What are the two most common signs of anaphylaxis?
The common signs of anaphylaxis found in other areas of the human body are:
- Skin: Urticaria ( hives) Angioedema (swelling) Erythema (flushing) Pruritus ( itching)
- Respiratory: Upper airway: Nasal congestion Sneezing Hoarseness Cough Oropharyngeal or laryngeal edema
- Lower airway: Shortness of breath Bronchospasms (a contraction of muscles that line the bronchi) Wheezing Chest tightness
What are common medication triggers for anaphylaxis?
- Foods, insect venom, and medical drugs are the most common triggers of anaphylaxis.
- The trigger profile in anaphylaxis is age-dependent.
- Among food triggers of anaphylaxis, peanuts are common in children.
- Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) and antibiotics are leading triggers of drug-induced anaphylaxis.
Are antihistamines and steroids helpful for anaphylaxis?
Prompt treatment of anaphylaxis is critical, with subcutaneous or intramuscular epinephrine and intravenous fluids remaining the mainstay of management. Adjunctive measures include airway protection, antihistamines, steroids, and beta agonists. Patients taking beta blockers may require additional measures.
What to do in an anaphylaxis emergency?
Practical points:
- Try to ensure that a person suffering an allergic reaction remains as still as possible
- Preferably they should be lying down. ...
- When dialling 999, say that the person is suffering from anaphylaxis (anna-fill-axis)
- Give clear and precise directions to the emergency operator, including the postcode of your location

What is the main cause of angioedema?
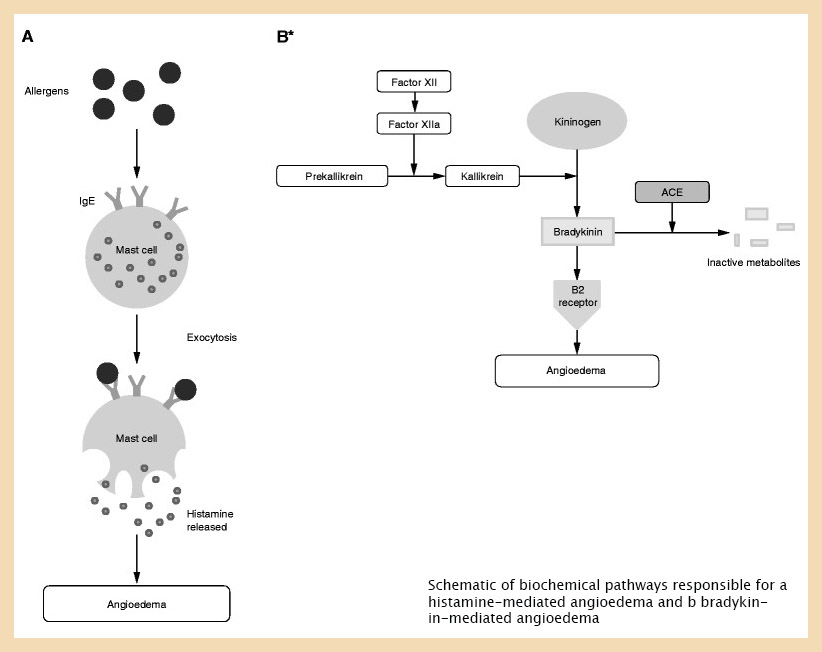
Angioedema is often the result of an allergic reaction. This is where the body mistakes a harmless substance, such as a certain food, for something dangerous. It releases chemicals into the body to attack the substance, which cause the skin to swell.
How does histamine cause angioedema?
Histamine-mediated angioedema occurs through an allergic mechanism, specifically a type I hypersensitivity reaction, which occurs after a patient has had prior “sensitization” to a particular antigen.
What is the difference between angioedema and anaphylaxis?
Angioedema is characterized by edema of the subcutaneous or submucosal tissues, which can cause airway compromise if the tongue or larynx is involved. Anaphylaxis ○ A life-threatening systemic allergic reaction characterized by acute onset and multiorgan involvement.
Does angioedema mean anaphylaxis?
Allergic angioedema This is the most common type, and it usually affects those with an allergy to a type of food, a medication, venom, pollen, or animal dander. In serious cases, there may be a severe allergic reaction known as anaphylaxis. The throat may swell, making it hard for the patient to breath.
How does bradykinin cause angioedema?
Bradykinin binds the bradykinin B2 receptor on the vascular endothelium, stimulating substance P release and inducing angioedema. C1 esterase inhibitor (C1-INH), which acts as a brake on the complement system, blocks bradykinin overproduction via the contact system.
Does epinephrine treat angioedema?
Treatment of angioedema includes histamine blockers (H1 and H2), steroids, and, in those with severe symptoms, epinephrine (intramuscular or subcutaneous). However, hereditary angioedema (HAE) is generally refractory to treatment with these drugs.
Can you have anaphylaxis without angioedema?
Urticaria and angioedema may occur together and as a part of an anaphylactic reaction, but either may occur alone and may not be due to non-immunoglobulin (IgE) mechanisms, although almost all urticaria is non-IgE mediated.
Is angioedema an IgE reaction?
In the former case, angioedema can be caused by allergic reactions caused by immunoglobulin E (IgE)-mediated hypersensitivity to foods or drugs that can also result in acute urticaria or a more generalized anaphylactic reaction.
What IgE level is anaphylaxis?
A Japanese retrospective study evaluated 393 patients (median age 8.3 years; ≥5 years old), defined as of high risk of a severe reaction [anaphylactic history or antigen-specific IgE (>30 kU/L) to egg, milk, wheat, or peanut], and observed anaphylaxis (WHO definition) in 48% of cases during in-hospital OFC.
What is Type 3 angioedema?
Hereditary angioedema with normal C1 inhibitor (HAE type III) is clinically characterized by recurrent angioedema affecting the skin, gastrointestinal tract, and larynx. Skin swellings are the most frequent symptoms of HAE type III.
What is the difference between edema and angioedema?
The swellings manifest as recurrent episodes of pronounced localized edema with ill-defined margins. Unlike other forms of edema, angioedema is nonpitting, often asymmetric and has a tendency not to involve gravitationally dependent areas. The skin is usually normal in color, but can be slightly erythematous.
What causes swelling in allergic reactions?
Your body produces the chemical histamine, which causes the blood vessels in the area to expand, leading to swelling of the skin. Substances known to trigger allergic angioedema include: certain types of food – particularly nuts, shellfish, milk and eggs.
Can histamine intolerance cause angioedema?
Considering that most of the foods reported by as trigger factors contain or release histamine, the researchers hypothesized that an intolerance reaction against histamine may be the cause of these patients' angioedema attacks.
Do Antihistamines help angioedema?
Although most cases of angioedema get better without treatment after a few days, medication is often used. For cases of allergic and idiopathic angioedema, antihistamines and oral steroids (steroid tablets) can be used to relieve the swelling.
What is bradykinin mediated angioedema?
Bradykinin-mediated angioedema is a rare disease, due to vasodilation and increased vascular permeability resulting from bradykinin. This kind of angioedema affects abdominal and/or upper airways. It differs clinically from histamine-mediated angioedema by the absence of urticaria or skin rash.
What foods trigger angioedema?
They pointed out that histamines released from foods such as cheese, alcohol, fish, tomatoes, strawberries, pineapples, nuts, citrus fruits, and kiwis could be linked to the triggering of angioedema attacks.
What causes angioedema in the body?
The following allergens can trigger angioedema: insect bites. pollen. poison oak or ivy. latex.
Why do people have angioedema?
Hereditary angioedema occurs in people with a family history of the condition, due to an inherited genetic mutation.
What is the swelling of the inner layer of the skin called?
Angioedema is a form of swelling in the deep part of the skin’s inner layer and below, and it may become severe. In some cases, this swelling occurs along with the appearance of hives. This is why angioedema is sometimes referred to as “giant hives.”
What is the best medicine for swelling?
However, those with moderate or severe symptoms may require certain medications to help relieve intense swelling. These medicines can include: epinephrine, if due to acute allergic reaction. antihistamines, such as loratadine and cetirizine, if due to an allergic reaction or angioedema where the cause is unknown.
What is the most common symptom of angioedema?
What are the symptoms of angioedema? The most common symptom of angioedema is swelling with a red colored rash beneath the surface of the skin. It may occur in a localized area on or near the feet, hands, eyes, or lips. In more severe cases, the swelling can spread to other parts of the body. Angioedema may or may not be accompanied by swelling ...
How to prevent allergic angioedema?
The best way to prevent allergic angioedema is to avoid known and suspected allergens. You should also try to avoid any known triggers that have caused angioedema for you in the past. Taking these preventive measures can help lower your risk of having another episode in the future.
What blood test is done for angioedema?
Your doctor will perform a series of blood tests if hereditary or acquired angioedema is suspected. These may include: C1 esterase inhibitor testing . checking levels of complement components, including C2 and C4. These tests measure the levels or function of certain proteins in the blood.
What causes angioedema?
Angioedema is the swelling of the deep layer of the skin. It is most often an allergic-type reaction to food or medications.
What is angioedema in the body?
What is angioedema? Angioedema is sudden swelling of the deep layer of your skin in one part of your body—most often in the face, mouth, or throat. But it can also affect the hands and feet, genitals, and the bowel wall. It is often an allergic reaction (to a food or medication, for example).
What are the signs and symptoms of angioedema?
Those with recurrent unexplained abdominal symptoms may have underlying angioedema. You must advocate for yourself because angioedema is not common, so understandably, your physician may not consider it. —Dr. Chandra Manuelpillai
Why do my lips swell?
3 Reasons Your Lips Are Swollen & Treatments. Lip swelling i soften caused by an allergic reaction. When in contact with certain foods or chemical, this can cause sudden lip swelling. In addition, taking certain medication like ACE inhibitors, an injury to the face, or angioedema can cause puffy lips. Read more.
What is the best medication for idiopathic angioedema?
Treating idiopathic angioedema often includes daily antihistamines. Speak to your doctor about how to treat it. Typically, when there is new swelling, you take the over-the-counter antihistamine diphenhydramine (Benadryl) and the prescription prednisone. But this treatment should be managed by your doctor.
Why is my face swollen?
Causes of a Swollen or Puffy Face & How to Find Relief. The most common causes of facial swelling arise from a dental or skin infection , or an allergic reaction which can also cause hives, wheezing, and vomiting. Other causes of face swelling include dehydration, hormonal imbalance, or physical trauma to the face.
What blood pressure medication causes a swollen thigh?
Drugs that are more likely to cause it include the class of blood pressure medicine called ACE inhibitors ( such as lisinopril), nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) like ibuprofen (Advil, Motrin) and aspirin.
What causes angioedema?
Angioedema can be classified into at least four types, acute allergic angioedema, non-allergic drug reactions, idiopathic angioedema, hereditary angioedema (HAE) and acquired C1 inhibitor deficiency.
What is angioedema?
Angioedema is a skin reaction similar to urticaria. It is most often characterised by an abrupt and short-lived swelling of the skin and mucous membranes. All parts of the body may be affected but swelling most often occurs around the eyes and lips. In severe cases, the internal lining of the upper respiratory tract and intestines may also be affected.
What are the clinical features of angioedema?
Symptoms and signs of angioedema may vary slightly between the different types of angioedema but in general, some or all of the following occur.
What is the difference between angioedema and urticaria?
What's the difference between angioedema and urticaria? Angioedema and urticaria are very similar in many ways and can co-exist and overlap. Urticaria occurs more commonly and is less severe than angioedema as it only affects the skin layers whereas angioedema affects the tissues beneath the skin ( subcutaneous tissue).
How long does it take for angioedema to go away?
In many cases, the swelling is self-limiting and resolves spontaneously after a few hours or days. In more severe cases where there is persistent swelling, itchiness or pain the following medications may be used.
What causes swelling in the skin?
Whatever the cause of angioedema, the actual mechanism behind the swelling is the same in all cases. Small blood vessels in the subcutaneous and/or submucosal tissues leak watery liquid through their walls and cause swelling. This same mechanism occurs in urticaria but just closer to the skin surface.
What is vibratory angioedema?
Vibratory angioedema. A form of chronic inducible urticaria. Localised vibratory urticaria is also due to a vibratory stimulus and is considered distinct from vibratory angioedema. Whatever the cause of angioedema, the actual mechanism behind the swelling is the same in all cases.
What is angioedema in urticaria?
INTRODUCTION. Angioedema is self-limited, localized swelling of the skin or mucosal tissues, which results from extravasation of fluid into the interstitium due to a loss of vascular integrity. Angioedema may occur in isolation, accompanied by urticaria, or as a component of anaphylaxis. The pathogenesis and causes of angioedema will be reviewed ...
What percentage of African Americans have angioedema?
African Americans were disproportionately affected, as they accounted for 42 percent of the admissions for angioedema, but only 16 percent of the state's population. The epidemiology of specific forms of angioedema, such as hereditary angioedema (HAE) due to C1 inhibitor (C1INH) deficiency, is discussed separately.
Is angioedema a rare disease?
Data regarding the epidemiology of angioedema are limited, although it affects both adults and children and is not a rare disorder. In a retrospective review of all hospital admissions in New York State over 13 years, angioedema was the second most common "allergic" disease to necessitate hospitalization, exceeded only by asthma [ 1 ]. In this study, the number of angioedema hospitalizations per year more than doubled during the study period, suggesting that the prevalence may be increasing.
How to avoid angioedema?
Prevention. You can avoid allergic episodes if you stay away from foods, medications , or other conditions that trigger angioedema. If you don’t know what’s causing your episodes, try to keep a diary to track foods, symptoms, and situations tied to your symptoms .
How many types of angioedema are there?
There are four types of angioedema, and they all have different causes.
What is swelling under skin called?
Angioedema is swelling beneath your skin. It can happen at many points on your body, including your:
How long does it take for angioedema to happen?
Allergic and drug-induced angioedema usually happen within an hour of exposure to your trigger. Hereditary and acquired types usually happen over many hours, but it can feel much faster if you wake up and suddenly discover swelling.
What is the name of the protein that makes your body swell?
Hereditary angioedema ( HAE ): This is rare. It happens when your body doesn’t make enough of a blood protein called C1 esterase inhibitor. That lets fluid from your blood move into other tissues, which brings swelling.
Can you pass angioedema to your children?
It’s different because it doesn’t happen until you’re older than 40. It usually happens when you have a weakened immune system. Unlike HAE, you can’t pass it on to your children.
Can ACE cause flare ups?
Certain blood pressure medicines called ang iotensin-converting enzyme (ACE) inhibitors can also cause flare-ups that can happen quickly. Even if you’ve been taking ACE inhibitors for a long time, sudden reactions can still happen.
What causes hives and angioedema?
Hives and angioedema can be caused by: Foods. Many foods can trigger reactions in people with sensitivities. Shellfish, fish, peanuts, tree nuts, soy, wheat, eggs and milk are frequent offenders. Medications. Many medications may cause hives or angioedema.
What is the treatment for angioedema?
Hives and angioedema are usually treated with antihistamine medication. Angioedema can be life-threatening if swelling of the tongue or in the throat blocks the airway.
How do you know if you have angioedema?
Angioedema is a reaction similar to hives that affects deeper layers of your skin. It can appear with hives or alone. Signs and symptoms include: Welts that form in minutes to hours. Swelling and redness, especially around the eyes, cheeks or lips. Pain or warmth in the affected areas.
How to treat angioedema in throat?
Hives and angioedema are usually treated with antihistamine medication. Angioedema can be life-threatening if swelling causes your throat or tongue to block your airway.
What causes hives in the upper respiratory tract?
Airborne allergens. Pollen and other allergens that you breathe in can trigger hives, sometimes accompanied by upper and lower respiratory tract symptoms. Environmental factors.
Can angioedema be life threatening?
Severe angioedema can be life-threatening if swelling of the tongue or in the throat blocks the airway.
What is the name of the area that is affected by angioedema?
Angioedema typically affects areas with loose connective tissue, such as the face, lips, mouth, and throat, larynx, uvula, extremities, and genitalia. Bowel wall angioedema presents as colicky abdominal pain. Angioedema can be distinguished clinically from other forms of edema by the following characteristics:
Is angioedema a localized swelling?
Angioedema is self-limited, localized subcutaneous (or submucosal) swelling, which results from extravasation of fluid into interstitial tissues. Angioedema may occur in isolation, accompanied by urticaria, or as a component of anaphylaxis. The clinical features, diagnosis, differential diagnosis, and management of angioedema will be reviewed here.