minutes and then go away. The symptoms may worsen when you climb stairs, exercise or feel stressed. Symptoms may improve when you stop exercising or take steps to manage stress. Importantly, angina can also manifest either as exertional shortness of breath, abdominal discomfort, fatigue, or in other ways in some people without the “typical” chest discomfort.
How long does chest pain last?
It can come on during daily activities or times of stress. Chest pain typically lasts longer than other types of angina. You may have pain for 10 to 30 minutes. Variant (Prinzmetal) angina: Coronary spasms cause this rare type.
What to do if you have heart disease and angina?
A note from Cleveland Clinic. If you have heart disease that causes angina, follow your healthcare provider’s recommendations for managing that condition. If you continue to have chest pain, talk to your provider. Treatments can relieve angina.
What tests are done to determine if you have angina?
After performing a physical exam, your provider may order one or more of these tests to find the cause of angina: Complete blood count (CBC). C hest X-rays. Cardiac stress test.
What causes chest pain?
Psychological Disorders That Can Cause Chest Pain. Panic disorders, anxiety, depression, emotional stress or other psychological disorders may also cause chest pain. In these psychological disorders, the chest pain is not related to angina or digestive causes but instead seems to be triggered by the emotional stress.
Why does my chest hurt?
Chest pain is also caused by irritation and swelling of the heart ( myocarditis) or its outer covering ( pericarditis ). This inflammation can be caused by an infection or happen after a heart attack or heart surgery. Pain from myocarditis or pericarditis is usually is sharp and in the center of the chest.
What is chest pain?
Chest pain is one of the most common symptoms of angina. You can learn more about Angina Causes and Risk Factors, but chest pain can also signal other problems. This is why it is very important to discuss your symptoms with your doctor to determine the underlying problem and the best course of treatment. In general, heart-related chest pain feels ...
How long does GERD pain last?
GERD can cause squeezing, burning pain, often located in the center of the chest that sometimes radiates to the back, neck, jaw or arms. It can last minutes to hours. Many times younger people having their first episode of angina or heart attack do not think that their chest discomfort is coming from their heart.
What causes chest pain and difficulty breathing?
In some cases, the pressure is so great it can cause a lung to collapse and even push the lungs, heart, and major vessels to the opposite side of the chest. This condition usually causes immediate chest pain and difficulty breathing. The pressure must be relieved immediately by a needle or tube through the chest wall.
Why does my abdomen feel like chest pain?
Pain radiating from the abdomen can also feel like chest pain. This type of pain can be caused by peptic ulcer disease, inflammation of the gallbladder, gallstones, inflammation of the pancreas (pancreatitis), kidney stones or inflammation of the appendix (appendicitis).
What is a pulmonary embolism?
Pulmonary Embolism (PE): If you have trouble breathing, call 911. It could be a heart attack or other type of medical emergency, such as a blood clot in the lung, which is called a pulmonary embolism (PE). The chest pain from PE usually comes on suddenly with difficulty breathing, especially when you take a deep breath. You are at greater risk for PE if you have had surgery in the past three months, a blood clotting disorder, or cancer, or if you take oral contraceptives. PE is a life-threatening situation. The clot must be dissolved by medication to allow the heart and lungs to work properly.
What causes chest pain?
Pulmonary embolism — a blood clot that has traveled into the vessels supplying the lungs—can cause chest pain. The pain is often accompanied by a fast or irregular heartbeat, sudden difficulty breathing, or feeling lightheaded or faint. Pulmonary embolisms can be life-threatening, so the symptoms warrant a call to 911.
Why does my chest hurt?
Tissues in the chest cavity can become inflamed due to injury, infection, or autoimmune conditions, in which the body's immune cells attack its own tissues. Common inflammatory causes of chest pain include the following: Costochondritis.
What is the pain in the center of the chest?
The classic symptom of pericarditis is a sharp, stabbing pain in the center or left side of the chest that worsens when you take a deep breath or lie down. The pain results from the irritated layers of the sac rubbing together.
What does it mean when you feel pressure in your chest?
Angina—feelings of pressure, heaviness, tightness. or pain in the chest—occurs when plaque in the coronary arteries partially blocks blood flow and the heart muscle isn't getting enough oxygen and nutrients. (You can learn more about angina in the Harvard Special Health Report Diseases of the Heart: A compendium of common heart condition and ...
What causes a stabbing pain in the chest?
Costochondritis. This condition, an inflammation in the chest wall between the ribs and the breastbone, can trigger a stabbing, aching pain that's often mistaken for a heart attack. Costochondritis is commonly caused by trauma or overuse injuries, often during contact sports, or it may accompany arthritis.
Where does gallbladder pain go?
Gallbladder pain is usually felt just below the breastbone and may extend to the right arm or between the shoulder blades. It occurs as the gallbladder contracts in an effort to pump bile around the gallstones that are blocking its passage to the liver.
How long does chest pain last?
Any time you're uncertain about the source of chest pain that is recurrent or lasts for several days , you should talk to your clinician. However, if you have chest pain that is building in intensity, has lasted for several minutes, and isn't relieved by resting, you should get immediate medical attention.
Overview
Symptoms
Causes
Risk Factors
Complications
- Angina (an-JIE-nuh or AN-juh-nuh) is a type of chest pain caused by reduced blood flow to the heart. Angina is a symptom of coronary artery disease. Angina is also called angina pectoris. Angina pain is often described as squeezing, pressure, heaviness, tightness or pain in the chest. It may feel like a heavy weight lying on the chest. Angina may b...
Prevention
- Angina symptoms include chest pain and discomfort. The chest pain or discomfort may feel like: 1. Burning 2. Fullness 3. Pressure 4. Squeezing Pain may also be felt in the arms, neck, jaw, shoulder or back. Other symptoms of angina include: 1. Dizziness 2. Fatigue 3. Nausea 4. Shortness of breath 5. Sweating The severity, duration and type of angina can vary. New or differ…